https://github.com/nschloe/maelstrom
Numerical simulation of magnetohydrodynamics.
https://github.com/nschloe/maelstrom
fenics mathematics navier-stokes physics python
Last synced: 23 days ago
JSON representation
Numerical simulation of magnetohydrodynamics.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/nschloe/maelstrom
- Owner: nschloe
- License: mit
- Created: 2014-05-13T20:46:36.000Z (about 11 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2021-03-19T09:46:06.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-30T11:32:49.050Z (about 2 months ago)
- Topics: fenics, mathematics, navier-stokes, physics, python
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 7.43 MB
- Stars: 31
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 6
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# maelstrom
[](https://circleci.com/gh/nschloe/maelstrom/tree/master)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/nschloe/maelstrom)
[](https://github.com/ambv/black)
[](https://maelstrom.readthedocs.io/en/master/)
maelstrom is a numerical software tool for the solution of magnetohydrodynamics
problems in cylindrical coordinates.
As such, maelstrom includes time integrators for the heat equation, for the
Navier--Stokes equations, and a stationary solver for the Maxwell equations,
each in cylindrial coordinates.
### Some details on the problem
The goal is to compute the flux of a liquid metal under the influence of a
magnetic field, modeled by
* the heat equation,
* Maxwell's equations, and
* the Navier-Stokes equations.
Heat and Navier-Stokes are coupled by buoyancy, heat and Maxwell by the Joule
effect, and Maxwell and Navier-Stokes by current induction and the Lorentz
force.
To simplify matters, it is assumed that the effect of the material flux does
not influence the electric and magnetic fields, i.e., the current induction
from moving molten metal in a magnetic field is neglected. This decouples
Maxwell's equations from the other two. Essentially, the task breaks down to
* computing Joule heating and Lorentz force, given a voltage distribution in
coils, and given those two quantities
* computing the the resulting material flux inside a container.
### Solving Maxwell's equations
Derivation of the involved formulas is best taken from [the
documentation](https://maelstrom.readthedocs.io/en/master/maelstrom.maxwell.html).
##### Some visualizations
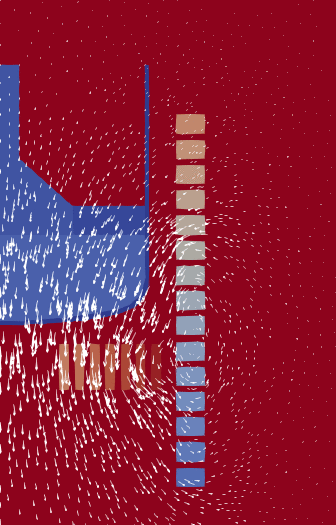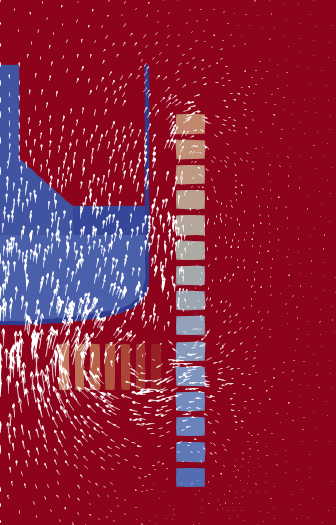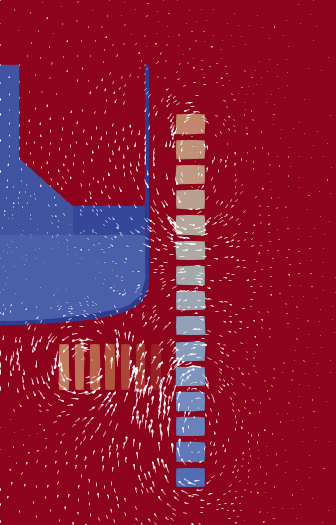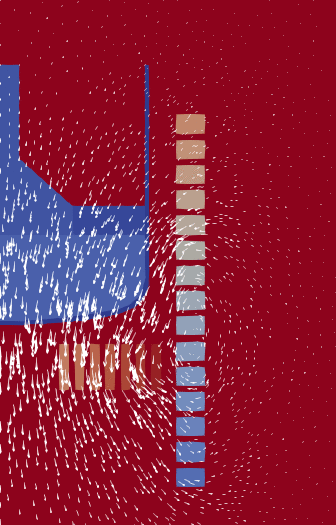
A typical cylindrical problem: A crucible with a liquid on the left, surrounded
by a number of electric coils (the squares). The arrows indicate the magnetic
field produced by current in those coils. Note that the actual domain where
Maxwell's equations are solved is much larger.
