https://github.com/orangex4/typst-sympy-calculator
Parse typst math expressions into sympy form for calc and define your custom functions in typst files.
https://github.com/orangex4/typst-sympy-calculator
calculator python sympy typst
Last synced: 10 days ago
JSON representation
Parse typst math expressions into sympy form for calc and define your custom functions in typst files.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/orangex4/typst-sympy-calculator
- Owner: OrangeX4
- License: mit
- Created: 2023-05-30T10:53:53.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-01-28T08:23:13.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-30T21:02:46.463Z (7 months ago)
- Topics: calculator, python, sympy, typst
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.96 MB
- Stars: 38
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 4
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.txt
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# [Typst Sympy Calculator](https://github.com/OrangeX4/typst-sympy-calculator)
## About
`Typst Sympy Calculator` parses **Typst Math Expressions** and converts it into the equivalent **SymPy form**. Then, **calculate it** and convert to typst math text.
It is designed for providing **people writing in typst** a ability to calculate something when writing math expression. It is based on `Sympy` module in `Python`.
The `typst-sympy-calculator` python package is a backend for a VS Code extension [`Typst Sympy Calculator`](https://github.com/OrangeX4/vscode-typst-sympy-calculator), and you also can use it just for parse typst math expression to sympy form in order to do things for yourself.
## Features
- **Default Math:**
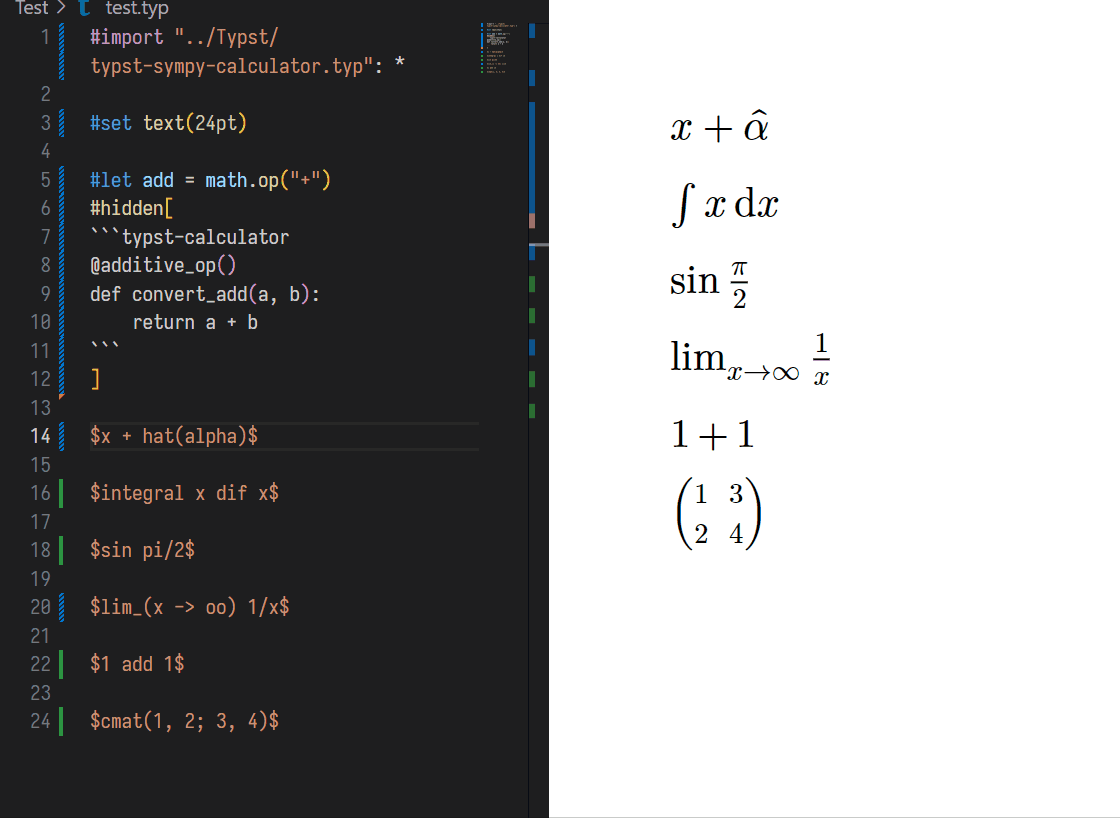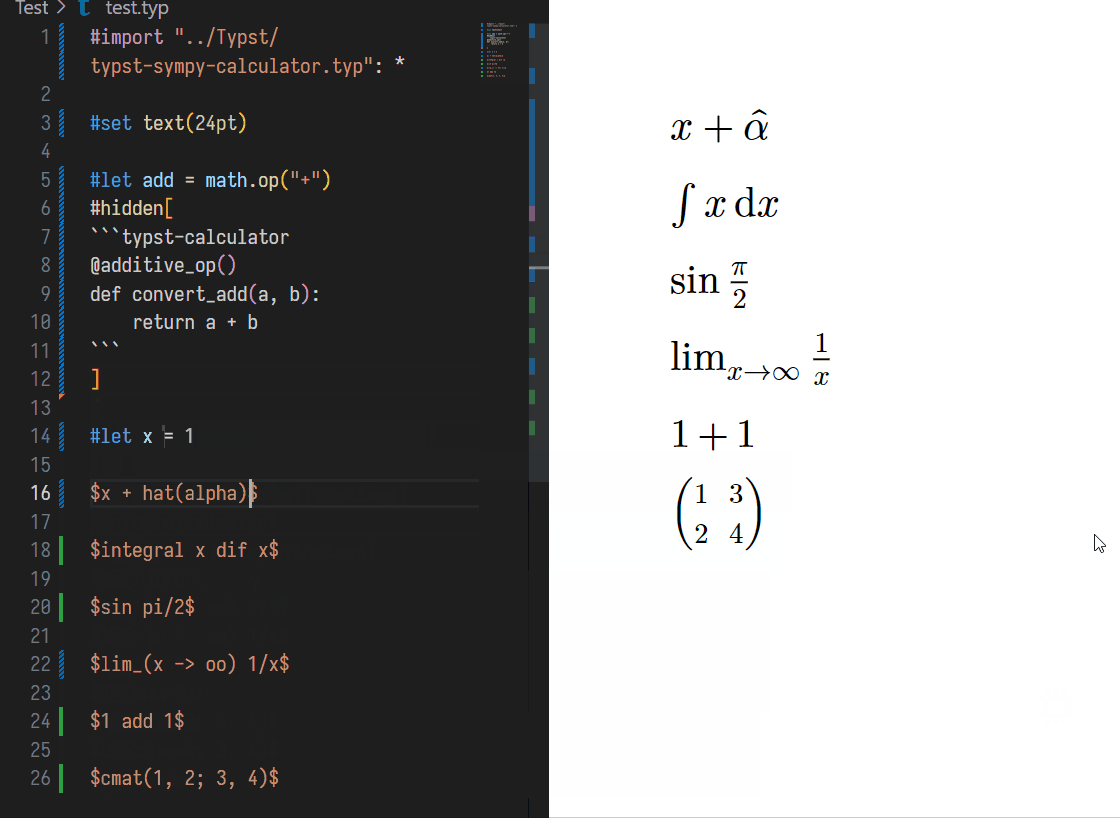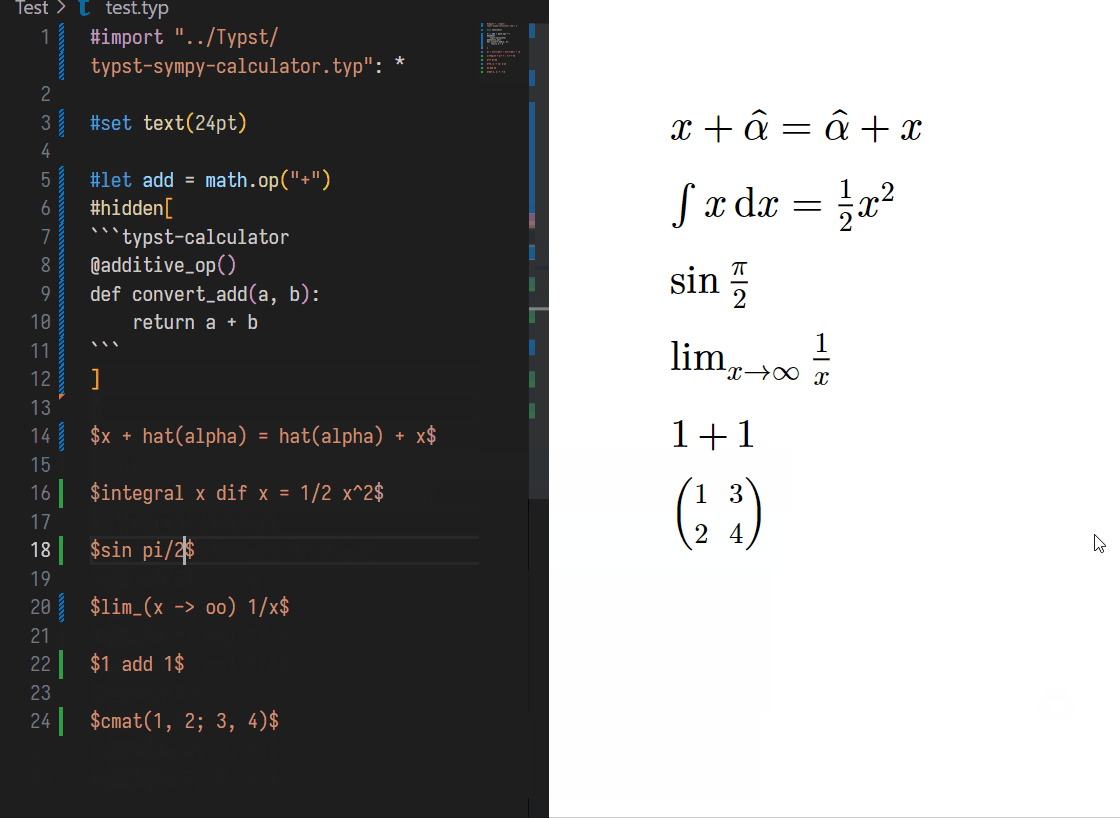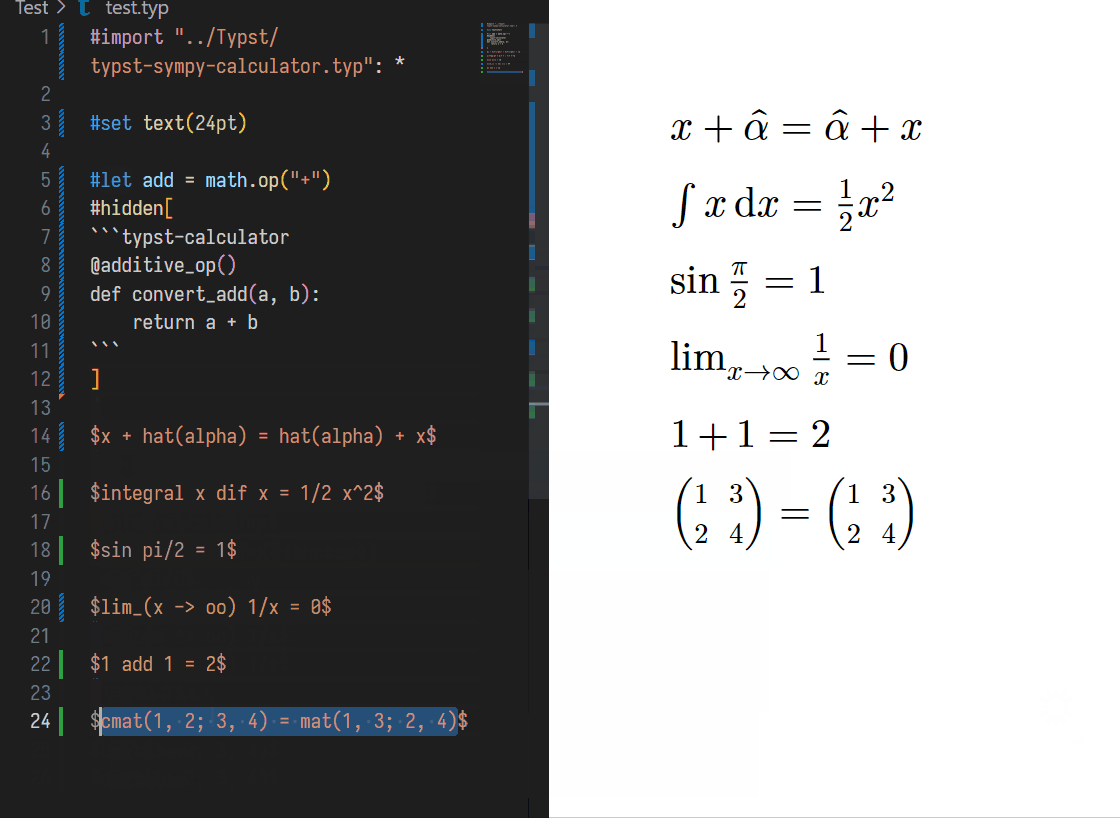
- [x] **Arithmetic:** Add (`+`), Sub (`-`), Dot Mul (`dot`), Cross Mul (`times`), Frac (`/`), Power (`^`), Abs (`|x|`), Sqrt (`sqrt`), etc...
