Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/mosnad-web01/phase-1-practice-toy-tale-master_roaa_alwesabi
https://github.com/mosnad-web01/phase-1-practice-toy-tale-master_roaa_alwesabi
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mosnad-web01/phase-1-practice-toy-tale-master_roaa_alwesabi
- Owner: Mosnad-Web01
- Created: 2024-08-20T10:40:34.000Z (5 months ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-20T11:12:26.000Z (5 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-08-20T13:14:51.508Z (5 months ago)
- Language: JavaScript
- Size: 21.5 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 0
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Toy Tale
## Learning Goals
- Set up event listeners to respond to user events
- Use `fetch()` to make a "GET" request, then render the returned toys to the
DOM
- Use `fetch()` to make a "POST" request to create a new toy, then add it to the
DOM
- Use `fetch()` to make a "PATCH" request that updates an existing toy, then
render the updated information to the DOM
## Introduction
You've got a friend in need! Your friend Andy recently misplaced all his toys!
Let's write an app that helps Andy keep track of them. For this lab, you will
need to pull together everything you've learned about manipulating the DOM,
responding to events, and communicating with the server. Specifically, you will
need to:
1. Access the list of toys from an API (mocked using JSON Server) and render
each of them in a "card" on the page
2. Hook up a form that enables users to add new toys. Create an event listener
so that, when the form is submitted, the new toy is persisted to the database
and a new card showing the toy is added to the DOM
3. Create an event listener that gives users the ability to click a button to
"like" a toy. When the button is clicked, the number of likes should be
updated in the database and the updated information should be rendered to the
DOM
The final product should look like this:
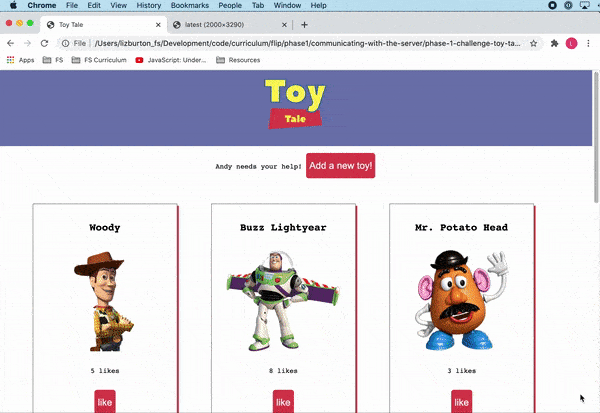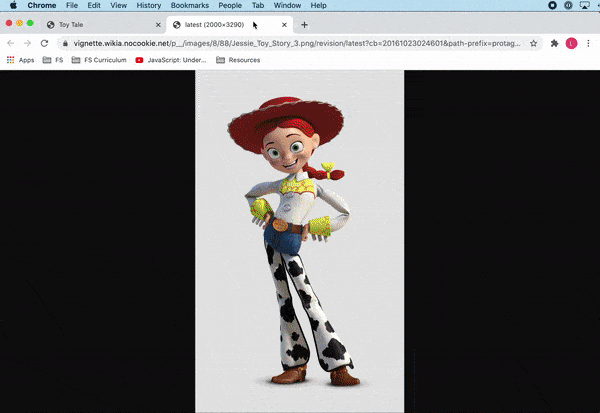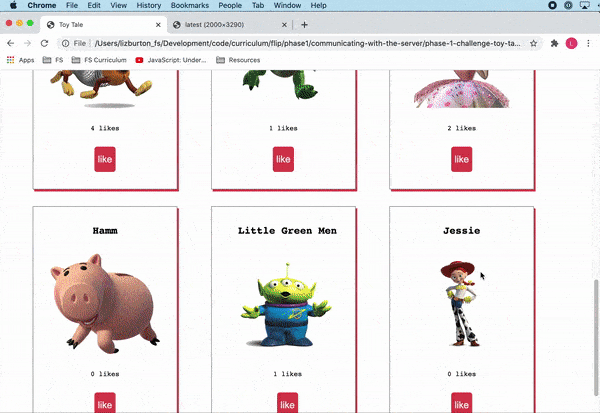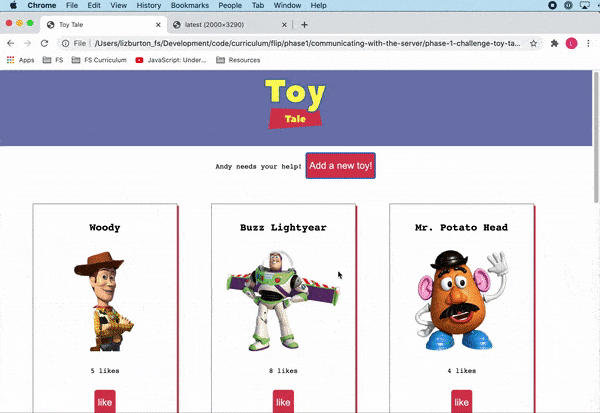
Note that this lab **does not contain tests**. You will be working from the
requirements described below and verifying that your code is working correctly
in the browser.
