Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/oscarotero/folk
Universal CMS to use with any web
https://github.com/oscarotero/folk
agnostic-to-frameworks cms content-management
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Universal CMS to use with any web
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/oscarotero/folk
- Owner: oscarotero
- Created: 2016-01-02T10:55:46.000Z (about 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-12-16T18:01:53.000Z (about 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-10-12T00:44:50.729Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: agnostic-to-frameworks, cms, content-management
- Language: PHP
- Homepage:
- Size: 8.91 MB
- Stars: 10
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 3
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# FOLK
The universal CMS
[](https://scrutinizer-ci.com/g/oscarotero/folk/?branch=master)
This is a framework-agnostic CMS that you can use to edit the content of your site. It works with any kind of websites, no matter if the content is stored in a database, yml files, json, etc.
Demo: https://oscarotero.com/folk/demo/
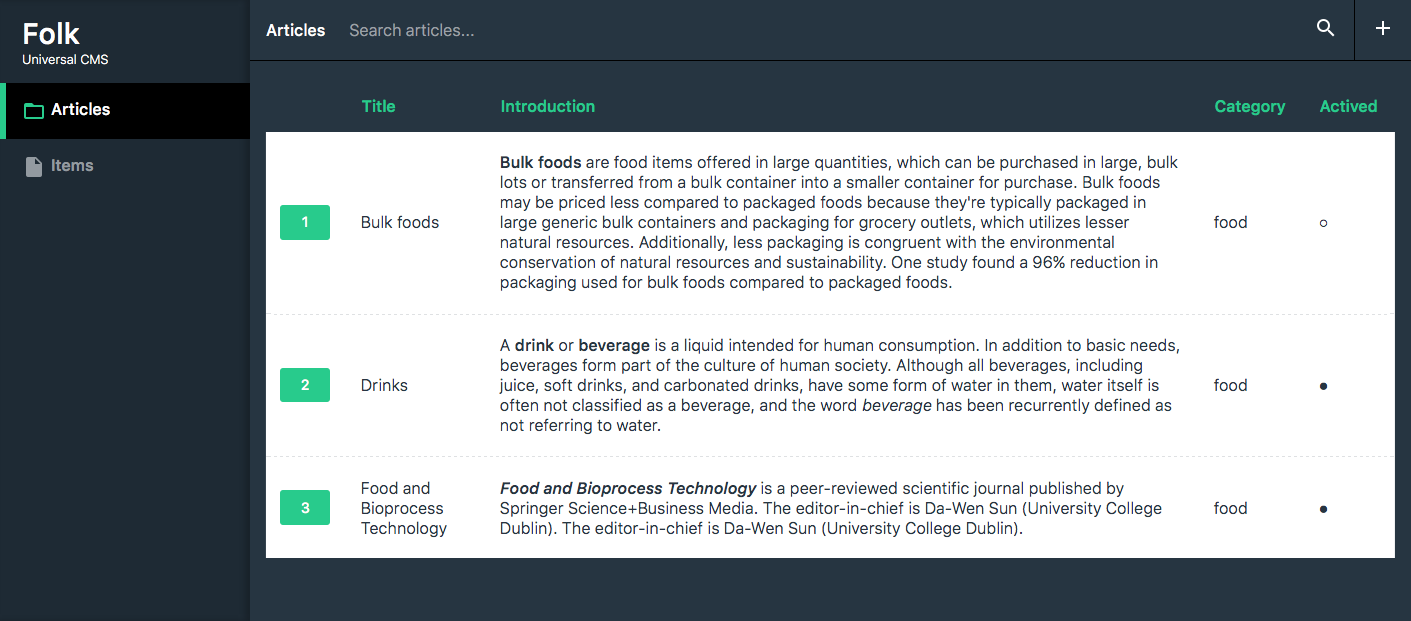
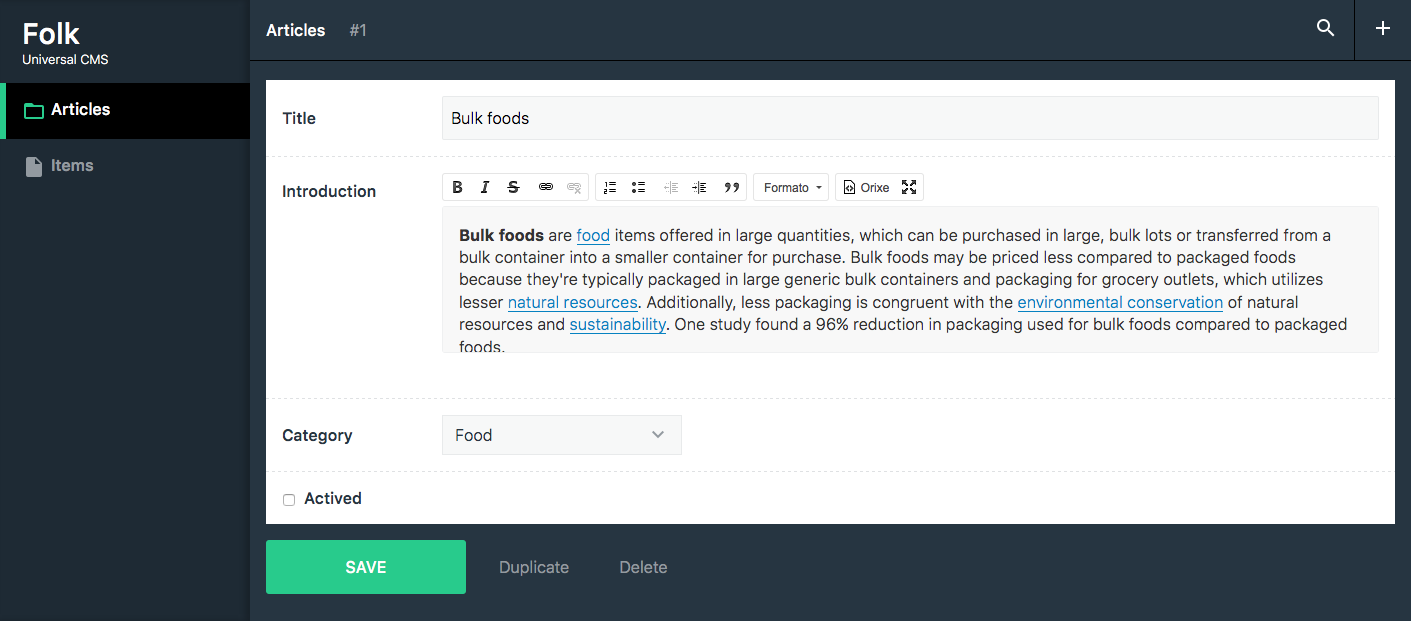
## Requirements
* PHP >= 7
* Composer
## Installation
This package is installable and autoloadable via Composer as [oscarotero/folk](https://packagist.org/packages/oscarotero/folk).
