https://github.com/misiektoja/github_monitor
Real-time tracking of Github users activities including profile and repositories changes
https://github.com/misiektoja/github_monitor
github github-api github-monitor osint pygithub python
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Real-time tracking of Github users activities including profile and repositories changes
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/misiektoja/github_monitor
- Owner: misiektoja
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2024-05-11T14:23:29.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-07-15T17:18:39.000Z (7 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-07-16T13:33:15.932Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: github, github-api, github-monitor, osint, pygithub, python
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 3.49 MB
- Stars: 27
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 8
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-osint - github_monitor - Tool for real-time tracking of GitHub users' activities including profile and repository changes with support for email alerts, CSV logging, detection when a user blocks or unblocks you and more (Social Media Tools / [↑](#-table-of-contents) GitHub)
README
# github_monitor
OSINT tool for real-time monitoring of GitHub users' activities, including profile and repository changes.
- Real-time tracking of GitHub users' activities, including profile and repository changes:
- new GitHub events for the user like new pushes, PRs, issues, forks, releases, reviews etc.
- repository changes such as updated stargazers, watchers, forks, issues, PRs, description and repo update dates
- added/removed followings and followers
- added/removed starred repositories
- added/removed public repositories
- changes in user name, email, location, company, bio and blog URL
- changes in profile visibility (public to private and vice versa)
- detection when a user blocks or unblocks you
- detection of account metadata changes (such as account update date)
- Email notifications for different events (new GitHub events, changed followings, followers, repositories, user name, email, location, company, bio, blog URL etc.)
- Saving all user activities with timestamps to the CSV file
- Clickable GitHub URLs printed in the console & included in email notifications (repos, PRs, commits, issues, releases etc.)
- Possibility to control the running copy of the script via signals
- Support for Public Web GitHub and GitHub Enterprise
1. [Requirements](#requirements)
2. [Installation](#installation)
* [Install from PyPI](#install-from-pypi)
* [Manual Installation](#manual-installation)
3. [Quick Start](#quick-start)
4. [Configuration](#configuration)
* [Configuration File](#configuration-file)
* [GitHub Personal Access Token](#github-personal-access-token)
* [GitHub API URL](#github-api-url)
* [Events to Monitor](#events-to-monitor)
* [Time Zone](#time-zone)
* [SMTP Settings](#smtp-settings)
* [Storing Secrets](#storing-secrets)
5. [Usage](#usage)
* [Monitoring Mode](#monitoring-mode)
* [Listing Mode](#listing-mode)
* [Email Notifications](#email-notifications)
* [CSV Export](#csv-export)
* [Check Intervals](#check-intervals)
* [Signal Controls (macOS/Linux/Unix)](#signal-controls-macoslinuxunix)
* [Coloring Log Output with GRC](#coloring-log-output-with-grc)
6. [Change Log](#change-log)
7. [License](#license)
* Python 3.10 or higher
* Libraries: [PyGithub](https://github.com/PyGithub/PyGithub), `requests`, `python-dateutil`, `pytz`, `tzlocal`, `python-dotenv`
Tested on:
* **macOS**: Ventura, Sonoma, Sequoia
* **Linux**: Raspberry Pi OS (Bullseye, Bookworm), Ubuntu 24, Rocky Linux 8.x/9.x, Kali Linux 2024/2025
* **Windows**: 10, 11
It should work on other versions of macOS, Linux, Unix and Windows as well.
```sh
pip install github_monitor
```
Download the *[github_monitor.py](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/misiektoja/github_monitor/refs/heads/main/github_monitor.py)* file to the desired location.
Install dependencies via pip:
```sh
pip install PyGithub requests python-dateutil pytz tzlocal python-dotenv
```
Alternatively, from the downloaded *[requirements.txt](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/misiektoja/github_monitor/refs/heads/main/requirements.txt)*:
```sh
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
- Grab your [GitHub personal access token](#github-personal-access-token) and track the `github_username` activities:
```sh
github_monitor -t "your_github_classic_personal_access_token"
```
Or if you installed [manually](#manual-installation):
```sh
python3 github_monitor.py -t "your_github_classic_personal_access_token"
```
To get the list of all supported command-line arguments / flags:
```sh
github_monitor --help
```
Most settings can be configured via command-line arguments.
