https://github.com/morzhanov/kuber-tools
Kubernetes popular tooling testing example.
https://github.com/morzhanov/kuber-tools
Last synced: 4 months ago
JSON representation
Kubernetes popular tooling testing example.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/morzhanov/kuber-tools
- Owner: morzhanov
- Created: 2021-10-26T17:26:54.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2021-10-29T20:48:02.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-12-30T04:18:58.869Z (6 months ago)
- Language: Go
- Size: 154 KB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# kuber-tools
Kubernetes popular tooling testing example. Kubernetes has a lot of useful tools for microservices development.
This repository aims to provide description of the range of those tools.
Tools:
- Kubernetes - open-source system for automating deployment, scaling, and management of containerized applications.
- K3D - kubernetes local cluster
- Minikube - kubernetes local cluster
- Docker Desktop Kubernetes cluster - kubernetes local cluster
- Kustomize - introduces a template-free way to customize application configuration that simplifies the use of off-the-shelf applications
- Helm - the package manager for Kubernetes
- Istio - Kubernetes service mesh
- Ambassador - Kubernetes popular API Gateway
- Rancher - tools for Kubernetes cluster deployment and management
- Flagger - tool that helps to create and manage a range of deployment strategies
- Crossplane - tools which declares external resources as Kubernetes components
- ArgoCD - declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes
This repository based on simple Go app. The app is deployed into local Kubernetes cluster.
- Order service - creates orders
- Payment service - performs payment when order being processed
- API Gateway service - simple APIGW service which proxies all requests to order and payment services

Table of Contents
=================
* [Local App Development](#local-app-development)
* [Docker Compose](#docker-compose)
* [Postman Collection](#postman-collection)
* [Guide](#guide)
* [Kubernetes Local Cluster Setup](#kubernetes-local-cluster-setup)
* [Minikube](#minikube)
* [K3D](#k3d)
* [Docker Desktop](#docker-desktop)
* [Istio](#istio)
* [Installation](#installation)
* [Accessing services outside the cluster](#accessing-services-outside-the-cluster)
* [Istio Dashboards](#istio-dashboards)
* [Add Jaeger Dashboard](#add-jaeger-dashboard)
* [Add Kiali Dashboard](#add-kiali-dashboard)
* [Add Prometheus and Grafana Dashboard](#add-prometheus-and-grafana-dashboard)
* [Deploying application on Local Kubernetes Cluster](#deploying-application-on-local-kubernetes-cluster)
* [Kustomize](#kustomize)
* [Deploying to kuber cluster via Kustomize](#deploying-to-kuber-cluster-via-kustomize)
* [Helm](#helm)
* [Installing](#installing)
* [Rancher](#rancher)
* [Ambassador](#ambassador)
* [Installation](#installation-1)
* [API Gateway setup](#api-gateway-setup)
* [Crossplane](#crossplane)
* [Installing Crossplane](#installing-crossplane)
* [Adding AWS RDS Instance to Kuber cluster](#adding-aws-rds-instance-to-kuber-cluster)
* [Flagger](#flagger)
* [Canary Deployment](#canary-deployment)
* [ArgoCD](#argocd)
* [Installation](#installation-2)
* [Adding Git repo](#adding-git-repo)
* [Other Argo Tools](#other-argo-tools)
## Local App Development
### Docker Compose
`docker` directory contains `docker-compose.yaml` file which deploys application dependent services (postgresq, mongodb, etc.)
It's useful to deploy this stack for the local development as it is consumes less resouces then Kubernetes cluster.
## Postman Collection
`kubetools.postman_collection.json` file contains Postman collection definition for apigw service interaction.