```
composer require oscarotero/folk
```
## Entities
The entities are classes to manage "things". It can be a database table, a file, a directory with files, etc. They must implement `Folk\Entities\EntityInterface` (or extend `Folk\Entities\AbstractEntity`). Let's see an example of an entity using a database table.
```php
namespace MyEntities;
use Folk\SearchQuery;
use Folk\Formats\FormatFactory;
use Folk\Formats\Group;
use Folk\Entities\AbstractEntity;
/**
* Entity to manage the posts
*/
class Posts extends AbstractEntity
{
public $title = 'Posts';
public $description = 'These are the posts of the blog';
/**
* List the posts
*
* @return array [id => data, ...]
*/
public function search(SearchQuery $search): array
{
$query = 'SELECT * FROM posts';
if ($search->getPage() !== null) {
$limit = $search->getLimit();
$offset = ($search->getPage() * $limit) - $limit;
$query .= " LIMIT {$offset}, {$limit}";
}
$pdo = $this->admin->get('pdo');
$result = $pdo->query($query);
$data = [];
while ($row = $result->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC)) {
$data[$row['id']] = $row;
}
return $data;
}
/**
* Create a new post
*
* @return mixed The post id
*/
public function create(array $data)
{
$pdo = $this->admin->get('pdo');
$statement = $pdo->prepare('INSERT INTO posts (title, text) VALUES (:title, :text)');
$statement->execute([
':title' => $data['title'],
':text' => $data['text'],
]);
return $pdo->lastInsertId();
}
/**
* Read a post
*
* @return array
*/
public function read($id): array
{
$pdo = $this->admin->get('pdo');
$statement = $pdo->prepare('SELECT * FROM posts WHERE id = ? LIMIT 1');
$statement->execute([$id]);
return $statement->fetch(PDO::FETCH_ASSOC);
}
/**
* Update a post
*/
public function update($id, array $data)
{
$pdo = $this->admin->get('pdo');
$statement = $pdo->prepare('UPDATE posts SET title = :title, text = :text WHERE id = :id LIMIT 1');
$statement->execute([
':title' => $data['title'],
':text' => $data['text'],
':id' => $data['id'],
]);
}
/**
* Delete a post
*/
public function delete($id)
{
$pdo = $this->admin->get('pdo');
$statement = $pdo->prepare('DELETE FROM posts WHERE id = ? LIMIT 1');
$statement->execute([$id]);
}
/**
* Returns the data scheme used by the posts.
*/
public function getScheme(FormatFactory $factory): Group
{
return $factory->group([
'title' => $factory->text()
->maxlength(200)
->label('The post title'),
'text' => $factory->html()
->label('The body'),
]);
}
/**
* Returns the label of a row.
* (used in autocomplete searches, select, etc)
*/
public function getLabel($id, array $data): string
{
return sprintf('%s (%d)', $data['title'], $id);
}
}
```
## Getting started
There's some predefined entities that you can extend and configure, for example to use with [simplecrud](https://github.com/oscarotero/simple-crud), or to save the content in yaml or json files, etc.
Once your entities are created, let's make them to run:
```php
use Folk\Admin;
use Entities\Posts;
//Create a Admin instance passing the root path and the http uri:
$uri = new Zend\Diactoros\Uri('http://my-site.com/admin');
$admin = new Admin(__DIR__, $uri);
//Set the pdo instance:
$admin['pdo'] = new PDO('mysql:dbname=database;charset=UTF8');
//Add set your entities classes
$admin->setEntities([
Posts::class
]);
//Run the web (using PSR-7 request/responses)
$request = Zend\Diactoros\ServerRequestFactory::fromGlobals();
$emitter = new Zend\Diactoros\Response\SapiEmitter();
$response = $admin($request);
$emitter->emit($response);
```
As you can see, this is a simple example with a simple mysql table. But the interface is flexible enought to work with any kind of data.
To know how to work with the scheme, visit [form-manager](https://github.com/oscarotero/form-manager/) project.