https://github.com/mmower/weft
Weft is a dynamic UI generation library for Cocoa applications (a component of Project Mentat)
https://github.com/mmower/weft
Last synced: 11 months ago
JSON representation
Weft is a dynamic UI generation library for Cocoa applications (a component of Project Mentat)
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mmower/weft
- Owner: mmower
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-07-21T15:42:41.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2019-08-28T12:22:11.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-07T14:45:39.990Z (about 1 year ago)
- Language: Objective-C
- Homepage:
- Size: 172 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Weft
*Version 0.9 - 22nd July 2019*
Weft is a framework designed to be embedded into a Cocoa application to allow the application to create custom user interfaces at run-time. The primary use-case is to allow a user-written script to create a custom form that can capture user data and return it to the script. Weft is a component of **Project Mentat**.
The Weft framework includes a `WeftRunner` class that accepts a UI definition as an XML string. Weft defines an XML syntax for creating elements such as textfields and buttons. The `WeftRunner` returns an `NSWindowController` instance that can display the UI, talk to the host application via a `WeftApplicationDelegate` protocol, and provide the data from form elements to the host application when the window is dismissed.
See the [Element Guide](#element-guide) for description of the Weft XML syntax.
## Example
For a more complete example see the [WeftHarness](https://github.com/mmower/weft/tree/master/WeftHarness) target in the Xcode project. Clone the project and run WeftHarness for a live demo.
[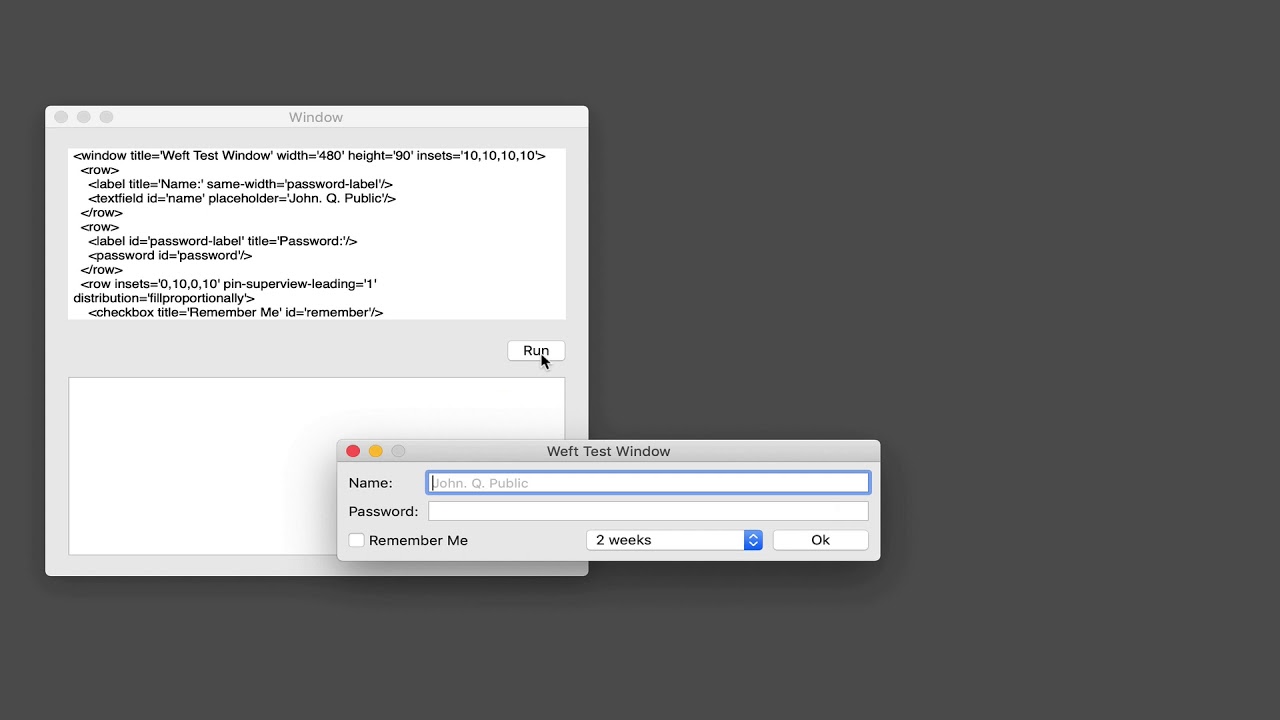](https://youtu.be/otrVXmkXs90)
### Installation
Weft is intended to be installed using the [Carthage](https://github.com/Carthage/Carthage) package manager. See the section on [installing frameworks into your application](https://github.com/Carthage/Carthage#getting-started).
