https://github.com/olivier127/rbac-bundle
PhpRBACBundle is symfony 7 bundle with full access control library for PHP. It provides NIST Level 2 Standard Hierarchical Role Based Access Control as an easy to use library to PHP developers. It's a rework of the phprbac.net library made by OWASP for synfony 7
https://github.com/olivier127/rbac-bundle
access-control access-management acl authorization permission permissions php phprbac rbac security symfony-bundle symfony6
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
PhpRBACBundle is symfony 7 bundle with full access control library for PHP. It provides NIST Level 2 Standard Hierarchical Role Based Access Control as an easy to use library to PHP developers. It's a rework of the phprbac.net library made by OWASP for synfony 7
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/olivier127/rbac-bundle
- Owner: Olivier127
- License: mit
- Created: 2022-03-18T08:58:32.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-18T10:47:44.000Z (3 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-31T09:03:42.984Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: access-control, access-management, acl, authorization, permission, permissions, php, phprbac, rbac, security, symfony-bundle, symfony6
- Language: PHP
- Homepage:
- Size: 136 KB
- Stars: 23
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 12
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# PhpRbacBundle
PhpRBACBundle is symfony 7 bundle with full access control library for PHP. It provides NIST Level 2 Standard Hierarchical Role Based Access Control as an easy to use library to PHP developers. It's a rework of the phprbac.net library made by OWASP for symfony 6.
## Table of Content
* [How it works ?](#how-it-works)
* [Installation](#installation)
* [Configuration](#configuration)
* [Prepare Symfony](#prepare-symfony)
* [Add PhpRbac configuration](#add-phprbac-configuration)
* [Roles and permissions creation](#roles-and-permissions-creation)
* [Make the rbac relations](#make-the-rbac-relations)
* [Assign Role to the user and check permission](#assign-role-to-the-user-and-check-permission)
* [RBAC for controller](#rbac-for-controller)
* [Voter based RBAC](#voter-based-rbac)
* [Symfony CLI commands](#symfony-cli-commands)
* [Twig functions](#twig)
## How it works ?
Go to https://phprbac.net/ :) to have the representation of permissions and roles as well as their interactions.
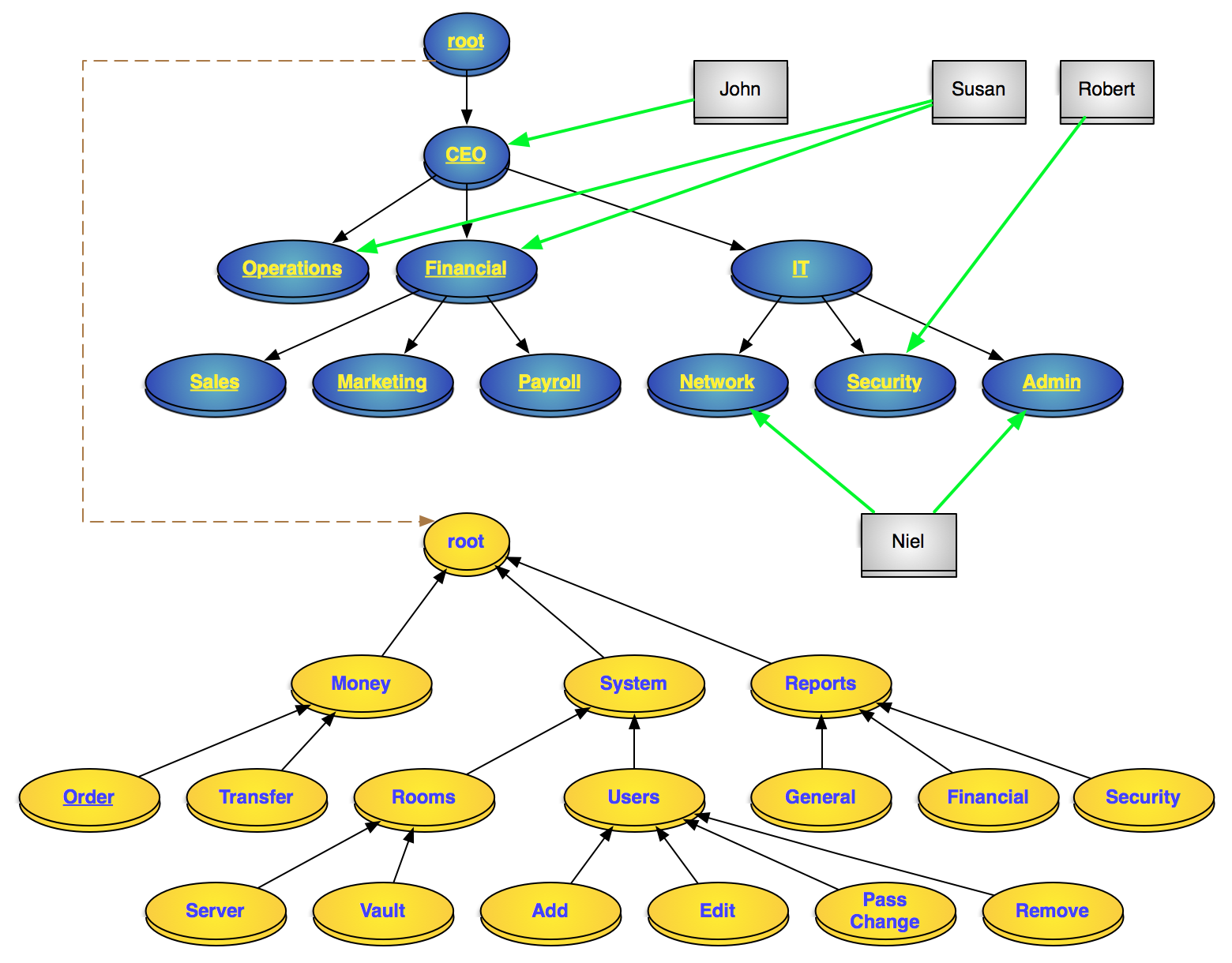
A hierarchical RBAC model of a system Blue: roles, Gray: users, Yellow: permissions
## Installation
just include the package with composer:
composer require olivier127/rbac-bundle
register the bundle inside config/bundles.php
```php
return [
...
PhpRbacBundle\PhpRbacBundle::class => ['all' => true],
