https://github.com/pbatard/uefi-ntfs
UEFI:NTFS - Boot NTFS or exFAT partitions from UEFI
https://github.com/pbatard/uefi-ntfs
arm arm64 c exfat gcc ia32 ntfs ntfs-boot ntfs-driver rufus uefi uefi-ntfs visual-studio x64
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
UEFI:NTFS - Boot NTFS or exFAT partitions from UEFI
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/pbatard/uefi-ntfs
- Owner: pbatard
- License: gpl-2.0
- Created: 2014-12-02T19:14:48.000Z (about 11 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-12-11T13:28:52.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-15T00:47:42.067Z (8 months ago)
- Topics: arm, arm64, c, exfat, gcc, ia32, ntfs, ntfs-boot, ntfs-driver, rufus, uefi, uefi-ntfs, visual-studio, x64
- Language: C
- Homepage:
- Size: 248 KB
- Stars: 827
- Watchers: 50
- Forks: 141
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE.txt
- Security: SECURITY.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-x - uefi-ntfs - Boot NTFS or exFAT partitions from UEFI (C)
README
[](https://github.com/pbatard/uefi-ntfs/actions)
[](https://scan.coverity.com/projects/pbatard-uefi-ntfs)
[](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-2.0.en.html)
UEFI:NTFS - Boot NTFS or exFAT partitions from UEFI
===================================================
UEFI:NTFS is a generic bootloader, that is designed to allow boot from NTFS or
exFAT partitions, in pure UEFI mode, even if your system does not natively
support it.
This is primarily intended for use with [Rufus](https://rufus.ie), but can also
be used independently.
In other words, UEFI:NTFS is designed to remove the restriction, which most
UEFI systems have, of only providing boot support from a FAT32 partition, and
enable the ability to also boot from NTFS partitions.
This can be used, for instance, to UEFI-boot a Windows NTFS installation media,
containing an `install.wim` that is larger than 4 GB (something FAT32 cannot
support) or to allow dual BIOS + UEFI boot of 'Windows To Go' drives.
As an aside, and because there appears to exist a lot of inaccurate information
about this on the Internet, it needs to be stressed out that there is absolutely
nothing in the UEFI specifications that actually forces the use of FAT32 for
UEFI boot. On the contrary, UEFI will happily boot from __ANY__ file system,
as long as your firmware has a driver for it. As such, it is only the choice of
system manufacturers, who tend to only include a driver for FAT32, that limits
the default boot capabilities of UEFI, and that leads many to __erroneously
believe__ that only FAT32 can be used for UEFI boot.
However, as demonstrated in this project, it is very much possible to work
around this limitation and enable any UEFI firmware to boot from non-FAT32
filesystems.
## Overview
The way UEFI:NTFS works, in conjunction with Rufus, is as follows:
* Rufus creates 2 partitions on the target USB disk (these can be MBR or GPT
partitions). The first one is an NTFS partition occupying almost all the
drive, that contains the Windows files (for Windows To Go, or for regular
installation), and the second is a very small FAT partition, located at the
very end, that contains an NTFS UEFI driver (see https://efi.akeo.ie) as well
as the UEFI:NTFS bootloader.
* When the USB drive boots in UEFI mode, the first NTFS partition gets ignored
by the UEFI firmware (unless that firmware already includes an NTFS driver,
in which case 2 boot options will be available, that perform the same thing)
and the UEFI:NTFS bootloader from the bootable FAT partition is executed.
* UEFI:NTFS then loads the relevant NTFS UEFI driver, locates the existing NTFS
partition on the same media, and executes the `/efi/boot/bootia32.efi`,
`/efi/boot/bootx64.efi`, `/efi/boot/bootarm.efi` or `/efi/boot/bootaa64.efi`
that resides there. This achieves the exact same outcome as if the UEFI
firmware had native support for NTFS and could boot straight from it.
## Secure Boot compatibility
* UEFI:NTFS is compatible with Secure Boot and has been signed by Microsoft.
* You can find Secure Boot signed binaries (for x86_64, x86_32 and ARM64) in the
[`uefi-ntfs.img` archive of Rufus](https://github.com/pbatard/rufus/tree/master/res/uefi).
