https://github.com/nopnop2002/esp-idf-ftpclient
ftp client for esp-idf
https://github.com/nopnop2002/esp-idf-ftpclient
esp-idf esp32 ftp ftp-client
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
ftp client for esp-idf
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/nopnop2002/esp-idf-ftpclient
- Owner: nopnop2002
- Created: 2019-10-06T01:15:23.000Z (about 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-30T00:50:47.000Z (9 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-31T17:19:22.855Z (9 months ago)
- Topics: esp-idf, esp32, ftp, ftp-client
- Language: C
- Homepage:
- Size: 146 KB
- Stars: 78
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 12
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# esp-idf-ftpClient
FTP Client for esp-idf.
# Software requirements
ESP-IDF V5.0 or later.
ESP-IDF V4.4 release branch reached EOL in July 2024.
# Installation
```
git clone https://github.com/nopnop2002/esp-idf-ftpClient
cd esp-idf-ftpClient/
idf.py menuconfig
idf.py flash
```
# Configuration


## File System Selection
This project supports the following file systems.
You can select any one using menuconfig.
- SPIFFS file system on Builtin SPI Flash Memory
- FAT file system on Builtin SPI Flash Memory
- LITTLEFS file system on Builtin SPI Flash Memory
- FAT file system on SPI peripheral SDCARD
- FAT file system on SDMMC peripheral SDCARD(Valid only for ESP32/ESP32S3)
- FAT file system on External SPI Flash Memory like Winbond W25Q64



Note:
The connection when using SDSPI, SDMMC, and External SPI flash Memory will be described later.
Note:
LITTLEFS requires ESP-IDF V5.2 or later.
## Partition table
Use ```partitions_example_spiffs.csv``` when you select SPIFFS file system on Builtin SPI Flash Memory.
Use ```partitions_example_fatfs.csv``` when you select FAT file system on Builtin SPI Flash Memory.
Use ```partitions_example_littlefs.csv``` when you select LITTLEFS file system on Builtin SPI Flash Memory.
__If you need more storage space in the Builtin SPI Flash Memory, you will need to modify these files.__
## Wifi Setting

## FTP Server Setting

- Public FTP Server
You can use [this](https://dlptest.com/ftp-test/) public FTP server for testing.
The files will be stored for 10 minutes before being deleted.
```
cd esp-idf-ftpClient
rm sdkconfig
cd main
cp Kconfig.projbuild Kconfig.projbuild.old
cp Kconfig.projbuild.dlptest Kconfig.projbuild
cd ..
idf.py menuconfig
idf.py build
```

- FTP Server using python
You can set up an FTP server with [this](https://github.com/nopnop2002/esp-idf-ftpClient/tree/master/python-ftp-server) script.
# Using FAT file system on SPI peripheral SDCARD
|ESP32|ESP32S2/S3|ESP32C2/C3/C6|SD card pin|Notes|
|:-:|:-:|:-:|:-:|:--|
|GPIO23|GPIO35|GPIO01|MOSI|10k pull up if can't mount|
|GPIO19|GPIO37|GPIO03|MISO||
|GPIO18|GPIO36|GPIO02|SCK||
|GPIO5|GPIO34|GPIO04|CS||
|3.3V|3.3V|3.3V|VCC|Don't use 5V supply|
|GND|GND|GND|GND||

__You can change it to any pin using menuconfig.__
Note:
This project doesn't utilize card detect (CD) and write protect (WP) signals from SD card slot.
# Using FAT file system on SDMMC peripheral SDCARD
On ESP32, SDMMC peripheral is connected to specific GPIO pins using the IO MUX.
__GPIO pins cannot be customized.__
GPIO2 and GPIO12 cannot be changed.
So using 4-line SD mode with ESP32 is very tricky.
Please see the table below for the pin connections.
|ESP32 pin|SD card pin|Notes|
|:-:|:-:|:--|
|GPIO14|CLK|10k pullup|
|GPIO15|CMD|10k pullup|
|GPIO2|D0|10k pullup or connect to GPIO00|
|GPIO4|D1|not used in 1-line SD mode; 10k pullup in 4-line SD mode|
|GPIO12|D2|not used in 1-line SD mode; 10k pullup in 4-line SD mode|
|GPIO13|D3|not used in 1-line SD mode, but card's D3 pin must have a 10k pullup
|N/C|CD|not used in this project|
|N/C|WP|not used in this project|
|3.3V|VCC|Don't use 5V supply|
|GND|GND||
- 1line mode