Add the following to your [Cartfile](https://github.com/Carthage/Carthage/blob/master/Documentation/Artifacts.md#cartfile):
github "https://github.com/mmower/weft"
Then run `carthage update --platform macOS` to download and build the framework before adding it to your application as described above.
Alternatively you can download and build the framework manually and copy it into your application, updating the embedded binaries section of your target in Xcode.
## Class, Categories, & Protocols Guide
Weft defines a number of classes, categories, and protocols that an application hosting Weft needs to interact with.
The `WeftRunner` class creates a `WeftApplication` from an XML string defining the interface. The definition is compiled into a tree of `NSView` objects representing the user-interface which in turn is wrapped in an `NSWindow` and returned via an `NSWindowController` that the host application can use to manage the UI. By implementing the methods of the `WeftApplicationDelegate` protocol the host application can respond to changes in the UI (e.g. buttons being pushed), the user dismissing the UI, and obtain the data stored in the data elements of the UI (e.g. textfield contents & checkbox states).
### WeftRunner (`class`)
The `WeftRunner` class is the host applications interface to the Weft framework. Each `WeftRunner` is responsible for managing an `NSWindow` and returns an `NSWindowController` to the host application by which it can control the display of the user interface.
#### Methods
##### `- (instancetype)initWithSource:(NSString *)source delegate:(id)delegate`
Creates an instance of `WeftRunner` to manage a `WeftApplication` defined by the `source` XML string. Associates a `WeftApplicationDelegate` provided by the host app to receive callbacks from the `WeftApplication` during the operation of the user interface.
##### `- (NSWindowController *)run`
Creates an `NSWindow` and `NSWindowController` to operate the user interface. The window controller instance is returned to the
##### `- (void)close`
### WeftApplication (`class`)
The `WeftApplication` class is used internally to represent the definition of the interface parsed from the source XML and the `NSView` elements that are used represent them in the live interface. Host applications do not create `WeftApplication` instances as this is the job of the `WeftRunner`. An instance of `WeftApplication` is passed to all delegate methods.
The lifecycle of `WeftApplication` instances is governed by the `WeftRunner`. The host application should not need to keep a references to `WeftApplication` itself. The result of calling methods on `WeftApplication` after the UI has been dismissed are undefined.
#### Methods
##### `- (NSDictionary *)values`
The `values` message can be sent to a `WeftApplication` to retrieve the current value of all data elements in the interface. The returned dictionary usese the `id` attributes of these elements as keys referencing appropriate attribute values (e.g. an `NSString` for the value of an `NSTextfield` specified by a `` element).
### WeftApplicationDelegate (`protocol`)
`WeftApplicationDelegate` defines 1 mandatory and 3 optional methods for allowing the host and `WeftApplication` to interact.
Note that if the delegate also supports the `NSTextFieldDelegate` protocol then it will be registered as the delegate for any `NSTextField` objects generated.
#### Mandatory methods
##### `- (void)weftApplication:(WeftApplication *)app complete:(BOOL)ok`
When the user clicks on the button represented by an `` or `` element the `WeftApplication` sends this message to its delegate. If an `` element was pressed the `complete:` argument is `YES` otherwise it is `NO`. The host is responsible for calling `-close` on the provided `NSWindowController` to dismiss the interface.
#### Optional methods
##### `- (void)weftApplication:(WeftApplication *)app buttonPushed:(NSButton *)button`
When the user clicks on a button represented by a `` element the `WeftApplication` sends this message to its delegate.
##### `- (void)weftApplication:(WeftApplication *)app radioSelected:(NSButton *)radio`
When the user selects a different radio button represented by `` element the `WeftApplication` sends this message to its delegate.
##### `- (void)weftApplication:(WeftApplication *)app checkboxToggled:(NSButton *)checkbox`
When the user selects or deselects a checkbox represented by the `` element the `WeftApplication` sends this message to its delegate.
### NSView+Weft (`category`)
Weft defines an `NSString *` property `elementId` on `NSView`.
#### `- (NSString *)elementId`
Returns the value that was specified using the `id` attribute that is mandary on data elements in Weft XML. For example `id` is a mandary attribute of the `` element. This allows the host application to relate the elements defined in the source to the dynamically generated `NSView` instances that represent them in the user interface. The host application code should not need to call the associated `-setElementId:` method itself, doing so may cause problems.
