Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/mhogg/pygeodesic
Python library to compute geodesic distance over a triangular based surface mesh
https://github.com/mhogg/pygeodesic
Last synced: 1 day ago
JSON representation
Python library to compute geodesic distance over a triangular based surface mesh
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mhogg/pygeodesic
- Owner: mhogg
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-03-16T06:00:39.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-26T18:22:37.000Z (3 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-08T03:09:28.749Z (6 days ago)
- Language: C++
- Size: 1.99 MB
- Stars: 83
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 2
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# pygeodesic
Python library to compute geodesic distance over a triangular based surface mesh.
A Cython wrapper of the C++ code by [Kirsanov](https://code.google.com/archive/p/geodesic/), which is an implementation of the exact geodesic algorithm for triangular mesh first described by Mitchell, Mount and Papadimitriou in 1987.
`pygeodesic` is similar to other libraries on PyPi (such as [gdist](https://pypi.org/project/gdist/) and [tvb-gdist](https://pypi.org/project/tvb-gdist/)), but:
* provides a wrapper of the GeodesicAlgorithmExact class
* exposes geodesic path (not just geodesic distance)
* licensed under MIT license similar to the orginal Kirsanov C++ code, rather than GPL
A good alternative to `pygeodesic` is [potpourri3d](https://pypi.org/project/potpourri3d/), which uses the *heat method* and *vector heat method* to compute geodesic distance over surfaces and point clouds. However, this library does not currently output the geodesic path on the surface.
## Requirements
A C++ compiler is required if you are not installing one of the precompiled wheels. Although `pygeodesic` is a Cython wrapper, Cython is not required as the cythonized C++ file is also provided.
[VTK](https://pypi.org/project/vtk/) is used for visualisation in the example notebooks.
## Installation
Install from PyPi:
```
pip install pygeodesic
```
Installation from source (from within folder containing `setup.py`):
```
python setup.py install
```
## Usage
Loading pygeodesic:
```python
import pygeodesic.geodesic as geodesic
```
To read the mesh files provided with the original C++ code:
```python
filename = r'data/flat_triangular_mesh.txt'
result = geodesic.read_mesh_from_file(filename)
if result:
points, faces = result
```
To calculate the geodesic distance and path between two points (the *source* and the *target*) on the mesh:
```python
# Initialise the PyGeodesicAlgorithmExact class instance
geoalg = geodesic.PyGeodesicAlgorithmExact(points, faces)
# Define the source and target point ids with respect to the points array
sourceIndex = 25
targetIndex = 97
# Compute the geodesic distance and the path
distance, path = geoalg.geodesicDistance(sourceIndex, targetIndex)
```
To calculate the geodesic distances from a single point (the source point) to all other points on the mesh:
```python
source_indices = np.array([25])
target_indices = None
distances, best_source = geoalg.geodesicDistances(source_indices, target_indices)
```
To calculate the geodesic distances from two source points to 3 target points:
```python
source_indices = np.array([25,100])
target_indices = np.array([0,10,50])
distances, best_source = geoalg.geodesicDistances(source_indices, target_indices)
```
For more detail, a Jupyter notebook is provided in the examples folder to show how to use `pygeodesic` to compute geodesic distances and paths.
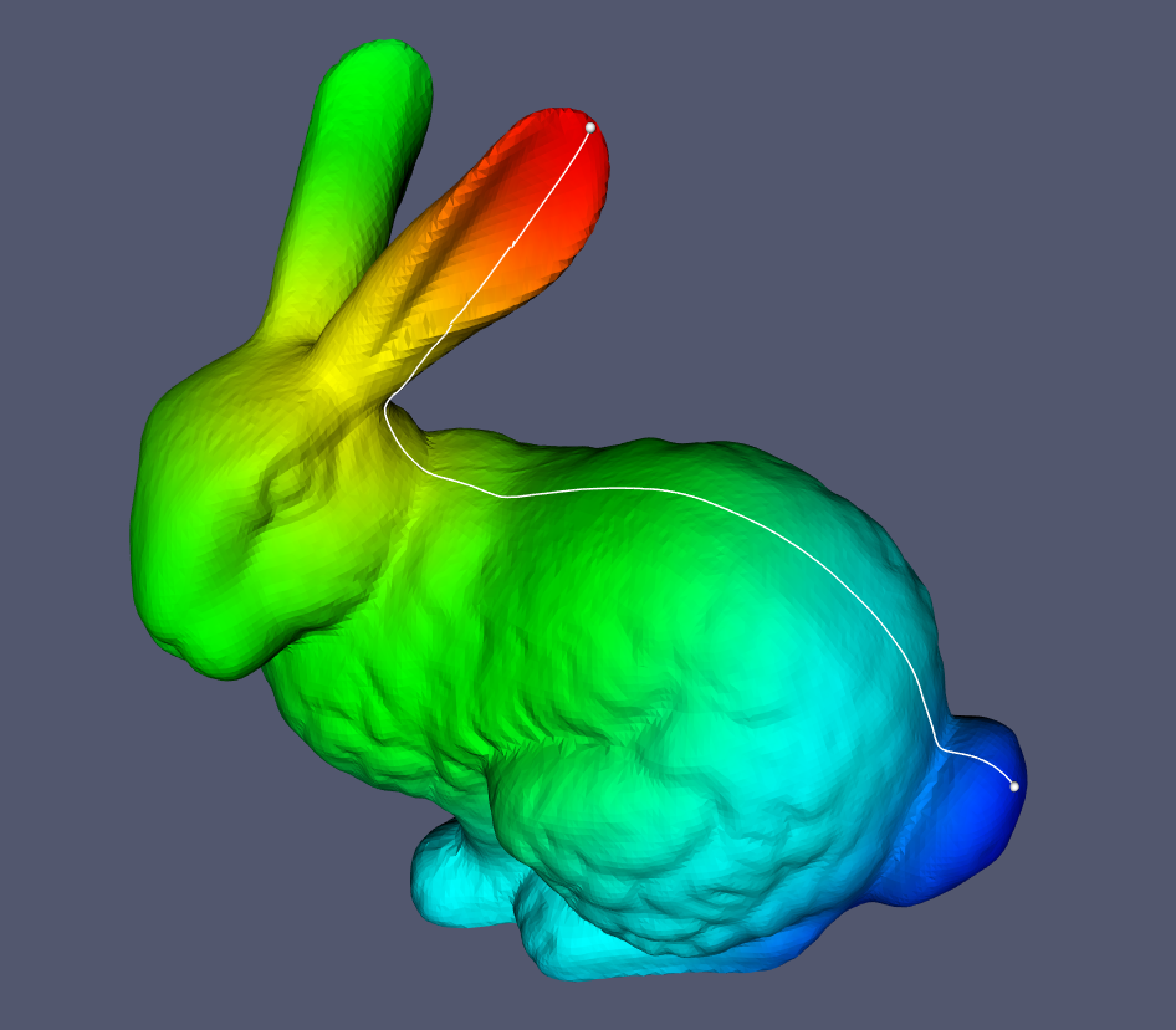
## Example using the Stanford Bunny
A Jupyter notebook is provided showing how to use `pygeodesic` to calculate the geodesic distance and path using the Stanford Bunny as an example.