https://github.com/ovinc/weatho
Python package to download, manage and plot weather data from Darksky / OpenWeatherMap APIs
https://github.com/ovinc/weatho
darksky darksky-api download openweathermap openweathermap-api plot python python-3 python3 weather weather-api
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
Python package to download, manage and plot weather data from Darksky / OpenWeatherMap APIs
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ovinc/weatho
- Owner: ovinc
- License: bsd-3-clause
- Created: 2021-01-17T17:28:56.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-01-25T15:27:43.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-17T15:17:23.521Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: darksky, darksky-api, download, openweathermap, openweathermap-api, plot, python, python-3, python3, weather, weather-api
- Language: Jupyter Notebook
- Homepage:
- Size: 550 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# About
Access, download and plot weather data from the following APIs:
- Darksky (https://darksky.net/dev)
- OpenWeatherMap (https://openweathermap.org/api)
Both sources require an API key to get access to the data. However, when dealing with data already downloaded as files and stored locally, the API key is not necessary.
# Install
```bash
pip install weatho
```
# Quick Start
```python
from weatho import Weather, plot
# source can be 'owm' or 'darksky'
w = Weather(location=(45.77, 4.84), source='owm', api_key='xyz')
# Get raw data from the API (source-dependent)
# --------------------------------------------
w.url() # get URL at which to downlowd data
w.fetch() # get data as a dictionary
# By default, current data; get historical data by passing a datetime.datetime:
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from pytz import timezone
tz = timezone('Europe/Paris')
date = tz.localize(datetime(2021, 1, 15, 12)) # 15 Jan. 2021 at Noon in Paris timezone
w.url(date)
w.fetch(date)
# Get and plot formatted, source-independent data
# -----------------------------------------------
w.current() # current weather conditions
w.hourly() # hourly data for present day, including forecast
# It is also possible to access historical data:
w.current(date)
w.hourly(date, until=date + timedelta(days=3))
# Plot hourly data:
plot(w.hourly())
```
There are also options to download the data directly as .json files in a folder and work from this data (see below).
For detailed examples, see the *Examples.ipynb* notebook (https://github.com/ovinc/weatho/blob/master/Examples.ipynb).
# Contents
## Weather class
The following methods are available from a `Weather` object:
- For raw, source-dependent data:
- `url()` and copy-paste the link into a browser (returns url link)
- `fetch()` to get the raw data from the internet (returns dict of data)
- `save()` to save the raw data into a .json file
- `load()` to get the raw data from a .json file (returns dict of data)
- For formatted, source-independent data for analysis and plotting:
- `current()`: returns a dict of values (data at specific time)
- `hourly()`: returns a dict of lists of values (hourly data), can be used in `plot()` directly.
- To download data from the API into local files, possibly in batch:
- `download()`: saves API data in .json format in a folder (threaded for multiple requests at the same time).
- `missing_days()`: checks if there are any missing files of data between specified dates in a folder.
- `download_missing_days()`: same as above, but also downloads the missing data in the folder.
*Note:* To access data from downloaded files, use `load()` to get raw data, and `hourly(path=...)` to get formatted data.
## Plotting weather data
- `plot()`: takes formatted hourly data from `hourly()` (either using the API or downloaded files) as input.
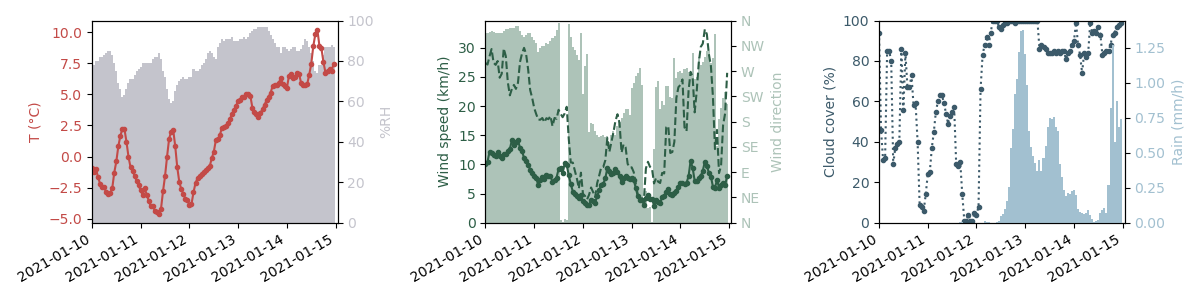
# Notes
## Date/time and timezone information
- It is preferable to use timezone-aware datetimes when specifying dates to the `Weather` methods.
- In particular, when calling `download()` or `hourly()`, care must be taken because *DarkSky* and *OpenWeatherMap* do not manage hourly data the same way:
- *DarkSky* generates hourly data from 00:00 to 23:59 in **local time** (of the requested location)
- *OpenWeatherMap* uses 00:00 to 23:59 in **UTC time**
This means that with *OpenWeatherMap*, calling `hourly()` with a `datetime(2021, 1, 15)` localized in Central European Time will return data from 14/01/2021, 1:00 to 15/01/2021 00:00 (included) in local time, while doing the same thing with *DarkSky* will return data from 15/01/2021, 0:00 to 15/01/2021 23:00 (included) in local time.
Data stored in *.json* files using download() follows this pattern. For example:
- *OWM_45.77,4.84,2021-01-15.json*: data from 00:00 to 23:00 (included) on 15 Jan. 2021, **UTC Time**
- *DarkSky_45.77,4.84,2021-01-15.json*: data from 00:00 to 23:00 (included) on 15 Jan. 2021, **local Time** (of the requested location)
In conclusion, to avoid problems with hourly data (`hourly()`, `download()`, etc.):
- with *DarkSky*, localize all datetimes to the **local timezone** of the place you're requesting weather for,
- with *OpenWeatherMap*, work with **UTC timezone**.
- for other calls (e.g. `fetch()`, `current()` etc.), localize to whatever timezone is more convenient to work with (if using naïve, local time of the computer will be used).
## Misc.
- If one gets the error `KeyError: 'hourly'`, it's likely that the data is not
downloaded correctly or inexistent. Check that the API key is correct and/or
test the download URL generated by `url()` in a browser.
- More data might be available compared to the ones in formatted data, see e.g. the raw dictionary returned by functions like `fetch()` or `load()`.
- For tests, the module `weatho.locations` stores coordinates of some cities/locations as a `coordinates` dictionary.
# Other information
## Python requirements
- Python >= 3.6
## Package requirements
(installed automatically by pip if necessary)
- requests
- matplotlib
- pytz
- importlib_metadata
## Author
Olivier Vincent
## License
BSD 3-Clause (see *LICENSE* file)