- [x] **Alphabet:** `a - z`, `A - Z`, `alpha - omega`, Subscript (`x_1`), Accent Bar(`hat(x)`), etc...
- [x] **Common Functions:** `gcd`, `lcm`, `floor`, `ceil`, `max`, `min`, `log`, `ln`, `exp`, `sin`, `cos`, `tan`, `csc`, `sec`, `cot`, `arcsin`, `sinh`, `arsinh`, etc...
- [x] **Funcion Symbol:** `f(x)`, `f(x-1,)`, `g(x,y)`, etc...
- [x] **Calculous:** Limit `lim_(x -> oo) 1/x`, Integration `integral_1^2 x dif x`, etc...
- [x] **Calculous:** Derivation (`dif/(dif x) (x^2 + 1)` is not supported, but you can use `derivative(expr, var)` instead), etc...
- [x] **Reduce:** Sum `sum_(k=1)^oo (1/2)^k`, Product `product_(k=1)^oo (1/2)^k`, etc...
- [x] **Eval At:** Evalat `x^2 bar_(x = 2)`, `x^2 "|"_(x = 2)`, etc...
- [x] **Linear Algebra:** Matrix to raw echelon form `rref`, Determinant `det`, Transpose `^T`, Inverse `^(-1)`, etc...
- [x] **Relations:** `==`, `>`, `>=`, `<`, `<=`, etc...
- [x] **Solve Equation:** Single Equation `x + 1 = 2`, Multiple Equations `cases(x + y = 1, x - y = 2)`, etc...
- [ ] **Logical:** `and`, `or`, `not`, etc...
- [ ] **Set Theory:** `in`, `sect`, `union`, `subset`, etc...
- [x] **Other:** Binomial `binom(n, k)` ...
- **Custom Math (in typst file):**
- [x] **Define Accents:** `#let acc(x) = math.accent(x, math.grave)`
- [x] **Define Operators:** `#let add = math.op("add")`
- [x] **Define Symbols:** `#let xy = math.italic("xy")` or `#let mail = symbol("🖂", ("stamped", "🖃"),)`
- [x] **Define Functions:**
```py
# typst-calculator
@func()
def convert_add(a, b):
return a + b
```
- **Typst Math Printer:**
- [x] Complete `TypstMathPrinter` in `TypstConverter.py`
- [ ] Custom Printer for `TypstCalculator.py` and `TypstCalculatorServer.py`
- **VS Code Extension:**
- [x] Develop a VS Code Extension for `Typst Calculator`
## Install
```bash
pip install typst-sympy-calculator
```
## Usage
### Difference Between `parse`, `converter`, `calculator`, `server`
- `TypstParser.py`: parse typst math expression to ANTLR abstract syntax tree with `TypstGrammar.g4`;
- `TypstConverter.py`:
- convert typst math expression to sympy expression via `TypstMathConverter`;
- convert sympy expression to typst math expression via `TypstMathPrinter`;
- has `decorators` for defining custom functions, operators;
- has `define_accent`, `define_symbol_base` and `define_function` for defining custom accents, symbols and functions;
- `TypstCalculator.py`:
- calculate sympy expression and convert to typst math expression;
- has `subs`, `simplify`, `evalf` methods;
- has `set_variance` and `unset_variance` for calculating with variance;
- `DefaultTypstCalculator`: define many useful functions, operators, accents, symbols;
- Accents, Alphabet, Greeks, Arithmetic, Common Functions, Calculous, Linear Algebra, etc...
- `TypstCalculatorServer`:
- has `init` method for initializing `TypstCalculator` with a typst file;
- **can define your custom functions on your typst file**;
- has `simplify`, `subs`, `evalf` methods for calculating with typst file;
It is a top-down design, so you can use `TypstCalculatorServer` directly, or use `TypstCalculator` with `TypstConverter`.
