https://github.com/nschloe/pygmsh
:spider_web: Gmsh for Python
https://github.com/nschloe/pygmsh
engineering mathematics mesh-generation meshing pypi python
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
:spider_web: Gmsh for Python
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/nschloe/pygmsh
- Owner: nschloe
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2013-10-03T21:40:30.000Z (over 12 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-10-04T10:11:37.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-14T05:55:53.035Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: engineering, mathematics, mesh-generation, meshing, pypi, python
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 3.42 MB
- Stars: 899
- Watchers: 39
- Forks: 162
- Open Issues: 58
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.txt
- Citation: CITATION.cff
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-fluid-dynamics - nschloe/pygmsh - Gmsh for Python.  (Meshing / Books)
- awesome-scientific-computing - pygmsh - Python interface for Gmsh. (Meshing / Triangular and tetrahedral meshing)
README
Gmsh for Python.
[](https://pypi.org/project/pygmsh/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/pygmsh/)
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1173105)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/pygmsh)
[](https://pypistats.org/packages/pygmsh)
[](https://discord.gg/hnTJ5MRX2Y)
[](https://pygmsh.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/pygmsh/actions?query=workflow%3Aci)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/nschloe/pygmsh)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/nschloe/pygmsh)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
pygmsh combines the power of [Gmsh](https://gmsh.info/) with the versatility of Python.
It provides useful abstractions from Gmsh's own Python interface so you can create
complex geometries more easily.
To use, install Gmsh itself and pygmsh from [pypi](https://pypi.org/project/pygmsh/):
```
[sudo] apt install python3-gmsh
pip install pygmsh
```
This document and the [`tests/`](https://github.com/nschloe/pygmsh/tree/main/tests/)
directory contain many small examples. See
[here](https://pygmsh.readthedocs.io/en/latest/index.html) for the full documentation.
#### Flat shapes
|  |
|  |
|  |
|
| :-------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------: |
| Polygon | Circle | (B-)Splines |
Codes:
```python
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.geo.Geometry() as geom:
geom.add_polygon(
[
[0.0, 0.0],
[1.0, -0.2],
[1.1, 1.2],
[0.1, 0.7],
],
mesh_size=0.1,
)
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
# mesh.points, mesh.cells, ...
# mesh.write("out.vtk")
```
```python
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.geo.Geometry() as geom:
geom.add_circle([0.0, 0.0], 1.0, mesh_size=0.2)
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
```python
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.geo.Geometry() as geom:
lcar = 0.1
p1 = geom.add_point([0.0, 0.0], lcar)
p2 = geom.add_point([1.0, 0.0], lcar)
p3 = geom.add_point([1.0, 0.5], lcar)
p4 = geom.add_point([1.0, 1.0], lcar)
s1 = geom.add_bspline([p1, p2, p3, p4])
p2 = geom.add_point([0.0, 1.0], lcar)
p3 = geom.add_point([0.5, 1.0], lcar)
s2 = geom.add_spline([p4, p3, p2, p1])
ll = geom.add_curve_loop([s1, s2])
pl = geom.add_plane_surface(ll)
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
The return value is always a [meshio](https://pypi.org/project/meshio/) mesh, so to
store it to a file you can
```python
mesh.write("test.vtk")
```
The output file can be visualized with various tools, e.g.,
[ParaView](https://www.paraview.org/).
With
```python
pygmsh.write("test.msh")
```
you can access Gmsh's native file writer.
