Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/mklabs/tabtab
tab completion helpers, for node cli programs & others. Inspired by npm completion
https://github.com/mklabs/tabtab
Last synced: 5 days ago
JSON representation
tab completion helpers, for node cli programs & others. Inspired by npm completion
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mklabs/tabtab
- Owner: mklabs
- License: mit
- Created: 2011-10-17T18:08:44.000Z (over 13 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-01-04T14:33:56.000Z (about 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-18T03:04:05.185Z (12 days ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.28 MB
- Stars: 372
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 38
- Open Issues: 43
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: readme.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# tabtab
[](https://travis-ci.org/mklabs/tabtab)
[](https://coveralls.io/github/mklabs/tabtab?branch=3.0.0)
A node package to do some custom command line `` completion for any
system command, for Bash, Zsh, and Fish shells.
Made possible using the same technique as npm (whose completion is quite
awesome) relying on a shell script bridge to do the actual completion from
node's land.
**Warning / Breaking changes**
- Windows is not supported
- Cache has been removed
- Now only support node `> 7.10.1`, for previous version with support for node
6 be sure to use tabtab `2.2.x`
## Table of Contents
- [Goal of this 3.0.0 version](#goal-of-this-300-version)
- [Installation](#installation)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [1. Install completion](#1-install-completion)
- [2. Log completion](#2-log-completion)
- [3. Parsing env](#3-parsing-env)
- [Completion mechanism](#completion-mechanism)
- [Completion install](#completion-install)
- [Completion uninstall](#completion-uninstall)
- [Debugging](#debugging)
- [API Documentation](#api-documentation)
- [Changelog](#changelog)
- [Credits](#credits)
## Goal of this 3.0.0 version
Simplify everything, major overhaul, rewrite from scratch.
