https://github.com/mrvautin/minipaas
A push-to-deploy PaaS system = 'git add' > 'git commit' > 'minipaas deploy'
https://github.com/mrvautin/minipaas
git javascript nodejs paas push-to-deploy remote server ssh
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
A push-to-deploy PaaS system = 'git add' > 'git commit' > 'minipaas deploy'
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mrvautin/minipaas
- Owner: mrvautin
- License: mit
- Created: 2017-05-11T06:09:35.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2017-05-15T11:25:42.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-04-15T00:20:25.443Z (over 1 year ago)
- Topics: git, javascript, nodejs, paas, push-to-deploy, remote, server, ssh
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 134 KB
- Stars: 8
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 3
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# miniPaaS
`miniPaaS` is simple push-to-deploy server setup without all the complexities. `miniPaaS` uses `pm2` on the remote server to manage the process, auto restarts, logs and more.
The purpose of `miniPaaS` is to be able to add local changes using Git, Commit those changes and deploy them to your remote server. When `miniPaaS` does the deployment, it will unpack the files, npm install and restart the app in `pm2`. If your app is running in `pm2` cluster mode, this will mean there **should** be no downtime to your application whilst the deployment takes place.
Note: You will need to setup `Apache` or `Nginx` yourself, `miniPaaS` does not handle this aspect of your application.
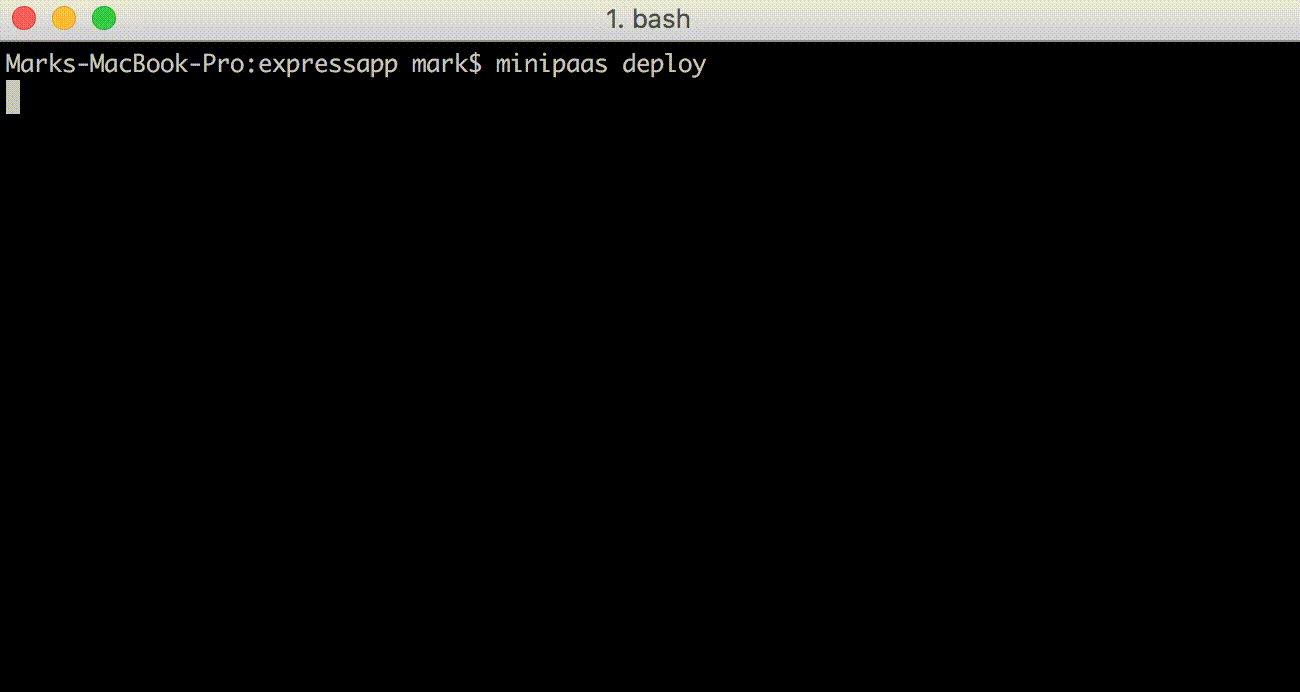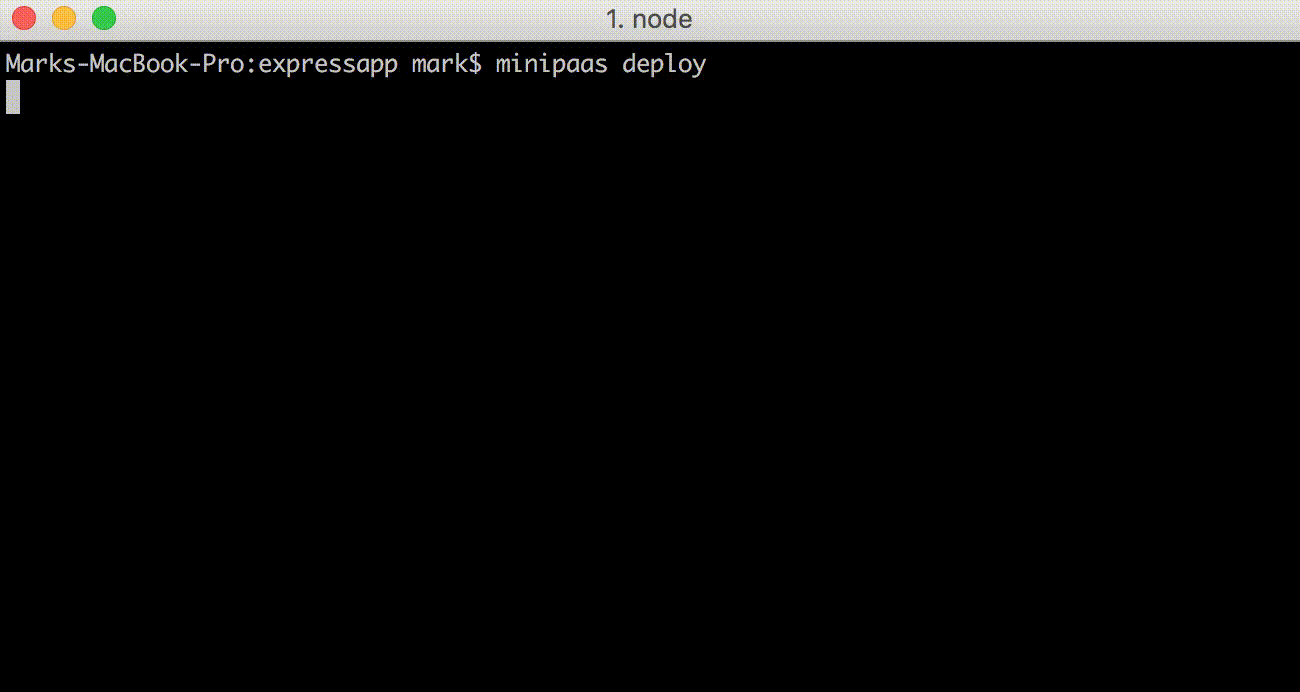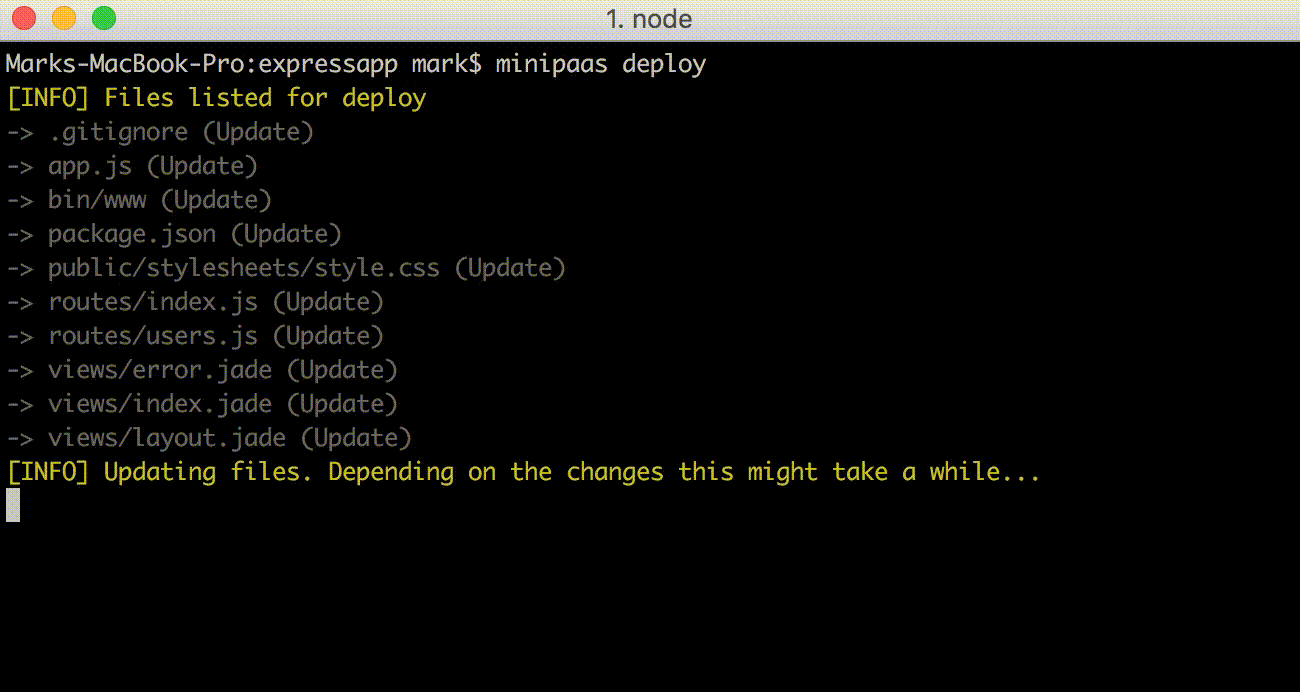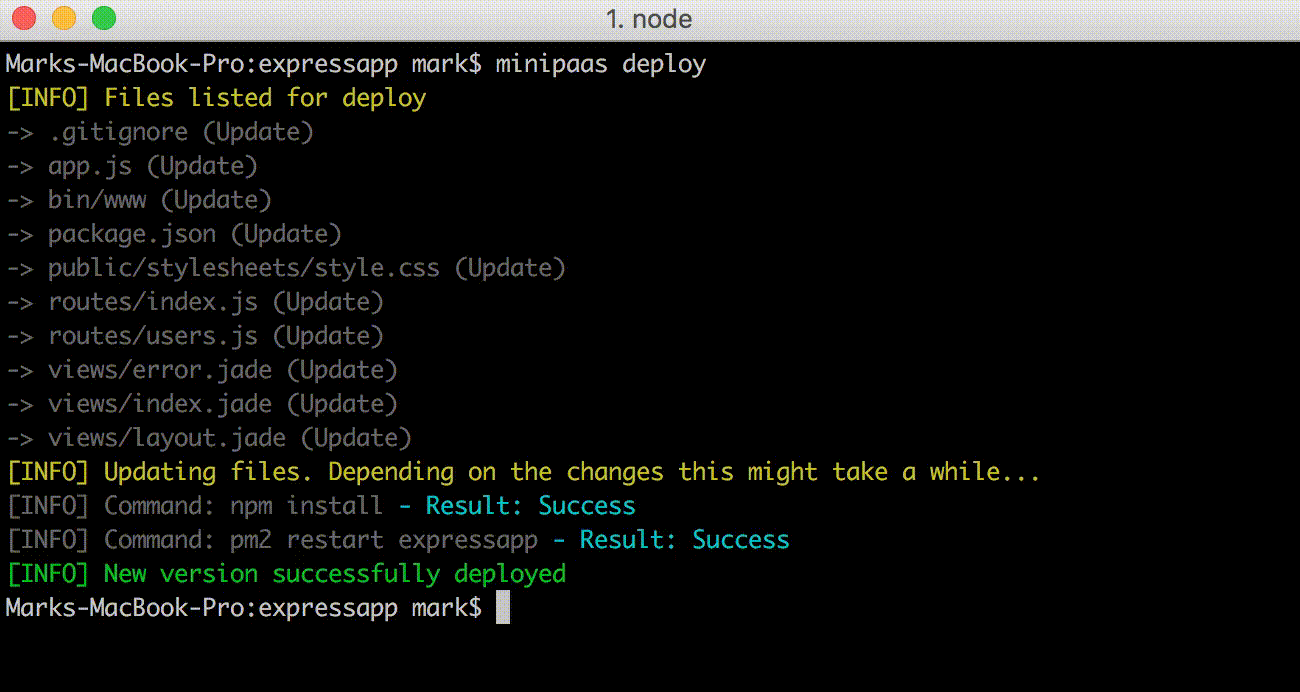
> Note: Remote Windows servers are not currently supported
## Installation
### # Local machine
You will need to install `miniPaaS` globally on your local machine using `npm`.
