https://github.com/mvoidex/hsdev
Haskell development tool
https://github.com/mvoidex/hsdev
backend developer-tools haskell
Last synced: 8 months ago
JSON representation
Haskell development tool
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/mvoidex/hsdev
- Owner: mvoidex
- License: bsd-3-clause
- Created: 2013-04-02T15:21:31.000Z (almost 13 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2020-11-04T20:12:19.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-04T08:38:30.645Z (9 months ago)
- Topics: backend, developer-tools, haskell
- Language: Haskell
- Size: 1.99 MB
- Stars: 129
- Watchers: 10
- Forks: 23
- Open Issues: 24
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# hsdev
[](http://hackage.haskell.org/package/hsdev) [](https://travis-ci.org/mvoidex/hsdev) [](https://gitter.im/mvoidex/hsdev?utm_source=badge&utm_medium=badge&utm_campaign=pr-badge&utm_content=badge) [![PayPal][paypal-donate-image]][paypal-donate-link] [![Flattr this git repo][flattr-donate-image]][flattr-donate-link]
[paypal-donate-image]: https://www.paypalobjects.com/en_US/i/btn/btn_donate_SM.gif
[paypal-donate-link]: https://www.paypal.com/cgi-bin/webscr?cmd=_donations&business=voidex%40live%2ecom&lc=US&no_note=0¤cy_code=USD&bn=PP%2dDonationsBF%3abtn_donate_SM%2egif%3aNonHostedGuest
[flattr-donate-image]: http://api.flattr.com/button/flattr-badge-large.png
[flattr-donate-link]: https://flattr.com/submit/auto?user_id=voidex&url=https://github.com/mvoidex/hsdev&title=hsdev&language=&tags=github&category=software
Haskell development library and tool with support of autocompletion, symbol info, go to declaration, find references, hayoo search etc.
Uses [fsnotify](http://hackage.haskell.org/package/fsnotify) to watch for changes.
## Installation
#### Stack
To install latest version with LTS resolver (14.10 should be fine), add these extra packages to your global stack project:
resolver: lts-14.10
extra-deps:
- hsdev-0.3.3.5
- haddock-api-2.21.0 # not required if you disable `docs` flag
- hdocs-0.5.3.1 # not required if you disable `docs` flag
And install with `stack install hsdev`
If you want to use latest nightly resolver and `ghc-8.8`, then there are some more extra deps required:
resolver: nightly-2019-10-19
extra-deps:
- hsdev-0.3.3.5
- Cabal-3.0.0.0
- haddock-api-2.23.0 # for `docs` flag
- haddock-library-1.8.0 # for `docs` flag
- hdocs-0.5.4.0 # for `docs` flag
- direct-sqlite-2.3.24
- git: https://github.com/mvoidex/sqlite-simple # actual version is broken
commit: cc94f6e303b19aeaed2ac21cbccf6f5c7b74274d
- semigroups-0.18.5
Install with `stack install hsdev`
Alternatively, you can `git clone https://github.com/mvoidex/hsdev` and install with `stack install` or `stack install --stack-yaml nightly.yaml`
#### Cabal
$ cabal sandbox init
$ cabal new-install hsdev
## Usage
Main idea is to hold in memory scanned sourced and installed modules, so that getting info about symbols and modules is fast.
It also doesn't require much work to integrate with some editor:
1. Create `hsdev run ...` process
2. Connect to it via socket
3. Send `scan` command with paths/files once
4. Use other commands to get completions, modules and symbols info; check and lint sources
##### Editors
1. [SublimeText](https://www.sublimetext.com/): [SublimeHaskell](https://packagecontrol.io/packages/SublimeHaskell) plugin
2. [Atom](https://atom.io/): work in progress, [atom-haskell-hsdev](https://github.com/mvoidex/atom-haskell-hsdev) plugin
## Start server
Use `hsdev start` to start remote server.
If you installed `hsdev` with `stack`, run server with `stack exec -- hsdev start` command, so that correct `$GHC_PACKAGE_PATH` is set where `hsdev` library installed.