## Guide
In order to deploy kubernetes cluster and add main tools perform next steps:
- Install local kubernetes cluster (via K3D, Minikube or Docker Desktop)
- Add Istio to the cluster
- Add Istio dashboards
- Deploy kustomize files
- Connect cluster to the Rancher or review resources via Lens or K9S
- Setup Ambassador API GW
- Perform requests from Postman
- Review Kiali/Jaeger/Prometheus Istio dashboards
- Try additional tools (could take a more time to investigate and setup):
- Flagger
- Crossplane
- ArgoCD
- Argo Workflows
- Argo Events
- Argo Rollouts
## Kubernetes Local Cluster Setup
Here described two option how to start kubernetes cluster locally:
- Minikube
- K3D
- Docker Desktop
### Minikube
```shell
# install minikube
brew install minikube
# start cluster
minikube start
# check cluster
kubectl get nodes
```
Open service on minikube:
```shell
minikube service apigw -n kubetools
|-----------|-------|----------------|---------------------------|
| NAMESPACE | NAME | TARGET PORT | URL |
|-----------|-------|----------------|---------------------------|
| kubetools | apigw | 3001-3001/3001 | http://192.168.49.2:30080 |
|-----------|-------|----------------|---------------------------|
🏃 Starting tunnel for service apigw.
|-----------|-------|-------------|------------------------|
| NAMESPACE | NAME | TARGET PORT | URL |
|-----------|-------|-------------|------------------------|
| kubetools | apigw | | http://127.0.0.1:51860 |
|-----------|-------|-------------|------------------------|
🎉 Opening service kubetools/apigw in default browser...
❗ Because you are using a Docker driver on darwin, the terminal needs to be open to run it.
```
### K3D
```shell
# download k3d
curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rancher/k3d/main/install.sh | bash
# create k3d cluster and open ports
k3d cluster create kubetools -p "30000-31652:30000-31652@server:0"
# check cluster
kubectl get nodes
```
### Docker Desktop
As an alternative you could use Kubernetes for Docker Desktop.
## Istio
Istio extends Kubernetes to establish a programmable, application-aware network using the powerful Envoy service proxy. Working with both Kubernetes and traditional workloads, Istio brings standard, universal traffic management, telemetry, and security to complex deployments.

### Installation
Download from Istio installation guide
To setup istio locally:
```shell
istioctl install --set profile=minimal
```
Note: before using Istio enable sidecar injection:
```shell
kubectl label namespace kubetools istio-injection=enabled
```
#### Accessing services outside the cluster
In order to access cluster services perform steps described in the setup guide
### Istio Dashboards
Istio service mesh has a variety of dashboards to monitor your cluster:
- Jaeger - for tracing
- Kiali - for service cluster architecture visualizations
- Prometheus and Grafana - for cluster metrics
#### Add Jaeger Dashboard
To enable Jaeger in Istio run:
```shell
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.11/samples/addons/jaeger.yaml
```
To enter Jaeger UI run:
```shell
istioctl dashboard jaeger
```

Image taken from istio-2020 repo.
#### Add Kiali Dashboard
To enable Kiali in Istio run:
```shell
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.11/samples/addons/kiali.yaml
```
To enter Kiali run:
```shell
istioctl dashboard kiali
```

Image taken from istio-2020 repo.
#### Add Prometheus and Grafana Dashboard
Grafana setup for Istio:
```shell
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.11/samples/addons/grafana.yaml
```
Prometheus setup for Istio:
```shell
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.11/samples/addons/prometheus.yaml
```
To enter Grafana run:
```shell
istioctl dashboard grafana
```
Visit `http://localhost:3000/dashboard/db/istio-mesh-dashboard` in your web browser

Image taken from istio-2020 repo.
## Deploying application on Local Kubernetes Cluster
Here described two option how to deploy Go application on kubernetes cluster locally:
- Kustomize
- Helm
### Kustomize
Kustomize is a standalone tool to customize Kubernetes objects through a kustomization file.

- `kustomize/bases` contains base configuration files for deployment, configmaps, services, etc.
- `kustomize/overlays` contains base overlay config for base files
- you could add new overlay to this directory to kustomize values in configs
#### Deploying to kuber cluster via Kustomize
To get kustomize build:
```shell
kustomize build kustomize/overlays/local
# or
kubectl kustomize kustomize/overlays/local
```
To deploy a stask to the kubernetes cluster:
```shell
kubectl apply -k kustomize/overlays/local
```
### Helm
Helm is a package manager that helps you to find, share, and use software that is built for Kubernetes. Helm streamlines the installation and management of Kubernetes applications, and is the equivalent of the apt, yum, or homebrew utilities for Kubernetes.
Helm uses a packaging format called Chart. A chart is a collection of files that describes a related set of Kubernetes resources. A single chart might be used to deploy something simple, like a memcached pod, or a complex deployment, like a full web app stack with HTTP servers, databases, and caches.