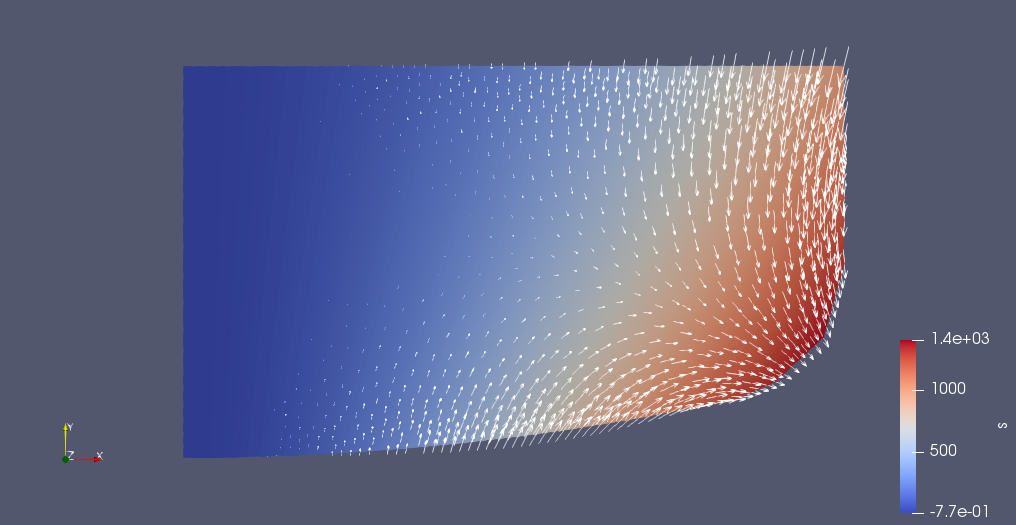
The Joule heat source (blue/red) and the Lorentz force (arrows) generated from
the above magnetic field.
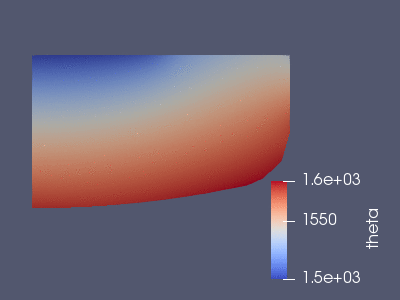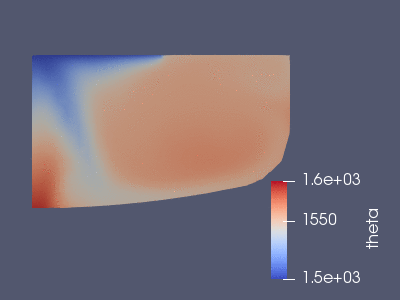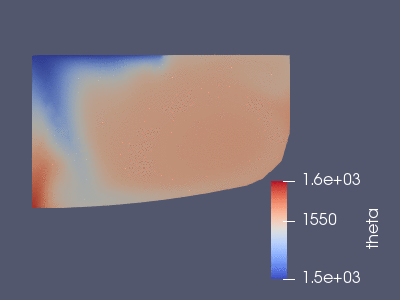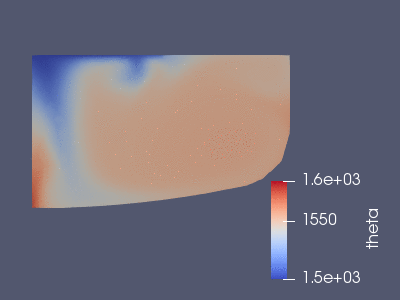
The temperature in the first 60 seconds of the full simulation. The Maxwell
equations are solved first, from this one gets the above Joule heat source and
the Lorentz force. These are added as external fources to the Boussinesq
simulation that we see here.
### Testing
To run the voropy unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
pytest
```
### License
maelstrom is published under the MIT license. See the file LICENSE for detailed
information.