Client commands then doesn't require running them with `stack exec`.
Specify `--db file.db`, where `hsdev` will store information (SQLite database, see [hsdev.sql](data/hsdev.sql) for schema).
Then you can connect to server and send requests (see [requests/responses](API.md)) or you can use `hsdev` itself. It will send command to server and outputs the response.
Scan sources, installed modules and you're ready to request various information: scope, completions, info about symbols etc.
Typical usage is:
PS> stack exec -- hsdev start
Server started at port 4567
PS> hsdev scan project ~/projects/hsdev --stack --silent
[]
PS> hsdev complete runC -f ./src/HsDev/Server/Commands.hs | jq -r '.[] | .id.name + \" :: \" + .info.type'
runClientM :: ServerM (ReaderT CommandOptions m) a
runConcurrently :: Concurrently a -> IO a
## Stack support
`hsdev` uses `stack` to build dependencies and to get corresponding package-dbs. As long as `hsdev` uses `ghc` as library, it passes `--compiler` and `--arch` options (since `0.1.7.2`) to `stack` in order to get compatible package-dbs built with same compiler.
## Building without `haddock`/`hdocs` dependency
Disable flag `docs` to build without these dependencies: `cabal configure -f-docs` or `stack install --flag hsdev:-docs`
### Commands
Run `hsdev -?` to get list of all commands or `hsdev -?` (`hsdev help `) to get detailed info.
* `version` — returns version number
* `start`, `run` and `stop` — server commands, start remote server, run server or stop remote server.
* `connect` — connect to server to send commands from command line (for debug)
* `ping` — ping server
* `listen` — connect to server and listen for its log (for debug)
* `set-log` — set log level
* `scan` — scan installed modules, cabal projects and files
* `scan project`, `scan file`, `scan package-dbs` — same as above, but with additional options
* `set-file-contents` — set data to use as file contents, used to work with unsaved files
* `docs`, `infer` — scan docs or infer types for sources
* `remove`, `remove-all` — unload data
* `packages`, `projects`, `sandboxes` — list information about specified modules, packages, projects or sandboxes
* `symbol`, `module`, `project`, `sandbox` — get info about symbol, module, project or sandbox
* `whoat`, `whois`, `lookup` — find project-visible or imported symbol
* `scope`, `scope modules` — get modules or declarations, accessible from file
* `usages` — find usages of symbol
* `complete` — get completions for file and input
* `hayoo` — search in hayoo
* `cabal list` — search packages info
* `lint`, `check`, `lint-check` — lint or check source files. These commands have some advantages over `ghc-mod` ones: `lint` uses `hlint` as library, `check` returns more precise source position and also uses project description to pass `-package` flags, these commands also can accept file contents
* `types` — get types for all source spans
* `flags`, `langs` — list ghc flags and language extensions
* `ghc eval` — evaluate expression
* `ghc type` — get type of expression
* `autofixes` — get suggestions to fix some warnings and errors
* `rename` — get regions to rename some symbol
* `refactor` — apply suggestions/renames from previous commands
#### TODO: Detailed commands description with examples
#### Scan
You can scan package-dbs, projects and files.
