https://github.com/mrdimosthenis/clj-synapses
A neural networks library for Clojure
https://github.com/mrdimosthenis/clj-synapses
clojure deep-learning functional-programming machine-learning neural-network
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
A neural networks library for Clojure
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mrdimosthenis/clj-synapses
- Owner: mrdimosthenis
- Created: 2021-08-13T22:28:51.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-08-15T08:14:40.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-21T01:26:39.129Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: clojure, deep-learning, functional-programming, machine-learning, neural-network
- Language: Clojure
- Homepage: https://cljdoc.org/d/org.clojars.mrdimosthenis/clj-synapses/1.0.3/doc/readme
- Size: 166 KB
- Stars: 1
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: readme.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-clojure - clj-synapses
README
# clj-synapses
A **neural networks** library for **Clojure**!
## Basic usage
### Install synapses
```clojure
[org.clojars.mrdimosthenis/clj-synapses "1.0.3"]
```
### Load the `net` namespace
```clojure
(require '[clj-synapses.net :as net])
```
### Create a random neural network by providing its layer sizes
```clojure
(def rand-network
(net/->net
[2 3 1]))
```
* Input layer: the first layer of the network has 2 nodes.
* Hidden layer: the second layer has 3 neurons.
* Output layer: the third layer has 1 neuron.
### Get the json of the random neural network
```clojure
(net/->json
rand-network)
;;=> "[[{\"activationF\" : \"sigmoid\", \"weights\" : [-0.5,0.1,0.8]},
;; {\"activationF\" : \"sigmoid\", \"weights\" : [0.7,0.6,-0.1]},
;; {\"activationF\" : \"sigmoid\", \"weights\" : [-0.8,-0.1,-0.7]}],
;; [{\"activationF\" : \"sigmoid\", \"weights\" : [0.5,-0.3,-0.4,-0.5]}]]"
```
### Create a neural network by providing its json
```clojure
(def network
(net/json->
"[[{\"activationF\" : \"sigmoid\", \"weights\" : [-0.5,0.1,0.8]},
{\"activationF\" : \"sigmoid\", \"weights\" : [0.7,0.6,-0.1]},
{\"activationF\" : \"sigmoid\", \"weights\" : [-0.8,-0.1,-0.7]}],
[{\"activationF\" : \"sigmoid\", \"weights\" : [0.5,-0.3,-0.4,-0.5]}]]"))
```
### Make a prediction
```clojure
(net/predict
network
[0.2 0.6])
;;=> [0.49131100324012494]
```
### Train a neural network
```clojure
(net/fit
network
0.1
[0.2 0.6]
[0.9])
```
The `fit` function returns a new neural network with the weights adjusted to a single observation.
## Advanced usage
### Fully train a neural network
In practice, for a neural network to be fully trained, it should be fitted with multiple observations, usually by
reducing over a collection.
```clojure
(reduce
(fn [acc [xs ys]]
(net/fit acc 0.1 xs ys))
network
[[[0.2 0.6] [0.9]]
[[0.1 0.8] [0.2]]
[[0.5 0.4] [0.6]]])
```
### Boost the performance
Every function is efficient because its implementation is based on lazy list and all information is obtained at a single
pass.
For a neural network that has huge layers, the performance can be further improved by using the parallel counterparts
of `net/predict` and `net/fit` (`net/par-predict` and `net/par-fit`).
### Create a neural network for testing
```clojure
(net/->net
[2 3 1]
1000)
```
We can provide a `seed` to create a non-random neural network. This way, we can use it for testing.
### Define the activation functions and the weights
```clojure
(require '[clj-synapses.fun :as fun])
(defn activation-f
[layer-index]
(condp = layer-index
0 fun/sigmoid
1 fun/identity
2 fun/leaky-re-lu
3 fun/tanh))
(defn weight-init-f
[layer-index]
(* (inc layer-index)
(- 1 (* 2.0 (rand)))))
(def custom-network
(net/->net
[4 6 8 5 3]
activation-f
weight-init-f))
```
* The `activation-f` function accepts the index of a layer and returns an activation function for its neurons.
* The `weight-initf` function accepts the index of a layer and returns a weight for the synapses of its neurons.
If we don't provide these functions, the activation function of all neurons is sigmoid, and the weight distribution of
the synapses is normal between -1.0 and 1.0.
### Draw a neural network
```clojure
(net/->svg
custom-network)
```
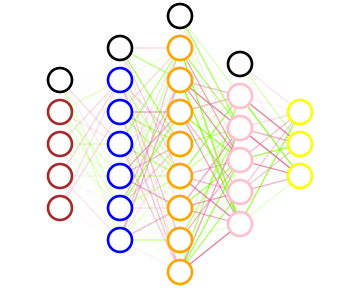
With its svg drawing, we can see what a neural network looks like. The color of each neuron depends on its activation
function while the transparency of the synapses depends on their weight.