Functional, less abstraction, clearer documentation, good test coverage,
support for node 10 without babel.
Up to date dependencies, easier to debug, easier to test.
Should still support bash, zsh and fish but bash is the primary focus of this
alpha version.
No binary file anymore, just a library (still debating with myself)
The goal of this rewrite is two-folded:
- Integrate nicely with [yo](https://github.com/yeoman/yo) (Yeoman)
- Have a robust and fast enough library for [yarn-completions](https://github.com/mklabs/yarn-completions)
## Installation
npm install tabtab
## Usage
Writing completion is a two-step process: Installation and Logging. Tabtab
provides just that.
Here is a basic example using
[minimist](https://www.npmjs.com/package/minimist) to parse arguments.
```js
#! /usr/bin/env node
const tabtab = require('tabtab');
const opts = require('minimist')(process.argv.slice(2), {
string: ['foo', 'bar'],
boolean: ['help', 'version', 'loglevel']
});
const args = opts._;
const completion = env => {
if (!env.complete) return;
// Write your completions there
if (env.prev === 'foo') {
return tabtab.log(['is', 'this', 'the', 'real', 'life']);
}
if (env.prev === 'bar') {
return tabtab.log(['is', 'this', 'just', 'fantasy']);
}
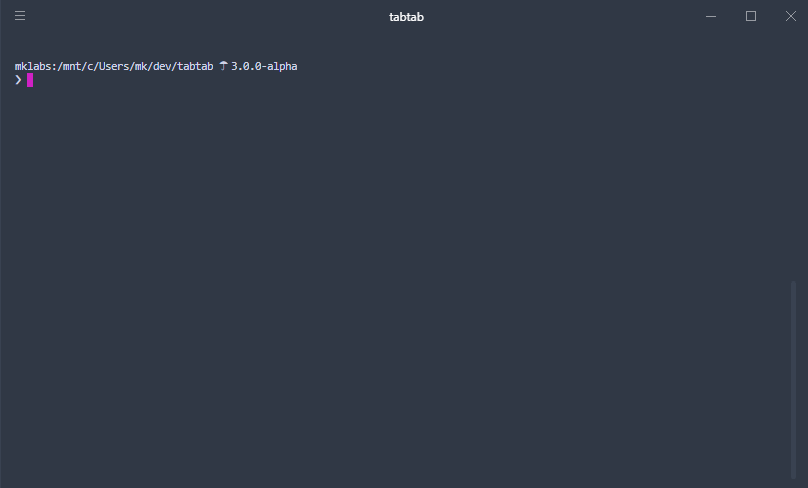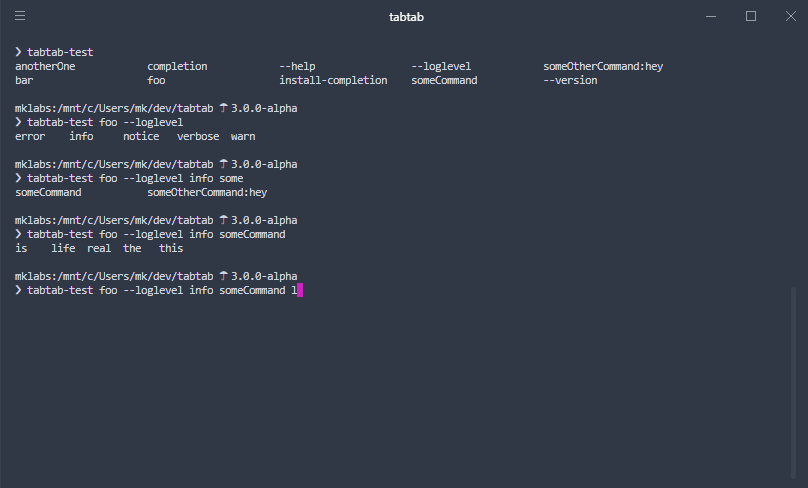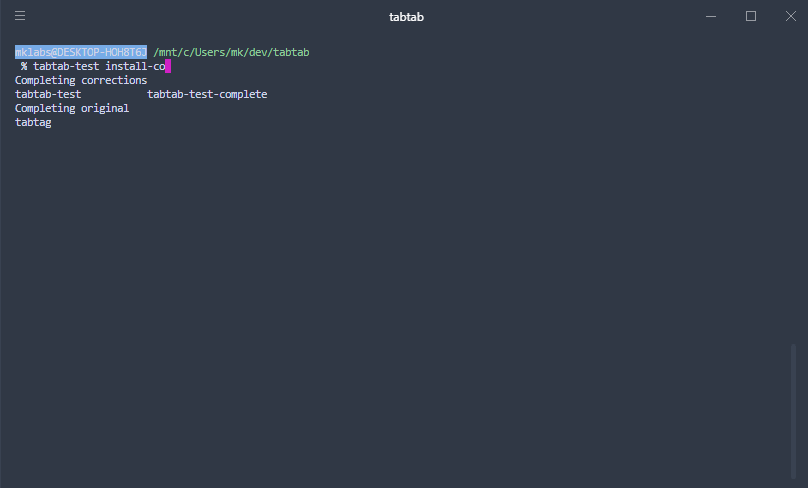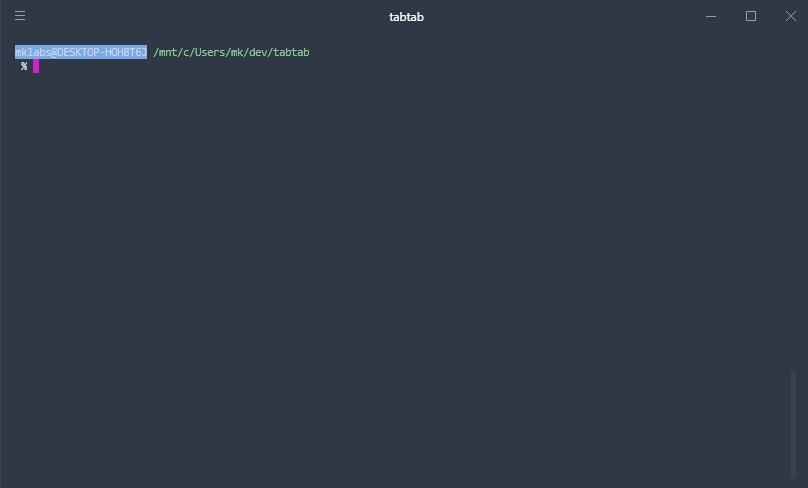
if (env.prev === '--loglevel') {
return tabtab.log(['error', 'warn', 'info', 'notice', 'verbose']);
}
return tabtab.log([
'--help',
'--version',
'--loglevel',
'foo',
'bar',
'install-completion',
'completion',
'someCommand:someCommand is some kind of command with a description',
{
name: 'someOtherCommand:hey',
description: 'You must add a description for items with ":" in them'
},
'anotherOne'
]);
};
const run = async () => {
const cmd = args[0];
// Write your CLI there
// Here we install for the program `tabtab-test` (this file), with
// completer being the same program. Sometimes, you want to complete
// another program that's where the `completer` option might come handy.