- 4line mode

On ESP32-S3, SDMMC peripheral is connected to GPIO pins using GPIO matrix.
__This allows arbitrary GPIOs to be used to connect an SD card.__
|ESP32-S3 pin|SD card pin|Notes|
|:-:|:-:|:--|
|GPIO36|CLK|10k pullup|
|GPIO35|CMD|10k pullup|
|GPIO37|D0|10k pullup|
|GPIO38|D1|not used in 1-line SD mode; 10k pullup in 4-line SD mode|
|GPIO33|D2|not used in 1-line SD mode; 10k pullup in 4-line SD mode|
|GPIO34|D3|not used in 1-line SD mode, but card's D3 pin must have a 10k pullup
|N/C|CD|not used in this project|
|N/C|WP|not used in this project|
|3.3V|VCC|Don't use 5V supply|
|GND|GND||
- 1line mode

- 4line mode

## Note about GPIO2 (ESP32 only)
GPIO2 pin is used as a bootstrapping pin, and should be low to enter UART download mode. One way to do this is to connect GPIO0 and GPIO2 using a jumper, and then the auto-reset circuit on most development boards will pull GPIO2 low along with GPIO0, when entering download mode.
- Some boards have pulldown and/or LED on GPIO2. LED is usually ok, but pulldown will interfere with D0 signals and must be removed. Check the schematic of your development board for anything connected to GPIO2.
## Note about GPIO12 (ESP32 only)
GPIO12 is used as a bootstrapping pin to select output voltage of an internal regulator which powers the flash chip (VDD_SDIO).
This pin has an internal pulldown so if left unconnected it will read low at reset (selecting default 3.3V operation).
When adding a pullup to this pin for SD card operation, consider the following:
- For boards which don't use the internal regulator (VDD_SDIO) to power the flash, GPIO12 can be pulled high.
- For boards which use 1.8V flash chip, GPIO12 needs to be pulled high at reset. This is fully compatible with SD card operation.
- On boards which use the internal regulator and a 3.3V flash chip, GPIO12 must be low at reset. This is incompatible with SD card operation.
* In most cases, external pullup can be omitted and an internal pullup can be enabled using a `gpio_pullup_en(GPIO_NUM_12);` call. Most SD cards work fine when an internal pullup on GPIO12 line is enabled. Note that if ESP32 experiences a power-on reset while the SD card is sending data, high level on GPIO12 can be latched into the bootstrapping register, and ESP32 will enter a boot loop until external reset with correct GPIO12 level is applied.
* Another option is to burn the flash voltage selection efuses. This will permanently select 3.3V output voltage for the internal regulator, and GPIO12 will not be used as a bootstrapping pin. Then it is safe to connect a pullup resistor to GPIO12. This option is suggested for production use.
# Using FAT file system on External SPI Flash Memory
I tested these SPI Flash Memory.
https://github.com/nopnop2002/esp-idf-w25q64
|#|W25Q64||ESP32|ESP32-S2/S3|ESP32-C2/C3/C6|
|:-:|:-:|:-:|:-:|:-:|:-:|
|1|/CS|--|GPIO5|GPIO10|GPIO4|
|2|MISO|--|GPIO19|GPIO13|GPIO3|
|3|/WP|--|3.3V|3.3V|3.3V|
|4|GND|--|GND|GND|GND|
|5|MOSI|--|GPIO23|GPIO11|GPIO1|
|6|SCK|--|GPIO18|GPIO12|GPIO2|
|7|/HOLD|--|3.3V|3.3V|3.3V|
|8|VCC|--|3.3V|3.3V|3.3V|