This can be done with the following command:
`npm install minipaas -g`
### # Remote server
You will need to install a few packages on your remote server before using `miniPaaS`. These include: `node`, `pm2` and `unzip`.
You can install these individually by using the following commands (skip anything which is already installed):
**Ubuntu:**
- Install Nodejs: `curl -sL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_6.x | sudo -E bash - && apt-get install nodejs`
- Install Unzip: `apt-get install unzip`
- Install PM2: `npm install pm2 -g`
**Centos:**
- Install Nodejs: `curl --silent --location https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_6.x | bash - && yum -y install nodejs`
- Install Unzip: `yum install unzip`
- Install PM2: `npm install pm2 -g`
## Usage
### # Init
Before using `miniPaaS` on your project you will need to run the `init` command on your application working directory. This initiates and creates a `.minipaas` config file in the root of your application directory.
The `init` command will lead to the following prompts which you can fill in for your application:
1. `App name` - Here you can supply a nice name for your application. This is used as the `pm2` process name if one is not provided.
2. `Host address` - Here you can supply your IP address or DNS or your remote server you want to deploy to
3. `Host SSH port` - Here you supply the port for SSH on your remote server
4. `Host username` - The username used to login via SSH
5. `Host password` - An optional password to connect to your server if a keyfile is not used
6. `Keyfile path` - The path to your local keyfile used to authenticate against your remote server
7. `Remote path to app` - This is the path to the root of your application hosted on your remote server
8. `disablePm2` - A boolean (true/false) value as to whether to disable the starting/restarting of the app in PM2
9. `The process name or index of app in PM2` - Here you can provide an existing PM2 process name or index. If left blank, a new process is started using the `App name` entered earlier
The `.minipaas` config file can also be manually edited:
``` json
{
"appName": "expressapp",
"hostAddress": "myexpressapp.com",
"hostPort": "22",
"hostUsername": "root",
"hostPassword": "",
"hostKeyFilePath": "/Users/myname/.ssh/id_rsa",
"remotePath": "/var/www/html/expressapp",
"pm2ProcessName": "expressapp"
}
```
### # Deploy
`miniPaaS` works with Git commits. For example you would:
1. Add your changes with `git add .`
2. Commit your changes with: `git commit -m 'My commit message'`
3. Deploy changes to remove server with: `minipaas deploy`
If you are deploying small changes to HTML or CSS etc and your application doesn't need to be restarted your can supply the `deploy` command a `norestart` switch. This makes the process quicker and less prone to downtime/errors as the changes are deployed and the app is not restarted.
### # List
Using the `minipaas list` command, you can receive a list of previous commits (only ones deployed using `miniPaaS`). You can then re-deploy a commit if you wish.
### # Compare
The `minipaas compare` command simply outputs the comparison of local files to the files on the remote server.
> Note: It does not compare the contents of the files.
### Rebuild
The `minipaas rebuild` command can be dangerous but also handy. This command removes **ALL** files from your remote directory and deploys all local files, does a `npm install` and restarts the `pm2` process.
> Note: This command is not recommended if your app stores local uploads or other files as they will be removed and cannot be retrieved.
### # Restart
The `minipaas restart ` simply restarts the PM2 process name. You can either supply the `minipaas restart` command with a PM2 process name or PM2 index number.
### # Help
By running `minipaas`, `minipaas -h` or `minipaas --help` you will receive your available options.