* Note however that, due to Microsoft [arbitrary restrictions regarding GPLv3](https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/t5/hardware-dev-center/updated-uefi-signing-requirements/ba-p/1062916)
the only drivers that can currently be used with UEFI:NTFS in a Secure Boot
environment are the GPLv2 licensed [ntfs-3g ones](https://github.com/pbatard/ntfs-3g).
Especially, the NTFS and exFAT drivers from EfiFs, which are derived from
GRUB 2.0, and therefore GPLv3, can not be submitted to Microsoft for signing.
* Finally, Microsoft's current Secure Boot signing policies require additional
validation for 32-bit ARM, therefore the 32-bit ARM binaries are not Secure
Boot signed. This does not affect 64-bit ARM (a.k.a. `ARM64`/`AARCH64`/`AA64`)
for which we have fully Secure Boot signed binaries.
## Prerequisites
* [Visual Studio 2022](https://www.visualstudio.com/vs/community/) or
[MinGW](http://www.mingw.org/)/[MinGW64](http://mingw-w64.sourceforge.net/)
(preferably installed using [msys2](https://sourceforge.net/projects/msys2/))
or gcc
* [QEMU](http://www.qemu.org) __v2.7 or later__
(NB: You can find QEMU Windows binaries [here](https://qemu.weilnetz.de/w64/))
* git
* wget, unzip, if not using Visual Studio
## Sub-Module initialization
For convenience, the project can be compiled against the gnu-efi library rather
than EDK2, so you may need to initialize the git submodules with:
```
git submodule update --init
```
## Compilation and testing
* If using the Visual Studio solution (`.sln`), just press F5 to have
the application compiled and launched in the QEMU emulator.
* If using gcc with gnu-efi, you should be able to simply issue `make`.
If needed you can also issue something like `make ARCH= CROSS_COMPILE=`
where `` is one of `ia32`, `x64`, `arm` or `aa64` and tuple is the one for
your cross-compiler (e.g. `aarch64-linux-gnu-`).
You can also debug through QEMU by specifying `qemu` to your `make` invocation.
Be mindful however that this turns the special `_DEBUG` mode on, and you should
run make without invoking `qemu` to produce proper release binaries.
* If using VS2022 with EDK2 on Windows, assuming that your EDK2 directory is in
`D:\edk2` and that `nasm` resides in `D:\edk2\BaseTools\Bin\Win32\`, you should
be able to issue:
set EDK2_PATH=D:\edk2
set NASM_PREFIX=D:\edk2\BaseTools\Bin\Win32\
set WORKSPACE=%CD%
set PACKAGES_PATH=%WORKSPACE%;%EDK2_PATH%
%EDK2_PATH%\edksetup.bat reconfig
build -a X64 -b RELEASE -t VS2022 -p uefi-ntfs.dsc
* If using gcc with EDK2 on Linux, and assuming that your edk2 directory resides
in `/usr/src/edk2`:
export EDK2_PATH="/usr/src/edk2"
export WORKSPACE=$PWD
export PACKAGES_PATH=$WORKSPACE:$EDK2_PATH
. $EDK2_PATH/edksetup.sh --reconfig
build -a X64 -b RELEASE -t GCC5 -p uefi-ntfs.dsc
## Download and installation
You can find a ready-to-use FAT partition image, containing the x86 and ARM
versions of the UEFI:NTFS loader (both 32 and 64 bit) and driver in the Rufus
project, under [/res/uefi](https://github.com/pbatard/rufus/tree/master/res/uefi).
If you create a partition of the same size at the end of your drive and copy
[`uefi-ntfs.img`](https://github.com/pbatard/rufus/blob/master/res/uefi/uefi-ntfs.img?raw=true)
there (in DD mode of course), then you should have everything you need to make
the first NTFS partition on that drive UEFI bootable.