#### Extrusions
| 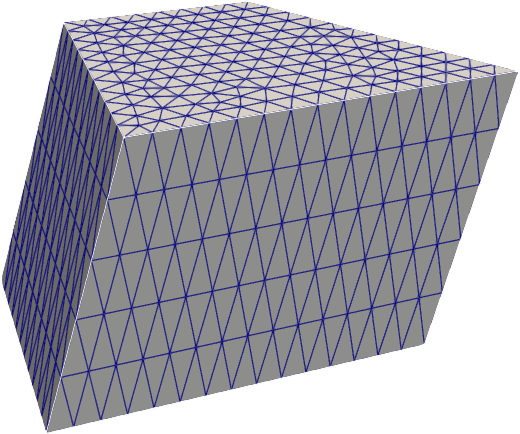 |
| 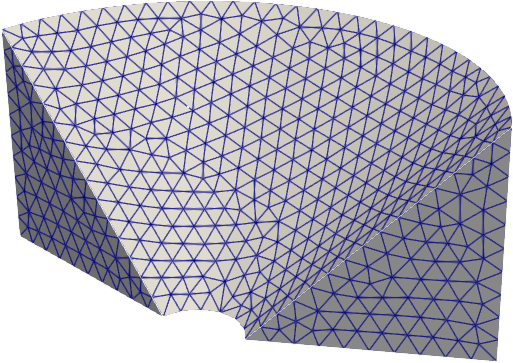 |
| 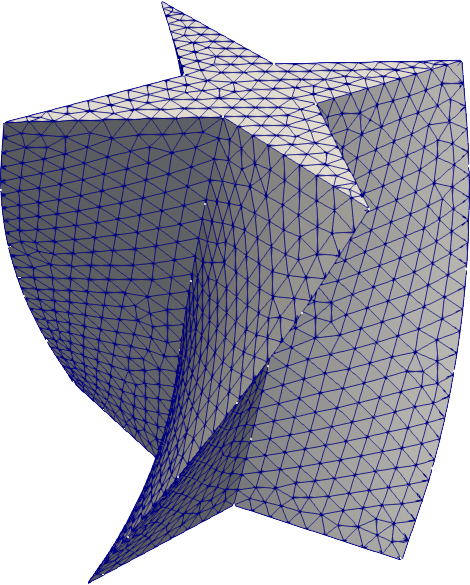 |
|
| :-------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-----------------------------------------------------------------: |
| `extrude` | `revolve` | `twist` |
```python
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.geo.Geometry() as geom:
poly = geom.add_polygon(
[
[0.0, 0.0],
[1.0, -0.2],
[1.1, 1.2],
[0.1, 0.7],
],
mesh_size=0.1,
)
geom.extrude(poly, [0.0, 0.3, 1.0], num_layers=5)
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
```python
from math import pi
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.geo.Geometry() as geom:
poly = geom.add_polygon(
[
[0.0, 0.2, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.2, 0.0],
[0.0, 1.2, 1.0],
],
mesh_size=0.1,
)
geom.revolve(poly, [0.0, 0.0, 1.0], [0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 0.8 * pi)
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
```python
from math import pi
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.geo.Geometry() as geom:
poly = geom.add_polygon(
[
[+0.0, +0.5],
[-0.1, +0.1],
[-0.5, +0.0],
[-0.1, -0.1],
[+0.0, -0.5],
[+0.1, -0.1],
[+0.5, +0.0],
[+0.1, +0.1],
],
mesh_size=0.05,
)
geom.twist(
poly,
translation_axis=[0, 0, 1],
rotation_axis=[0, 0, 1],
point_on_axis=[0, 0, 0],
angle=pi / 3,
)
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
#### OpenCASCADE
| 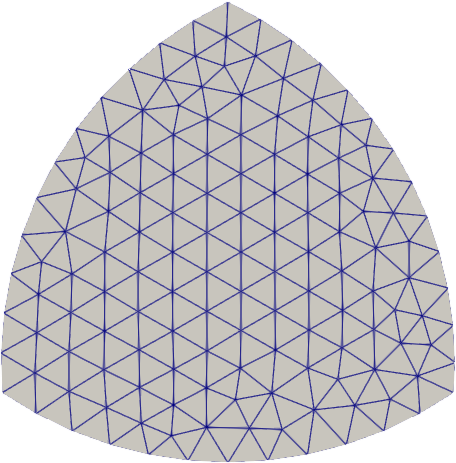 |
|  |
|  |
|
| :------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :---------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------------: |
| | |
Gmsh also supports OpenCASCADE (`occ`), allowing for a CAD-style geometry specification.
