https://github.com/muchdogesec/txt2detection
A command line tool that takes a txt file containing threat intelligence and turns it into a detection rule.
https://github.com/muchdogesec/txt2detection
detection-engineering detection-rules siem
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
A command line tool that takes a txt file containing threat intelligence and turns it into a detection rule.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/muchdogesec/txt2detection
- Owner: muchdogesec
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2024-10-08T10:17:16.000Z (8 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-02-03T10:51:29.000Z (4 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-03T11:38:18.973Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: detection-engineering, detection-rules, siem
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://www.dogesec.com
- Size: 283 KB
- Stars: 5
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# txt2detection
## Overview

A command line tool that takes a txt file containing threat intelligence and turns it into a detection rule.
## The problems
To illustrate the problem, lets walk through the current status quo process a human goes through when going from idea (threat TTP) to detection rule:
1. read and understand threat using their own research, aided by external sources (blogs, intel feed, etc.)
* problems: lots of reports, threats described in a range of ways, reports contain differing data
2. understand what logs or security data can be used to detect this threat
* problems: log schemas are unknown to analyst, TTPs often span many logs making it hard to ensure your detection rule has full coverage
3. convert the logic created in step 1 into a detection rule (SQL/SPL/KQL, whatever) to search logs identified at step 2
* problems: hard to convert what has been understood into a logical detection rule (in a detection language an analyst might not be familiar with)
4. modify the detection rule based on new intelligence as it is discovered
* problems: this is typically overlooked as people create and forget about rules in their detection tools
## The solution
Use the AI to process threat intelligence, create and keep them updated.
txt2detection allows a user to enter some threat intelligence as a file to considered be turned into a detection.
1. User uploads intel report
2. Based on the user input, AI prompts structured and sent to produce an intelligence rule
3. Rules converted into STIX objects
## tl;dr
[](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uJWXYKyu3Xg)
[Watch the demo](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uJWXYKyu3Xg).
## Usage
### Setup
Install the required dependencies using:
```shell
# clone the latest code
git clone https://github.com/muchdogesec/txt2detection
cd txt2detection
# create a venv
python3 -m venv txt2detection-venv
source txt2detection-venv/bin/activate
# install requirements
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
```
### Set variables
txt2detection has various settings that are defined in an `.env` file.
To create a template for the file:
```shell
cp .env.example .env
```
To see more information about how to set the variables, and what they do, read the `.env.markdown` file.
### Run
```shell
python3 txt2detection.py \
--input_file FILE.txt \
...
```
* `--input_file` (required): the file to be converted. Must be `.txt`
* `--name` (required): name of file, max 72 chars. Will be used in the STIX Report Object created.
* `--report_id` (OPTIONAL): Sometimes it is required to control the id of the `report` object generated. You can therefore pass a valid UUIDv4 in this field to be assigned to the report. e.g. passing `2611965-930e-43db-8b95-30a1e119d7e2` would create a STIX object id `report--2611965-930e-43db-8b95-30a1e119d7e2`. If this argument is not passed, the UUID will be randomly generated.
* `--tlp_level` (optional): Options are `clear`, `green`, `amber`, `amber_strict`, `red`. Default if not passed, is `clear`.
* `--labels` (optional): comma seperated list of labels. Case-insensitive (will all be converted to lower-case). Allowed `a-z`, `0-9`. e.g.`label1,label2` would create 2 labels.
* `--created` (optional): by default all object `created` times will take the time the script was run. If you want to explicitly set these times you can do so using this flag. Pass the value in the format `YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.sssZ` e.g. `2020-01-01T00:00:00.000Z`
* `--use_identity` (optional): can pass a full STIX 2.1 identity object (make sure to properly escape). Will be validated by the STIX2 library. If none passed, the default SIEM Rules identity will be used.