If you want to have it stored persistently, generate a default config template and save it to a file named `github_monitor.conf`:
```sh
github_monitor --generate-config > github_monitor.conf
```
Edit the `github_monitor.conf` file and change any desired configuration options (detailed comments are provided for each).
### GitHub Personal Access Token
Go to your GitHub Apps settings: [https://github.com/settings/apps](https://github.com/settings/apps)
Then click **Personal access tokens → Tokens (classic) → Generate new token (classic)**.
Provide the `GITHUB_TOKEN` secret using one of the following methods:
- Pass it at runtime with `-t` / `--github-token`
- Set it as an [environment variable](#storing-secrets) (e.g. `export GITHUB_TOKEN=...`)
- Add it to [.env file](#storing-secrets) (`GITHUB_TOKEN=...`) for persistent use
- Fallback: hard-code it in the code or config file
If you store the `GITHUB_TOKEN` in a dotenv file you can update its value and send a `SIGHUP` signal to reload the file with the new token without restarting the tool. More info in [Storing Secrets](#storing-secrets) and [Signal Controls (macOS/Linux/Unix)](#signal-controls-macoslinuxunix).
By default the tool uses Public Web GitHub API URL: [https://api.github.com](https://api.github.com)
If you want to use GitHub Enterprise API URL then change `GITHUB_API_URL` (or use `-x` flag) to: `https://{your_hostname}/api/v3`
You can limit the type of events that will be monitored and reported by the tool. You can do it by changing the `EVENTS_TO_MONITOR` configuration option.
By default all events are monitored, but if you want to limit it, then remove the `ALL` keyword and leave the events you are interested in, for example:
```
EVENTS_TO_MONITOR=['PushEvent','PullRequestEvent', 'IssuesEvent', 'ForkEvent', 'ReleaseEvent']
```
By default, time zone is auto-detected using `tzlocal`. You can set it manually in `github_monitor.conf`:
```ini
LOCAL_TIMEZONE='Europe/Warsaw'
```
You can get the list of all time zones supported by pytz like this:
```sh
python3 -c "import pytz; print('\n'.join(pytz.all_timezones))"
```
### SMTP Settings
If you want to use email notifications functionality, configure SMTP settings in the `github_monitor.conf` file.
Verify your SMTP settings by using `--send-test-email` flag (the tool will try to send a test email notification):
```sh
github_monitor --send-test-email
```
It is recommended to store secrets like `GITHUB_TOKEN` or `SMTP_PASSWORD` as either an environment variable or in a dotenv file.
Set environment variables using `export` on **Linux/Unix/macOS/WSL** systems:
```sh
export GITHUB_TOKEN="your_github_classic_personal_access_token"
export SMTP_PASSWORD="your_smtp_password"
```
On **Windows Command Prompt** use `set` instead of `export` and on **Windows PowerShell** use `$env`.
Alternatively store them persistently in a dotenv file (recommended):
```ini
GITHUB_TOKEN="your_github_classic_personal_access_token"
SMTP_PASSWORD="your_smtp_password"
```
By default the tool will auto-search for dotenv file named `.env` in current directory and then upward from it.
You can specify a custom file with `DOTENV_FILE` or `--env-file` flag:
```sh
github_monitor --env-file /path/.env-github_monitor
```
You can also disable `.env` auto-search with `DOTENV_FILE = "none"` or `--env-file none`:
```sh
github_monitor --env-file none
```
As a fallback, you can also store secrets in the configuration file or source code.
To monitor specific user activities and profile changes, simply enter the GitHub username as a command-line argument (`github_username` in the example below):
```sh
github_monitor github_username
```
It will track all user profile changes (e.g. changed followers, followings, starred repositories, username, email, bio, location, blog URL, number of repositories) and also all GitHub events (e.g. new pushes, PRs, issues, forks, releases etc.).