Once you're done, be sure to commit and push your code up to GitHub, then submit
the assignment using CodeGrade. Even though this practice lab does not have
tests, it must still be submitted through CodeGrade in order to be marked as
complete in Canvas.
## Start Up the Server
All of the toy data is stored in the `db.json` file. You'll want to access this
data using a JSON server. Run `json-server --watch db.json` to start the server.
> **Note**: For users of the [Live Server VSCode extension][live-server], if the
> page is reloading when you initiate a fetch request, you'll need to set up
> some additional configuration for Live Server to play nicely with
> `json-server`. Follow the steps in [this gist][live-server settings] (you'll
> only need to do this once), then come back to this lesson.
[live-server]:
https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ritwickdey.LiveServer
[live-server settings]:
https://gist.github.com/ihollander/cc5f36c6447d15dea6a16f68d82aacf7
This will create a server storing all of our lost toy data with restful routes
at `http://localhost:3000/toys`. You can also check out the information for each
individual toy at `http://localhost:3000/toys/:id`.
> **Note:** we are using `:id` here as a variable value that indicates the path
> to a specific toy. To navigate (or send a request) to that path, the `id`
> number will be inserted into the URL in place of `:id`, e.g.,
> `http://localhost:3000/toys/1`
Open a second tab in the terminal then open `index.html` in the browser and take
a look at the page. The CSS has all been provided for you so that, when you
create the cards to display each toy, you just need to add a CSS class to style
them.
If you click on the "Add a new toy!" button, you'll see that it exposes a form
where the user can submit information for a new toy. To re-hide the form, click
the button a second time. If you take a look inside `index.js`, you'll see that
the code implementing that functionality has been provided for you. You will be
writing the code to wire up the "Create Toy" button.
## Instructions
### Fetch Andy's Toys
On the `index.html` page, there is a `div` with the `id` "toy-collection."
When the page loads, make a 'GET' request to fetch all the toy objects. With the
response data, make a `
` for each toy and add it to the
toy-collection `div`.
### Add Toy Info to the Card
Each card should have the following child elements:
- `h2` tag with the toy's name
- `img` tag with the `src` of the toy's image attribute and the class name
"toy-avatar"
- `p` tag with how many likes that toy has
- `button` tag with a class "like-btn" and an id attribute set to the toy's id
number
After all of that, the toy card should look something like this:
```html
Woody

4 Likes
Like ❤️
```
### Add a New Toy
When a user submits the toy form, two things should happen:
- A `POST` request should be sent to `http://localhost:3000/toys` and the new
toy added to Andy's Toy Collection.
- If the post is successful, the toy should be added to the DOM without
reloading the page.
In order to send a POST request via `fetch()`, give the `fetch()` a second
argument of an object. This object should specify the method as `POST` and also
provide the appropriate headers and the JSON data for the request. The headers
and body should look something like this:
```js
headers:
{
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Accept: "application/json"
}
body: JSON.stringify({
"name": "Jessie",
"image": "https://vignette.wikia.nocookie.net/p__/images/8/88/Jessie_Toy_Story_3.png/revision/latest?cb=20161023024601&path-prefix=protagonist",
"likes": 0
})
```
For examples, refer to the [documentation][fetch docs].
### Increase a Toy's Likes
When a user clicks on a toy's like button, two things should happen:
- A `patch` request (i.e., `method: "PATCH"`) should be sent to the server at
`http://localhost:3000/toys/:id`, updating the number of likes that the
specific toy has
- If the patch is successful, the toy's like count should be updated in the DOM
without reloading the page
The `patch` request enables us to **update** an existing toy. The request will
look very similar to our "POST" request **except** that we need to include the
`id` of the toy we're updating in the path.
To get this working, you will need to add an event listener to each toy's "Like"
button. When the button is clicked for a toy, your code should:
1. capture that toy's id,
2. calculate the new number of likes,
3. submit the `patch` request, and
4. update the toy's card in the DOM based on the `Response` returned by the
fetch request.
The headers and body should look something like this:
```js
headers:
{
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Accept: "application/json"
}
body: JSON.stringify({
"likes": newNumberOfLikes
})
```
The `patch` method updates the property or properties included in the body of a
`fetch` request but leaves the remaining properties as they are. For our
example, the `likes` property will be updated by our `patch` request but the
`id`, `name`, and `image` properties will remain unchanged.
If your request isn't working, make sure your headers and keys match the
[documentation][fetch docs].
> **HINT**: You will be creating two event listeners for this lab. The first one
> will be on the "Create Toy" button, which is provided in the app's
> `index.html` file. The second one, however, will be on the "Likes" button on
> each individual toy card. Given that the toy cards will be rendered to the DOM
> dynamically from the `Response` returned by the `fetch` "GET" request, think
> about **when** it makes sense to add the event listener to each toy's "Like"
> button.
## Conclusion
Once you get everything working, take a moment to appreciate how far you've
come. You now have the skills needed to respond to user events, persist changes
to a database, and manipulate the DOM in response. You have created your first
fully-functioning web app that combines all three of the pillars.
Congratulations!
[fetch docs]:
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Fetch_API/Using_Fetch#Supplying_request_options