The structural elements create the outline of the user interface. All Weft interfaces start with a `` which, by default, contains a `col` with no insets and using a distribution of `fillequal` into which further elements can be places. This simplifies in that the user does not need to specify a container for elements. Further `` and `` elements may be used to structure the interface into rows and columns as required.
#### \
##### Example
A `` element specifies the top-level window and contains all other elements.
…
##### Attributes
* title: Title for the window
* width: initial width of the window (this may be changed if the layout ends up wider)
* height: initial height of the window (this may be changed if the layout ends up taller)
* insets: a comma-separated set of values for the top,left,bottom,right margin of the window
#### \
A `` organises its contents horizontally. Internally a row is represented via an `NSStackView` whose `orientation` property is set to `NSUserInterfaceLayoutOrientationHorizontal`.
##### Attributes
* `insets` - a series of values used as a margin between the edge of the row and its contents. Specified as `top`, `left`, `bottom`, `right`
* `spacing` - number of points of spacing between elements
* `distribution` - controls how contents are distributed across the width of the row. Valid values are `equalcentering`, `equalspacing`, `fill`, `fillequally`, `fillproportionally`, `gravity`
#### \
A `` organises its contents vertically. Internally a col is represented via an `NSStackView` whose `orientation` property is set to `NSUserInterfaceLayoutOrientationVertical`.
##### Attributes
See [row](#row-element)
### Data Elements
Data elements represent the input controls that appear within the UI layout and have values that can be obtained via the [`- values`](#weftapplication-methods-values) method.
#### Mandatory Attributes
The following attributes are mandatory for all data elements:
* `id`: a unique identifier for the element that will be associated with its correspdonding `NSView` instance via the [`-elementId`](#nsview-methods-element-id) method.
#### Optional Attributes
The following attributes are supported for all data elements but are optional:
* `gravity`: when the data element is placed into a `` or `` whose distribution is set to `gravity` then this attribute specifies the gravity area into which the control will be placed. Valid values are `leading`, `center`, and `trailing` for `` elements and `top`, `center`, and `bottom` for `` elements.
* `same-width`:
* `same-height`:
* `pin-superview`:
* `pin-superview-leading`:
* `pin-superview-top`:
* `pin-superview-trailing`:
* `pin-superview-bottom`:
#### \
A `` creates an `NSTextField` that supports a single line of editable text.
##### Attributes
* `default`: default value to user for the textfield
* `placeholder`: value to be displayed in textfield if there is no value
* `tooltip`: value to be displayed as a tooltip
* `disabled`: set to `1` to disable this control
#### \
A `` creates an `NSTextView` that supports editing a longer text. The initial content of the textbox should be added between the opening and closing tags.
##### Example
Here is the text of your message.
##### Attributes
#### \
A `` creates an `NSSecureTextField` that allows for editing sensitive values such as passwords and prevents them appearing on screen.
##### Attributes
#### \
A `` element specifies a push-button (`NSButton`) control.
##### Attributes
* `id`: unique identifier for the button. Will be sent to the delegate.
#### \
An `` element specifies an **Ok** button. It is a special type of button that, when pushed, sends the `WeftApplicationDelegate` a message `- (void)weftApplication:(WeftApplication *)app complete:(BOOL)ok` passing `YES` as the `complete` value.
##### Attributes
* `title`: the title to appear on the ok button
#### \
A `` element specifies a **Cancel** button. It is a special type of button that, when pushed, sends the `WeftApplicationDelegate` a message `- (void)weftApplication:(WeftApplication *)app complete:(BOOL)ok` passing `NO` as the `complete` value.
##### Attributes
#### \
A `` element specifies an on/off checkbox control.
##### Attributes
* `id`: unique identifier for the checkbox. Will be used as a data key
* `title`: string for the label associated with the checkbox
* `disabled`: specify a value of `1` to have the control be disabled
* `gravity`: if in a `` or `` using the `gravity` distribution specify a value of `leading`,
#### \
##### Attributes
#### \
##### Attributes
#### \
##### Attributes
## Acknowledgements
Philosophically Weft was inspired by [Pashua](https://www.bluem.net/en/projects/pashua/) and [Cocoa Dialog](https://cocoadialog.com/) which demonstrated that such an approach was viable. Also [XAML](https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/framework/wpf/advanced/xaml-overview-wpf) and [XUL](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Mozilla/Tech/XUL) which encouraged a need for simplicity of purpose. Weft is made possible by Apple AutoLayout and `NSStackView`.
## License
Weft is released under the MIT license, see the [`LICENSE`](LICENSE) file for details.