https://github.com/mobizt/firebaseclient
🔥Fast and reliable async Firebase client library for Arduino.
https://github.com/mobizt/firebaseclient
arduino cloud-firestore-database cloud-messaging esp32 esp8266 firebase firebase-storage google-cloud-functions google-cloud-storage raspberry-pi-pico realtime-database
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
🔥Fast and reliable async Firebase client library for Arduino.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mobizt/firebaseclient
- Owner: mobizt
- License: mit
- Created: 2024-01-20T10:13:24.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-07-30T09:50:05.000Z (5 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-07-30T11:56:49.705Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: arduino, cloud-firestore-database, cloud-messaging, esp32, esp8266, firebase, firebase-storage, google-cloud-functions, google-cloud-storage, raspberry-pi-pico, realtime-database
- Language: C
- Homepage:
- Size: 8.68 MB
- Stars: 214
- Watchers: 11
- Forks: 18
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# FirebaseClient
 [](https://github.com/mobizt/FirebaseClient/stargazers) 
   
## Introduction
Async Firebase Client library for Arduino Documentation.
This is the `REST APIs Firebase Client` library that supports the following `Firebase` and `Google Cloud` products in one place.
- `Firebase Realtime Database`
- `Cloud Firestore Database`
- `Cloud Messaging`
- `Firebase Storage`
- `Google Cloud Functions`
- `Google Cloud Storage`
- `Security Rules Management`
This Firebase library is quite comprehensive which covers many applications.
It is suitable for all serverless applications e.g. data logging, automation and IoTs. You can choose what options and services you want to use (see [Library Build Options](#library-build-options)).
There are many types of authentications supported and you can manage the user account with sign up (user/guest), delete, verify the user and reset the user password.
This library also supports auto- and one-time authentications and you can force the library to re-authenticate any time.
This library also provides the OTA firmware update functionalities by using your Realtime Database data or Firebase/Cloud Storage object (file).
Note that the Firestore data change listening and Realtime Database disconnected event are not support by the Firebase REST API.
The [bare minimum code examples](/examples/BareMinimum/) provide the basic guidelines for library usage concepts. There is a little more code that needs to be written but it is still simple and understandable.
You can create your own wrapper class as you want that provides the callback-free, cleaner and simpler API. See the [Wrapper example](/examples/RealtimeDatabase/Wrapper/) for how to.
You can use security rules to fully control the Firebase services access instead of relying only on the authentication credentials and tokens. For access control using custom claims and security rule use case, see [AccessControl](/examples/RealtimeDatabase/AccessControl/AccessControl.ino) example.
This library also provides the test tools (web client app) that are simple and ready to try without coding.
To see how Firebase Realtime Database provides the efficient, fast and reliable performance when work with this library, see [StreamPerformanceTest](/examples/RealtimeDatabase/StreamPerformanceTest/) example.
To test notification sending with Firebase Cloud Messaging by using our FCM Web Client App, see [WebClient](/examples/Messaging/WebClient/) example.
## Changes since v2.1.0
The library since v2.1.0 is network independent. All network data and management classes are removed.
Users have to define the macros or build options in their sketch before including the library header file. See [Library Build Options](#library-build-options) section for the available options.
The SSL client can be set via `AsyncClientClass::setClient()` or in the `AsyncClientClass` constructors without the network options.
The `AsyncClientClass` methods that are related to the networks are removed.
## Supported Devices
ESP8266, ESP32 and all 32-bit MCU except for Atmel AVR.
## Installation
- ### Using Library Manager
At Arduino IDE, go to menu **Sketch** -> **Include Library** -> **Manage Libraries...**
In Library Manager Window, search **"firebase"** in the search form then select **"FirebaseClient"**.
Click **"Install"** button.
For `PlatformIO` IDE, use the following command.
**pio lib install "FirebaseClient""**
Or at **PIO Home** -> **Library** -> **Registry** then search **FirebaseClient**.
In case ESP32, PlatformIO's platform-espressif32 core is outdated. You should use [pioarduino](https://github.com/pioarduino) platform instead.
- ### Manual installation
For `Arduino IDE`, download the zip file from the repository (Github page) by select **Code** dropdown at the top of repository, select **Download ZIP**
From Arduino IDE, select menu **Sketch** -> **Include Library** -> **Add .ZIP Library...**.
Choose **FirebaseClient-main.zip** that previously downloaded.
Rename folder from **FirebaseClient-main** to **FirebaseClient**.
Go to menu **Files** -> **Examples** -> **FirebaseClient** and choose one from examples.
- ### RP2040/RP2350 Arduino SDK installation
For Arduino IDE, the Arduino-Pico SDK can be installed from Boards Manager by searching pico and choose Raspberry Pi Pico/RP2040 to install.
For PlatformIO, the Arduino-Pico SDK can be installed via platformio.ini
```ini
[env:rpipicow]
platform = https://github.com/maxgerhardt/platform-raspberrypi.git
board = rpipicow
framework = arduino
board_build.core = earlephilhower
monitor_speed = 115200
board_build.filesystem_size = 1m
```
See this Arduino-Pico SDK [documentation](https://arduino-pico.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) for more information.
> [!NOTE]
> You cannot install Arduino IDE and Arduino library in Microsoft's `OneDrive` folder because the `OneDrive` folder is the sandbox or virtual folder instead of real folder which causes the path error when compilation.
## Usages
For new `Firebase` users, please read the [Project Preparation and Setup](#project-preparation-and-setup) section for preparing the Firebase project.
For new library user that the project was setup and prepared, see the [bare minimun examples](/examples/BareMinimum/) to start using this library with minimum code that is required by this library.
For more examples, please click [here](/examples/).
### Working Principle
This library can be used in two modes i.e. async mode and await or sync mode.
With async mode, the task will be stored in the FIFO queue. The result of the running task can be obtained via the callback function or the proxy object that assign when calling the functions.
The `AsyncClientClass` is the proxy class that provides the queue for async tasks and also the information of task process when working in await or sync mode.
The async task that is stored in the queue contains the preprocess HTTP request data (headers without auth tokens and payload).
The SSL Client that is assigned with the `AsyncClientClass` constructor will be the network client used for all async tasks in its queue.
The result of a async task can be obtained from the `AsyncResult` class object. This object provides the debug, authentication process event, error information and the response payload of the request.
If no async callback function is assigned with the function, the `AsyncResult` class object should be assigned otherwise it will work in sync mode.
In this case, it should be polling read for new available information from the `AsyncResult` at the end of the loop function.
In the await or sync mode, task will be processed immediately and waits for the end of process when the response is complete or time out or error occurred.
The information (debug/error) can be obtained by the `AsyncClientClass` that assign with the function. The response payload or processed value will be obtained if no errors.
The authentications support by this library covers user, service account (admin) and no authentications.
There are authentication classes that store the sign-in and authentication credentials whuch can be used temporary as it will be duplicated to use later.
The authentication tokens are also supported e.g. custom (signed JWT token), ID and access tokens. The refresh token also supports. User can use third party app/services to create these auth token when sign-in and authentication credentials are sensitive and not allowed to store in the sketch.
These authentication tokens (excepts for Reltime Database secret) are the short-lived tokens. It will be expired in 60 minutes.
The `FirebaseApp` class will be used to handle the authentication task. Some function that executes in the loop function will keep the authentication process running e.g. `FirebaseApp::loop`.
The authentication process is the task that involved auth token generation using sign-in, auth credentials and tokens that user assigned with the `initializeApp` function.
The `initializeApp` function is the static function which also allows the authentication process to work in async and await or sync modes.
In version 2.x.x and later, when assign the timeout (> 0) to the `initializeApp` function, the authentication task will be processed in await or sync mode.
The callback function assigned with `initializeApp` function will provide the auth process event, debug and error information while authenticating in async and sync modes.
In version 2.x.x, the `FirebaseApp` class can also maintain the async tasks that stored in other `AsyncClientClass`s.
The details for all classes used in this library are available. Click the following links for details.
- [RealtimeDatabase Class](resources/docs/realtime_database.md)
- [Firestore::Databases Class](resources/docs/firestore_database.md)
- [Firestore::Documents Class](resources/docs/firestore_database_document.md)
- [Firestore::Values Class](/resources//docs//firestore_database_values.md)
- [Messaging Class](resources/docs/messaging.md)
- [MessagingInstance Class](resources/docs/messaging_instance.md)
- [Storage Class](resources/docs/storage.md)
- [CloudStorage Class](resources/docs/cloud_storage.md)
- [CloudFunctions Class](resources/docs/cloud_functions.md)
- [Security Ruls Management Class](resources/docs/rules.md)
- [Authentications Classes](resources/docs/auth_class.md).
- [AsyncClient Class](/resources//docs//async_client.md)
- [AsyncResult Class](/resources//docs//async_result.md)
- [FirebaseApp Class](/resources//docs/firebase_app.md)
- [FirebaseClient Class](/resources/docs/firebase_client.md)
- [File and Blob Classes](/resources/docs/file_config.md)
- [JSON Writer Class](/resources//docs/json_writer.md)
- [Some Placeholder Class](/resources/docs/placeholders.md)
### OTA Update
The OTA firmware update is supported using bin file stored in `Firebase Storage` and `Google Cloud Storage` buckets or base64 encoded data stored in `Realtime Database`.
The Arduino devices that natively supported OTA firmware update are `ESP8266`, `ESP32` and `Raspberry Pi Pico`.
Since FirebaseClient v1.3.1, the OTA update in Arduino SAMD21 boards that use NINA firmware and WiFi101 firmware was supported using [Internal_Storage_OTA](https://github.com/mobizt/Internal_Storage_OTA) library.
The [Internal_Storage_OTA](https://github.com/mobizt/Internal_Storage_OTA) is the modified version of [WiFi101OTA](http://www.arduino.cc/en/Reference/WiFi101OT) library which contains only four required files e.g. `Internal_Storage_OTA.h`, `InternalStorage.h`, `InternalStorage.cpp`and `OTAStorage.h`.
To allow OTA update in SAMD21 Arduino boards, you have to include `Internal_Storage_OTA.h` in your sketch.
Then assign the `InternalStorage` class object to be used for `Realtime Database` via `RealtumeDatabase::setOTAStorage`, for `Google Cloud Storage` via `CloudStorage::setOTAStorage` and for `Firebase Storage` via `Storage::setOTAStorage`
In SAMD21 Arduino boards, if `OTA Storage` was not set before calling OTA function, the error `OTA Storage was not set` will be occurred.