To scan global and user package-dbs, run
PS> hsdev scan package-dbs --global-db --user-db --silent
[]
PS> hsdev module -h -m System.IO | jq -r '.[].location.package'
base-4.12.0.0
To scan project use `scan project`, which will also scan dependens package-dbs (unless `--no-deps` flag set)
PS> hsdev scan project ~/projects/hsdev --stack --silent
[]
PS> hsdev module -f ~/projects/hsdev/src/HsDev/Client/Commands.hs | jq -r '.[].exports[] | .id.name + \" :: \" + .info.type'
runClient :: (ToJSON a, ServerMonadBase m) => CommandOptions -> ClientM m a -> ServerM m Result
runCommand :: ServerMonadBase m => Command -> ClientM m Value
To scan file use `scan file`:
PS> hsdev scan file ~/projects/hs/Main.hs --stack --silent
[]
PS> hsdev module -f ~/projects/hs/Main.hs | jq -r '.[].exports[] | .id.name + \" :: \" + .info.type'
main :: IO ()
#### Whois/whoat
Get information for symbol in context of source file. Understand qualified names and also names qualified with module shortcut (`import ... as`), note `M.` qualified for `map`, and local definition `toResult`:
PS> dev whois M.lookup --file .\src\HsDev\Client\Commands.hs | json | % { $_.id.name + ' :: ' + $_.info.type }
lookup :: Ord k => k -> Map k a -> Maybe a
PS> hsdev whoat 64 1 -f .\src\HsDev\Client\Commands.hs | json | % { $_.id.name + ' :: ' + $_.info.type }
toValue :: m a -> m Value
PS> hsdev whoat 55 32 -f .\src\HsDev\Client\Commands.hs | json | % { $_.id.name + ' :: ' + $_.info.type }
toResult :: ReaderT CommandOptions m a -> m Result
#### Usages
Returns all places where symbol is used
PS> hsdev usages Data.Map.toList | json | % { $_.in.name, $_.at.line, $_.at.column -join ':' }
Data.Deps:33:90
Data.Deps:57:62
HsDev.Symbols.Types:93:12
HsDev.Symbols.Types:95:54