If you have not set `GITHUB_TOKEN` secret, you can use `-t` flag:
```sh
github_monitor github_username -t "your_github_classic_personal_access_token"
```
By default, the tool looks for a configuration file named `github_monitor.conf` in:
- current directory
- home directory (`~`)
- script directory
If you generated a configuration file as described in [Configuration](#configuration), but saved it under a different name or in a different directory, you can specify its location using the `--config-file` flag:
```sh
github_monitor --config-file /path/github_monitor_new.conf
```
If you want to monitor changes to user's public repositories (e.g. new stargazers, watchers, forks, changed descriptions etc.) then use the `-j` flag:
```sh
github_monitor github_username -j
```
By default, only user-owned repos are tracked. To include forks and collaborations, set `GET_ALL_REPOS` to `True` or use the `-a` flag:
```sh
github_monitor github_username -j -a
```
If for any reason you do not want to monitor GitHub events for the user (e.g. new pushes, PRs, issues, forks, releases etc.), then use the `-k` flag:
```sh
github_monitor github_username -k
```
The tool runs until interrupted (`Ctrl+C`). Use `tmux` or `screen` for persistence.
You can monitor multiple GitHub users by running multiple instances of the script.
The tool automatically saves its output to `github_monitor_.log` file. It can be changed in the settings via `GITHUB_LOGFILE` configuration option or disabled completely via `DISABLE_LOGGING` / `-d` flag.
There is another mode of the tool that displays various requested information (`-r`, `-g`, `-f` and `-l` flags).
If you want to display a list of public repositories (with some basic statistics) for the user then use the `-r` flag:
```sh
github_monitor github_username -r
```
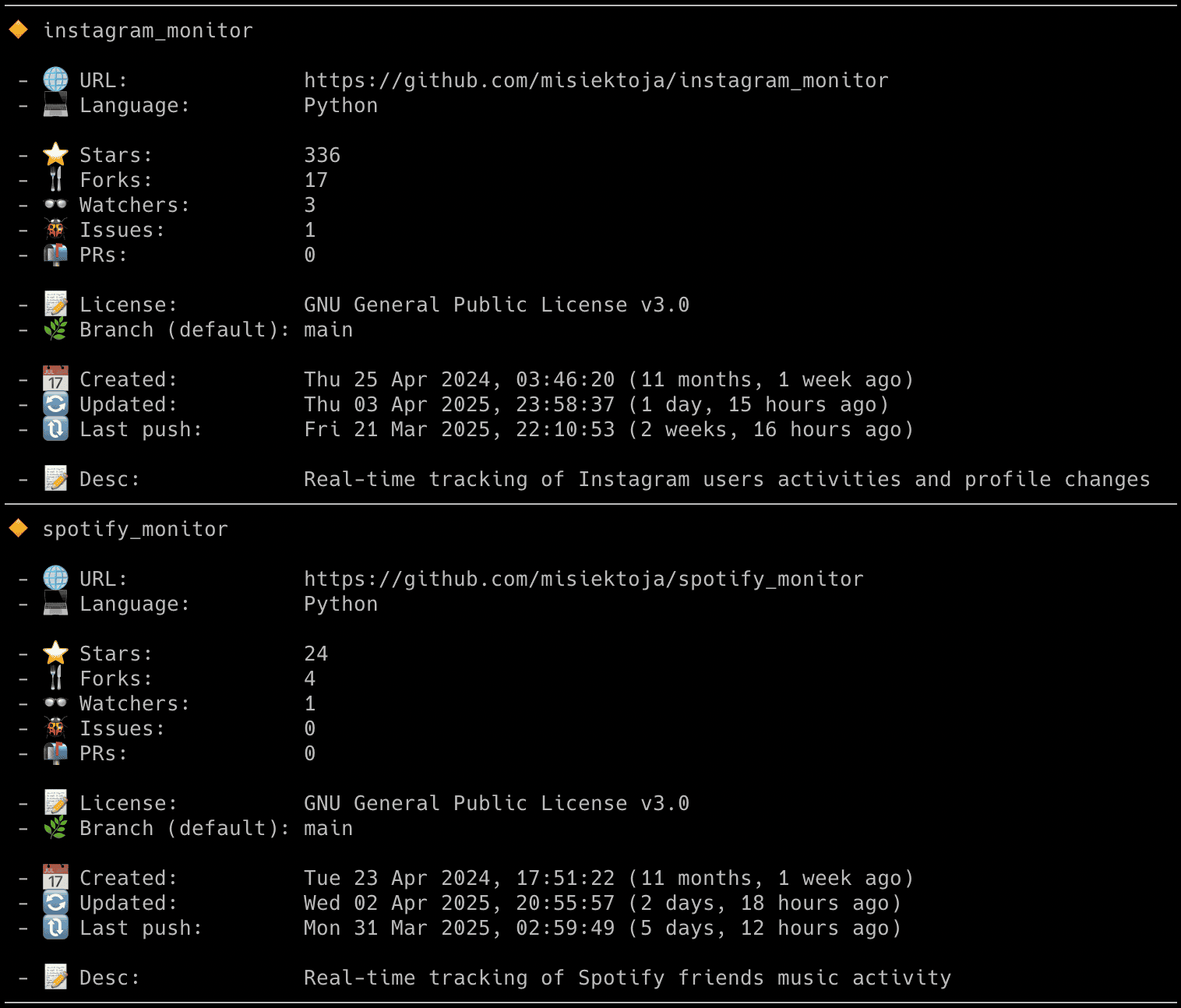
By default, only user-owned repos are listed. To include forks and collaborations, set `GET_ALL_REPOS` to `True` or use the `-a` flag:
```sh
github_monitor github_username -r -a
```
If you want to display a list of repositories starred by the user then use the `-g` flag:
```sh
github_monitor github_username -g
```
If you want to display a list of followers and followings for the user then use the `-f` flag.
