https://github.com/pawap90/acho-bot
🐶💬 A Twitch chatbot powered by Notion
https://github.com/pawap90/acho-bot
nodejs notion notion-api twitch twitch-bot typescript
Last synced: 8 months ago
JSON representation
🐶💬 A Twitch chatbot powered by Notion
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/pawap90/acho-bot
- Owner: pawap90
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-09-22T11:54:55.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2022-02-25T23:30:19.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2023-06-14T17:50:17.247Z (over 2 years ago)
- Topics: nodejs, notion, notion-api, twitch, twitch-bot, typescript
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 468 KB
- Stars: 9
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[](https://github.com/pawap90/acho-bot/actions/workflows/build.yml)

Use Notion to configure your Twitch chatbot commands!
- [Features](#features)
- [Manage your Twitch Chatbot from Notion](#manage-your-twitch-chatbot-from-notion)
- [Assign Permissions to each Command](#assign-permissions-to-each-command)
- [Specific user permissions](#specific-user-permissions)
- [Commands view](#commands-view)
- [Scripted commands](#scripted-commands)
- [Single account](#single-account)
- [Status view](#status-view)
- [Built-in commands](#built-in-commands)
- [Placeholder commands](#placeholder-commands)
- [Quick start](#quick-start)
- [Dependencies](#dependencies)
- [Development](#development)
- [Test](#test)
- [Extend it](#extend-it)
- [Environment variables](#environment-variables)
# Features
## Manage your Twitch Chatbot from Notion
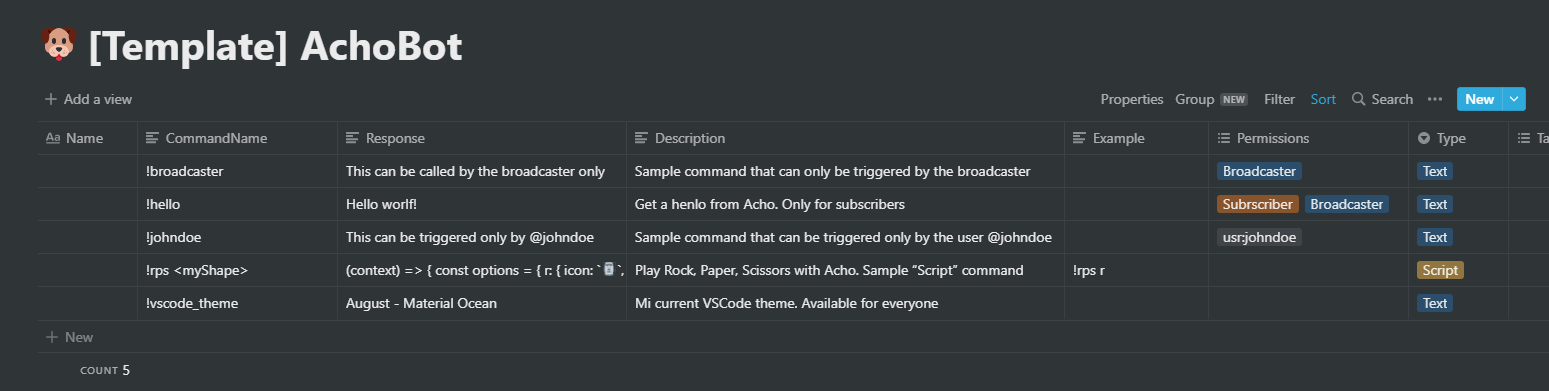
Add, update or delete commands in a Notion database. AchoBot will use the information from Notion to answer your viewers when they invoke a command.
## Assign Permissions to each Command
The database includes a `Permissions` column where you can specify who can invoke each command. Leave it empty, and everyone will have access to it.
The column accepts one or more of the following values:
- Broadcaster
- Moderator
- Subscriber
- Viewer
### Specific user permissions
You can also create commands that can only be invoked by a single specific user. To do that use the value `usr:`, for example: `usr:paulasantamaria`
## Commands view
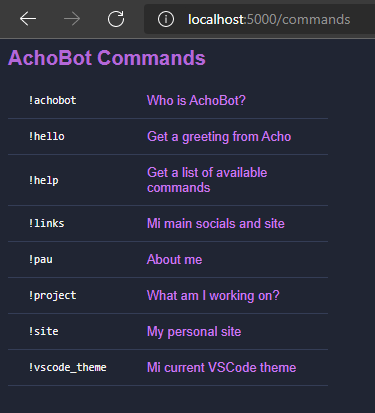
Navigate to `/commands` to get a list of every public command. Your viewers can use it to see the available commands.
Also, you can navigate to `/commands?mode=image` to get a ready-to-download image you can add to your Twitch panels.
## Scripted commands
You can specify the type of command in the "Type" column. Available options are:
- Text
- Script
Text commands return a plain text response. E.g: "Welcome to the stream".
Scripted commands can implement some logic (JavaScript) and receive parameters.
For example, imagine the following command `!say `:
```js
(context) => {
const textToPrint = context.params.text;
return `You said: ${textToPrint}`;
}
```
When a viewer invokes it: `!say hello`
Output: `You said: hello`
> This feature is new and still has some limitations and issues. Writing code in a Notion DB cell is not ideal 😅.
## Single account
The chatbot service will work only for the accounts and channels specified in the environment variables.
If any other account tries to log in using the chatbot authorization endpoints, it will get an authorization error.
The service is not currently designed to handle multiple accounts. This is a limitation, but it also makes the hosting and configuration of the service easier.
## Status view
Use the status view to see if your bot's Twitch account is correctly authorized.
You can use this view in OBS to get real-time feedback on your chatbot status (it auto-updates every minute).
## Built-in commands
Built-in commands are defined in the codebase instead of Notion. They usually require more logic and access to resources unavailable to the Notion commands. There are currently two built-in commands that you can use:
- `!help` prints a list of available commands.
- `!refresh` invalidates the command cache, so next time a command is triggered, the app needs to go to Notion to retrieve the commands, thus updating them to the latest version. Only available for Broadcaster and Moderators.
## Placeholder commands
Some commands are triggered via code but defined in Notion. This allows AchoBot to react to certain events (like a user logging in or subscribing) while also allowing each user to specify what they want AchoBot to do in each case.
Right now, the only placeholder command is:
- `!welcome`: Executed when AchoBot joins the chat room immediately after a stream starts. If you define this command in Notion when the bot logs in, it can say hi and leave some relevant information in the chat. E.g., "Hi, I'm AchoBot! Type !help to see what I can do".
# Quick start
## Dependencies
- [Node.js](https://nodejs.org/en/)
- [npm](https://www.npmjs.com/)
- Notion API Key
- Notion Database
- Twitch Account
- Twitch Application
> To get a detailed step-by-step guide on how to setup the project including every dependency, check out [AchoBot setup - Full guide](https://github.com/pawap90/acho-bot/wiki/AchoBot-setup---Full-guide)
1. Setup your Notion Database. Generate it using the following Notion template: [[Template] AchoBot](https://familiar-freckle-76f.notion.site/350b171ebc30462fbdcb8391cb2f088a?v=0cf2e1a5f5bc476e827d2705e2bdc223)
> Press "Duplicate" to copy the template in your Notion. The template comes with a few sample commands; feel free to delete them and add your own.
2. Clone the repo
```
git clone https://github.com/pawap90/acho-bot
```
3. Build the project
```
npm run build
```
> You can find the transpiled code in the `_dist` folder.
4. Make sure to set up all the [Environment variables](#environment-variables)
5. Run it
```
npm start
```
6. Open the site in your browser (e.g., http://localhost:5000 if you are running it locally) and press the link to log in with your bot's Twitch account. This will give the application permissions to use the chat on your bot's behalf, so it can start answering commands.
> Once you start streaming, if the service is running and you authorized the bot (step 6), the bot will automatically log in to the chat. Give the bot's account moderator permissions so it can reply to commands without limitations. Type this in the chat: `/mod bot_username`
## Development
1. Clone the repo
```
git clone https://github.com/pawap90/acho-bot
```
2. Install dependencies: Run the following command from the project's root folder:
```sh
npm install
```
3. Setup a `.env` file in the root as explained in the [Environment variables](#environment-variables) section.
4. Start the local development server:
```sh
npm run dev
```
### Test
To run the available tests, use:
```
npm test
```
### Extend it
The project is designed to be easily extensible. To know more: [AchoBot wiki - Extend AchoBot](https://github.com/pawap90/acho-bot/wiki/Extend-AchoBot)
## Environment variables
These are the environment variables required to run the project. Make sure to set the values with your own data.
```
TWITCH_BOT_CLIENTID=
TWITCH_BOT_CLIENTSECRET=
TWITCH_BOT_USERNAME=
TWITCH_CHANNELS=
TMI_DEBUG=true
TMI_LOGLEVEL=info
PORT=5000
TWITCH_BOT_REDIRECTURI=http://localhost:5000/api/twitch/auth/token
SESSION_SECRET=
NOTION_APIKEY=
NOTION_DATABASEID=
NOTION_VERSION=2021-08-16
```
When running the project locally using `npm run dev`, you should set the environment variables within a `.env` file in the root.