Finally, once the OTA update was finished, in case [Internal_Storage_OTA](https://github.com/mobizt/Internal_Storage_OTA), you have to call `InternalStorage.apply()` to apply the update and then restart.
Some OTA libraries that provide `Storage Class` object that derived from the modified version of Arduino WiFi101OTA's `OTAStorage` class can also be used.
## Project Preparation and Setup
Click here for details.
You have to setup the Firebase project to use `Firebase products`. Visit [Understand Firebase Projects](https://firebase.google.com/docs/projects/learn-more) to learn more about Firebase projects.
For new Firebase user, go to the [Google Firebase Console](https://console.firebase.google.com/), sign in to your Google account, and create a new project as the following images.

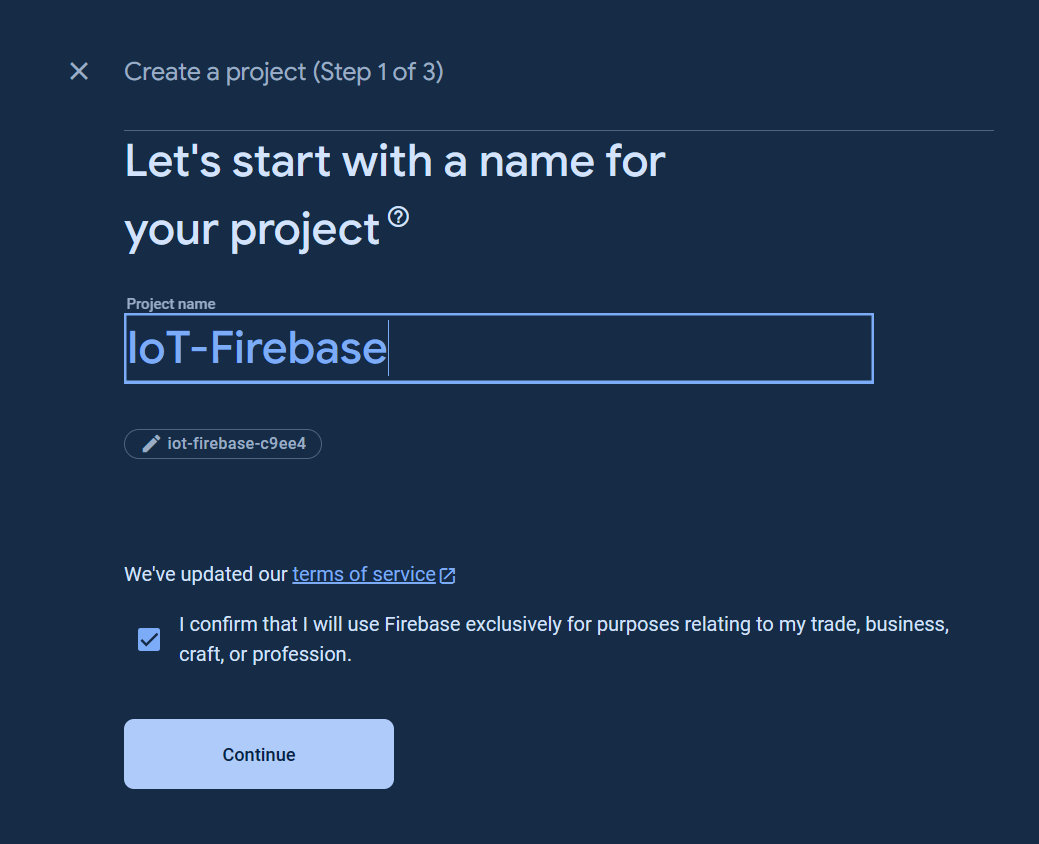
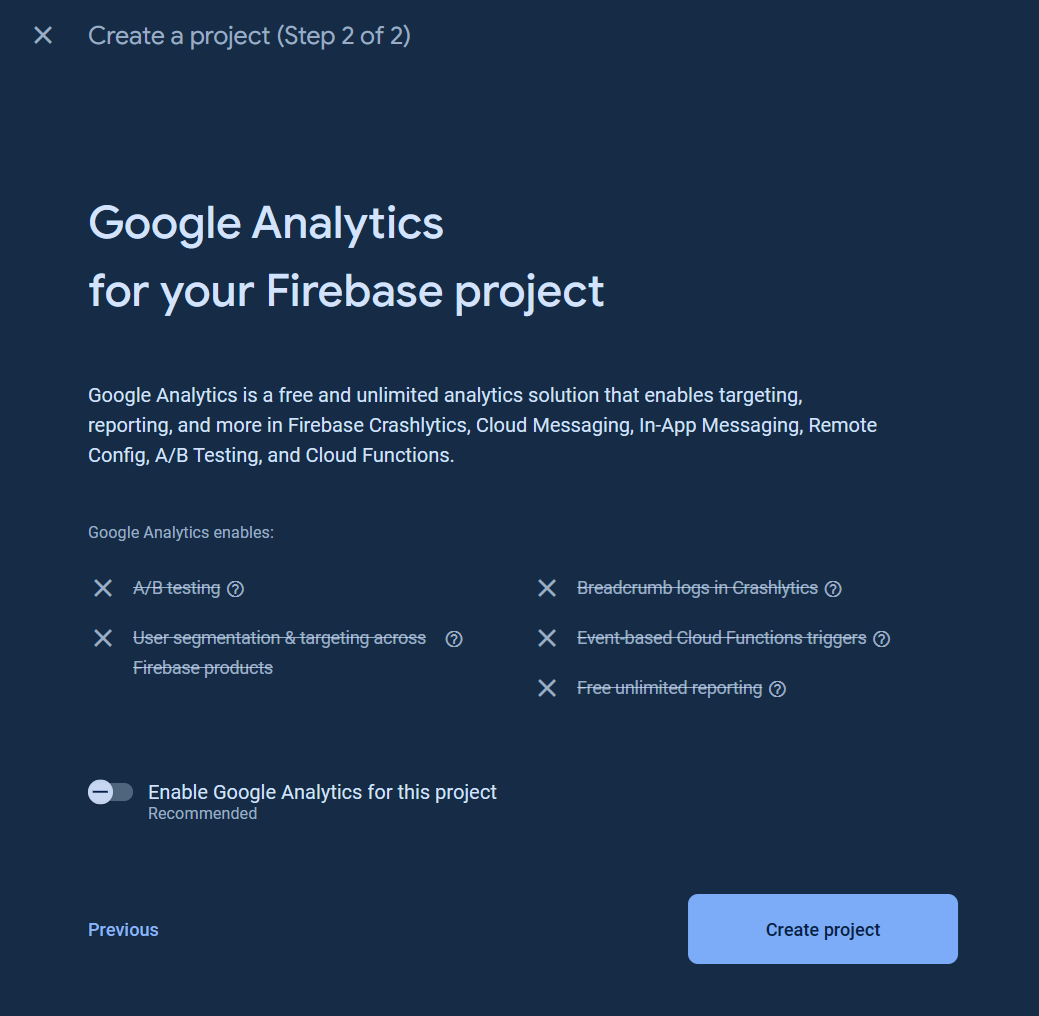
Click `All products` button.

### Authentication Getting Started
When `custom token`, `ID token` authorization are used via `CustomAuth`, `UserAuth`, `CustomToken` and `IDToken`, the `Authentication` service is needed and must be set up otherwise the `HTTP status code 400` error will show in the async callback.
> [!NOTE]
> The `Authentication` service is not required for `OAuth2.0 access token authentication using service account` authentication and legacy token (database secret) authorization.
To get started with `Authentication`, choose `Authentication` and click `Get started` button.

Under Sign-in providers, choose Email/Password.
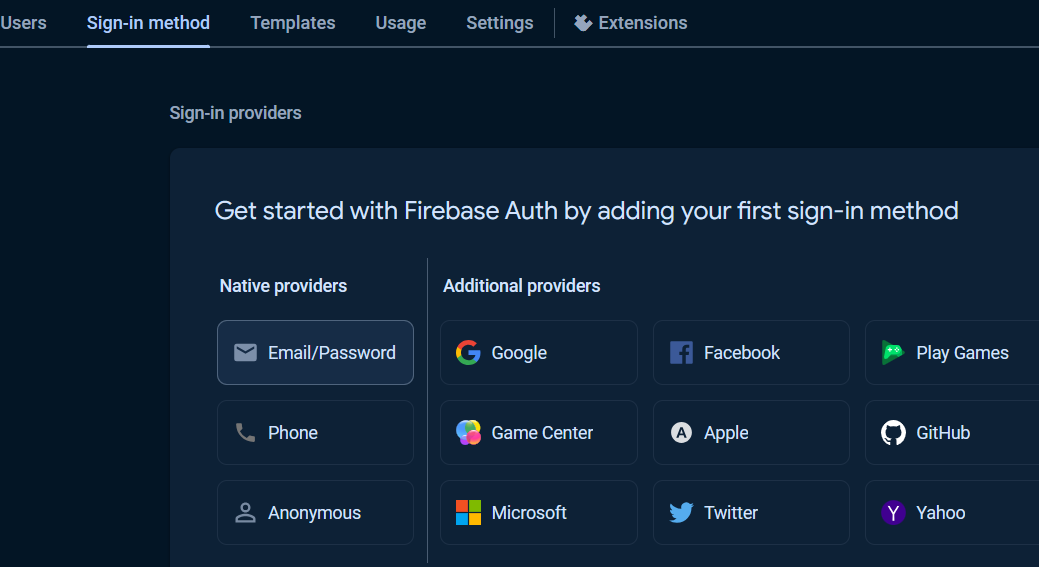
Select `Enable` check option in `Email/Password` section, and click `Save` button.