**RECOMMEND: see the usage of decorators like `@func()` in [DefaultTypstCalculator.py](https://github.com/OrangeX4/typst-sympy-calculator/blob/main/DefaultTypstCalculator.py).**
For the usage, you can see the unit test part `if __name__ == '__main__':` in each files.
### Sympy Expressions and Typst Math Text
```python
from TypstCalculatorServer import TypstCalculatorServer
server = TypstCalculatorServer()
typst_math = r'1 + 1'
expr = server.sympy(typst_math)
print(server.typst(expr))
```
```python
from TypstCalculator import TypstCalculator
calculator = TypstCalculator()
typst_math = r'1 + 1'
expr = calculator.sympy(typst_math)
print(calculator.typst(expr))
```
```python
from TypstConverter import TypstMathConverter
converter = TypstMathConverter()
typst_math = r'1 + 1'
expr = converter.sympy(typst_math)
print(converter.typst(expr))
```
### Typst Calculator Server
The simplest way to use it is just like `TypstCalculatorServer.py`:
```python
from TypstCalculatorServer import TypstCalculatorServer
server = TypstCalculatorServer()
typst_file = os.path.abspath(r'./tests/test.typ')
server.init(typst_file)
server.return_text = True # otherwise just return sympy form
expr = server.simplify('1 + 1', typst_file)
print(expr) # 2
server.enable_subs = False
expr = server.simplify('a + 1', typst_file)
print(expr) # a + 1
server.enable_subs = True
expr = server.simplify('a + 1', typst_file)
print(expr) # 2
expr = server.simplify('b + 1', typst_file)
print(expr) # a + 2
expr = server.simplify('cmat(1, 2)', typst_file)
print(expr) # mat(1; 2)
expr = server.simplify('f(1) + f(1)', typst_file)
print(expr) # 2 f(1)
expr = server.simplify('xy + mail + mail.stamped', typst_file)
print(expr) # mail + mail.stamped + xy
expr = server.solve('x + y + z = 1')
print(expr) # y = -x - z + 1, z = -x - y + 1, x = -y - z + 1
expr = server.solve('cases(x + y + z = 1, x = 2)')
print(expr) # cases(x = 2, z = -y - 1), cases(y = -z - 1, x = 2), y = -x - z + 1, z = -x - y + 1
expr = server.solve('cases(x^2 + y = 4, y = 2)')
print(expr) # x = sqrt(4 - y), cases(y = 2, x = sqrt(2)), cases(y = 2, x = -sqrt(2)), x = -sqrt(4 - y)
expr = server.solve('cases(x < 2, x > 1)')
print(expr) # 1 < x and x < 2
```
and the typst files `tests/test.typ`
```typst
#import "cal.typ": *
// set variances
#let a = 1
#let b = $a + 1$
```
and `tests/cal.typ` just like:
```typst
// define accents
#let acc(x) = math.accent(x, math.grave)
// define operators
#let add = math.op("add")
#let f = math.op("f")
// define symbols
#let xy = math.italic("xy")
#let mail = symbol("🖂", ("stamped", "🖃"),)
```
### Default Typst Calculator
If you have not a typst file, you can use `DefaultTypstCalculator.py`, it define many useful functions and symbols just like:
```python
# Symbols
abc = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
for c in abc:
calculator.define_symbol_base(c)
calculator.define_symbol_base(c.upper())
# Functions
@func()
def convert_sin(expr):
return sympy.sin(expr)
```
So you can use it by:
```python
from DefaultTypstCalculator import get_default_calculator
calculator = get_default_calculator(complex_number=True)
calculator.return_text = True
operator, relation_op, additive_op, mp_op, postfix_op, \
reduce_op, func, func_mat, constant = calculator.get_decorators()
expr = calculator.simplify('1 + 1')
assert expr == '2'
expr = calculator.evalf('1/2', n=3)
assert expr == '0.500'
calculator.set_variance('a', '1/2')
expr = calculator.simplify('a + 1')
assert expr == '3/2'
calculator.unset_variance('a')
expr = calculator.simplify('a + 1')
assert expr == 'a + 1' or expr == '1 + a'
expr = calculator.evalf('pi', n=3)
assert expr == '3.14'
expr = calculator.simplify('max(1, 2)')
assert expr == '2'
calculator.define_function('f')
expr = calculator.simplify('f(1) + f(1) - f(1)')
assert expr == 'f(1)'
expr = calculator.simplify('lim_(x -> oo) 1/x')
assert expr == '0'
```
### Variances
You can **ASSIGN** variance a value using same assignment form in typst:
```typst
#let x = 1
// Before
$ x $
// Shift + Ctrl + E
// After
$ x = 1 $
```
PS: You can use grammar like `y == x + 1` to describe the relation of equality.