```sh
github_monitor github_username -f
```
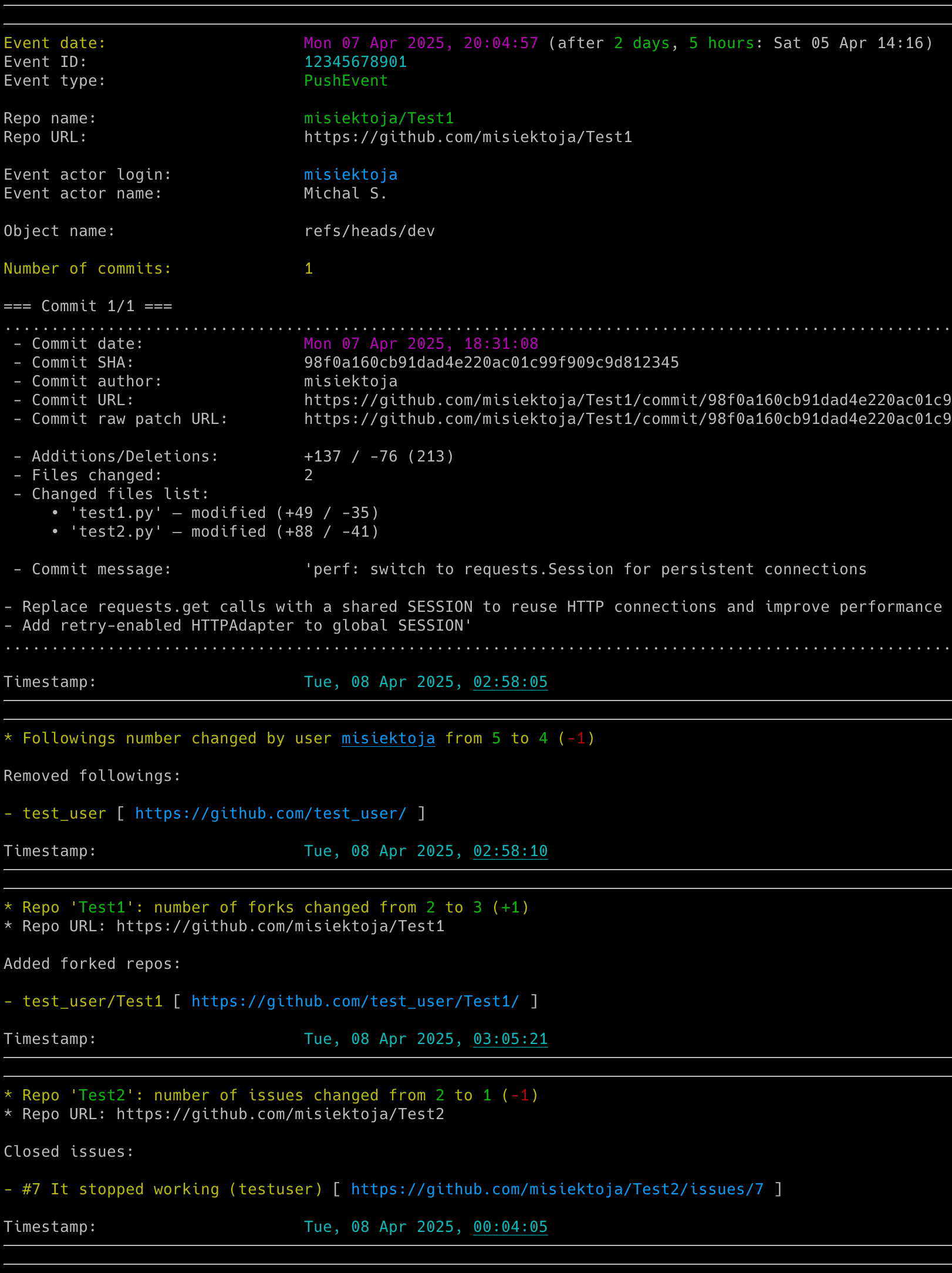
If you want to get the list of recent GitHub events for the user then use the `-l` flag. You can also add the `-n` flag to specify how many events should be displayed. By default, it shows the last 5 events.
