https://github.com/piomin/sample-hazelcast-spring-datagrid
sample spring-boot applications integrated with hazelcast imdg, and providing hot cache with hazelcast and striim
https://github.com/piomin/sample-hazelcast-spring-datagrid
caching data-grid hazelcast hibernate jpa-caching kubernetes minikube mysql spring-boot spring-data-hazelcast spring-data-jpa striim-cluster
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
sample spring-boot applications integrated with hazelcast imdg, and providing hot cache with hazelcast and striim
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/piomin/sample-hazelcast-spring-datagrid
- Owner: piomin
- Created: 2017-04-27T08:35:08.000Z (over 8 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-05T02:18:47.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-05T03:23:39.296Z (10 months ago)
- Topics: caching, data-grid, hazelcast, hibernate, jpa-caching, kubernetes, minikube, mysql, spring-boot, spring-data-hazelcast, spring-data-jpa, striim-cluster
- Language: Java
- Homepage: https://piotrminkowski.com/
- Size: 119 KB
- Stars: 37
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 13
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: readme.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Hazelcast With Spring Boot Demo Project [](https://twitter.com/piotr_minkowski)
In this project I'm demonstrating you the most interesting features of [Hazelcast](https://hazelcast.com/) and its integration with Spring Boot and Spring Data to build cache or distributed in-memory data grid.
## Getting Started
Currently you may find here some examples of application that integrates Hazelcast with Spring Boot and Spring Data. Some of them are divided into the branches and described in a separated articles on my blog. Here's a full list of available examples:
1. Using Hazelcast as 2nd level JPA Cache for **Hibernate** and **MySQL** database. The example is available in the branch [master](https://github.com/piomin/sample-hazelcast-spring-datagrid/tree/master). A detailed guide may be find in the following article: [JPA caching with Hazelcast, Hibernate and Spring Boot](https://piotrminkowski.com/2017/05/08/jpa-caching-with-hazelcast-hibernate-and-spring-boot/).
2. Using Hazelcast with [Striim](https://www.striim.com/) for enabling hot cache between **MySQL** database and in-memory data grid. The example is available in the branch [striim](https://github.com/piomin/sample-hazelcast-spring-datagrid/tree/striim). A detailed guide may be find in the following article: [Hazelcast Hot Cache with Striim](https://piotrminkowski.com/2017/08/09/hazelcast-hot-cache-with-striim/).
3. Using Hazelcast cluster on **Kubernetes** with Spring Boot. The example is available in the branch [master](https://github.com/piomin/sample-hazelcast-spring-datagrid/tree/master). A detailed guide may be find in the following article: [Hazelcast With Spring Boot on Kubernetes](https://piotrminkowski.com/2020/01/31/hazelcast-with-spring-boot-on-kubernetes/).
4. Using Hazelcast cluster with Spring Boot that programically stores data in the two sources: **MySQL** and Hazelcast. The example is available in the branch [master](https://github.com/piomin/sample-hazelcast-spring-datagrid/tree/master). A detailed guide may be find in the following article: [In-memory Data Grid with Hazelcast](https://piotrminkowski.com/2017/05/10/in-memory-data-grid-with-hazelcast/).
### Usage
In the most cases you need to have Maven and JDK8+. In the third example with Kubernetes you will have to run **Minikube** on your machine. The best way to run the sample applications is with IDEs like IntelliJ IDEA or Eclipse.
## Architecture
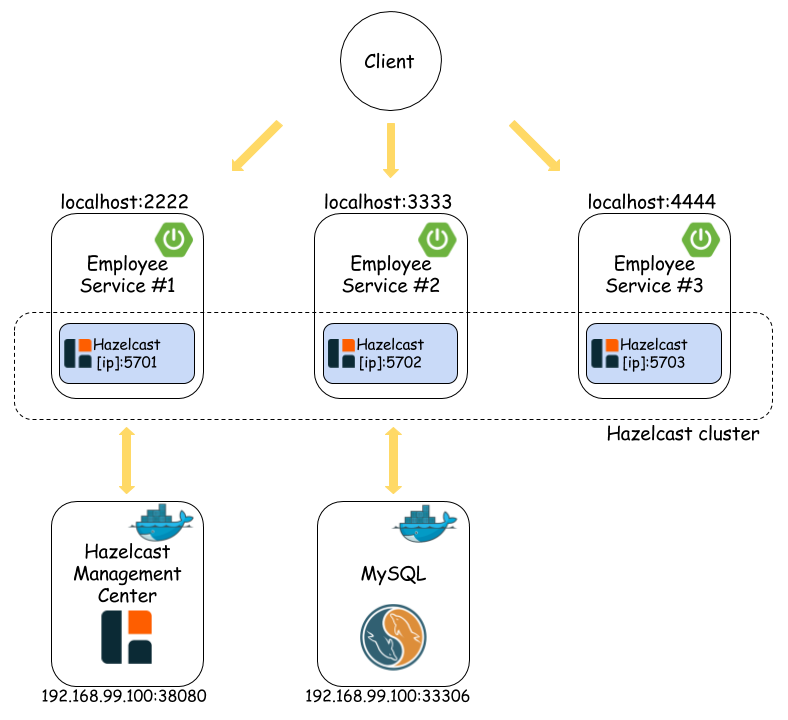
Our sample microservices-based system consists of the following modules:
- **employee-service** - a module which is a simple Spring Boot application for storing `Employee` objects in Hazelcast and MySQL (optionally)
- **person-service** - a module which is a simple Spring Boot application for storing `Person` objects in Hazelcast and MySQL (optionally)
- **employee-service-kubernetes** - a module dedicated only for 3rd example based on Kubernetes.
The following picture illustrates the architecture for running Hazelcast on Kubernetes (**Minikube**) (**Example 3**).

The following picture illustrates the architecture for running Hazelcast with **Striim** as a hot cache for MySQL database (**Example 2**).

The following picture illustrates the architecture for running Hazelcast with Spring Boot as in-memory data grid that programically stores data in two sources (**Example 4**).