Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/oalee/ai-android-object-detector
A simple android java AI object detector application
https://github.com/oalee/ai-android-object-detector
Last synced: 16 days ago
JSON representation
A simple android java AI object detector application
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/oalee/ai-android-object-detector
- Owner: oalee
- Created: 2023-11-07T15:08:49.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-11-11T12:00:07.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-09T12:59:26.455Z (4 months ago)
- Language: Java
- Size: 5.54 MB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: readme.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Simple Android AI Realtime Object Detection

This Android app leverages the TensorFlow Object Detection API and a pre-trained EfficientDet-Lite2 model for real-time object detection. It's designed for devices running Android 9 and above, providing an intuitive and efficient user experience.
### Demo
https://github.com/oalee/ai-android-object-detector/assets/14542859/6d7a19ec-d81a-4ad8-bb14-5385f1ec179a
### Requirements
- JDK 17
- Android SDK 34
### How to build
1. Clone the repository
2. Run `./gradlew assembleDebug` to build the project
Alternatively, you can import the project into Android Studio and build it from there.
### How to run
1. Connect an Android device to your computer
2. Run `./gradlew installDebug` to install the app on your device
Alternatively, you can run the app from Android Studio.
## Architecture Design
The app adopts the Model-View-ViewModel (MVVM) architecture, enhancing maintainability, scalability, and testability. This design facilitates a clean separation of concerns and promotes a more structured and intuitive development process.
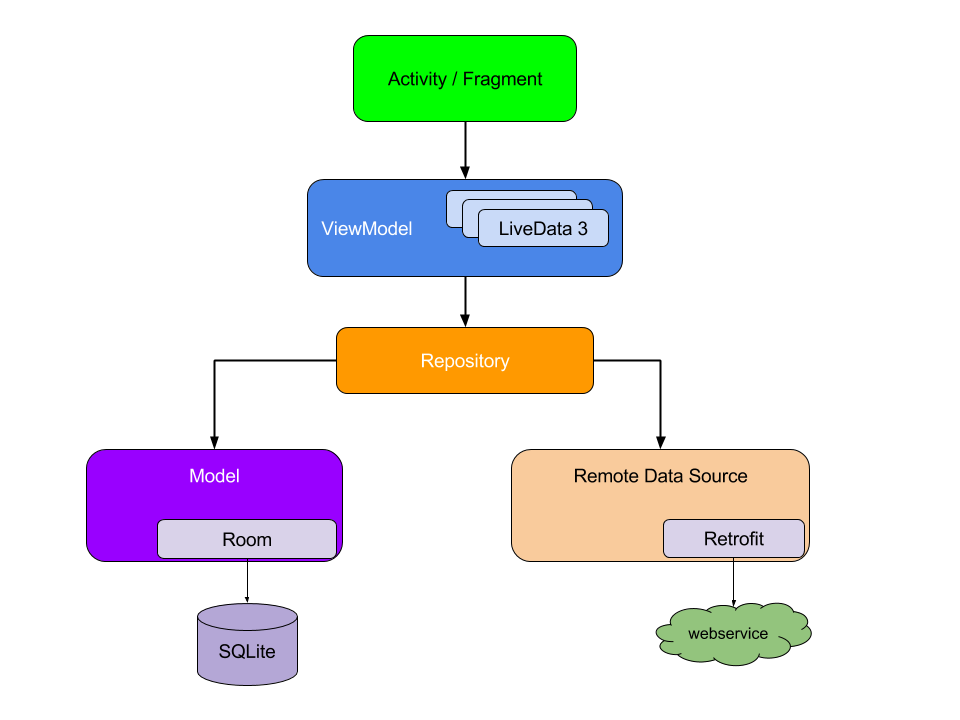
On a high level, the app consists of the following components:
- UI Layer: Responsible for displaying data and managing user interactions.
- ViewModel Layer: Acts as a mediator between the UI and the business logic, managing the app's data flow.
- Business Logic Layer: Handles data operations and communicates with various data sources.