### Measure the difference between the expected and predicted values
```clojure
(require '[clj-synapses.stats :as stats])
(def exp-and-pred-vals
[[[0.0 0.0 1.0] [0.0 0.1 0.9]]
[[0.0 1.0 0.0] [0.8 0.2 0.0]]
[[1.0 0.0 0.0] [0.7 0.1 0.2]]
[[1.0 0.0 0.0] [0.3 0.3 0.4]]
[[0.0 0.0 1.0] [0.2 0.2 0.6]]])
```
* Root-mean-square error
```clojure
(stats/rmse
exp-and-pred-vals)
;;=> 0.6957010852370435
```
* Classification accuracy score
```clojure
(stats/score
exp-and-pred-vals)
;;=> 0.6
```
### Load the `codec` namespace
```clojure
(require '[clj-synapses.codec :as codec])
```
* One hot encoding is a process that turns discrete attributes into a list of 0.0 and 1.0.
* Minmax normalization scales continuous attributes into values between 0.0 and 1.0.
```clojure
(def setosa
{"petal_length" "1.5"
"petal_width" "0.1"
"sepal_length" "4.9"
"sepal_width" "3.1"
"species" "setosa"})
(def versicolor
{"petal_length" "3.8"
"petal_width" "1.1"
"sepal_length" "5.5"
"sepal_width" "2.4"
"species" "versicolor"})
(def virginica
{"petal_length" "6.0"
"petal_width" "2.2"
"sepal_length" "5.0"
"sepal_width" "1.5"
"species" "virginica"})
(def dataset
[setosa
versicolor
virginica])
```
You can use a `codec` to encode and decode a data point.
### Create a `codec` by providing the attributes and the data points
```clojure
(def preprocessor
(codec/->codec
[["petal_length" false]
["petal_width" false]
["sepal_length" false]
["sepal_width" false]
["species" true]]
dataset))
)
```
* The first parameter is a vector of pairs that define the name and the type (discrete or not) of each attribute.
* The second parameter is a collection that contains the data points.
### Get the json of the codec
```clojure
(codec/->json
preprocessor)
;;=> "[{\"Case\" : \"SerializableContinuous\",
;; \"Fields\" : [{\"key\" : \"petal_length\",\"min\" : 1.5,\"max\" : 6.0}]},
;; {\"Case\" : \"SerializableContinuous\",
;; \"Fields\" : [{\"key\" : \"petal_width\",\"min\" : 0.1,\"max\" : 2.2}]},
;; {\"Case\" : \"SerializableContinuous\",
;; \"Fields\" : [{\"key\" : \"sepal_length\",\"min\" : 4.9,\"max\" : 5.5}]},
;; {\"Case\" : \"SerializableContinuous\",
;; \"Fields\" : [{\"key\" : \"sepal_width\",\"min\" : 1.5,\"max\" : 3.1}]},
;; {\"Case\" : \"SerializableDiscrete\",
;; \"Fields\" : [{\"key\" : \"species\",\"values\" : [\"virginica\",\"versicolor\",\"setosa\"]}]}]"
```
### Create a codec by providing its json
```clojure
(codec/json->
"[{\"Case\" : \"SerializableContinuous\",
\"Fields\" : [{\"key\" : \"petal_length\",\"min\" : 1.5,\"max\" : 6.0}]},
{\"Case\" : \"SerializableContinuous\",
\"Fields\" : [{\"key\" : \"petal_width\",\"min\" : 0.1,\"max\" : 2.2}]},
{\"Case\" : \"SerializableContinuous\",
\"Fields\" : [{\"key\" : \"sepal_length\",\"min\" : 4.9,\"max\" : 5.5}]},
{\"Case\" : \"SerializableContinuous\",
\"Fields\" : [{\"key\" : \"sepal_width\",\"min\" : 1.5,\"max\" : 3.1}]},
{\"Case\" : \"SerializableDiscrete\",
\"Fields\" : [{\"key\" : \"species\",\"values\" : [\"virginica\",\"versicolor\",\"setosa\"]}]}]")
```
### Encode a data point
```clojure
(def encoded-setosa
(codec/encode
preprocessor
setosa))
;; [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0]
```
### Decode a data point
```clojure
(codec/decode
preprocessor
encoded-setosa)
;;=> {"species" "setosa"
;; "sepal_width" "3.1"
;; "petal_width" "0.1",
;; "petal_length" "1.5"
;; "sepal_length" "4.9"}
```