if (cmd === 'install-completion') {
await tabtab
.install({
name: 'tabtab-test',
completer: 'tabtab-test'
})
.catch(err => console.error('INSTALL ERROR', err));
return;
}
if (cmd === 'uninstall-completion') {
// Here we uninstall for the program `tabtab-test` (this file).
await tabtab
.uninstall({
name: 'tabtab-test'
})
.catch(err => console.error('UNINSTALL ERROR', err));
return;
}
// The completion command is added automatically by tabtab when the program
// is completed.
if (cmd === 'completion') {
const env = tabtab.parseEnv(process.env);
return completion(env);
}
};
run();
```
Please refer to the
[examples/tabtab-test-complete](./examples/tabtab-test-complete) package for a
working example. The following usage documentation is based on it.
### 1. Install completion
To enable completion for a given program or package, you must enable the
completion on your or user's system. This is done by calling `tabtab.install()`
usually behind a `program install-completion` command or something similar.
```js
// Here we install for the program `tabtab-test`, with completer being the same
// program. Sometimes, you want to complete another program that's where the
// `completer` option might come handy.
tabtab.install({
name: 'tabtab-test',
completer: 'tabtab-test'
})
.then(() => console.log('Completion installed'))
.catch(err => console.error(err))
```
The method returns a promise, so `await / async` usage is possible. It takes an
`options` parameter, with:
- `name`: The program to complete
- `completer`: The program that does the completion (can be the same program).
`tabtab.install()` will ask the user which SHELL to use, and optionally a path
to write to. This will add a new line to either `~/.bashrc`, `~/.zshrc` or
`~/.config/fish/config.fish` file to source tabtab completion script.
Only one line will be added, even if it is called multiple times.
### 2. Log completion
Once the completion is enabled and active, you can write completions for the
program (here, in this example `tabtab-test`). Briefly, adding completions is
as simple as logging output to `stdout`, with a few particularities (namely on
Bash, and for descriptions), but this is taken care of by `tabtab.log()`.
```js
tabtab.log([
'--help',
'--version',
'command'
'command-two'
]);
```
This is the simplest way of adding completions. You can also use an object,
instead of a simple string, with `{ name, description }` property if you want
to add descriptions for each completion item, for the shells that support them
(like Zsh or Fish). Or use the simpler `name:description` form.
```js
tabtab.log([
{ name: 'command', description: 'Description for command' },
'command-two:Description for command-two'
]);
```
The `{ name, description }` approach is preferable in case you have completion
items with `:` in them.
Note that you can call `tabtab.log()` multiple times if you prefer to do so, it
simply logs to the console in sequence.
### 3. Parsing env
If you ever want to add more intelligent completion, you'll need to check and
see what is the last or previous word in the completed line, so that you can
add options for a specific command or flag (such as loglevels for `--loglevel`
for instance).
Tabtab adds a few environment variables for you to inspect and use, this is
done by calling `tabtab.parseEnv()` method.
```js
const env = tabtab.parseEnv(process.env);
// env:
//
// - complete A Boolean indicating whether we act in "plumbing mode" or not
// - words The Number of words in the completed line
// - point A Number indicating cursor position
// - line The String input line
// - partial The String part of line preceding cursor position
// - last The last String word of the line
// - lastPartial The last word String of partial
// - prev The String word preceding last
```
Usually, you'll want to check against `env.last` or `env.prev`.
```js
if (env.prev === '--loglevel') {
tabtab.log(['error', 'warn', 'info', 'notice', 'verbose']);
}
```
## Completion mechanism
Feel free to browse the [scripts](./scripts) directory to inspect the various
template files used when creating a completion with `tabtab.install()`.
Here is a Bash completion snippet created by tabtab.
```bash
###-begin-tabtab-test-completion-###
if type complete &>/dev/null; then
_tabtab-test_completion () {
local words cword
if type _get_comp_words_by_ref &>/dev/null; then
_get_comp_words_by_ref -n = -n @ -n : -w words -i cword
else
cword="$COMP_CWORD"
words=("${COMP_WORDS[@]}")
fi
local si="$IFS"
IFS=$'\n' COMPREPLY=($(COMP_CWORD="$cword" \
COMP_LINE="$COMP_LINE" \
COMP_POINT="$COMP_POINT" \
tabtab-test completion -- "${words[@]}" \
2>/dev/null)) || return $?