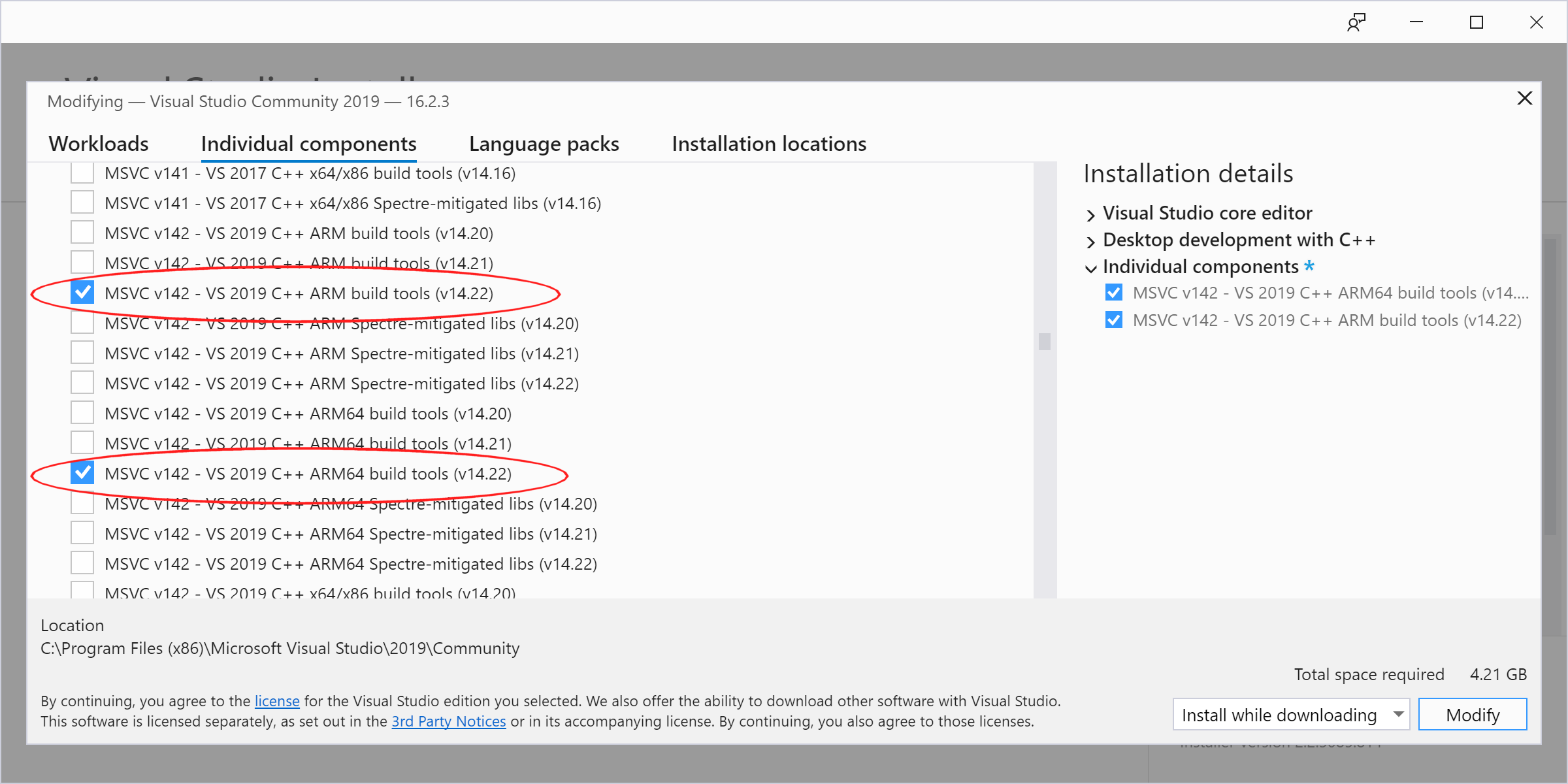
## Visual Studio 2022 and ARM/ARM64 support
Please be mindful that, to enable ARM or ARM64 compilation support in Visual Studio
2022, you __MUST__ go to the _Individual components_ screen in the setup application
and select the ARM/ARM64 build tools there, as they do __NOT__ appear in the default
_Workloads_ screen: