https://github.com/paololeonardi/WaterfallGrid
A waterfall grid layout view for SwiftUI.
https://github.com/paololeonardi/WaterfallGrid
ios macos swift swift-package-manager swiftui swiftui-grid tvos visionos watchos waterfall-layout
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
A waterfall grid layout view for SwiftUI.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/paololeonardi/WaterfallGrid
- Owner: paololeonardi
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-10-27T21:28:16.000Z (about 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-07-26T00:09:26.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-20T06:08:57.575Z (9 months ago)
- Topics: ios, macos, swift, swift-package-manager, swiftui, swiftui-grid, tvos, visionos, watchos, waterfall-layout
- Language: Swift
- Homepage:
- Size: 3.42 MB
- Stars: 2,499
- Watchers: 20
- Forks: 126
- Open Issues: 12
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-swiftui-libraries - WaterfallGrid - A waterfall grid layout view for SwiftUI. (Grid / Content)
- fucking-about-SwiftUI - WaterfallGrid
- awesome-starts - paololeonardi/WaterfallGrid - A waterfall grid layout view for SwiftUI. (Swift)
- awesome-swiftui - WaterfallGrid - A waterfall grid layout view for SwiftUI (UI / Grid)
- awesome-swiftui - WaterfallGrid - 核心优势:SwiftUI原生不支持瀑布流,这个库可快速实现“小红书式”不等高网格布局。 (四、开源库精选(解决80%开发场景,附核心优势) / 5. 布局增强)
README
# WaterfallGrid
A waterfall grid layout view for SwiftUI.
[](https://swiftpackageindex.com/paololeonardi/WaterfallGrid)
[](https://swiftpackageindex.com/paololeonardi/WaterfallGrid)
## Features
- [x] Irregular grid of content.
- [x] Columns number different per device orientation.
- [x] Spacing and grid padding customizable.
- [x] Horizontal or vertical scroll direction.
- [x] Items update can be animated.
## Usage
### Initialization
You can create a grid that displays the elements of collection by passing your collection of data and a closure that provides a view for each element in the collection. The grid transforms each element in the collection into a child view by using the supplied closure.
WaterfallGrid works with identifiable data (like SwiftUI.List). You can make your data identifiable in one of two ways: by passing along with your data a key path to a property that uniquely identifies each element, or by making your data type conform to the Identifiable protocol.
**Example 1**
A grid of views of type `Image` from a collection of data identified by a key path.
```swift
WaterfallGrid((0..<10), id: \.self) { index in
Image("image\(index)")
.resizable()
.aspectRatio(contentMode: .fit)
}
```
**Example 2**
A grid of views of type `RectangleView` from a collection of `Identifiable` data.
```swift
WaterfallGrid(rectangles) { rectangle in
RectangleView(rectangle: rectangle)
}
```
or, for simple cases like this, just:
```swift
WaterfallGrid(rectangles, content: RectangleView.init)
```
### Grid Style
To customise the appearance of the grid call the `gridStyle` function and pass the parameters you want to customise.
**Columns**
```swift
WaterfallGrid(cards) { card in
CardView(card: card)
}
.gridStyle(columns: 2)
```
```swift
WaterfallGrid(cards, content: CardView.init)
.gridStyle(
columnsInPortrait: 2,
columnsInLandscape: 3
)
```
**Spacing and Padding**
```swift
WaterfallGrid(rectangles, content: RectangleView.init)
.gridStyle(spacing: 8)
.padding(EdgeInsets(top: 16, leading: 8, bottom: 16, trailing: 8))
```
**Animation**
```swift
WaterfallGrid(rectangles, content: RectangleView.init)
.gridStyle(animation: .easeInOut(duration: 0.5))
```
### Scroll Behaviour
**Embed in ScrollView & Indicators option**
```swift
ScrollView(showsIndicators: true) {
WaterfallGrid(rectangles, content: RectangleView.init)
}
```
**Horizontal Scroll Direction**
```swift
ScrollView(.horizontal) {
WaterfallGrid(rectangles, content: RectangleView.init)
.scrollOptions(direction: .horizontal)
}
```


### A Complete Example
```swift
ScrollView(.horizontal, showsIndicators: false) {
WaterfallGrid(cards) { card in
CardView(card: card)
}
.gridStyle(
columnsInPortrait: 2,
columnsInLandscape: 3,
spacing: 8,
animation: .easeInOut(duration: 0.5)
)
.scrollOptions(direction: .horizontal)
.padding(EdgeInsets(top: 16, leading: 8, bottom: 16, trailing: 8))
}
```
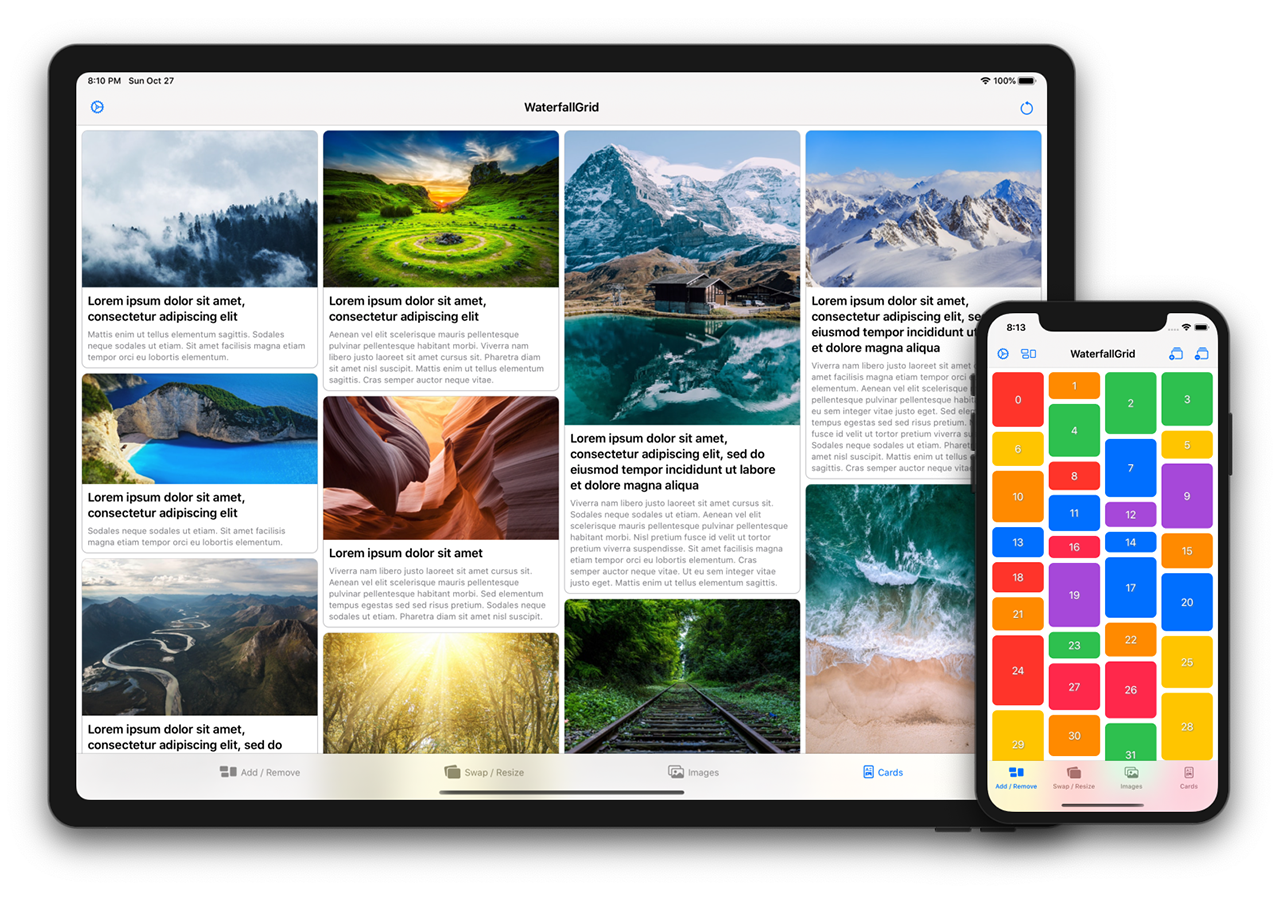
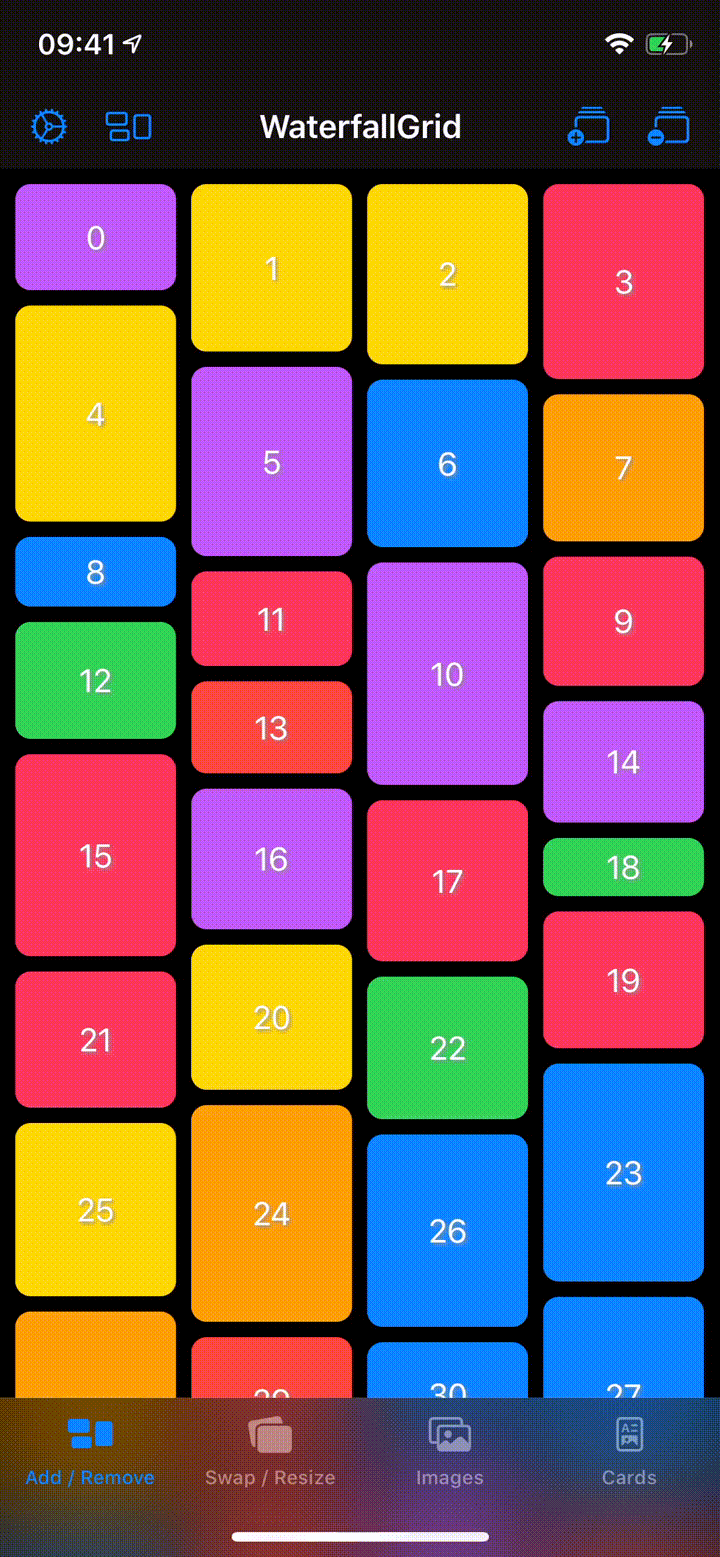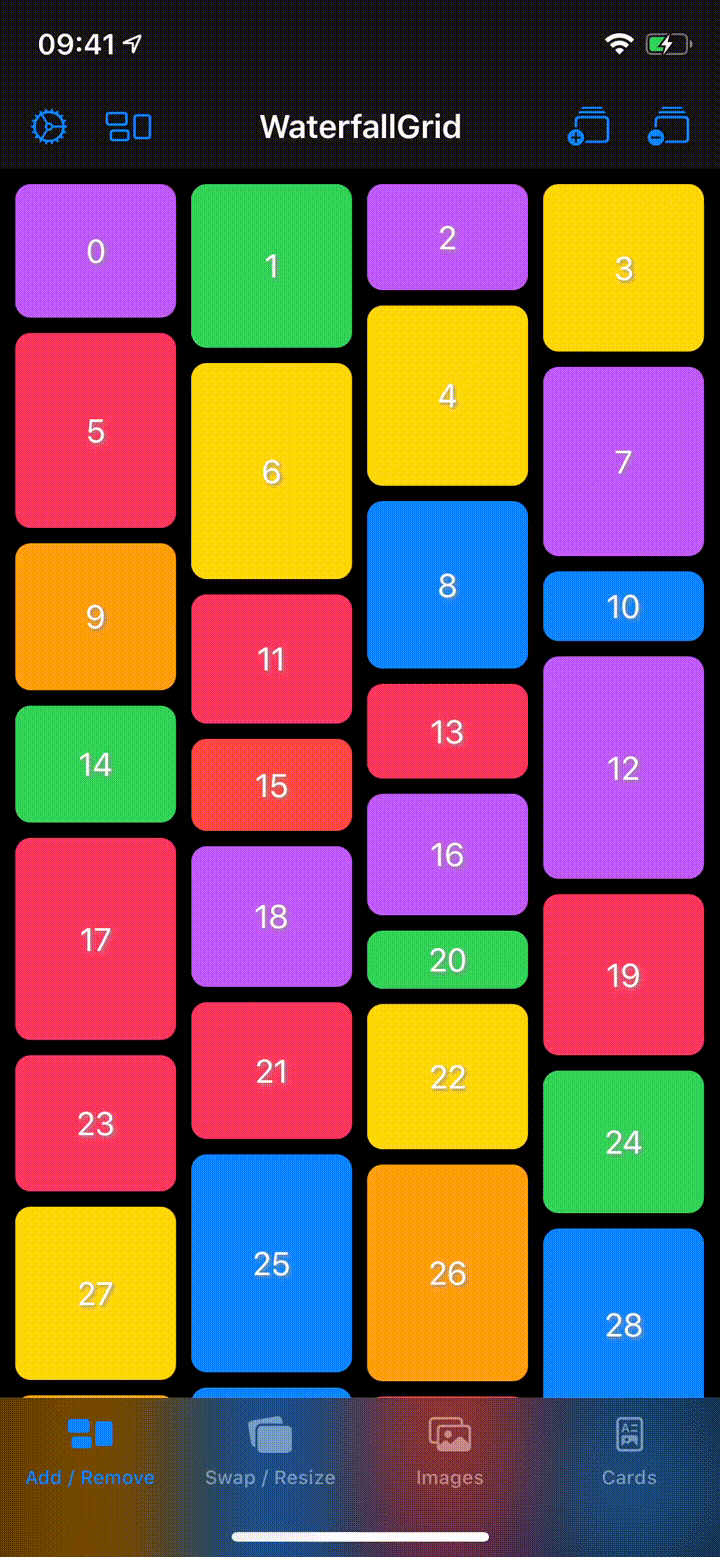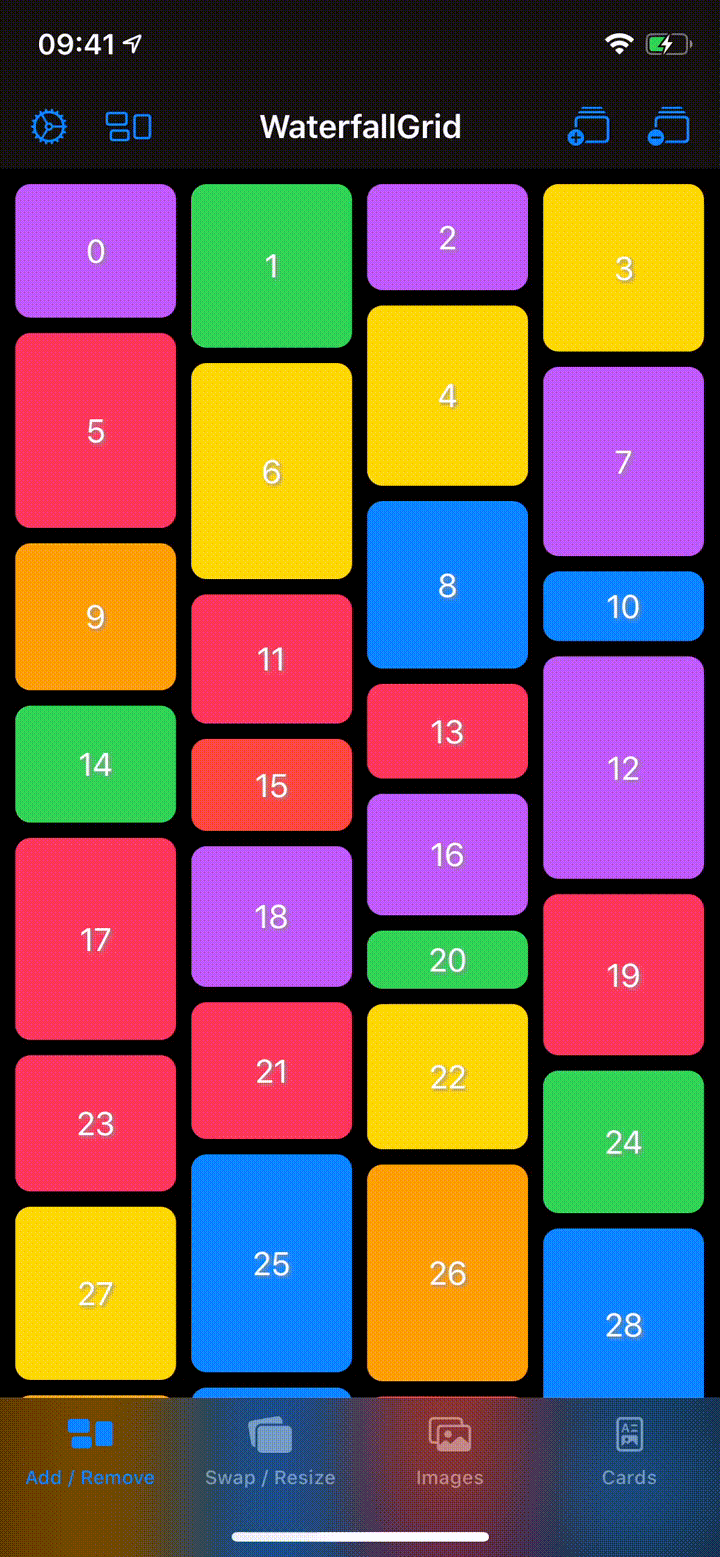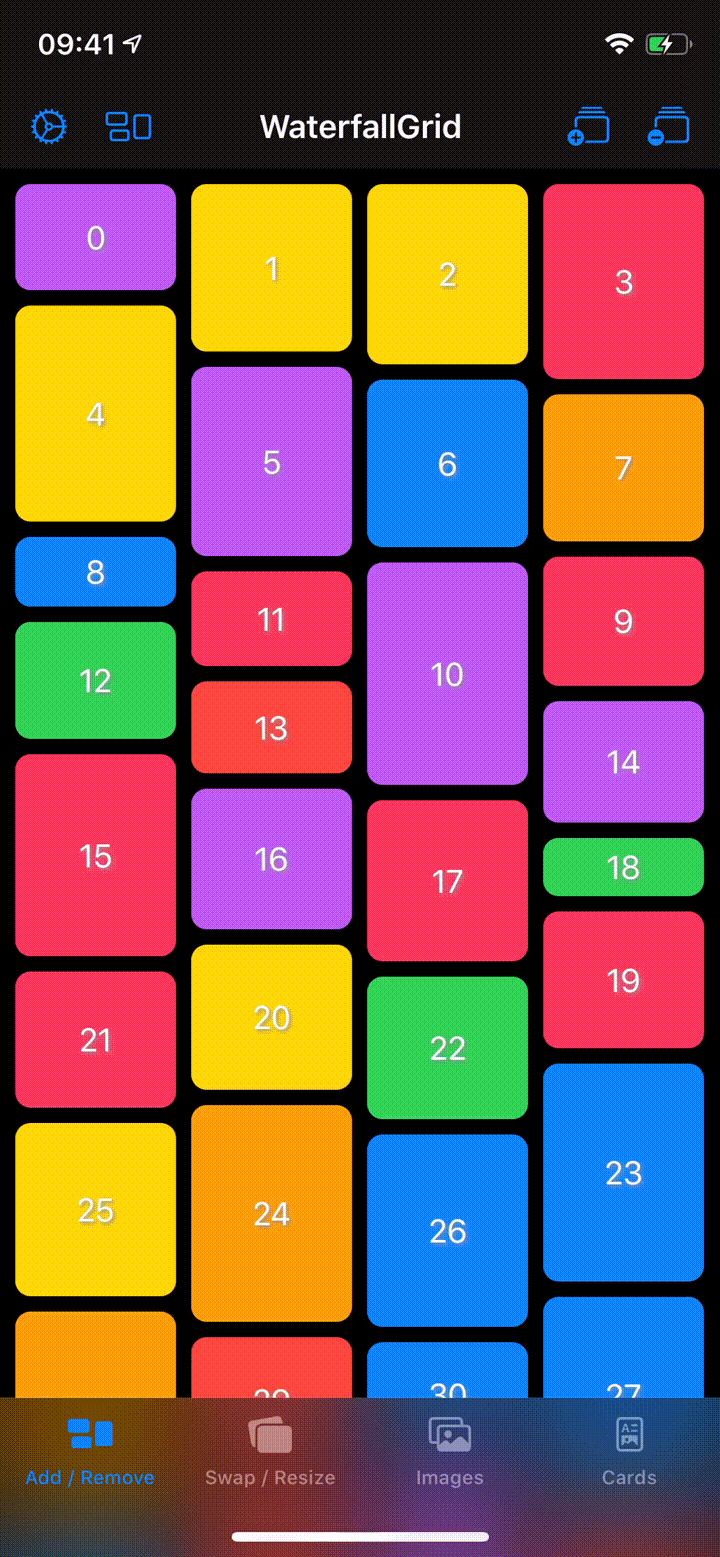
## Sample App
Explore the `WaterfallGridSample` app for some more detailed and interactive examples.

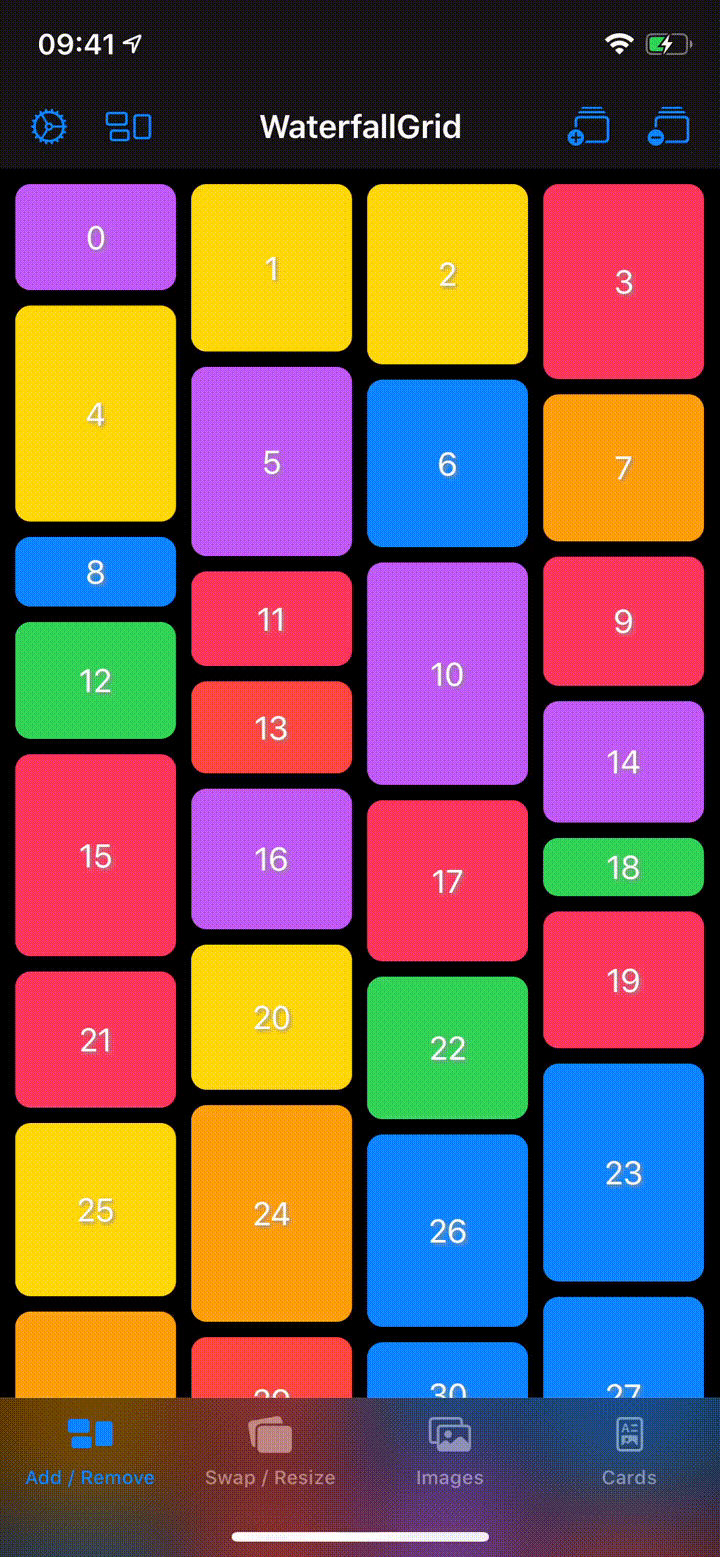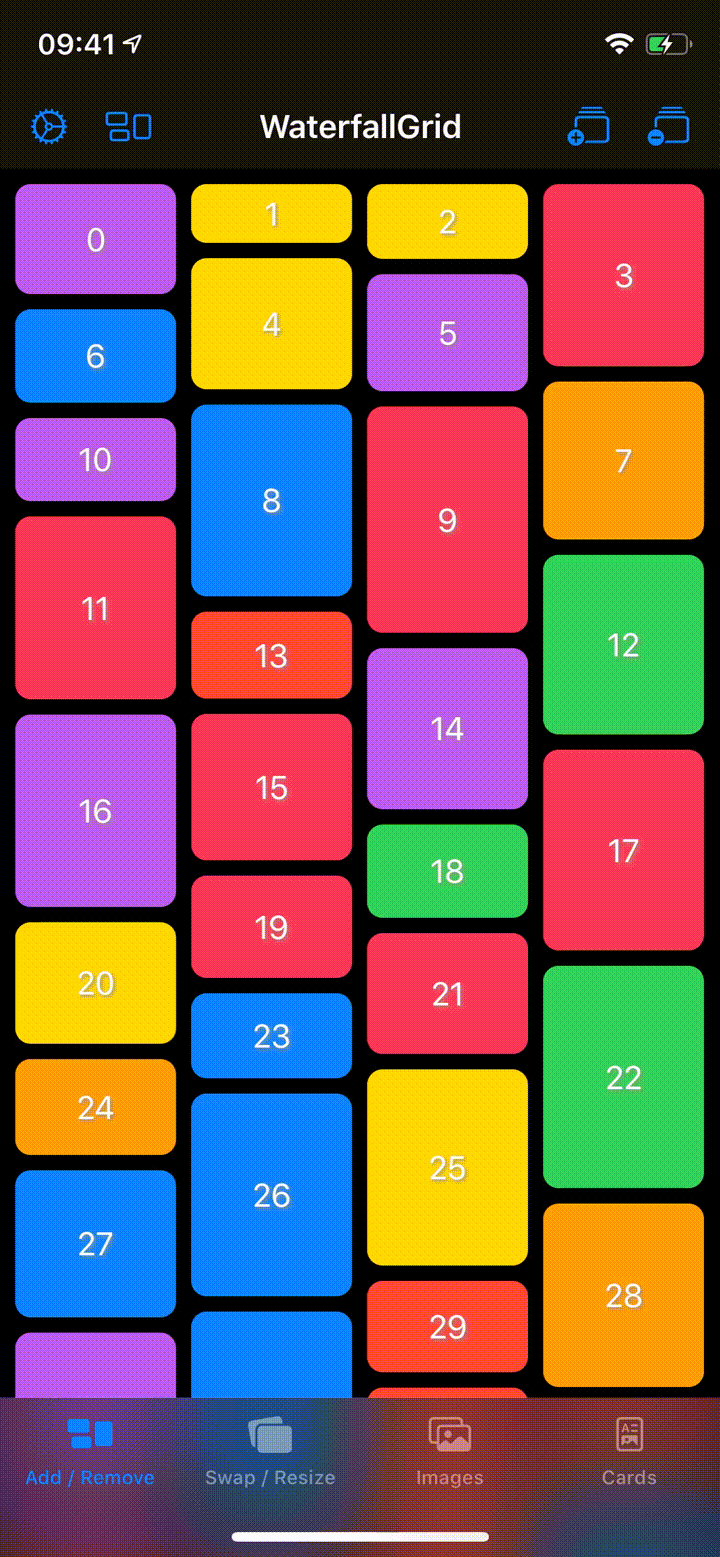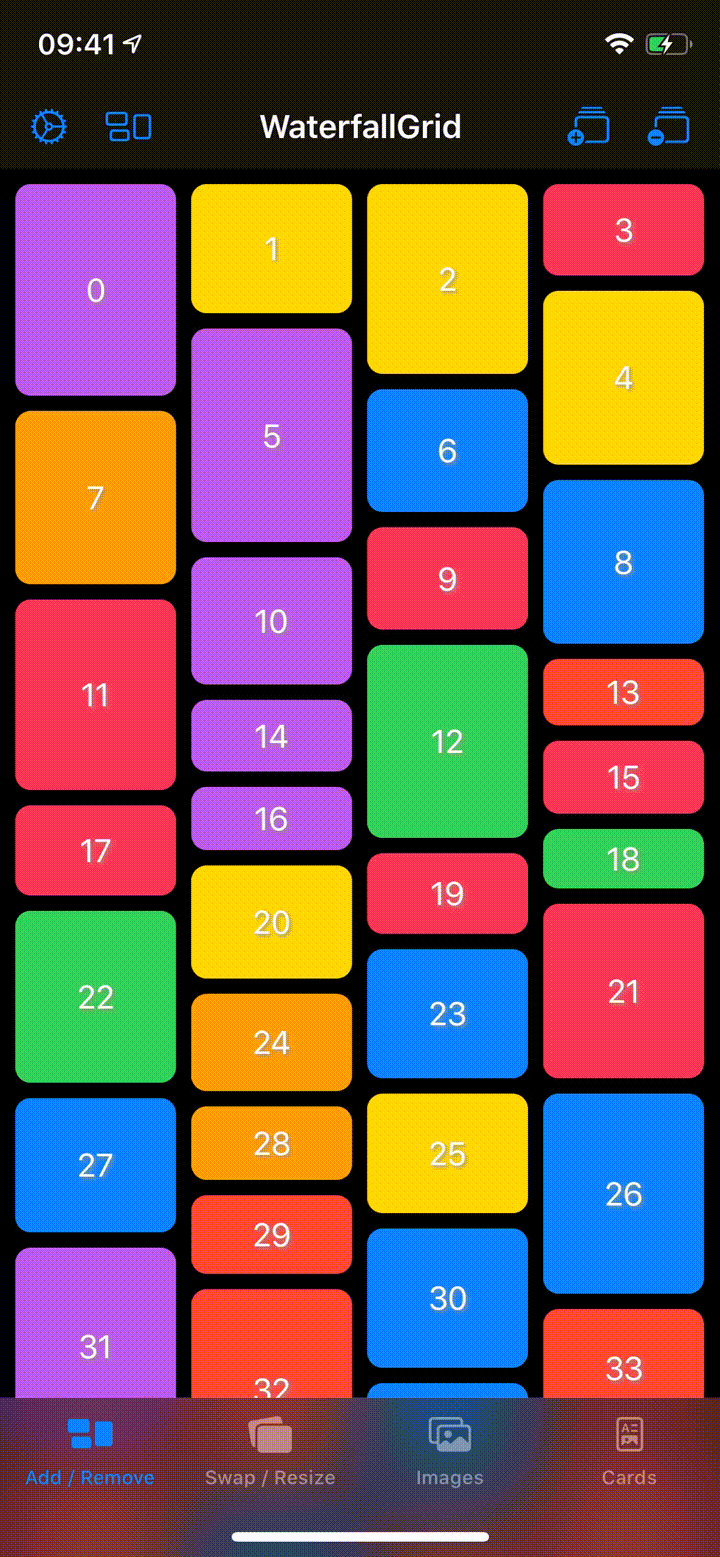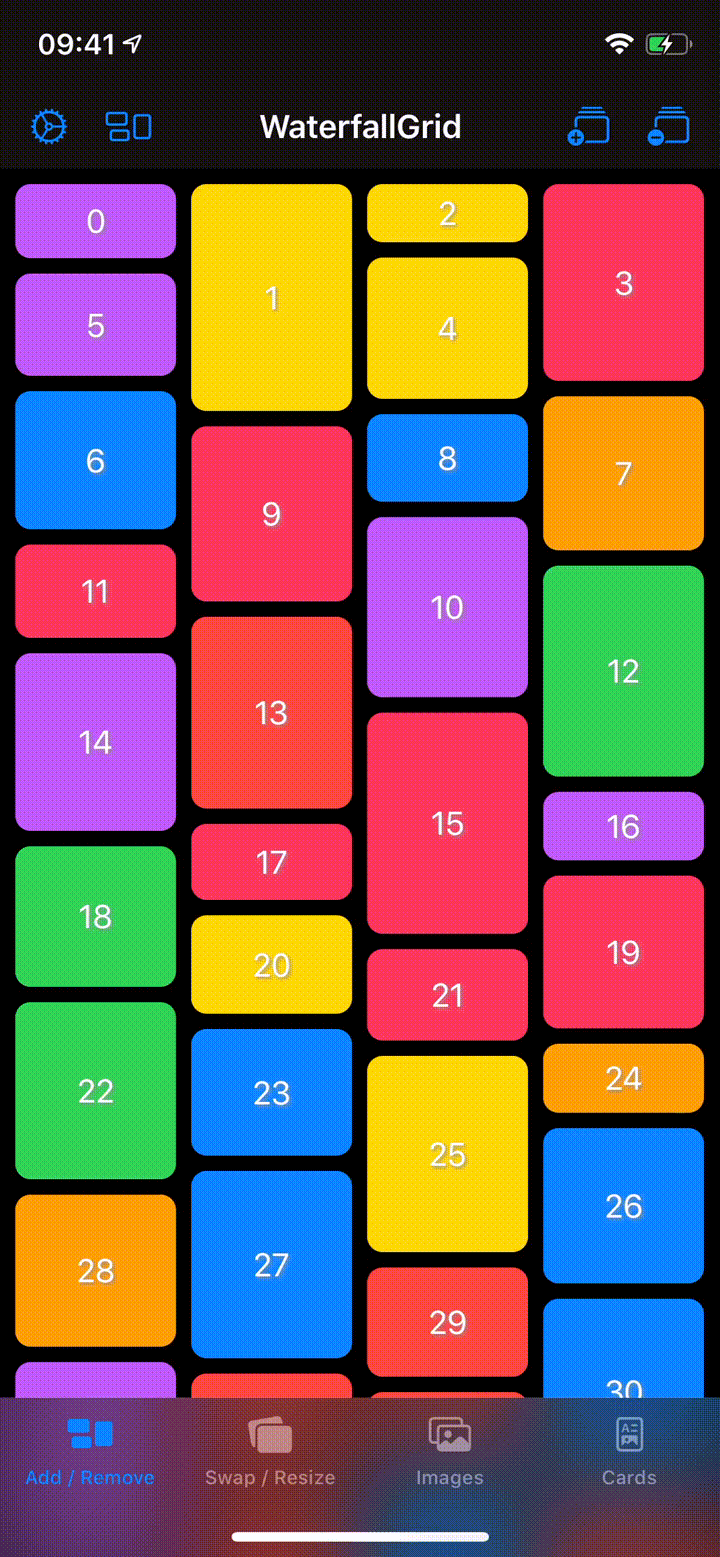
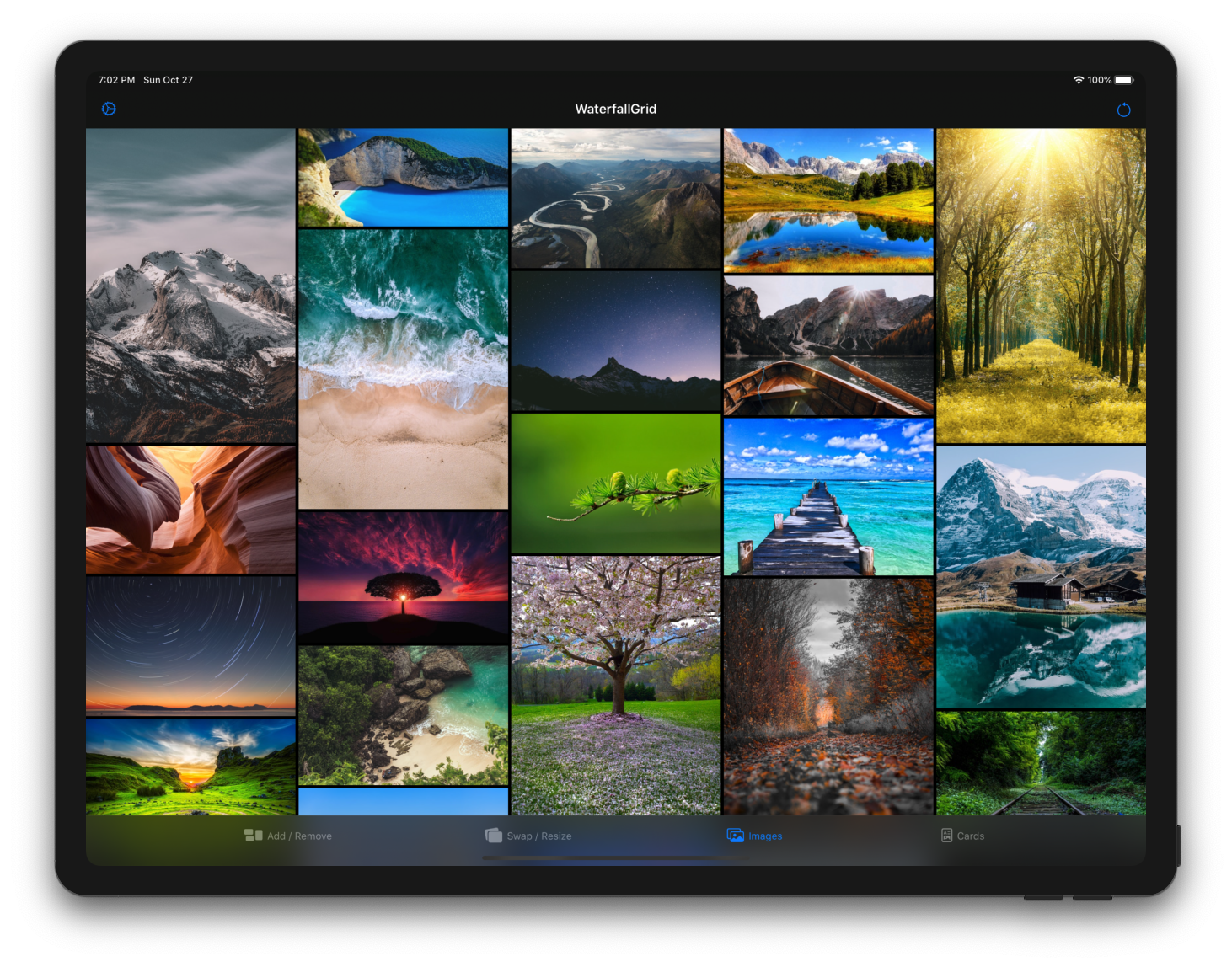
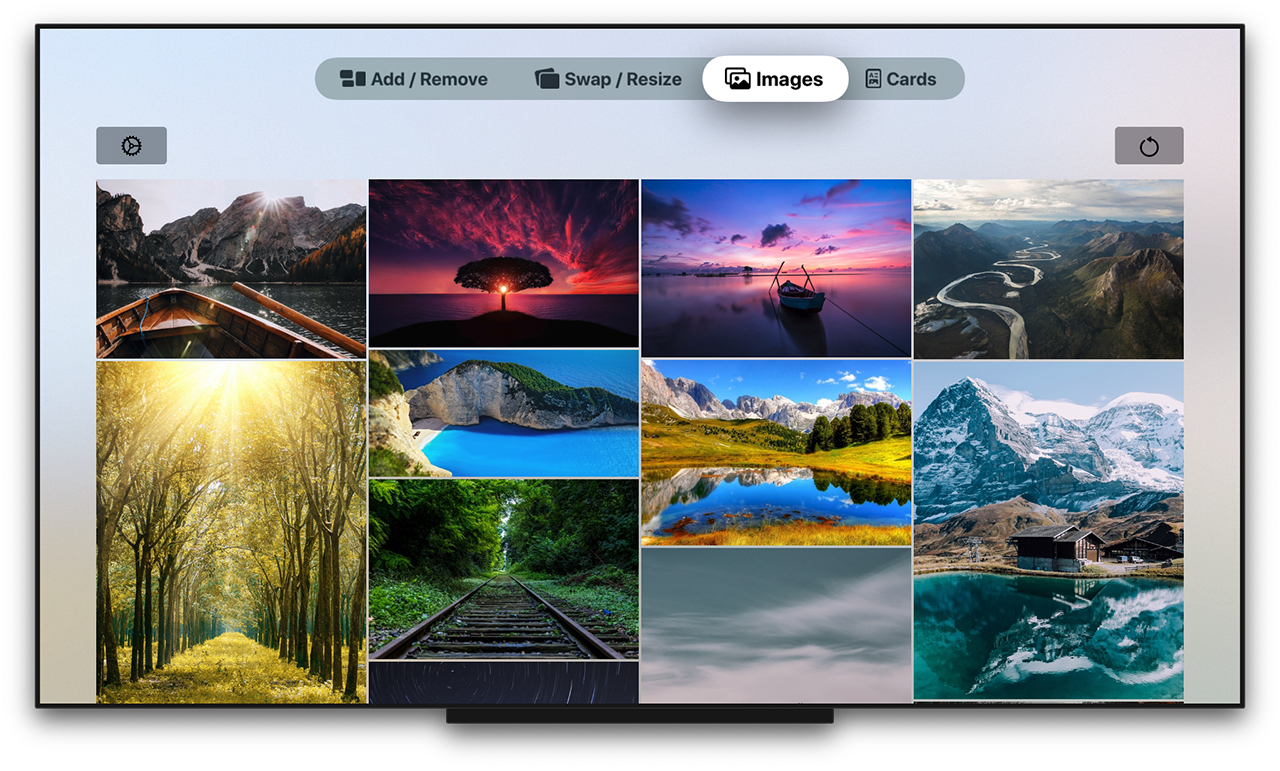
## Installation
### Swift Package Manager
**App dependency**
select File > Swift Packages > Add Package Dependency and enter the repository URL ([Adding Package Dependencies to Your App](https://developer.apple.com/documentation/xcode/adding_package_dependencies_to_your_app))
**Package dependency**
Add it as a dependency within your `Package.swift` manifest:
```swift
dependencies: [
.package(url: "https://github.com/paololeonardi/WaterfallGrid.git", from: "1.1.0")
]
```
### CocoaPods
You can install `WaterfallGrid` via CocoaPods by adding the following line to your `Podfile`:
```ruby
pod 'WaterfallGrid', '~> 1.1.0'
```
Run the `pod install` command to download the library
and integrate it into your Xcode project.
## Migration Guides
- [WaterfallGrid 1.0.0 Migration Guide](https://github.com/paololeonardi/WaterfallGrid/wiki/WaterfallGrid-1.0.0-Migration-Guide)
## Versioning
For the versions available, see the [releases on this repository](https://github.com/paololeonardi/WaterfallGrid/releases).
## Contributing
Contributions are more than welcome. Please create a GitHub issue before submitting a pull request to plan and discuss implementation.
## Author
* [Paolo Leonardi](https://github.com/paololeonardi) ([@paololeonardi](https://twitter.com/paololeonardi))
## Credits
WaterfallGrid was inspired by the following projects:
* QGrid - https://github.com/Q-Mobile/QGrid
* Grid - https://github.com/SwiftUIExtensions/Grid
* The SwiftUI Lab - https://swiftui-lab.com
## License
WaterfallGrid is available under the MIT license. See the [LICENSE](LICENSE) file for more info.