```sh
github_monitor github_username -l -n 10
```
If you want to not only display, but also save the list of recent GitHub events to a CSV file, use the `-l` flag with `-b` indicating the CSV file. As before, you can add the `-n` flag to specify how many events should be displayed/saved:
```sh
github_monitor github_username -l -n 10 -b github_username.csv
```
To enable email notifications for all user profile changes (e.g. changes in followers, followings, starred repositories, username, email, bio, location, blog URL and number of repositories):
- set `PROFILE_NOTIFICATION` to `True`
- or use the `-p` flag
```sh
github_monitor github_username -p
```
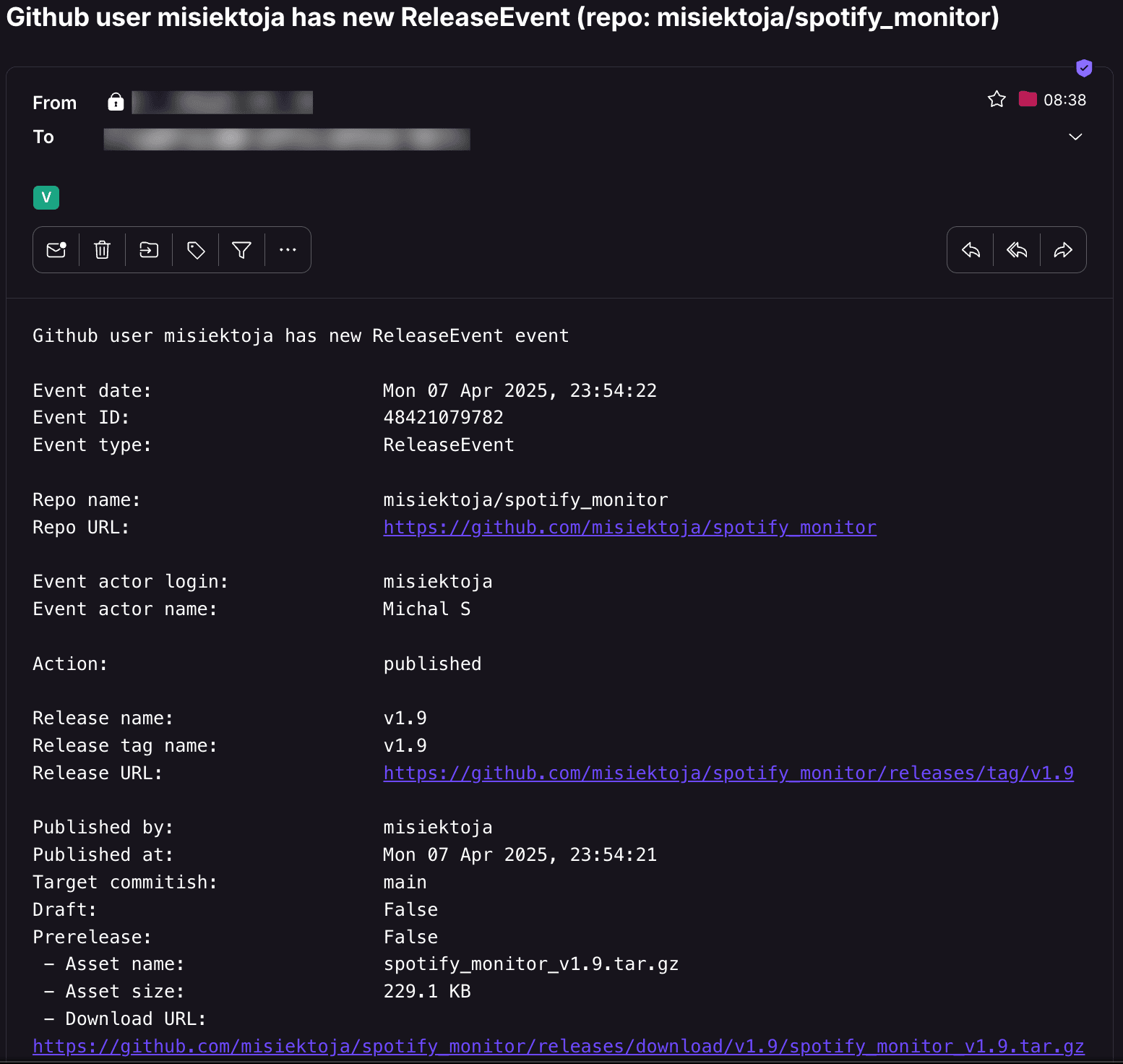
To receive email notifications when new GitHub events appear for the user (e.g. new pushes, PRs, issues, forks, releases etc.):
- set `EVENT_NOTIFICATION` to `True`
- or use the `-s` flag
```sh
github_monitor github_username -s
```
To get email notifications when changes in user repositories are detected (e.g. changes in stargazers, watchers, forks, descriptions, etc., except for the update date):
- set `REPO_NOTIFICATION` to `True`
- or use the `-q` flag
```sh
github_monitor github_username -q
```
To be informed whenever changes in the update date of user repositories are detected:
- set `REPO_UPDATE_DATE_NOTIFICATION` to `True`
- or use the `-u` flag
```sh
github_monitor github_username -u
```
The last two options (`-q` and `-u`) only work if tracking of repositories changes is enabled (`-j`).
To disable sending an email on errors (enabled by default):
- set `ERROR_NOTIFICATION` to `False`
- or use the `-e` flag
```sh
github_monitor github_username -e
```
You can combine all email notifications flags together if needed.
Make sure you defined your SMTP settings earlier (see [SMTP settings](#smtp-settings)).
Example email:
If you want to save all GitHub user events, profile changes and repository updates to a CSV file, set `CSV_FILE` or use `-b` flag:
```sh
github_monitor -b github_username.csv