#### Installing
On Mac OS Helm could be installed via brew:
```shell
brew install helm
```
Other installation options available in the guide
## Rancher
Rancher is a complete software stack for teams adopting containers. It addresses the operational and security challenges of managing multiple Kubernetes clusters, while providing DevOps teams with integrated tools for running containerized workloads.

In order to add Rancher to monitor the cluster we can deploy it as Docker image and connect our existing cluster.
Deploying Rancher:
```shell
docker run -d --restart=unless-stopped \
-p 4000:80 -p 4001:443 \
--privileged \
rancher/rancher:latest
```
## Ambassador
Ambassador is an API Gateway for cloud-native applications that routes traffic between heterogeneous services and maintains decentralized workflows. It acts as a single entry point and supports tasks like service discovery, configuration management, routing rules, and rate limiting. It provides great flexibility and ease of configuration for your services.

### Installation
```shell
kubectl apply -f https://app.getambassador.io/yaml/edge-stack/latest/aes-crds.yaml && \
kubectl wait --for condition=established --timeout=90s crd -lproduct=aes && \
kubectl apply -f https://app.getambassador.io/yaml/edge-stack/latest/aes.yaml && \
kubectl -n kubetools wait --for condition=available --timeout=90s deploy -lproduct=aes
```
### API Gateway setup
We'will create example ambassador configuration for kubetools/apigw service.
At first we should create mapping for apigw service to ambassador:
```yaml
---
apiVersion: getambassador.io/v3alpha1
kind: Mapping
metadata:
name: apigw
namespace: kubetools
spec:
hostname: "*"
prefix: /
service: apigw
```
And apply it:
```shell
kubectl apply -f ./ambassador/mapping.yaml
```
In order to access ambassador outside the cluster we should store it URL:
```shell
export AMBASSADOR_LB_ENDPOINT=$(kubectl -n kubetools get svc ambassador -o "go-template={{range .status.loadBalancer.ingress}}{{or .ip .hostname}}{{end}}")
```
After configuration is applied we could test the apigw service locally
```shell
curl https://$AMBASSADOR_LB_ENDPOINT/payment/
```
## Crossplane
Crossplane goes beyond simply modelling infrastructure primitives as custom resources - it enables you to define new custom resources with schemas of your choosing.

As an example we can deploy AWS RDS Instance using crossplane, and it will be assigned to our cluster.
### Installing Crossplane
This should install Crossplane locally:
```shell
curl -sL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/crossplane/crossplane/release-1.5/install.sh | sh
```
Install simple configuration for AWS (in prod it's better to use custom configuration):
```shell
kubectl crossplane install configuration registry.upbound.io/xp/getting-started-with-aws:v1.5.0
```
Wait until all packages become healthy:
```shell
watch kubectl get pkg
```
### Adding AWS RDS Instance to Kuber cluster
We can use Crossplane created Portgres instance instead of locally deployed by Kustomize file `kustomize/bases/postgresql`.
Using an AWS account with permissions to manage RDS databases:
```shell
AWS_PROFILE=default && echo -e "[default]\naws_access_key_id = $(aws configure get aws_access_key_id --profile $AWS_PROFILE)\naws_secret_access_key = $(aws configure get aws_secret_access_key --profile $AWS_PROFILE)" > creds.conf
```
Create a Provider Secret:
```shell
kubectl create secret generic aws-creds -n crossplane-system --from-file=creds=./creds.conf
```
The AWS provider supports provisioning an RDS instance via the RDSInstance managed resource it adds to Crossplane:
```shell
apiVersion: database.aws.crossplane.io/v1beta1
kind: RDSInstance
metadata:
name: rdspostgres
spec:
forProvider:
region: us-east-1
dbInstanceClass: db.t2.small
masterUsername: masteruser
allocatedStorage: 20
engine: postgres
engineVersion: "12"
skipFinalSnapshotBeforeDeletion: true
writeConnectionSecretToRef:
namespace: kubetools
name: aws-rdspostgres-conn
```
Note: RDSInstance is a Managed resource (MR). With Crossplane you could create a more complex Composite resources (XR):