### UX Design
The app was was designed to be simple and intuitive to use. The app consists of three screens:
- Camera screen: Displays the camera feed and detected objects real time, and allows the user to take a picture and go to the gallery screen
- Gallery screen: Displays a list of images taken by the user, and allows the user to navigate to the image details screen
- Image details screen: Displays the image and detected objects
### Built With
Following are the key frameworks and libraries that were used to build the app, and are selected as per best practices and guidelines from Google and the Android community, and to ensure the app's performance, scalability, and maintainability.
- [ModelViewViewModel (MVVM)](https://developer.android.com/jetpack/guide) For data observation, lifecycle management, and UI-data binding.
- [LiveData](https://developer.android.com/topic/libraries/architecture/livedata) To observe changes in the data and update the UI accordingly
- [ViewModel](https://developer.android.com/topic/libraries/architecture/viewmodel) To store and manage UI-related data in a lifecycle conscious way
- [Data Binding](https://developer.android.com/topic/libraries/data-binding) To bind UI components in layouts to data sources
- [TensorFlow Lite](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite)
- [Object Detection API](https://www.tensorflow.org/lite/models/object_detection/overview) To detect objects in real time
- [Hilt Dependency Injection](https://developer.android.com/training/dependency-injection/hilt-android) For managing dependencies, improving testability, and reducing boilerplate code and improve developer experience
- [CameraX](https://developer.android.com/training/camerax) To access the camera and preview the camera feed
- [Navigation Component](https://developer.android.com/guide/navigation) For managing fragment-based navigation.
- [RoomDB Persistence Library](https://developer.android.com/training/data-storage/room) For local data storage and retrieval.
- [Glide Image Loading Library](https://github.com/bumptech/glide) For efficient image loading.
- [ConstraintLayout](https://developer.android.com/training/constraint-layout) For responsive UI design.
### Code Organization
The app's source code is organized into distinct modules, each focusing on a specific aspect of the app's functionality:
- `core`: Contains the core classes and interfaces that are shared across the app
- `di`: Contains the dependency injection classes and interfaces
- `camera`: Contains the classes that are related to the camera
- `data`: Defines the data models and data sources. This package offers a unified AppRepository class that handles data operations, business logic and communicates with various data sources. The data sources are organized into the following sub-packages:
- `source`
- `local`: Contains the classes that are related to the local database
- `remote`: Contains the classes that are related to the remote API (currently not used)
- `model`: Contains the data models
- `ml`: Contains the classes that are related to machine learning
- `utils`: Contains the utility classes (e.g., bitmap, image, etc.)
- `ui`: Contains the UI classes: Generally, each screen has its own package and each package contains a fragment, a view model, and optionally components that are related to the screen (e.g., adapters, etc.)
- `camera`: Contains the classes that are related to the camera screen
- `gallery`: Contains the classes that are related to the gallery screen
- `analysis`: Contains the classes that are related to the image details screen and detected objects analysis
#### Implementation Details
The app follows these high-level design principles:
- ViewModel and LiveData:
- The ViewModel defines LiveData objects that are observed by the UI. This ensures a reactive user interface that updates in response to data changes.
- LiveData objects are generally exposed as immutable data, meaning only the ViewModel can set their values. This maintains data integrity and security.
- The UI layer observes these LiveData objects and updates the interface accordingly.
- User Interaction Handling:
- UI layer observes LiveData objects exposed by the ViewModel and updates the interface accordingly.
- The UI layer notifies the ViewModel of user interactions.
- The ViewModel handles these interactions, processing them according to the app's business logic.
- This design keeps the UI layer simple and focused solely on user interaction and display.
- Business Logic Binding:
- Dependencies such as AppRepository and CameraHelper are injected into the ViewModel using Hilt.
- This setup allows efficient handling and transformation of data between the UI and the data source.
#### Testing
The app was tested on two android devices:
- Pixel 7 Pro (Android 14)
- Nokia X71 (Android 9)