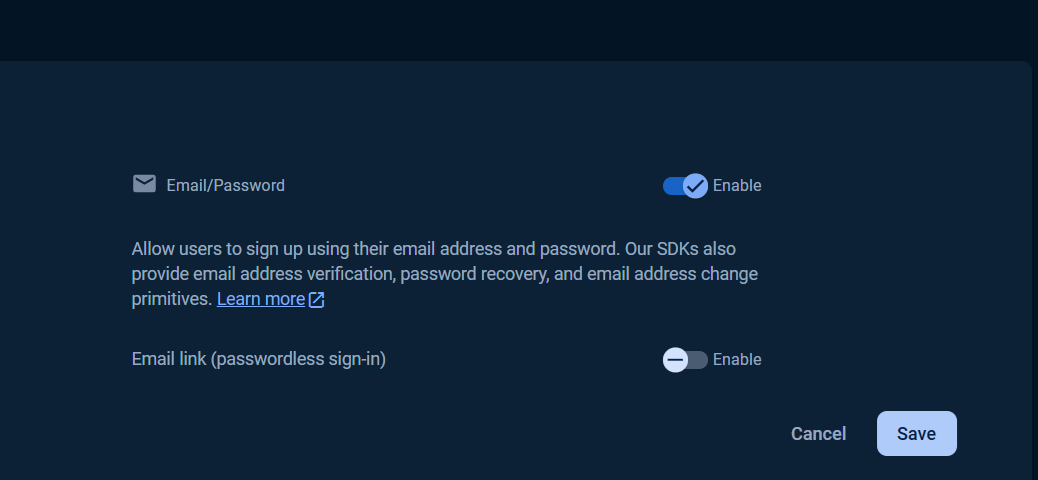
Then click `Users` tab, click `Add user` button.
Fill in the `Email` and `Password` and click `Add user` button.
Once the `Authentication` was setup, the `Web API Key` will be generated. See the `Project Settings` page for `Web API Key`.
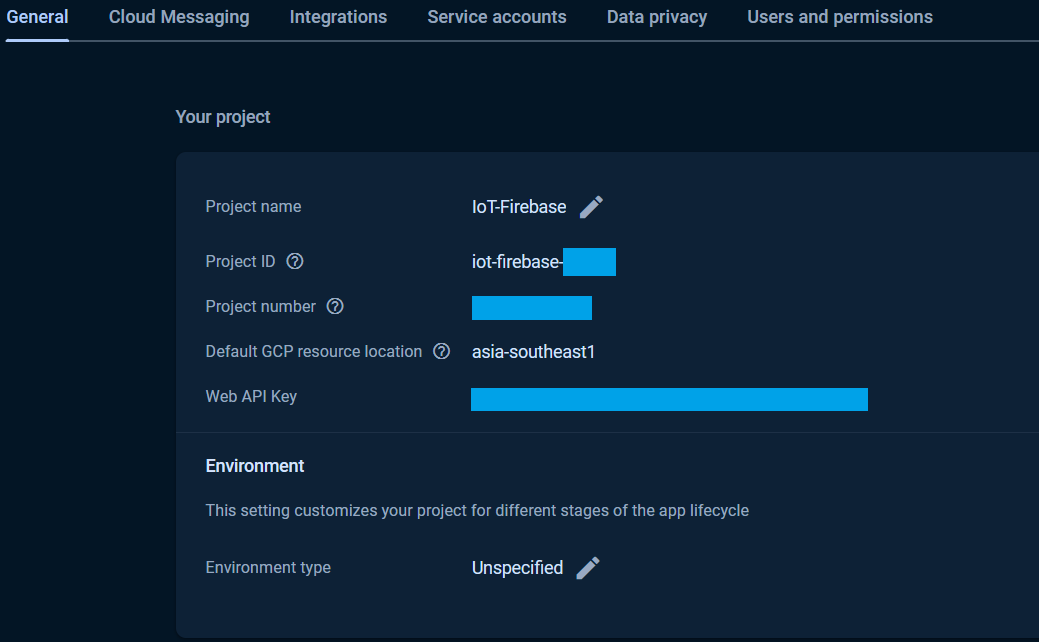
The `Web API Key` is used in all `custom token`, `ID token` authentications that used via the `CustomAuth`, `UserAuth`, `CustomToken` and `IDToken` provider classes and it was assign to the `API_KEY` in the exampless.
See [API Keys Overview](https://cloud.google.com/api-keys/docs/overview) and [Authenticate by using API keys](https://cloud.google.com/docs/authentication/api-keys) for more details.
At the `Authentication` page, under `Sign-in method` tab, other Sign-in providers can be added.
To add `Anonymous` sign-in provider, click `Add new provider` button.
Select enable check option in Email/Password section, and click `Save` button.
### Realtime Database Getting Started
To get started with `Firebase Realtime Database`, choose `Realtime Database` and click `Create Database`.

Set up your `Database options` and `Security rules`.
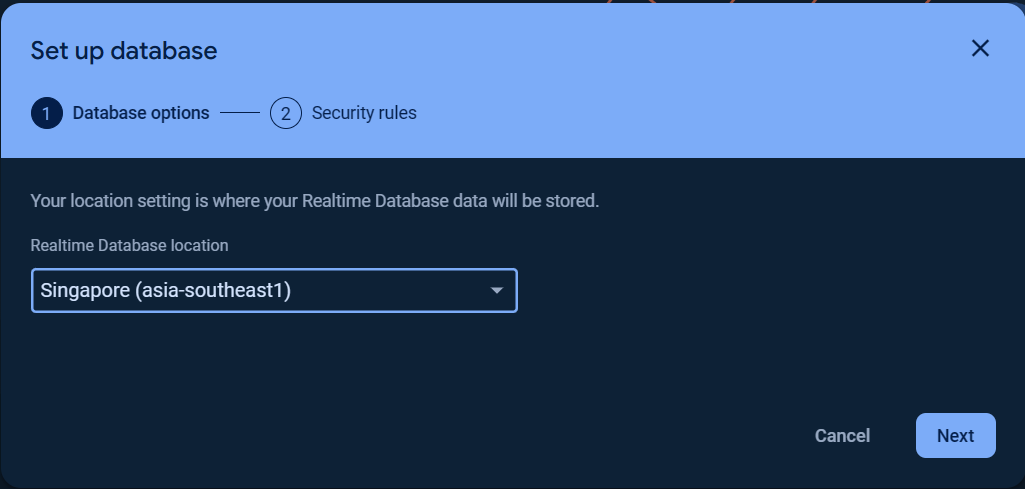
#### Note for Realtime Database location selection
Refer to this [Realtime Database locations](https://firebase.google.com/docs/projects/locations#rtdb-locations), the `Database URL scheme` depends on the `Region name` (Realtime Database location) you selected.
In some Arduino boards that works with [`WiFiNINA`](https://github.com/arduino/nina-fw) and `WiFi101` firmwares, the database URL that ends with `firebasedatabase.app` may not work after the SSL certificate was upload into the board firmware which causes Realtime Database server connection failure.
This issue was found on MKR 1000 WiFi board with `WiFi101`firmware at the moment while MKR WiFi 1010 with [`WiFiNINA`](https://github.com/arduino/nina-fw) firmware does not have certificate issue.
We don't investigate in to the Arduino firmwares to find the root cause, then `us-central1` region for `DATABASE_NAME.firebaseio.com` URL should be selected for this case.
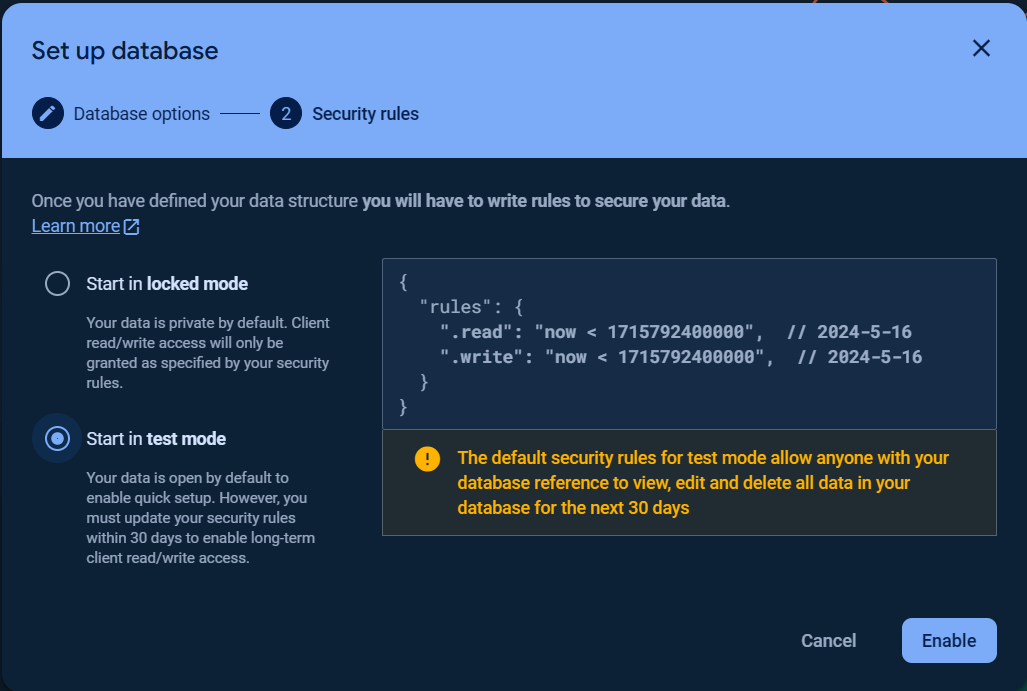
You can choose `Start in locked mode` or `Start in test mode` for `Security rules`.
Once the database was created, click the `Rules` tab and change the `Security rules` as following to allow the basic authentication, click `Publish` button to apply the changes.