You can review difference between managed and composite resources in the docs
Creating the above instance will cause Crossplane to provision an RDS instance on AWS. You can view the progress with the following command:
```shell
kubectl get rdsinstance rdspostgres
```
When provisioning is complete, you should see `READY: True` in the output. You can take a look at its connection secret that is referenced under `spec.writeConnectionSecretToRef`:
```shell
kubectl describe secret aws-rdspostgres-conn -n kubetools
```
## Flagger
is a progressive delivery tool that automates the release process for applications running on Kubernetes. It reduces the risk of introducing a new software version in production by gradually shifting traffic to the new version while measuring metrics and running conformance tests.
Flagger implements several deployment strategies (Canary releases, A/B testing, Blue/Green mirroring) using a service mesh (App Mesh, Istio, Linkerd, Open Service Mesh) or an ingress controller (Contour, Gloo, NGINX, Skipper, Traefik) for traffic routing. For release analysis, Flagger can query Prometheus, Datadog, New Relic, CloudWatch or Graphite and for alerting it uses Slack, MS Teams, Discord and Rocket.
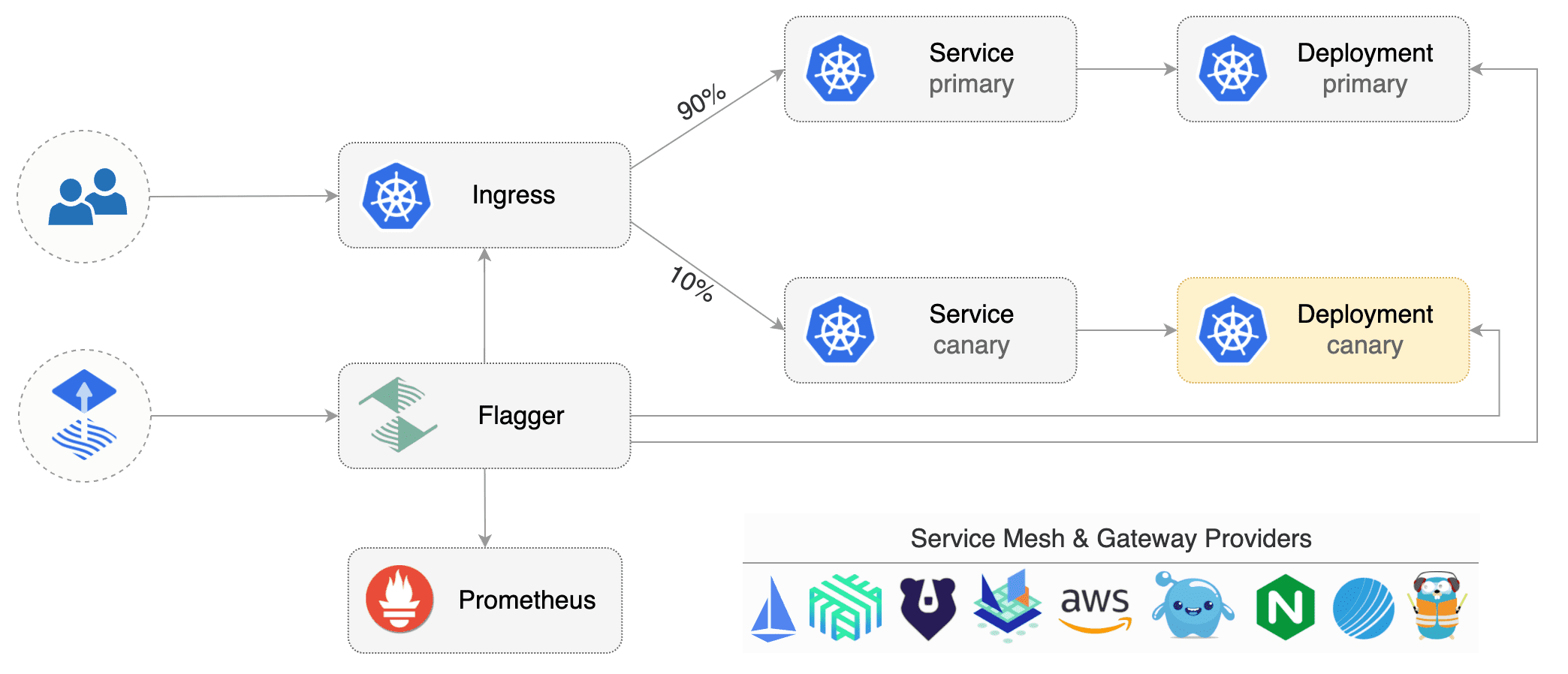
More info: Flagger docs
### Canary Deployment
When you deploy a new version of an app, Flagger gradually shifts traffic to the canary, and at the same time, measures the requests success rate as well as the average response duration. You can extend the canary analysis with custom metrics, acceptance and load testing to harden the validation process of your app release process.