HsDev.Symbols.Types:104:74
HsDev.Symbols.Types:104:94
...
#### AutoFixes/Rename/Refactor
Autofix commands used to assist for automatic fix of some warnings and hints from `hlint`. `autofixes` command parses `check` and `lint` command output, and returns `corrections` — data with regions and suggestions to fix. `refactor` command perform fix of selected corrections and also updates positions of other corrections, such that they stay relevant. These updated corrections can be used to pass them to `refactor` again.
Example of interactive command, based on this command in SublimeHaskell:
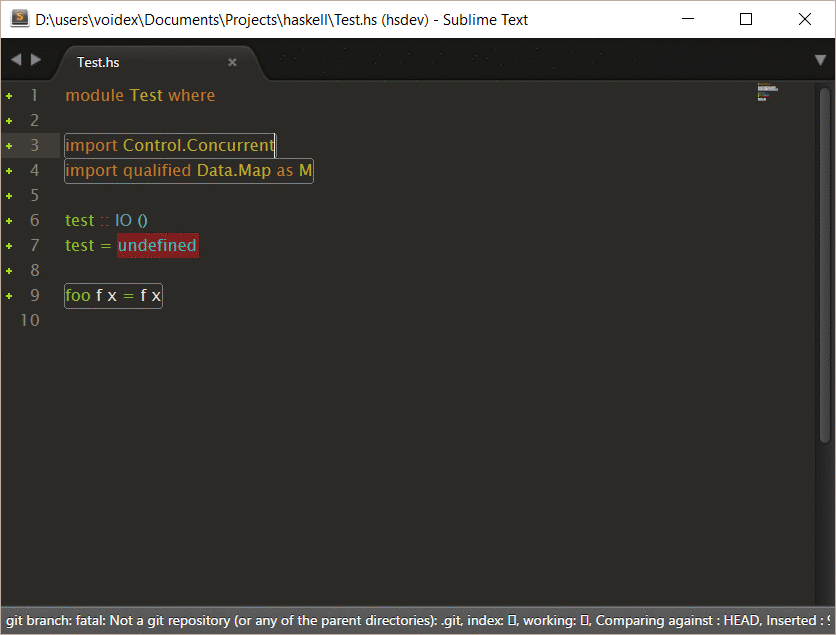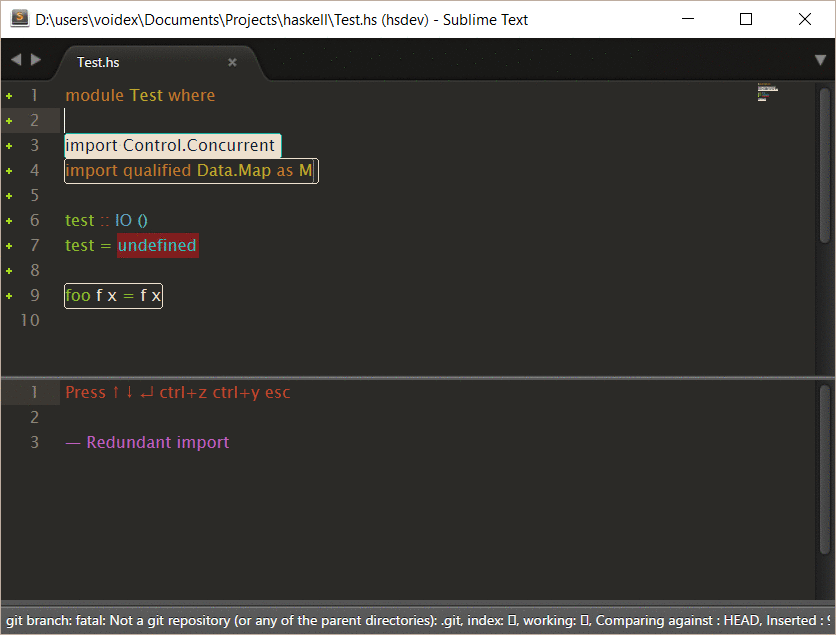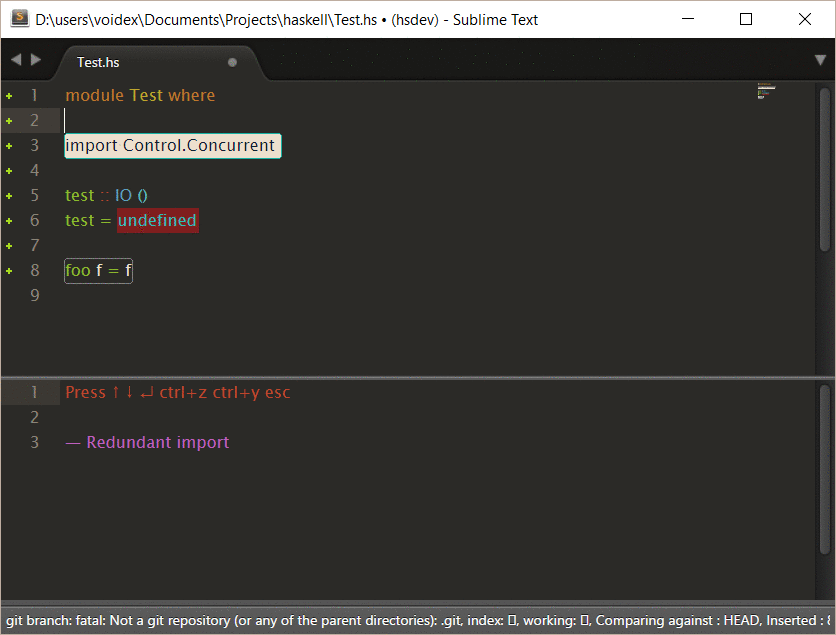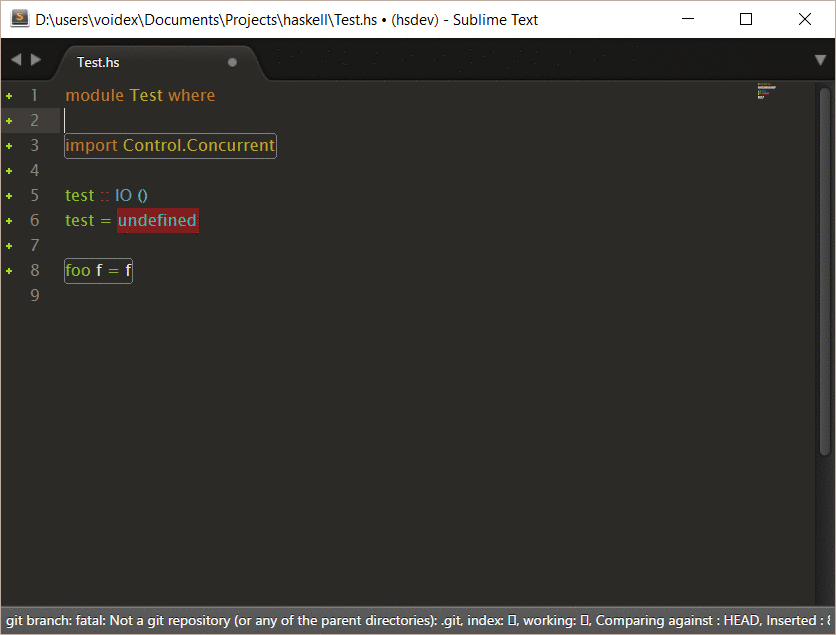
Rename generates corrections to rename symbol
# Get corrections
PS> $corrs = hsdev check-lint ..\haskell\Test.hs | hsdev autofixes --stdin
# Apply first correction, other corrections passed as --rest param to update their positions
# Result is updated --rest corrections, which can be used again
PS> $corrs2 = ($corrs | jq '[.[1]]' -c -r) | hsdev refactor --pure --rest (escape ($corrs | jq '.[1:5]' -c -r)) --stdin
# One more
PS> $corrs2 | hsdev refactor --stdin --pure
### Examples
PS> hsdev start --db hsdev.db
Server started at port 4567
PS> hsdev scan --cabal
{}
PS> hsdev scan --project hsdev
{}
PS> hsdev module --project hsdev -h | json | % { $_.name } | select -first 3
HsDev.Database.Update
HsDev.Client.Commands
HsDev.Scan
PS> hsdev symbol enumProject --src | json | % { $_.id.name + ' :: ' + $_.info.type }
enumProject :: Project -> m ScanContents
PS> hsdev complete tr -f .\tools\hsdev.hs | json | % { $_.id.name }
traverse
traverseDirectory
...
PS> hsdev stop
{}