];
```
Add the PhpRbacBundle\Entity\UserRoleTrait inside the User entity class to add the rbac role relation.
Update the database schema with doctrine migration or doctrine schema update to create all the tables
## Configuration
### Prepare Symfony
Specify the different sections requiring prior authentication in the firewall security configuration section.
Access control only applies to authenticated sections of the website. Therefore, we will use basic ROLE_USER for all users. ROLE_ADMIN can be used for the main administrator but his rights will only be allocated by being associated with the role '/' of the roles tree.
example :
```yaml
# config/packages/security.yaml
security:
# ...
role_hierarchy:
ROLE_ADMIN: ROLE_USER
access_control:
- { path: ^/backend, roles: ROLE_USER }
- { path: ^/todolist, roles: ROLE_USER }
```
### Add PhpRbac configuration
You must create your own entities for driving permissions and roles.
example :
```php
/* src/Entity/Role.php */
namespace App\Entity;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
use PhpRbacBundle\Entity\Role as EntityRole;
use PhpRbacBundle\Repository\RoleRepository;
#[ORM\Entity(repositoryClass: RoleRepository::class)]
#[ORM\Table('rbac_roles')]
class Role extends EntityRole
{
}
```
```php
/* src/Entity/Permission.php */
namespace App\Entity;
use Doctrine\ORM\Mapping as ORM;
use PhpRbacBundle\Entity\Permission as EntityPermission;
use PhpRbacBundle\Repository\PermissionRepository;
#[ORM\Entity(repositoryClass: PermissionRepository::class)]
#[ORM\Table('rbac_permissions')]
class Permission extends EntityPermission
{
}
```
add php_rbac.yaml to associate theses entities to the rbac core
```yaml
# config/packages/php_rbac.yaml
php_rbac:
no_authentication_section:
default: deny
resolve_target_entities:
user: App\Entity\User
role: App\Entity\Role
permission: App\Entity\Permission
```
### Roles and permissions creation
Add all the roles and the permissions you need with the RoleManager and the PermissionManager
examples :
to add a permission to the root
```php
/** @var PhpRbacBundle\Core\PermissionManager $manager */
$manager = $this->container->get(PermissionManager::class);
$permission = $manager->add("notepad", "Notepad", PermissionManager::ROOT_ID);
```
To add a chain or permission
```php
/** @var PhpRbacBundle\Core\PermissionManager $manager */
$manager = $this->container->get(PermissionManager::class);
$manager->addPath("/notepad/todolist/read", ['notepad' => 'Notepad', 'todolist' => "Todo list", "read" => "Read Access"]);
```
## Make the rbac relations
Adding roles use same methods
for the example, i use the chain role "/editor/reviewer". The reviewer is the subrole of the editor, the editor is the subrole of the root "/".