Create a canary custom resource (code could be found in the canary.yml file).
Apply the Canary CRD:
```shell
kubectl apply -f ./flagger/canary.yaml
```
When the canary analysis starts, Flagger will call the pre-rollout webhooks before routing traffic to the canary. The canary analysis will run for five minutes while validating the HTTP metrics and rollout hooks every minute.
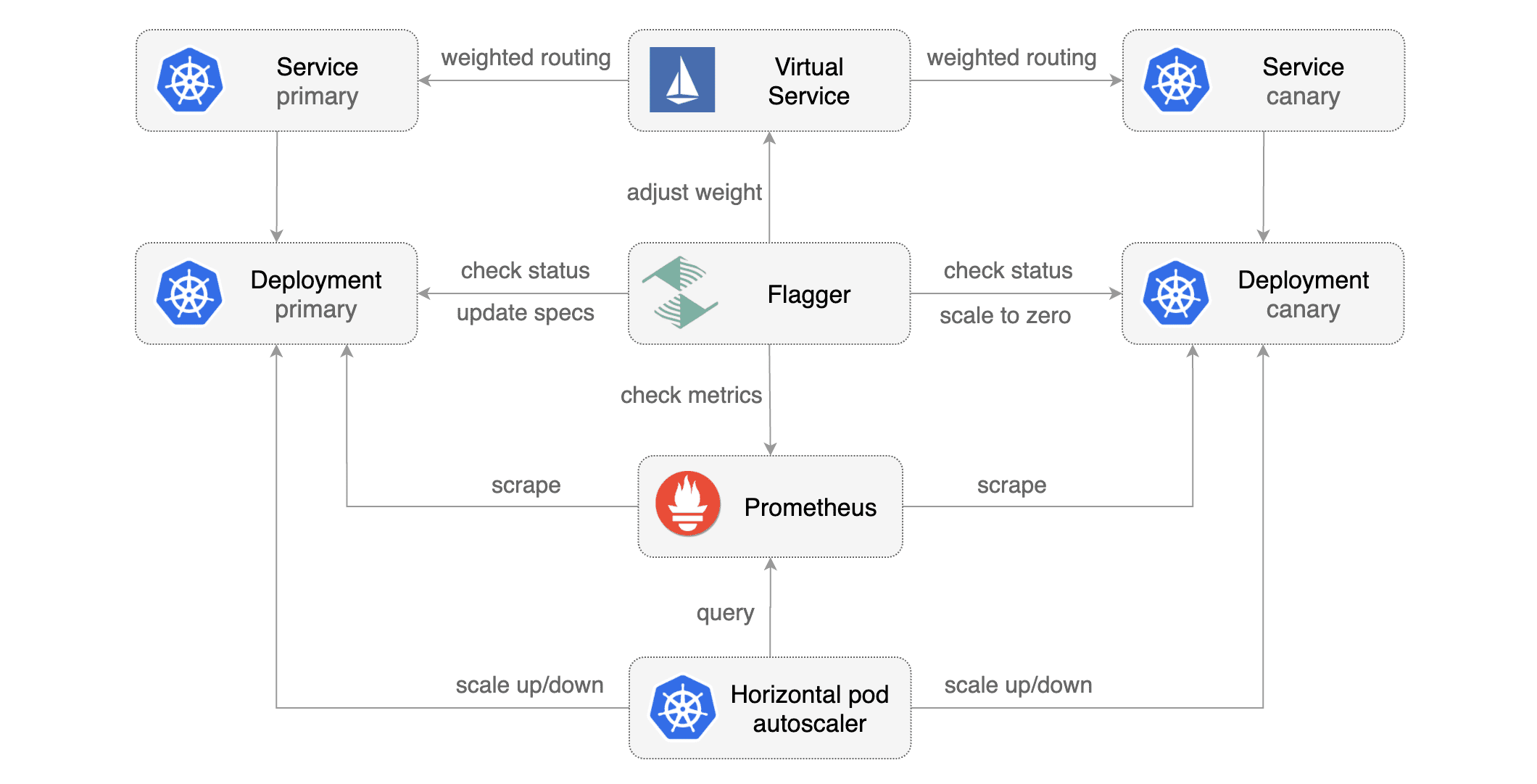
After a couple of seconds Flagger will create the canary objects:
```shell
# applied
deployment.apps/apigw
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/apigw
kubetools/apigw
# generated
deployment.apps/apigw-primary
horizontalpodautoscaler.autoscaling/apigw-primary
service/apigw
service/apigw-canary
service/apigw-primary
destinationrule.networking.istio.io/apigw-canary
destinationrule.networking.istio.io/apigw-primary
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/apigw
```
For automated canary promotion review docs
## ArgoCD
Argo CD has App of Apps pattern for cluster bootstrapping. That allows us programmatically and automatically create Argo CD apps instead of creating each application manually. Concept is simple; create one Argo CD application looking some git repo path and place all Argo CD application definition files into there. So that once any application definition file created on that git repo path, Argo CD application is also created automatically. Inspiring with that, it can be created or managed any Kubernetes object even Argo CD itself.
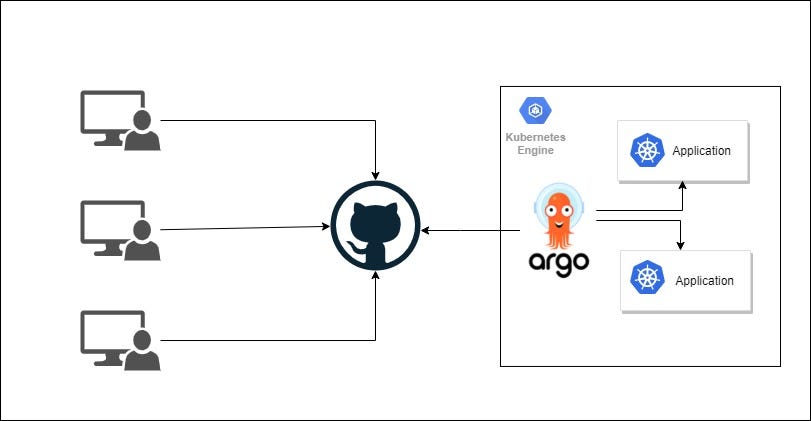
More info in the article
### Installation
Run yaml script to install ArgoCD on Kubernetes cluster:
```shell
kubectl apply -n argocd -f \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/argoproj/argo-cd/stable/manifests/install.yaml
```
Result:
```shell