```yaml
{
"rules": {
".read": "auth != null",
".write": "auth != null"
}
}
```
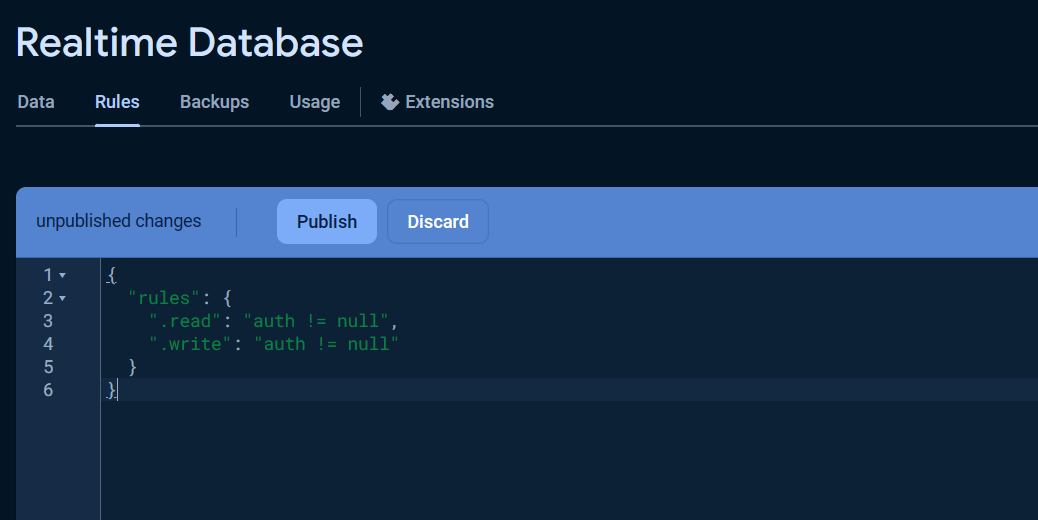
The warning `Your security rules are not secure. Any authenticated user can steal, modify, or delete data in your database.` will be displayed due to insecure rules which you can change it for more secure later.
Visit [Understand Firebase Realtime Database Security Rules](https://firebase.google.com/docs/database/security) to learn more about security rules.
The reference url is the `DATABASE_URL` that defined and used in the `Realtime Database` examples can be obtained from the `Data` tab as the following.
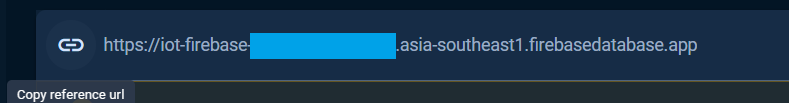
The reference url or database url also can be taken from the `Service Account` key file, see [Service Account](#service-account) section.
#### Realtime Database Legacy Usage
The database secret is the secret key for privileged accessing the `Realtime Database` service.
The database secret is now currently deprecated. Alternatively, to use the `Realtime Database` with the same privileged access as database secret but secured, the `OAuth2.0 access token authentication using service account` via `ServiceAuth` provider class is recommended.
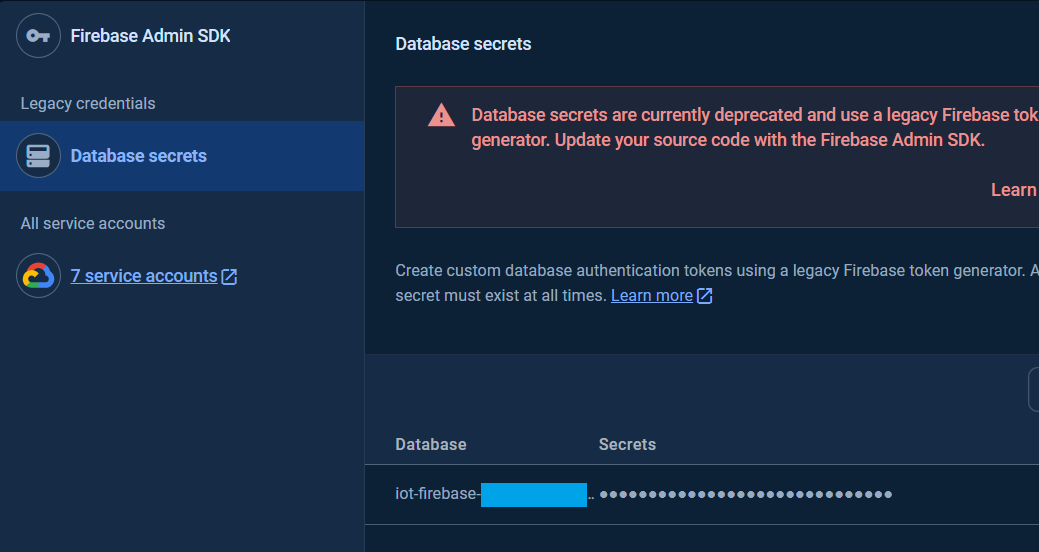
To get the database secret, in the `Project Settings` page in the [`Google Firebase Console`](https://console.firebase.google.com/), under the `Service accounts` Tab, click `Database secret`.
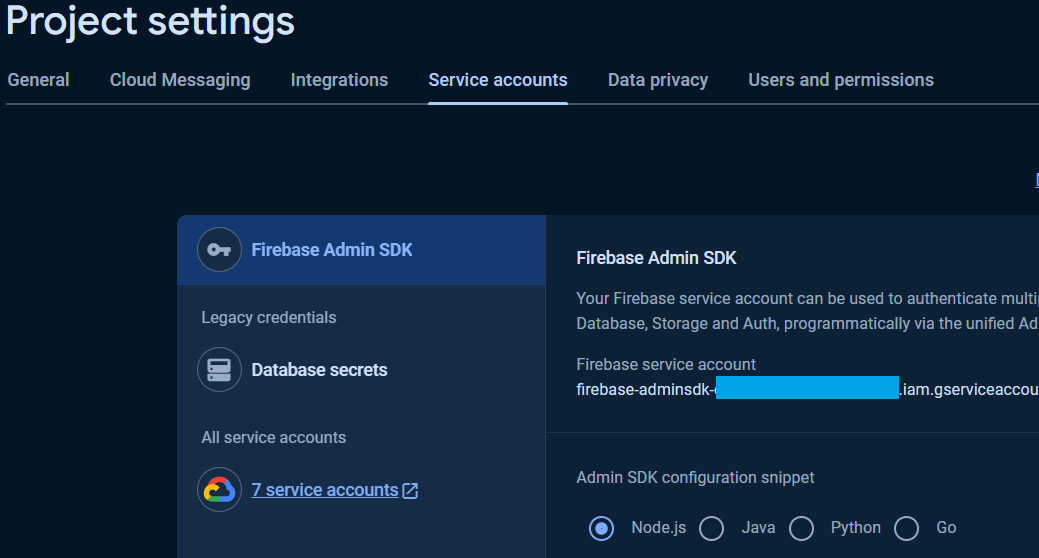
The database secret for the databases are available in the `Secrets` column.
### Google Cloud Firestore Database Getting Started
To get started with `Cloud Firestore Database`, choose `Cloud Firestore` and click `Create database`.

Set up your database `Name and Location` and `Security rules`.
> [!NOTE]
> The first database name (ID) is `(default)` which cannot be changed.
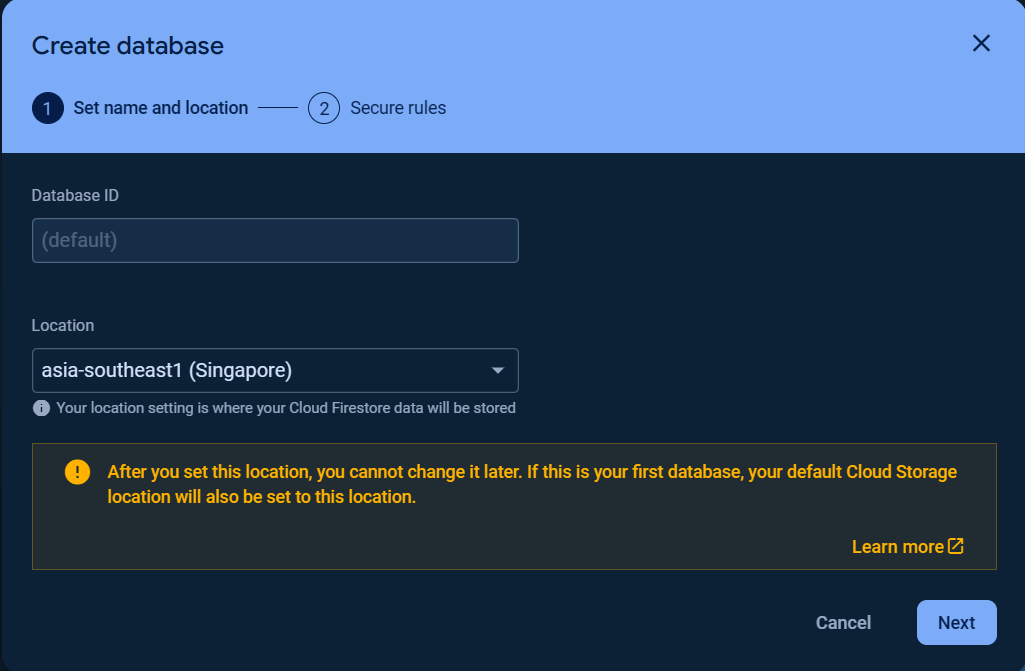
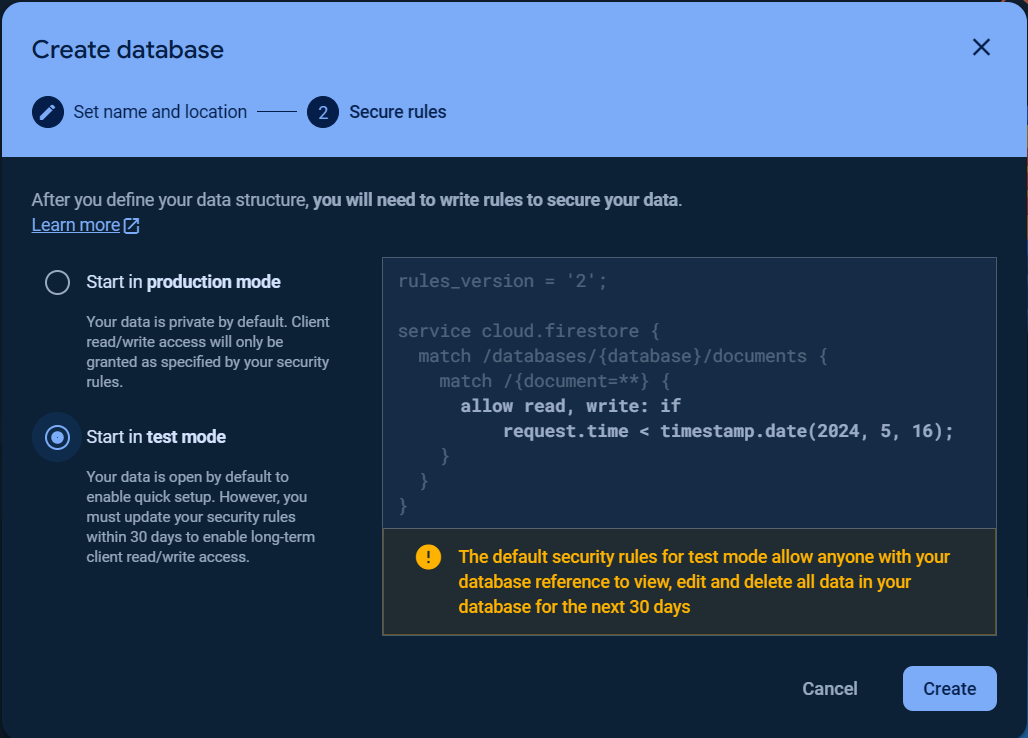
Once the database was created, click the `Rules` tab and change the `Security rules` as following to allow the basic authentication, click `Publish` button to apply the changes.