```python
from math import pi, cos
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.occ.Geometry() as geom:
geom.characteristic_length_max = 0.1
r = 0.5
disks = [
geom.add_disk([-0.5 * cos(7 / 6 * pi), -0.25], 1.0),
geom.add_disk([+0.5 * cos(7 / 6 * pi), -0.25], 1.0),
geom.add_disk([0.0, 0.5], 1.0),
]
geom.boolean_intersection(disks)
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
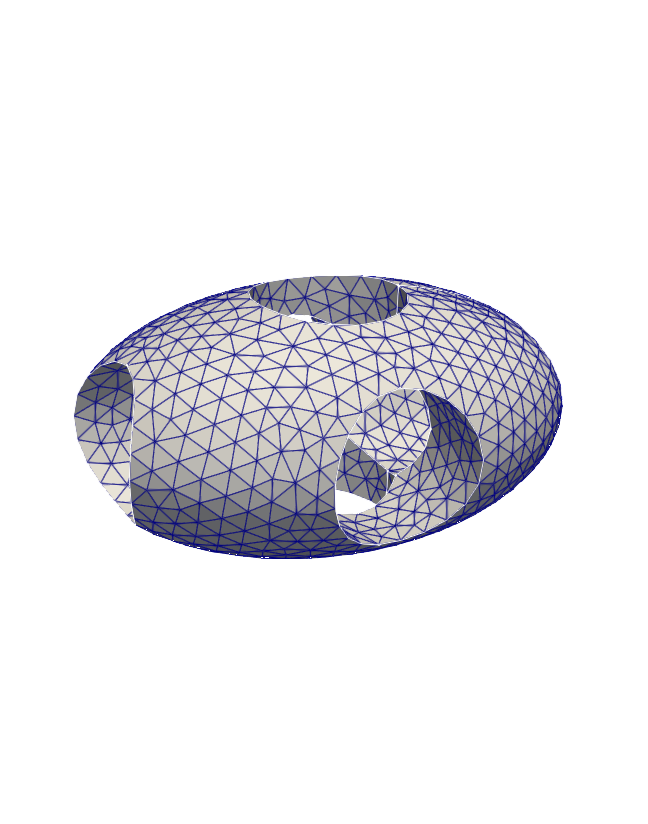
```python
# ellpsoid with holes
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.occ.Geometry() as geom:
geom.characteristic_length_max = 0.1
ellipsoid = geom.add_ellipsoid([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], [1.0, 0.7, 0.5])
cylinders = [
geom.add_cylinder([-1.0, 0.0, 0.0], [2.0, 0.0, 0.0], 0.3),
geom.add_cylinder([0.0, -1.0, 0.0], [0.0, 2.0, 0.0], 0.3),
geom.add_cylinder([0.0, 0.0, -1.0], [0.0, 0.0, 2.0], 0.3),
]
geom.boolean_difference(ellipsoid, geom.boolean_union(cylinders))
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
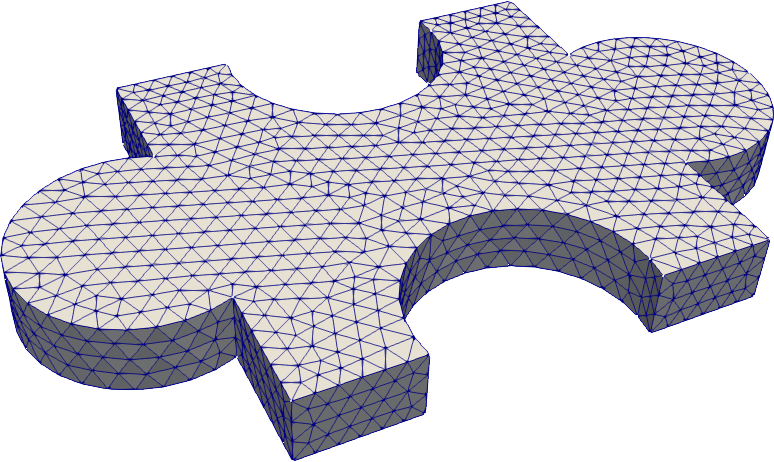
```python
# puzzle piece
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.occ.Geometry() as geom:
geom.characteristic_length_min = 0.1
geom.characteristic_length_max = 0.1
rectangle = geom.add_rectangle([-1.0, -1.0, 0.0], 2.0, 2.0)
disk1 = geom.add_disk([-1.2, 0.0, 0.0], 0.5)
disk2 = geom.add_disk([+1.2, 0.0, 0.0], 0.5)
disk3 = geom.add_disk([0.0, -0.9, 0.0], 0.5)
disk4 = geom.add_disk([0.0, +0.9, 0.0], 0.5)
flat = geom.boolean_difference(
geom.boolean_union([rectangle, disk1, disk2]),
geom.boolean_union([disk3, disk4]),
)
geom.extrude(flat, [0, 0, 0.3])
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
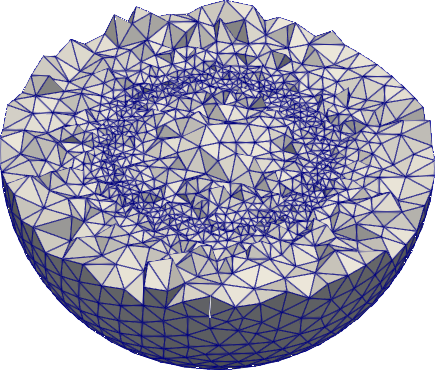
#### Mesh refinement/boundary layers
|  |
|  |
|  |
|
| :---------------------------------------------------------------------: | :------------------------------------------------------------------------------: | :-------------------------------------------------------------------------------: |