Pods:
argocd-application-controller-6b47c9bd78-kp6dj
argocd-dex-server-7b6d8776d8-knsxx
argocd-redis-99fb49846-l466k
argocd-repo-server-b664bd94b-bmtwr
argocd-server-768879948c-sx875
Services:
argocd-dex-server
argocd-metrics
argocd-redis
argocd-repo-server
argocd-server
argocd-server-metrics
```
Next we will need to install argocd cli:
```shell
brew install argocd
argocd login
argocd account update-password
```
After that we are able to add clusters to ArgoCD. We will need to add `kubetools` cluster.
### Adding Git repo
We could add our github repository to be managed by ArgoCD via single script:
```shell
argocd app create kubetools --repo https://github.com/morzhanov/kuber-tools.git \
--path kustomize/overlays/local \
--sync-policy automatic \
--dest-server http://your-kuber-cluster-url.svc
--dest-namespace kubetools
```
After that ArgoCD will watch the repo and update Kubernetes cluster on kustomize/overlays/local changes.
### Other Argo Tools
In addition to the ArgoCD, Argo has some other useful tools for Kubernetes cluster:
- Argo Workflows - Argo Workflows is an open source container-native workflow engine for orchestrating parallel jobs on Kubernetes.
- Argo Workflows - Argo Events is an event-driven workflow automation framework for Kubernetes. It allows you to trigger 10 different actions (such as the creation of Kubernetes objects, invoke workflows or serverless workloads) on over 20 different events (such as webhook, S3 drop, cron schedule, messaging queues - e.g. Kafka, GCP PubSub, SNS, SQS).
- Argo Workflows - Argo Rollouts is a Kubernetes controller and set of CRDs which provide advanced deployment capabilities such as blue-green, canary, canary analysis, experimentation, and progressive delivery features to Kubernetes. (Could be used instead of Flagger).