* `--external_refs` (optional): txt2detection will automatically populate the `external_references` of the report object it creates for the input. You can use this value to add additional objects to `external_references`. Note, you can only add `source_name` and `external_id` values currently. Pass as `source_name=external_id`. e.g. `--external_refs txt2stix=demo1 source=id` would create the following objects under the `external_references` property: `{"source_name":"txt2stix","external_id":"demo1"},{"source_name":"source","external_id":"id"}`
* `--detection_language_key` (required): the detection rule language you want the output to be in. You can find a list of detection language keys in `config/detection_languages.yaml`
* `ai_provider` (required): defines the `provider:model` to be used. Select one option. Currently supports:
* Provider (env var required `OPENROUTER_API_KEY`): `openrouter:`, providers/models `openai/gpt-4o`, `deepseek/deepseek-chat` ([More here](https://openrouter.ai/models))
* Provider (env var required `OPENAI_API_KEY`): `openai:`, models e.g.: `gpt-4o`, `gpt-4o-mini`, `gpt-4-turbo`, `gpt-4` ([More here](https://platform.openai.com/docs/models))
* Provider (env var required `ANTHROPIC_API_KEY`): `anthropic:`, models e.g.: `claude-3-5-sonnet-latest`, `claude-3-5-haiku-latest`, `claude-3-opus-latest` ([More here](https://docs.anthropic.com/en/docs/about-claude/models))
* Provider (env var required `GOOGLE_API_KEY`): `gemini:models/`, models: `gemini-1.5-pro-latest`, `gemini-1.5-flash-latest` ([More here](https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/models/gemini))
* Provider (env var required `DEEPSEEK_API_KEY`): `deepseek:`, models `deepseek-chat` ([More here](https://api-docs.deepseek.com/quick_start/pricing))
e.g.
```shell
python3 txt2detection.py \
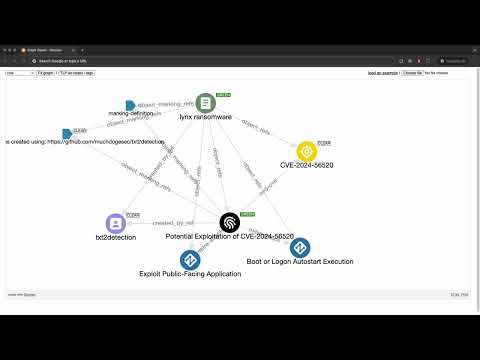
--input_file tests/files/CVE-2024-56520.txt \
--name "CVE-2024-56520" \
--tlp_level green \
--labels label1,label2 \
--external_refs txt2stix=demo1 source=id \
--detection_language spl \
--ai_provider openrouter:openai/gpt-4o \
--report_id a70c4ca8-77d5-4c6f-96fb-9726ec89d242 \
--use_identity '{"type":"identity","spec_version":"2.1","id":"identity--8ef05850-cb0d-51f7-80be-50e4376dbe63","created_by_ref":"identity--9779a2db-f98c-5f4b-8d08-8ee04e02dbb5","created":"2020-01-01T00:00:00.000Z","modified":"2020-01-01T00:00:00.000Z","name":"siemrules","description":"https://github.com/muchdogesec/siemrules","identity_class":"system","sectors":["technology"],"contact_information":"https://www.dogesec.com/contact/","object_marking_refs":["marking-definition--94868c89-83c2-464b-929b-a1a8aa3c8487","marking-definition--97ba4e8b-04f6-57e8-8f6e-3a0f0a7dc0fb"]}'
```
e.g.
```shell
python3 txt2detection.py \
--input_file tests/files/EC2-exfil.txt \
--name "EC2 exfil" \
--tlp_level green \
--detection_language sigma \
--ai_provider openrouter:openai/gpt-4o \
--report_id b02df393-995d-421e-b66c-721000e058d2
```
## Adding new detection languages
Adding a new detection language is fairly trivial. However, there is a implicit understanding the model understands the detection rule structure. Results can therefore be mixed, so it is worth testing in detail.
All you need to do is add a new record in `config/detection_languages.yaml`.
## Support
[Minimal support provided via the DOGESEC community](https://community.dogesec.com/).
## License
[Apache 2.0](/LICENSE).