| | |
```python
# boundary refinement
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.geo.Geometry() as geom:
poly = geom.add_polygon(
[
[0.0, 0.0],
[2.0, 0.0],
[3.0, 1.0],
[1.0, 2.0],
[0.0, 1.0],
],
mesh_size=0.3,
)
field0 = geom.add_boundary_layer(
edges_list=[poly.curves[0]],
lcmin=0.05,
lcmax=0.2,
distmin=0.0,
distmax=0.2,
)
field1 = geom.add_boundary_layer(
nodes_list=[poly.points[2]],
lcmin=0.05,
lcmax=0.2,
distmin=0.1,
distmax=0.4,
)
geom.set_background_mesh([field0, field1], operator="Min")
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
```python
# mesh refinement with callback
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.geo.Geometry() as geom:
geom.add_polygon(
[
[-1.0, -1.0],
[+1.0, -1.0],
[+1.0, +1.0],
[-1.0, +1.0],
]
)
geom.set_mesh_size_callback(
lambda dim, tag, x, y, z: 6.0e-2 + 2.0e-1 * (x**2 + y**2)
)
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
```python
# ball with mesh refinement
from math import sqrt
import pygmsh
with pygmsh.occ.Geometry() as geom:
geom.add_ball([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], 1.0)
geom.set_mesh_size_callback(
lambda dim, tag, x, y, z: abs(sqrt(x**2 + y**2 + z**2) - 0.5) + 0.1
)
mesh = geom.generate_mesh()
```
#### Optimization
pygmsh can optimize existing meshes, too.
```python
import meshio
mesh = meshio.read("mymesh.vtk")
optimized_mesh = pygmsh.optimize(mesh, method="")
```
You can also use the command-line utility
```
pygmsh-optimize input.vtk output.xdmf
```
where input and output can be any format supported by
[meshio](https://pypi.org/project/meshio/).
### Testing
To run the pygmsh unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
pytest
```
### Building Documentation
Docs are built using [Sphinx](http://www.sphinx-doc.org/en/stable/).
To build, run
```
sphinx-build -b html doc doc/_build
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).