Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/mikolalysenko/rle-funcs
Functional programming primitives and abstractions for narrowband level sets
https://github.com/mikolalysenko/rle-funcs
Last synced: 7 days ago
JSON representation
Functional programming primitives and abstractions for narrowband level sets
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mikolalysenko/rle-funcs
- Owner: mikolalysenko
- Created: 2013-01-14T19:27:32.000Z (almost 12 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2013-02-14T19:59:09.000Z (almost 12 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-12-16T22:35:32.566Z (10 days ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Size: 711 KB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
rle-funcs
=========
Basic primitives for merging and combining multiphase solid objects. This is part of the [rle narrowband level set library](https://github.com/mikolalysenko/rle-core).
Installation
============
You can install it via rle-funcs:
npm install rle-funcs
Example
=======
Here is an example showing how to implement the update rule for a 3D version of the Game of Life using narrowband level sets:
//Bounds for birth
var SURVIVE_LO = 4;
var SURVIVE_HI = 5;
var BIRTH_LO = 5;
var BIRTH_HI = 5;
//Set up neighborhood stencil
var MOORE_1 = require("rle-stencil").moore(1);
var CENTER_INDEX = 13;
//Compute the next state of the cellular automaton
function nextState(state) {
return require("rle-funcs").apply(state, MOORE_1, function(phases, distances, retval) {
//Count neighbors
var neighbors = 0;
for(var i=0; i<27; ++i) {
if(i !== CENTER_INDEX && phases[i]) {
++neighbors;
}
}
//Compute next state
if(phases[CENTER_INDEX]) {
if(SURVIVE_LO <= neighbors && neighbors <= SURVIVE_HI) {
retval[0] = 1;
return;
}
} else if(BIRTH_LO <= neighbors && neighbors <= BIRTH_HI) {
retval[0] = 1;
return;
}
retval[0] = 0;
return;
});
}
//Initialize state and tick in your main loop
If you want to [see it in action, here is a demo](http://mikolalysenko.github.com/rle-core/life3d/index.html). Other examples of using rle-funcs can be found in [rle-csg](https://github.com/mikolalysenko/rle-csg) and [rle-morphology](https://github.com/mikolalysenko/rle-morphology) which are built on top of this library:
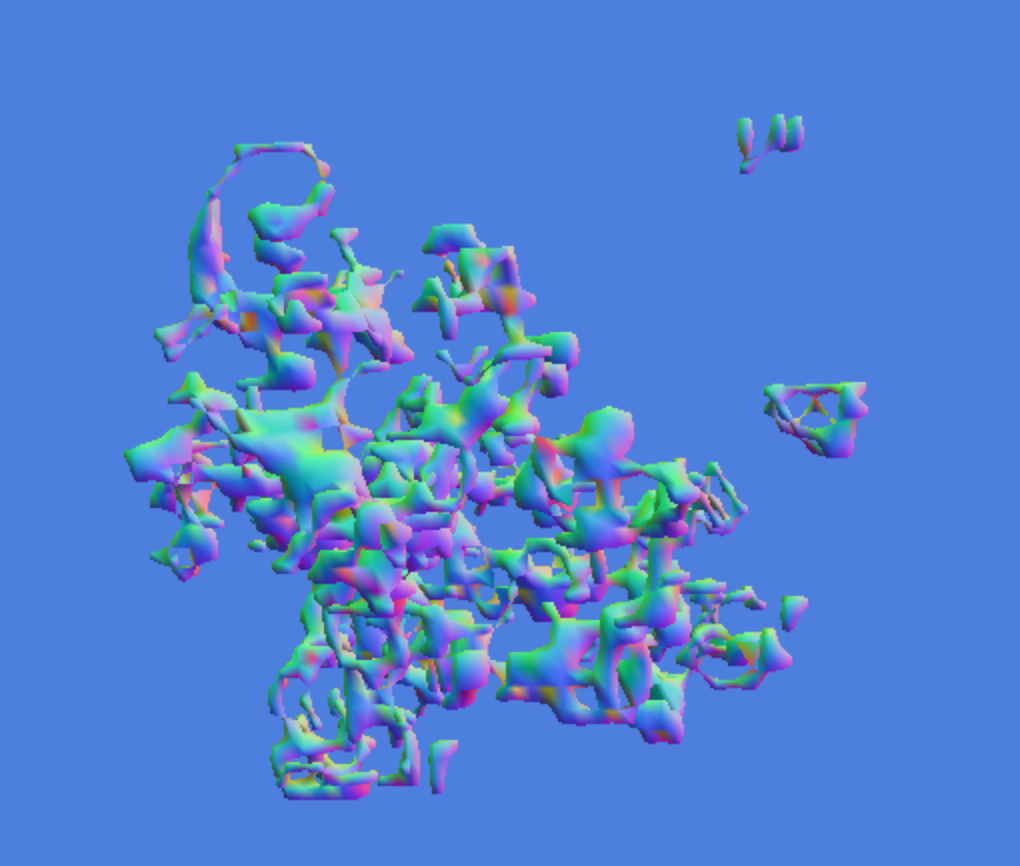
Usage
=====
`merge(volumes, stencil, merge_func)`
----------------------------
This merges a collection of volumes together. This acts like a generalized boolean operation amongst the volumes. It is a very flexible, and very general function
* `volumes`: An array of volumes
* `stencil`: A stencil
* `merge_func(phases, distances, retval)`: A function that takes 3 arguments:
* `phases`: An array of length `volumes.length * stencil.length` of material phases.
* `distances`: An array of length `volumes.length * stencil.length` of distances to the material boundary
* `retval`: A length two array for the return value of the function. The first item is the new phase and the second item is the distance to the phase boundary.
Returns: A new volume which is the result of calling merge_func at every point in the volumes.
`mergePoint(volumes, merge_func)`
---------------------------------
This is an optimized version of merge where the stencil is a single point.
`apply(volume, stencil, merge_func)`
------------------------------
This is an optimized version of `merge` that takes only a single volume as input, instead of an array. Useful for implementing cellular automata and other local differential equations.
`applyPoint(volume, merge_func)`
---------------------------------
Optimized version `apply` that assumes `stencil` is a single point.
Credits
=======
(c) 2013 Mikola Lysenko