IFS="$si"
if type __ltrim_colon_completions &>/dev/null; then
__ltrim_colon_completions "${words[cword]}"
fi
}
complete -o default -F _tabtab-test_completion tabtab-test
fi
###-end-tabtab-test-completion-###
```
The system is quite simple (though hard to nail it down, thank you npm). A new
Bash function is created, which is invoked whenever `tabtab-test` is tab
completed. This function then invokes the completer `tabtab-test completion`
with `COMP_CWORD`, `COMP_LINE` and `COMP_POINT` environment variables (which is
parsed by `tabtab.parseEnv()`).
The same mechanism can be applied to Zsh and Fish.
### Completion install
As described in the [`Usage > Install Completion`](#1-install-completion)
section, installing a completion involves adding a new line to source in either
`~/.bashrc`, `~/.zshrc` or `~/.config/fish/config.fish` file.
In the `3.0.0` version, it has been improved to only add a single line instead
of multiple ones, one for each completion package installed on the system.
This way, a single line is added to enable the completion of for various
programs without cluttering the Shell configuration file.
Example for `~/.bashrc`
```bash
# tabtab source for packages
# uninstall by removing these lines
[ -f ~/.config/tabtab/__tabtab.bash ] && . ~/.config/tabtab/__tabtab.bash || true
```
It'll load a file `__tabtab.bash`, created in the `~/.config/tabtab` directory,
which will hold all the source lines for each tabtab packages defining a
completion.
```bash
# tabtab source for foo package
# uninstall by removing these lines
[ -f ~/.config/tabtab/foo.bash ] && . ~/.config/tabtab/foo.bash || true
# tabtab source for tabtab-test package
# uninstall by removing these lines
[ -f ~/.config/tabtab/tabtab-test.bash ] && . ~/.config/tabtab/tabtab-test.bash || true
```
### Completion uninstall
You can follow the file added in your SHELL configuration file and disable a
completion by removing the above lines.
Or simply disable tabtab by removing the line in your SHELL configuration file.
Or, you can use `tabtab.uninstall()` to do this for you.
```js
if (cmd === 'uninstall-completion') {
// Here we uninstall for the program `tabtab-test`
await tabtab
.uninstall({
name: 'tabtab-test'
})
.catch(err => console.error('UNINSTALL ERROR', err));
return;
}
```
## Debugging
tabtab internally logs a lot of things, using the
[debug](https://www.npmjs.com/package/debug) package.
When testing a completion, it can be useful to see those logs, but writing to
`stdout` or `stderr` while completing something can be troublesome.
You can use the `TABTAB_DEBUG` environment variable to specify a file to log to
instead.
export TABTAB_DEBUG="/tmp/tabtab.log"
tail -f /tmp/tabtab.log
# in another shell
tabtab-test
See [tabtabDebug.js](./lib/utils/tabtabDebug.js) file for details.
## API Documentation
Please refer to [api](./api) directory to see generated documentation (using
[jsdoc2md](https://github.com/jsdoc2md/jsdoc-to-markdown))
## Changelog
Please refer to [CHANGELOG](./CHANGELOG.md) file to see all possible changes to this project.
## Credits
npm does pretty amazing stuff with its completion feature. bash and zsh
provides command tab-completion, which allow you to complete the names
of commands in your $path. usually these functions means bash
scripting, and in the case of npm, it is partially true.
there is a special `npm completion` command you may want to look around,
if not already.
npm completion
running this should dump [this
script](https://raw.github.com/isaacs/npm/caafb7323708e113d100e3e8145b949ed7a16c22/lib/utils/completion.sh)
to the console. this script works with both bash/zsh and map the correct
completion functions to the npm executable. these functions takes care
of parsing the `comp_*` variables available when hitting tab to complete
a command, set them up as environment variables and run the `npm
completion` command followed by `-- words` where words match value of
the command being completed.
this means that using this technique npm manage to perform bash/zsh
completion using node and javascript. actually, the comprehensiveness of npm
completion is quite amazing.
this whole package/module is based entirely on npm's code and @isaacs
work.
* * *
> [mit](./LICENSE) · > [mklabs.github.io](https://mklabs.github.io) · > [@mklabs](https://github.com/mklabs)