Note: You will get an error. It works fine after a few resets. At the moment, it is not stable.
```
I (2121) FTP: Initializing external SPI Flash
I (2121) FTP: Pin assignments:
I (2121) FTP: MOSI: 23 MISO: 19 SCLK: 18 CS: 5
E (2131) memspi: no response
E (2131) FTP: Failed to initialize external Flash: ESP_ERR_INVALID_RESPONSE (0x108)
```
After reset
```
I (1621) FTP: Initializing external SPI Flash
I (1621) FTP: Pin assignments:
I (1631) FTP: MOSI: 23 MISO: 19 SCLK: 18 CS: 5
I (1631) spi_flash: detected chip: winbond
I (1641) spi_flash: flash io: dio
I (1641) FTP: Initialized external Flash, size=8192 KB, ID=0xef4017
I (1651) FTP: Adding external Flash as a partition, label="storage", size=8192 KB
I (1661) FTP: Initializing FAT file system
I (1661) FTP: Mount FAT filesystem on /root
```
# Using ESP32-CAM
The ESP32-CAM development board has a micro SD card slot on the board.
It is connected to the ESP32 by SDMMC with 4-line Mode.
__No equipment other than the development board is required.__
It works very stably.



# Using LilyGo ESP32-S2
The LilyGo ESP32-S2 development board has a micro SD card slot on the board.
It is connected to the ESP32 by SPI, and the peripheral power is supplied from GPIO14.
__No equipment other than the development board is required.__
It works very stably.
|ESP32 pin|SPI bus signal|
|:-:|:-:|
|GPIO11|MOSI|
|GPIO13|MISO|
|GPIO12|SCK|
|GPIO10|CS|
|GPIO14|POWER|