```yaml
rules_version = '2';
service cloud.firestore {
match /databases/{database}/documents {
match /{document=**} {
allow read, write: if request.auth.uid != null;
}
}
}
```
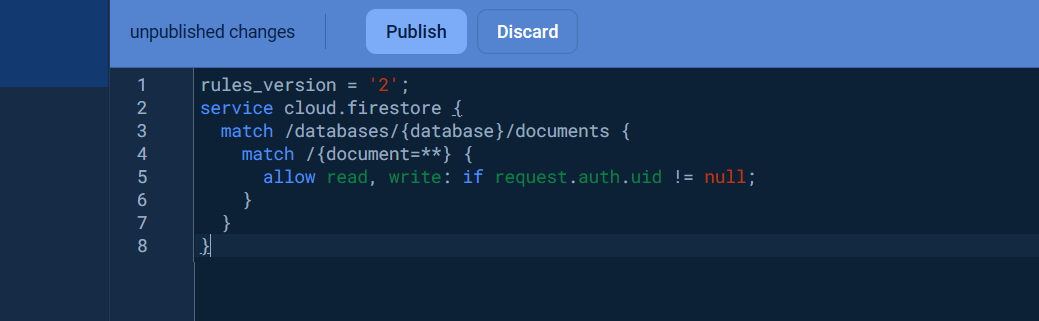
Visit [Get started with Cloud Firestore Security Rules](https://firebase.google.com/docs/firestore/security/get-started) to learn more about security rules.
### Storage Getting Started
To get started with `Storage`, choose `Storage` and click `Get started`.

Then set the `Secure Rules for Cloud Storage` and `Cloud Storage location`.
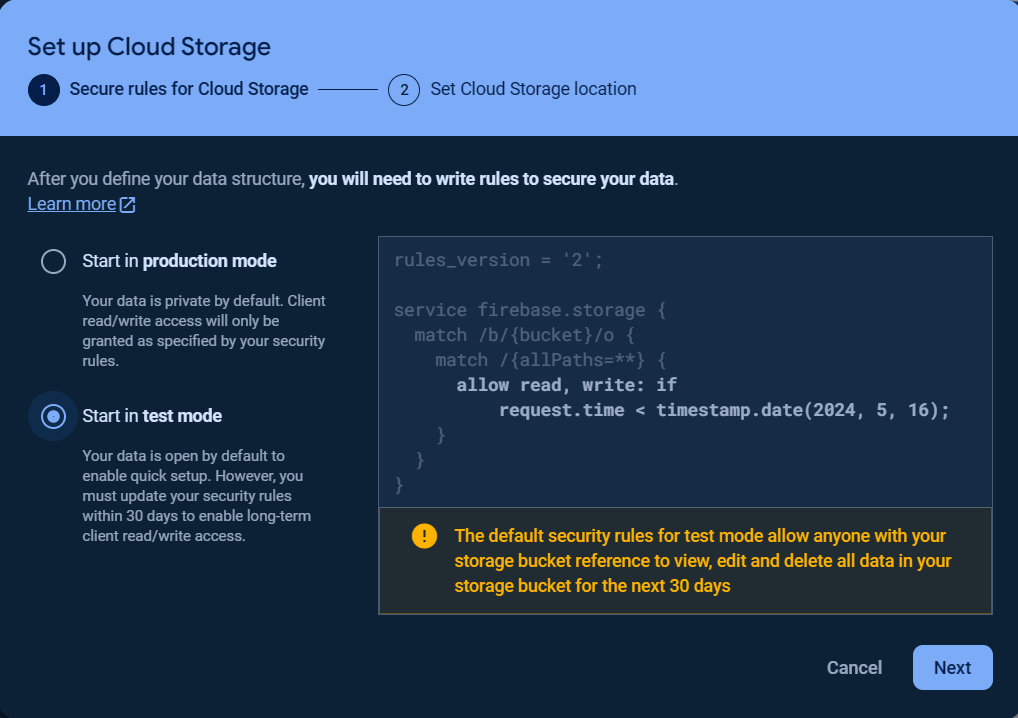
Once the storage bucket was created, click the `Rules` tab and change the `Security rules` as following to allow the basic authentication, click `Publish` button to apply the changes.
```yaml
rules_version = '2';
service firebase.storage {
match /b/{bucket}/o {
match /{allPaths=**} {
allow read, write: if request.auth.uid != null
}
}
}
```
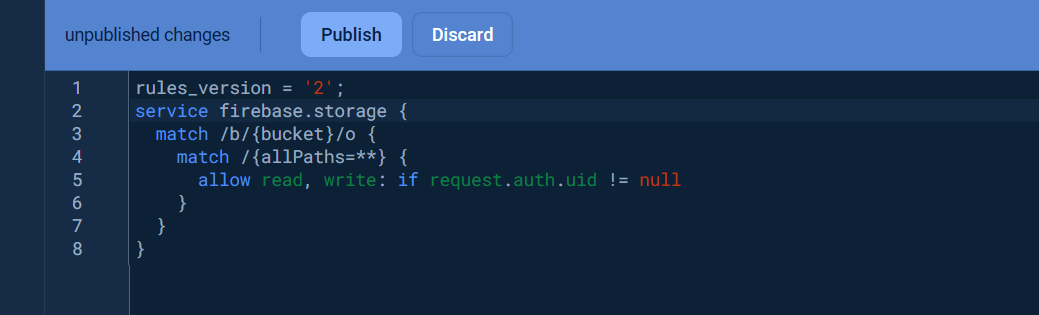
Visit [Get started with Firebase Security Rules](https://firebase.google.com/docs/storage/security/get-started) to learn more about security rules.
The folder path is the `STORAGE_BUCKET_ID` that defined and used in the Storage examples can be obtained from the `Files` tab as the following.
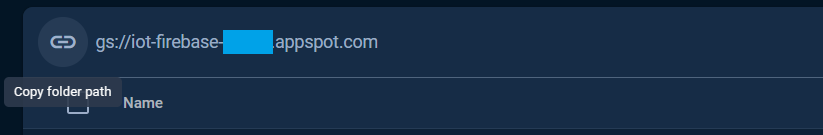
The folder path or the `STORAGE_BUCKET_ID` also can be taken from the `Service Account` key file, see [Service Account](#service-account) section.
### Google Cloud Functions Getting Started
To use the `Cloud Functions` for running your backend automate code, the billing plan for the project is needed to be upgraded to at least `Blaze` plan.
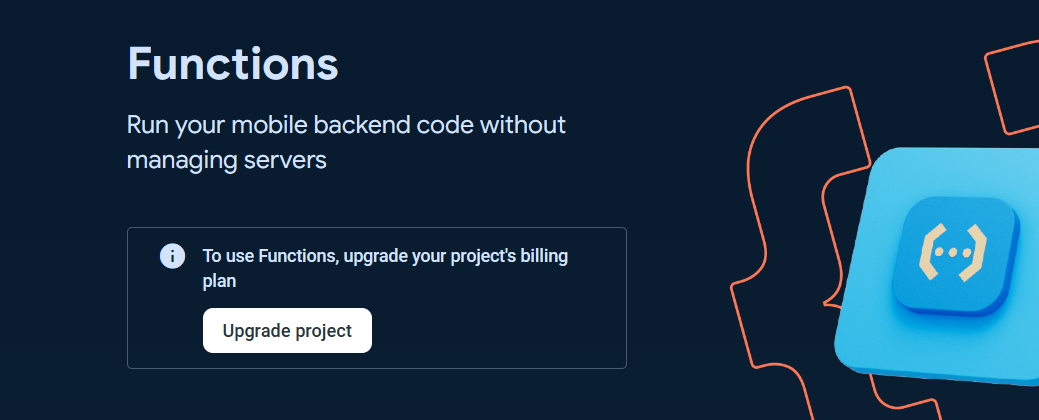
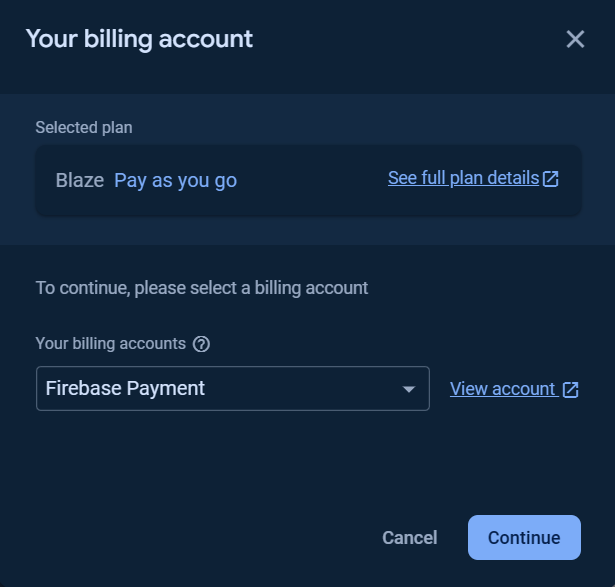
You can `Set a billing budget` at this step or skip it.