### Hayoo in GHCi
You can use this `ghci.conf` to allow search from `ghci`:
:set prompt "λ> "
import Control.Monad.Error
import HsDev.Tools.Hayoo
import Data.List (intercalate)
:{
let
showHayooFunction f =
(hayooName f ++ " :: " ++ hayooSignature f) :
(map ('\t':) $
lines (untagDescription (hayooDescription f)) ++
["-- Defined in '" ++ intercalate ", " (hayooModules f) ++ "', " ++ hayooPackage f])
showHayoo = concatMap showHayooFunction . resultResult
:}
:def hayoo \s -> return $ "runErrorT (hayoo \"" ++ s ++ "\" Nothing) >>= (mapM_ putStrLn) . either (return . (\"Error: \" ++)) showHayoo"
Usage:
λ> :hayoo (a -> c) -> (b -> c)
query :: (a -> c) -> b -> c
query f x walks the structure x (bottom up) and applies f
to every a, appending the results.
-- Defined in 'Text.Pandoc.Walk', pandoc-types
...
### JSON
#### PowerShell
I'm using PowerShell and `json` function from [PSUtils](https://github.com/mvoidex/PSUtils) to parse JSON output, which returns `PSObject`, that can be inspected in common way:
PS> hsinspect module GHC -g "-package ghc" | json | % { $_.module.declarations } | % { $_.name + ' :: ' + $_.decl.type } | select -first 5
ABE :: id -> id -> HsWrapper -> TcSpecPrags -> ABExport id
ABExport :: data ABExport id
ACoAxiom :: CoAxiom Branched -> TyThing
AConLike :: ConLike -> TyThing
ATyCon :: TyCon -> TyThing
#### [jq](http://stedolan.github.io/jq/)
Another way is to use [jq](http://stedolan.github.io/jq/) tool, which is pretty simple:
PS> hsinspect module GHC -g "-package ghc" | jq -r '.module.declarations[range(0;5)] | .name + \" :: \" + .decl.type'
ABE :: id -> id -> HsWrapper -> TcSpecPrags -> ABExport id
ABExport :: data ABExport id
ACoAxiom :: CoAxiom Branched -> TyThing
AConLike :: ConLike -> TyThing
ATyCon :: TyCon -> TyThing