```php
/** @var PhpRbacBundle\Core\RoleManager $manager */
$manager = $this->container->get(RoleManager::class);
$manager->addPath("/editor/reviewer", ['editor' => 'Editor', 'reviewer' => "Reviewer"]);
```
Assign permissions to roles
```php
/** @var PhpRbacBundle\Core\RoleManager $manager */
$manager = $this->container->get(RoleManager::class);
$editorId = $manager->getPathId("/editor");
$editor = $manager->getNode($editorId);
$reviewerId = $manager->getPathId("/editor/reviewer");
$reviewer = $manager->getNode($reviewerId);
$manager->assignPermission($editor, "/notepad");
$manager->assignPermission($reviewer, "/notepad/todolist/read");
$manager->assignPermission($reviewer, "/notepad/todolist/write");
```
The editor role will have /notepad permission and all sub permissions while the reviewer role will only have `/notepad/todolist/read` and `/notepad/todolist/write` permissions
### Assign Role to the user and check permission
If the `UserRoleTrait` is in the class `User`, you will have `addRbacRole`.
Just add the role in this entity
```php
/** @var PhpRbacBundle\Core\RoleManager $manager */
$manager = $this->container->get(RoleManager::class);
$editorId = $manager->getPathId("/editor");
$editor = $manager->getNode($editorId);
$user = $userRepository->find($userId);
$user->addRbacRole($user);
$userRepository->add($user, true);
```
To test a user's permission or role, use the PhpRbacBundle\Core\Rbac class.
```php
$rbacCtrl = $this->container->get(Rbac::class);
$rbacCtrl->hasPermission('/notepad', $userId);
$rbacCtrl->hasRole('/editor/reviewer', $userId);
```
## RBAC for controller
Just add attribute is granted like this example. The attributes `IsGranted` and `HasRole` check the security with the current user.
```php
namespace App\Controller;
...
use PhpRbacBundle\Attribute\AccessControl as RBAC;
#[Route('/todolist')]
#[RBAC\IsGranted('/notepad/todolist/read')]
class TodolistController extends AbstractController
{
#[RBAC\IsGranted('/notepad/todolist/read')]
#[Route('/', name: 'app_todolist_index', methods: ['GET'])]
public function index(TodolistRepository $todolistRepository): Response
{
...
}
#[RBAC\IsGranted('/notepad/todolist/write')]
#[Route('/new', name: 'app_todolist_new', methods: ['GET', 'POST'])]
public function new(Request $request, TodolistRepository $todolistRepository): Response
{
...
}
#[RBAC\IsGranted('/notepad/todolist/read')]
#[Route('/{id}', name: 'app_todolist_show', methods: ['GET'])]
public function show(Todolist $todolist): Response
{
...
}
#[RBAC\IsGranted('/notepad/todolist/write')]
#[Route('/{id}/edit', name: 'app_todolist_edit', methods: ['GET', 'POST'])]
public function edit(Request $request, Todolist $todolist, TodolistRepository $todolistRepository): Response
{
...
}
#[RBAC\IsGranted('/notepad/todolist')]
#[Route('/{id}', name: 'app_todolist_delete', methods: ['POST'])]
public function delete(Request $request, Todolist $todolist, TodolistRepository $todolistRepository): Response
{
...
}
}
```
the first RBAC\IsGranted on the class check the lowest permission to access to the controller with the current user.
The `RBAC\IsGranted` on each action check the minimum permission to make action work.
In the example :
- The permission `/notepad/todolist/read` gives the access to the all controller and so index and show action.
- The permission `/notepad/todolist/write` gives the access to edit the todolist
- The permission `/notepad/todolist` parent to the read and write permission gives the access to delete
The permission `/notepad/todolist` has also the read and write permission.
## Voter based Rbac
With RbacVoter, you can use symfony security to check the user rbac permissions (not the roles).
example:
```php
#[IsGranted('/todolist/index', statusCode: 403, message: 'Access denied for user')]
#[Route('/', name: 'app_todo_list_index', methods: ['GET'])]
public function index(TodoListRepository $todoListRepository): Response
```
You need to set the security access control to be unanimous (all the voter must be ok)
add this lines to `config/packages/security.yaml`
```yaml
security:
...
access_decision_manager:
strategy: unanimous
allow_if_all_abstain: false
```
## Symfony CLI commands
The install command sets the root node role and permission and associates them.
```shell
security:rbac:install
```
Add permission into the rbac permissions tree
```shell
security:rbac:permission:add
```
Add permission into the rbac roles tree
```shell
security:rbac:role:add
```
Assign a permission to a role
```shell
security:rbac:role:assign-permission
```
Assign a role to a user
```shell
security:rbac:user:assign-role
```
Theses commandes are interactives.
## Twig
test if user has a role
```twig
{% if hasRole('/the/role') %}
...
{% endif %}
```
test if user has a permission
```twig
{% if hasPermission('/the/permission') %}
...
{% endif %}
```