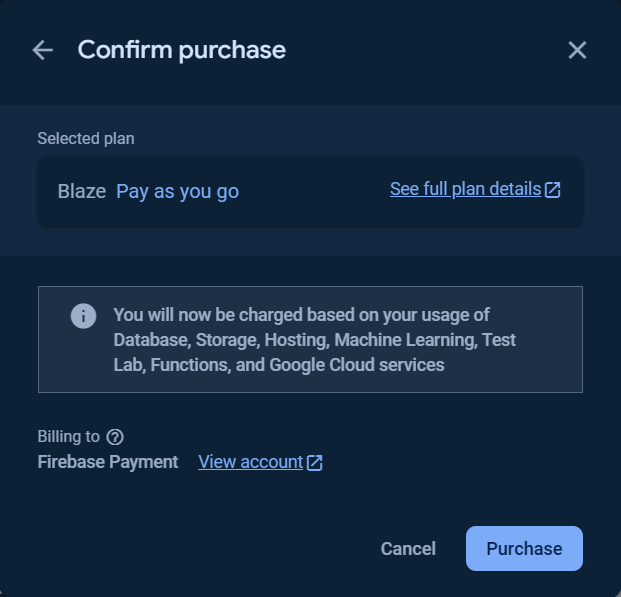
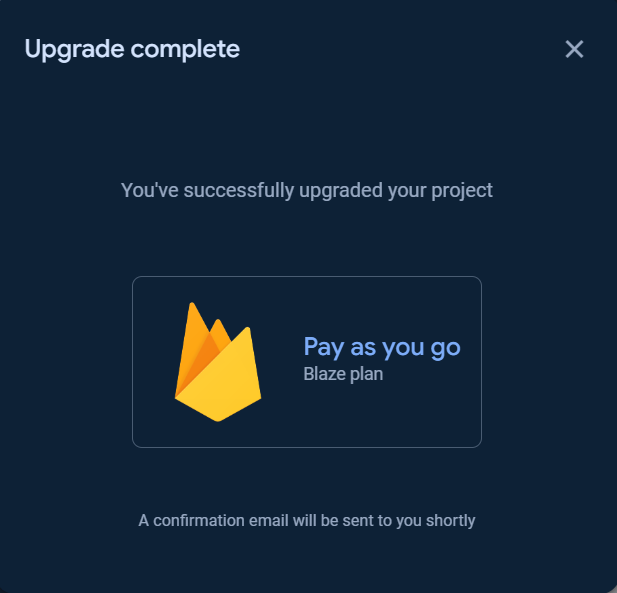
Click the `Get started` button and follow the steps as show in the following images.
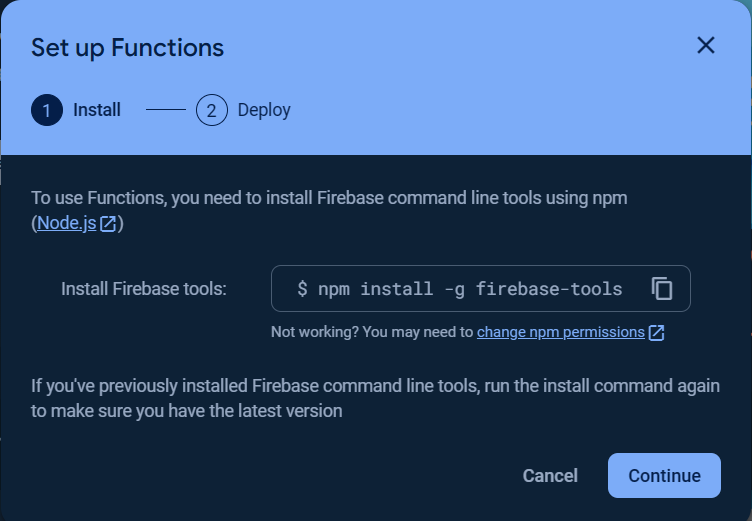
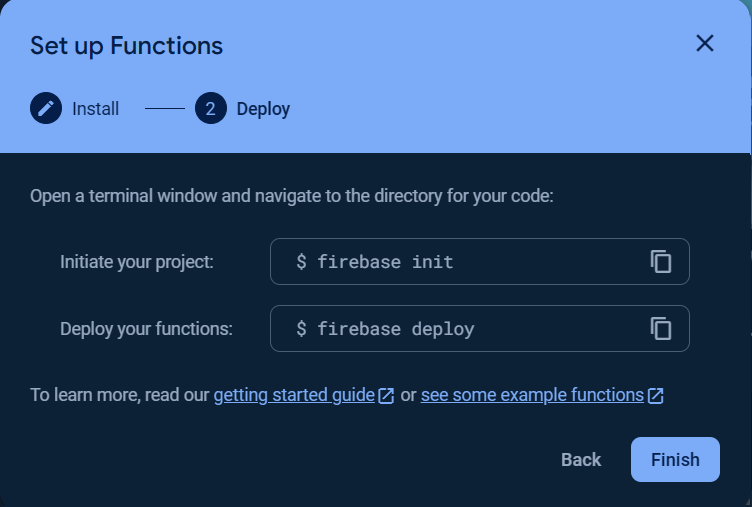
> [!IMPORTANT]
> The `Cloud Build API` and `Cloud Run Admin API` must be enabled, click [here](https://console.developers.google.com/apis/library/cloudbuild.googleapis.com) to enable `Cloud Build API`and [here](https://console.cloud.google.com/apis/library/run.googleapis.com) to enable `Cloud Run Admin API`.
### Cloud Messaging Getting Started
Create an app (iOS, Android, Web, or Unity app) for getting started.
The following steps showed the web app (Javascript) is created.
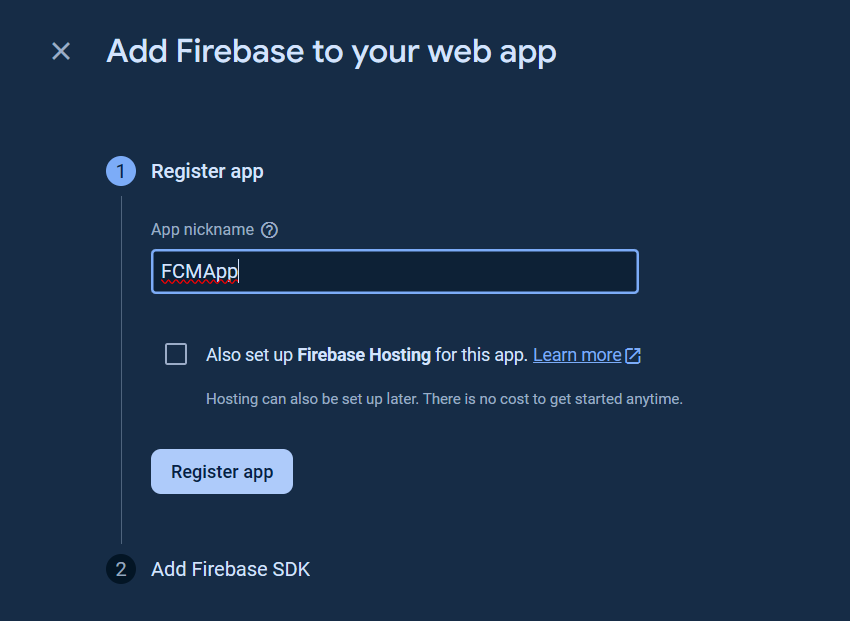
Add the Firebase SDK and click `Continue to console` button.
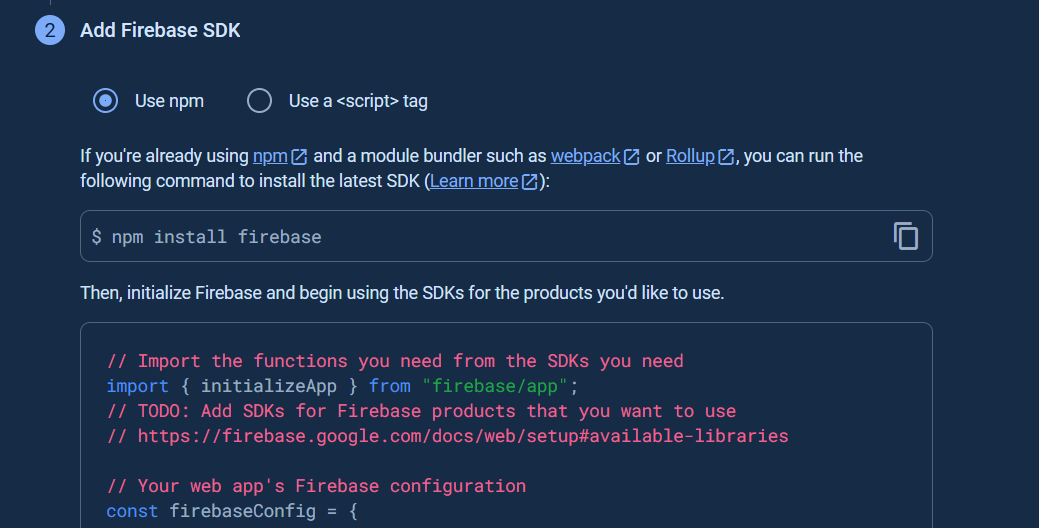
After you register the web app in your Firebase project, the next step is you have to use Firebase SDK to use the Firebase services (FCM for this case).
The FCM web app that consists of html document and related scripts requirs the server (local or remote) to run, you cannot access or browse your web app by opening the file from your local computer via file protocol (file://).
The FCM SDK is supported only in pages served over HTTPS. This is due to its use of service workers, which are available only on HTTPS sites (remote host) or HTTP (local host). If you need a provider, Firebase Hosting is recommended and provides a no-cost tier for HTTPS hosting on your own domain.
There are the choises that you can access the Firebase SDK in your web app.
1. Install the [Firebase SDK](https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/setup/#add-sdks-initialize) using the [Firebase CLI](https://firebase.google.com/docs/cli/).
2. Access the Firebase SDK via [the global CDN or npm for Node.js apps](https://firebase.google.com/docs/web/alt-setup).
This library provides the ready to test **FCM Web Client App** in [examples/Messaging/WebClient](examples/Messaging/WebClient/). You can host this FCM web app files (fcm.html and fcm.php) in your local (php) server (localhost via http) or remote (php) server (https only).
You can open [examples/Messaging/WebClient/fcm.html](examples/Messaging/WebClient/fcm.html) via web browser to review and follow the instructions on that page.
In Windows 11 PC, even notification is granted for your site in the brower notification settings, the notification may go directly to the notification center instead of displaying pop-up, if **Do not disturb** is **On** in the **System > Notifications** of Windows settings and you have to turn it **Off** to allow the notification pop-up to show.