# API
Based on [ftplib](https://nbpfaus.net/~pfau/ftplib/ftplib.html) V4.0-1.
## Server Connection
- ftpClientConnect() - Connect to a remote server
- ftpClientLogin() - Login to remote machine
- ftpClientQuit() - Disconnect from remote server
- ftpClientSetOptions() - Set Connection Options
## Directory Functions
- ftpClientChangeDir() - Change working directory
- ftpClientMakeDir() - Create a directory
- ftpClientRemoveDir() - Remove a directory
- ftpClientDir() - List a remote directory
- ftpClientNlst() - List a remote directory
- ftpClientChangeDirUp() - Change to parent directory
- ftpClientPwd() - Determine current working directory
## File to File Transfer
- ftpClientGet() - Retreive a remote file
- ftpClientPut() - Send a local file to remote
- ftpClientDelete() - Delete a remote file
- ftpClientRename() - Rename a remote file
## File to Program Transfer
These routines allow programs access to the data streams connected to remote files and directories.
- ftpClientAccess() - Open a remote file or directory
- ftpClientRead() - Read from remote file or directory
- ftpClientWrite() - Write to remote file
- ftpClientClose() - Close data connection
# Using long file name support
By default, FATFS file names can be up to 8 characters long.
If you use filenames longer than 8 characters, you need to change the values below.
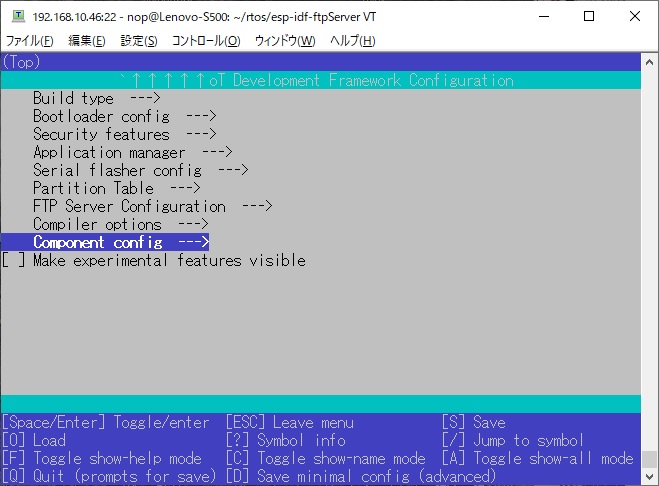
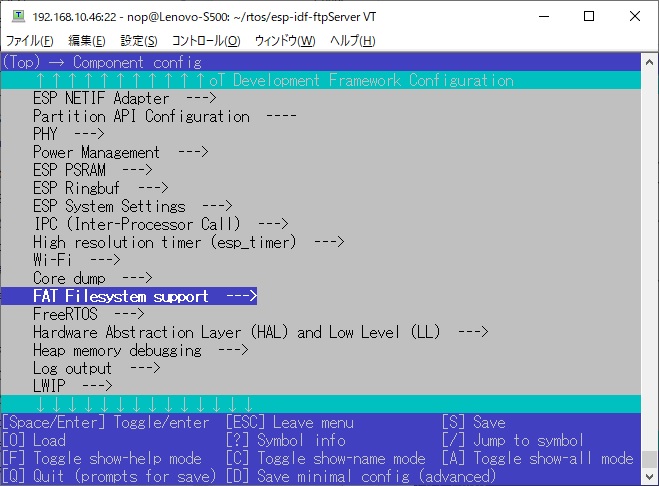
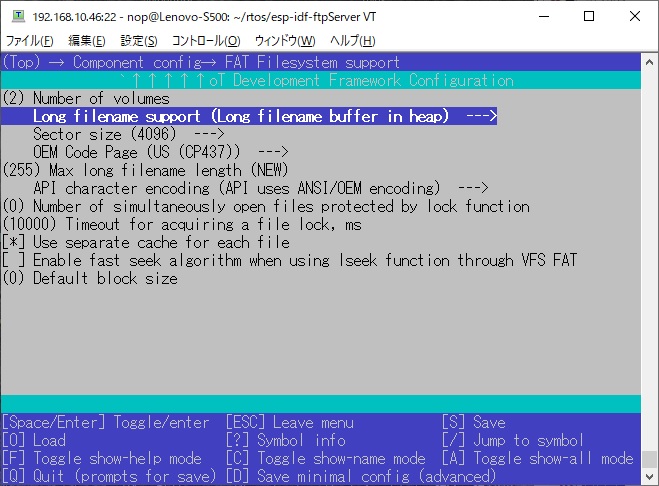
# Screen Shot

- Get remote file list
- Write local file
- Put file to server
- Remove local file
- Get file from sever
- Read local file
# Truble shooting
By changing this, you can see the response from the server:
```
#define FTP_CLIENT_DEBUG 2
```
# How to use this component in your project
Create idf_component.yml in the same directory as main.c.
```
YourProject --+-- CMakeLists.txt
+-- main --+-- main.c
+-- CMakeLists.txt
+-- idf_component.yml
```
Contents of idf_component.yml.
```
dependencies:
nopnop2002/ftpClient:
path: components/ftpClient/
git: https://github.com/nopnop2002/esp-idf-ftpClient.git
```
When you build a projects esp-idf will automaticly fetch repository to managed_components dir and link with your code.
```
YourProject --+-- CMakeLists.txt
+-- main --+-- main.c
| +-- CMakeLists.txt
| +-- idf_component.yml
+-- managed_components ----- nopnop2002__ftpClient
```
# Reference
- FTP Server using FAT File system.
Since it uses the FAT file system instead of SPIFFS, directory operations are possible.
https://github.com/nopnop2002/esp-idf-ftpServer
- File copy using scp.
https://github.com/nopnop2002/esp-idf-scp-client
- File copy using smb.
https://github.com/nopnop2002/esp-idf-smb-client