If you want to see the bonding of variances, you can press `Shift + Ctrl + P`, and input `typst-sympy-calculator: Show Current variances`, then you will get data like:
```typst
y = x + 1
z = 2 x
```
### Functions
You can **DEFINE** a function using same form in typst:
```typst
#let f = math.op("f")
// Before
$ f(1) + f(1) $
// Shift + Ctrl + E
// After
$ f(1) + f(1) = 2 f(1) $
```
### Symbols
You can **DEFINE** a symbol using same form in typst:
```typst
#let xy = math.italic("xy")
#let email = symbol("🖂", ("stamped", "🖃"),)
$ xy + email + email.stamped $
```
### Accents
You can **DEFINE** a accent using same form in typst:
```typst
#let acc(x) = math.accent(x, math.grave)
$ acc(x) $
```
### Decorators for Operators
You can **DEFINE** a operator using same form in typst:
```typst
#let add = math.op("+")
'''typst-calculator
@additive_op()
def convert_add(a, b):
return a + b
'''
// Before
$ 1 add 1 $
// Shift + Ctrl + E
// After
$ 1 add 1 = 2 $
```
Or just use `'''typst-sympy-calculator` or `'''python \n # typst-calculator` to define a operator.
there are some decorators you can use:
- `@operator(type='ADDITIVE_OP', convert_ast=convert_ast, name=name, ast=False)`: Define a common operator;
- `@func()`: Define a function, receive args list;
- `@func_mat()`: Define a matrix function, receive single arg `matrix`;
- `@constant()`: Define a constant, receive no args but only return a constant value;
- `@relation_op()`: Define a relation operator, receive args `a` and `b`;
- `@additive_op()`: Define a additive operator, receive args `a` and `b`;
- `@mp_op()`: Define a multiplicative operator, receive args `a` and `b`;
- `@postfix_op()`: Define a postfix operator, receive args `a`;
- `@reduce_op()`: Define a reduce operator, receive args `expr` and `args = (symbol, sub, sup)`;
It is important that the function name MUST be `def convert_{operator_name}`, or you can use decorator arg `@func(name='operator_name')`, and the substring `_dot_` will be replaced by `.`.
There are some examples (from [DefaultTypstCalculator.py](https://github.com/OrangeX4/typst-sympy-calculator/blob/main/DefaultTypstCalculator.py)):
```python
# Functions
@func()
def convert_binom(n, k):
return sympy.binomial(n, k)
# Matrix
@func_mat()
def convert_mat(mat):
return sympy.Matrix(mat)
# Constants
@constant()
def convert_oo():
return sympy.oo
# Relation Operators
@relation_op()
def convert_eq(a, b):
return sympy.Eq(a, b)
# Additive Operators
@additive_op()
def convert_plus(a, b):
return a + b
# Mp Operators
@mp_op()
def convert_times(a, b):
return a * b
# Postfix Operators
@postfix_op()
def convert_degree(expr):
return expr / 180 * sympy.pi
# Reduces
@reduce_op()
def convert_sum(expr, args):
# symbol, sub, sup = args
return sympy.Sum(expr, args)
```
## Contributing
1. Clone it by `git clone https://github.com/OrangeX4/typst-calculator.git`
2. Install dependencies by `pip install -r requirements.txt`
3. Compile ANTLR grammar by `python ./scripts/compile.py`
4. Debug or add your code with `TypstCalculatorServer.py` or `TypstCalculator.py`, etc...
It is welcome to create an issue or pull request.
## Thanks
- [augustt198 / latex2sympy](https://github.com/augustt198/latex2sympy)
- [purdue-tlt / latex2sympy](https://github.com/purdue-tlt/latex2sympy)
- [ANTLR](https://www.antlr.org/)
- [Sympy](https://www.sympy.org/en/index.html)
## License
This project is licensed under the MIT License.