The app (iOS, Android, Web and Unity) registration token or `DEVICE_TOKEN` is a unique token string that identifies each client app instance. The registration token is required for single device and device group messaging. Note that registration tokens must be kept secret, see [this](https://firebase.google.com/docs/cloud-messaging/concept-options#credentials) for more info.
### Service Account
A service account is a special kind of account (bot or application account) that belongs to app instead of to an individual end user. Service accounts enable server-to-server interactions between an app and a Google service.
#### Types of service accounts
In Google Cloud services, there are several different types of service accounts:
- User-managed service accounts: Service accounts that you create and manage. These service accounts are often used as identities for workloads.
- Default service accounts: User-managed service accounts that are created automatically when you enable certain Google Cloud services e.g. `Firebase Admin SDK Service Account`. You are responsible for managing these service accounts.
- Google-managed service accounts: Google-created and Google-managed service accounts that allow services to access resources on your behalf.
A `Firebase Admin SDK Service Account` is created automatically when you create a Firebase project or add Firebase to a Google Cloud project and it is used to communicate with Firebase.
The `Service Account` credentials are required for the `ServiceAuth` and `CustomAuth` classes.
To generate and download `Service Account` private key file, in the `Project Settings` page in the [`Google Firebase Console`](https://console.firebase.google.com/), click `Service accounts` tab and `Generate new private key`.
To use `Service Account` in your sketch, open the .json file that is already downloaded with the text editor.
```json
{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "...",
"private_key_id": "...",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n...\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "...",
"client_id": "...",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "...",
"universe_domain": "googleapis.com"
}
```
Copy the `project_id`, `client_email` and `private_key` from .json file and paste to these defines in the example.
```cpp
#define FIREBASE_PROJECT_ID "..." // Taken from "project_id" key in JSON file.
#define FIREBASE_CLIENT_EMAIL "..." // Taken from "client_email" key in JSON file.
const char PRIVATE_KEY[] PROGMEM = "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n...\n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n"; // Taken from "private_key" key in JSON file.
```
Normally `Firebase Admin SDK Service Account` is used in Firebase APIs authentication/authorization.
To access `Google Cloud APIs` e.g. `Google Cloud Storage`, `Google Cloud Functions` services, you have to update the service account permissions.
#### Service Account Permissions
When the `Firebase Admin SDK Service Account` was used for Google Cloud APIs authentication/authorization, you have to update its permissive roles.
The `Basic roles` are highly permissive roles that used to grant principals broad access to Google Cloud resources.
We can add one of `Basic roles` i.e. `Editor` and/or `Owner`.
To add the Basic's `Owner` or `Editor` roles, go to the [Identity and Access Management console](https://console.cloud.google.com/iam-admin).
Then choose the project, and select the `VIEW BY PRINCIPALS` tab.
From the table displayed, look at the `firebase-adminsdk` in the `Name` column, then click the pencil icon on the right side in this table row to `Edit principal`.
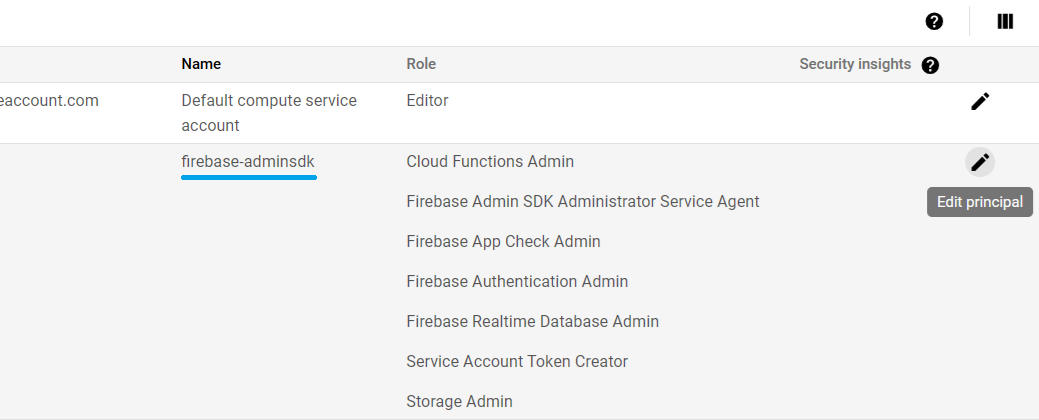
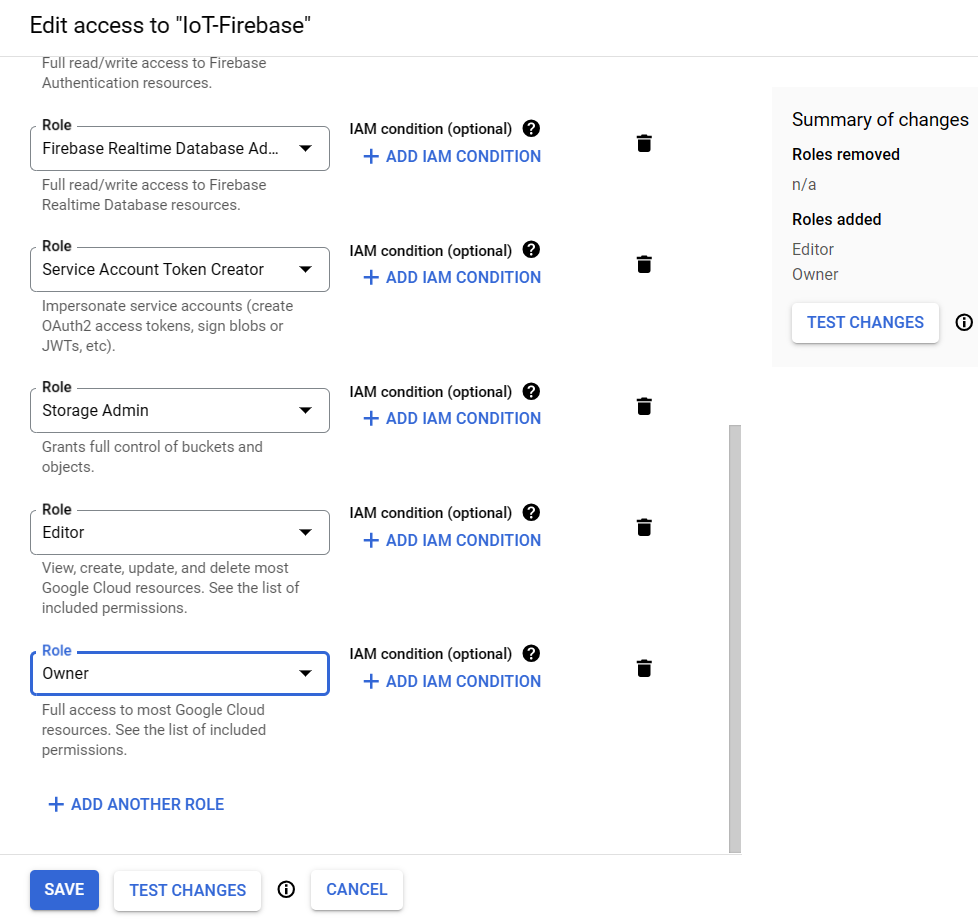
Add the role `Editor` and/or `Owner` under the `Basic` roles and click `Save` button.
Wait a few minutes for the action to propagate after adding roles.
## Memory Options
- ### Memory Options for ESP8266
When you update the ESP8266 Arduino Core SDK to v3.x.x, the memory for Heap and stack can be choosen from the IDE.
You can choose the Heap memory between internal and external memory chip from IDE e.g. Arduino IDE and PlatformIO on VSCode or Atom IDE.
- #### Arduino IDE
For ESP8266 devices that don't have external SRAM/PSRAM chip installed, choose the MMU **option 3**, 16KB cache + 48KB IRAM and 2nd Heap (shared).
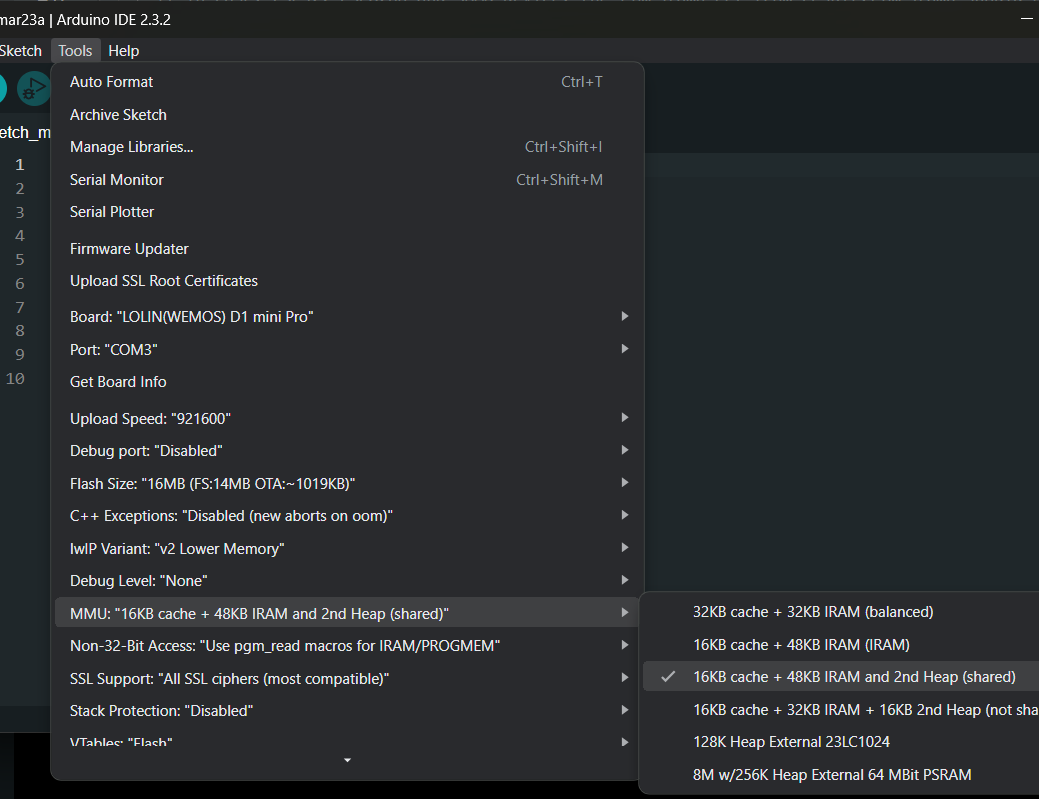
For ESP8266 devices that have external 23LC1024 SRAM chip installed, choose the MMU **option 5**, 128K External 23LC1024.