```
The file will be automatically created if it does not exist.
If you want to customize the polling interval, use `-c` flag (or `GITHUB_CHECK_INTERVAL` configuration option):
```sh
github_monitor -c 900
```
It is generally not recommended to use values lower than 10 minutes as new events are very often delayed by GitHub API.
### Signal Controls (macOS/Linux/Unix)
The tool has several signal handlers implemented which allow to change behavior of the tool without a need to restart it with new configuration options / flags.
List of supported signals:
| Signal | Description |
| ----------- | ----------- |
| USR1 | Toggle email notifications for all user's profile changes (-p) |
| USR2 | Toggle email notifications for new GitHub events (-s) |
| CONT | Toggle email notifications for user's repositories changes (except for update date) (-q) |
| PIPE | Toggle email notifications for user's repositories update date changes (-u) |
| TRAP | Increase the user check interval (by 1 min) |
| ABRT | Decrease the user check interval (by 1 min) |
| HUP | Reload secrets from .env file |
Send signals with `kill` or `pkill`, e.g.:
```sh
pkill -USR1 -f "github_monitor "
```
As Windows supports limited number of signals, this functionality is available only on Linux/Unix/macOS.
### Coloring Log Output with GRC
You can use [GRC](https://github.com/garabik/grc) to color logs.
Add to your GRC config (`~/.grc/grc.conf`):
```
# monitoring log file
.*_monitor_.*\.log
conf.monitor_logs
```
Now copy the [conf.monitor_logs](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/misiektoja/github_monitor/refs/heads/main/grc/conf.monitor_logs) to your `~/.grc/` and log files should be nicely colored when using `grc` tool.
Example:
```sh
grc tail -F -n 100 github_monitor_.log
```
See [RELEASE_NOTES.md](https://github.com/misiektoja/github_monitor/blob/main/RELEASE_NOTES.md) for details.
Licensed under GPLv3. See [LICENSE](https://github.com/misiektoja/github_monitor/blob/main/LICENSE).