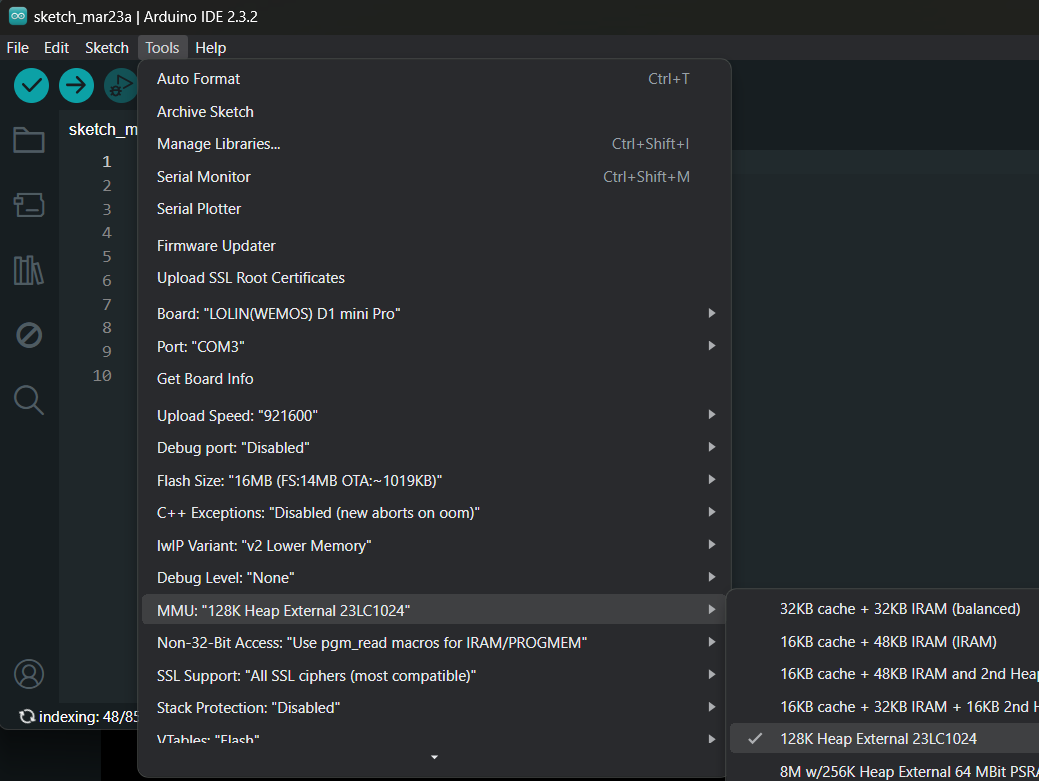
For ESP8266 devices that have external ESP-PSRAM64 chip installed, choose the MMU **option 6**, 1M External 64 MBit PSRAM.
- #### PlatformIO IDE
The MMU options can be selected from build_flags in your project's platformio.ini file
For ESP8266 devices that don't not have external SRAM/PSRAM chip installed, add build flag as below.
```ini
[env:d1_mini]
platform = espressif8266
build_flags = -D PIO_FRAMEWORK_ARDUINO_MMU_CACHE16_IRAM48_SECHEAP_SHARED
board = d1_mini
framework = arduino
monitor_speed = 115200
```
For ESP8266 devices that have external 23LC1024 SRAM chip installed, add build flag as below.
```ini
[env:d1_mini]
platform = espressif8266
;128K External 23LC1024
build_flags = -D PIO_FRAMEWORK_ARDUINO_MMU_EXTERNAL_128K
board = d1_mini
framework = arduino
monitor_speed = 115200
```
For ESP8266 devices that have external ESP-PSRAM64 chip installed, add build flag as below.
```ini
[env:d1_mini]
platform = espressif8266
;1M External 64 MBit PSRAM
build_flags = -D PIO_FRAMEWORK_ARDUINO_MMU_EXTERNAL_1024K
board = d1_mini
framework = arduino
monitor_speed = 115200
```
- #### ESP8266 and SRAM/PSRAM Chip connection
Most ESP8266 modules don't have the built-in SRAM/PSRAM on board. External memory chip connection can be done via SPI port as below.
```
23LC1024/ESP-PSRAM64 ESP8266
CS (Pin 1) GPIO15
SCK (Pin 6) GPIO14
MOSI (Pin 5) GPIO13
MISO (Pin 2) GPIO12
/HOLD (Pin 7 on 23LC1024 only) 3V3
Vcc (Pin 8) 3V3
Vcc (Pin 4) GND
```
Once the external Heap memory was selected in IDE, to allow the library to use the external memory, you can define this macro in your sketch before including the library header file `FirebaseClient.h`.
```cpp
#define ENABLE_PSRAM
```
This macro was defined by default when you installed or update the library.
- ### Memory Options for ESP32
In ESP32 module that has PSRAM installed, you can enable it and set the library to use this external memory instead.
- #### Arduino IDE
To enable PSRAM in ESP32 module.
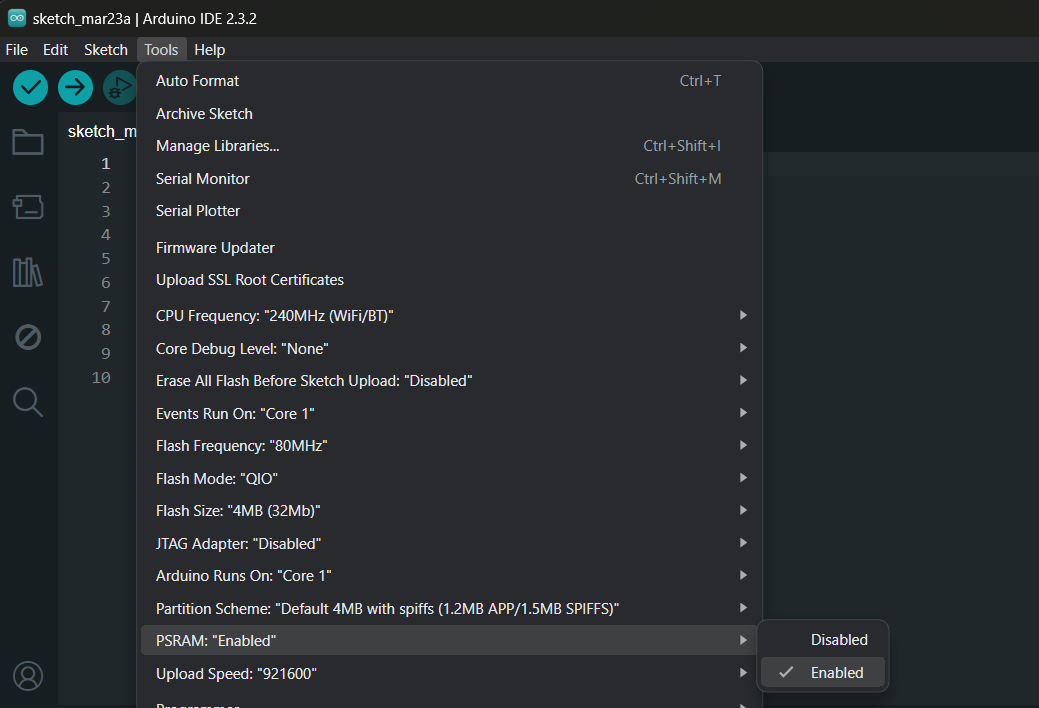
- #### PlatformIO IDE
In PlatformIO on VSCode or Atom IDE, add the following build_flags in your project's platformio.ini file.
```ini
build_flags = -DBOARD_HAS_PSRAM -mfix-esp32-psram-cache-issue
```
As in ESP8266, once the external Heap memory was selected in IDE, to allow the library to use the external memory, you can define this macro in your sketch before including the library header file `FirebaseClient.h`.
```cpp
#define ENABLE_PSRAM
```
## Library Build Options
The library build options are defined as preprocessor macros (`#define name`).
Since version 2.1.0, there are no predefined build options, user needs to define what he wants to use before compiling.
The build options can be defined before including the library header file `FirebaseClient.h` or as the compiler build flags.
The available options are the following.
```cpp
ENABLE_DATABASE // For RTDB compilation
ENABLE_FIRESTORE // For Firestore compilation
ENABLE_FIRESTORE_QUERY // For Firestore Query feature compilation
ENABLE_MESSAGING // For Firebase Cloud Messaging compilation
ENABLE_STORAGE // For Firebase Storage compilation
ENABLE_CLOUD_STORAGE // For Google Cloud Storage compilation
ENABLE_FUNCTIONS // For Google Cloud Functions compilation
ENABLE_RULESETS // For RuleSets compilation
ENABLE_PSRAM // For enabling PSRAM support
ENABLE_OTA // For enabling OTA updates support
ENABLE_FS // For enabling Flash filesystem support
FIREBASE_ASYNC_QUEUE_LIMIT // For maximum async queue limit (number).
FIREBASE_PRINTF_PORT // For Firebase.printf debug port class object.
FIREBASE_PRINTF_BUFFER // Firebase.printf buffer size.
// For enabling authentication and token
ENABLE_SERVICE_AUTH
ENABLE_CUSTOM_AUTH
ENABLE_USER_AUTH
ENABLE_ACCESS_TOKEN
ENABLE_CUSTOM_TOKEN
ENABLE_ID_TOKEN
ENABLE_LEGACY_TOKEN
```
## Known Issues
### Slow Arduino IDE Compilation Speed
Normally this issue can be existed due to large anount of files to be compiled and anti virus software interference.
This library contains the large anount of C files from `BearSSL` engine used in the internal `ESP_SSLClient` library which will be used only when the `ServiceAuth`, `CustomAuth` and `ESP_SSLClient` classes are used. This can increase the compilation time.
If `ServiceAuth`, `CustomAuth` and `ESP_SSLClient` classes are not used in your code, you can remove or delete the `src/client` folder to reduce the Arduino IDE compilation time.
## License
The codes and examples in this repository are licensed under the MIT License.
Copyright (c) 2025, Suwatchai K. All rights reserved.
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
*The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.*
`THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.`
*Last updated 2025-09-16 UTC.*