https://github.com/precise-simulation/distmesh
DistMesh - simple 2D and 3D mesh generator for MATLAB and Octave (with GUI support)
https://github.com/precise-simulation/distmesh
matlab mesh mesh-generation octave
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
DistMesh - simple 2D and 3D mesh generator for MATLAB and Octave (with GUI support)
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/precise-simulation/distmesh
- Owner: precise-simulation
- License: other
- Created: 2022-05-09T07:24:08.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2022-05-09T07:36:56.000Z (almost 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-01T02:52:59.093Z (12 months ago)
- Topics: matlab, mesh, mesh-generation, octave
- Language: MATLAB
- Homepage: https://www.featool.com/grid/2018/03/06/Matlab-Mesh-Generation-Comparison.html
- Size: 33.2 KB
- Stars: 6
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
DistMesh - A Simple Mesh Generator for MATLAB
=============================================
About DistMesh
--------------
DistMesh is a simple MATLAB and
[GNU Octave](https://www.gnu.org/software/octave/) code for automatic
generation of unstructured 2D triangular and 3D tetrahedral volume
meshes.
This repository contains a slightly modified, consolidated, and
refactored version of DistMesh, which also can be used from a
graphical user interface (GUI) together with the FEATool Multiphysics
Octave and [MATLAB PDE and FEM Toolbox](https://www.featool.com).
Note that a Julia implementation of this DistMesh version is also
available in the
[DistMesh-Julia repository](https://github.com/precise-simulation/distmesh-julia)
as well as
QuadMesh - unstructured quadrilateral mesh generation based on distance functions.


Description
-----------
The DistMesh algorithm was invented by Per-Olof Persson and Gilbert
Strang in the Department of Mathematics at MIT. More detailed
descriptions of the original DistMesh method and MATLAB mesh
generation code can be found in the SIAM Review paper and other
references linked below.
The simplicity of the DistMesh algorithm is due to using signed
distance functions (level sets) to specify and describe domains,
geometries, and regions to mesh. Distance functions specify the
shortest distance from any point in space to the boundary of the
domain, where the sign of the function is positive outside the region,
negative inside, and zero on the boundary. This definition is used to
identify if a point is located in or outside of the
geometry. Moreover, the gradient of the distance function points in
the direction of the boundary, allowing points outside to be
efficiently moved back to the domain.
A simple example is the unit circle in two dimensions, which has the
distance function _d(r) = r-1_, where _r = sqrt(x^2+y^2)_ is the
distance from the origin. For more complicated geometries the distance
function can be computed by interpolation between values on a grid,
which is a common representation for level set methods.
For the mesh generation procedure, DistMesh uses the Delaunay
triangulation routine in MATLAB and Octave and tries to optimize the
node locations by a force-based smoothing procedure. The topology is
regularly updated by Delaunay. The boundary points are only allowed to
move tangentially to the boundary by projections using the distance
function. This iterative procedure typically results in very uniform
and well-shaped high quality meshes.
Modifications
-------------
In addition to cleanup, refactoring, and consolidation, this DistMesh
implementation has been modified in the following ways:
- CAD geometry and GUI support (with the FEATool Multiphysics Toolbox)
- 2D and 3D cases merged and handled in one code base.
- Full support for mesh generation in both MATLAB and Octave.
- Support for constrained edges (and constraint functions).
- Delaunay function selection depending on MATLAB or Octave version
(with constrained Delaunay triangulation if available).
- _fd_ and _fh_ can both be specified as function handles and as cell
arrays of a function handle/string names with optional calling
arguments.
- Alternative optimized edge pair computation.
- Optional number of re-tracing steps for grid points outside domain.
- Added statistics and timing output.
Usage
-----
To use the this mesh generation code, simply download the stand alone
[distmesh](https://github.com/precise-simulation/distmesh/blob/master/distmesh.m)
source code and run it in MATLAB or Octave. The function syntax is as follows
[ P, T, STAT ] = DISTMESH( FD, FH, H0, BBOX, P_FIX, E_FIX, IT_MAX, FID, FIT )
where **FD** is a function handle to the geometry description that
should take evaluation coordinates and points as input. For example
fd = @(p) sqrt(sum(p.^2,2)) - 1; specifies the distance
function for a unit circle (both function handles, string function
names, and anonymous functions are supported). Similar to _FD_, **FH**
a function describing the desired relative mesh size distribution. For
example fh = @(p) ones(size(p,1),1); specifies a uniform
distribution where _FH_ evaluates to _1_ at all points. **H0** is a
numeric scalar specifying the initial edge lengths, and **BBOX** is a
2 by 2 in 2D (or 2 by 3 in 3D) bounding box of the domain (enclosing
the zero contour/level set of _FD_). **P_FIX** optionally specifies a
number of points that should always be present (fixed) in the
resulting mesh. **E_FIX** can be sets of edge vertex indices to
constrain, or alternatively a cell array with function handle to call.
**IT_MAX** sets the maximum number of grid generation iterations
allowed (default _1000_). Finally, **FID** specifies a file
identifies for output (default _1_ = terminal output), **FIT** is an
optional % function to call every iteration to check for early
termination.
The DistMesh MATLAB function returns the grid point vertices in **P**,
triangulated simplices in **T**, as well as an optional statistics
struct **STAT** including timings and convergence information.
Input:
FD: Distance function d(x,y,(z))
FH: Scaled edge length function h(x,y,(z))
H0: Initial edge length
BBOX: Bounding box [xmin,ymin,(zmin); xmax,ymax,(zmax)]
P_FIX: Fixed node positions (N_P_FIX x 2/3)
E_FIX: Constrained edges (N_E_FIX x 2)
IT_MAX: Maximum number of iterations
FID: Output file id number (default 1 = terminal)
Output:
P: Grid vertex/node coordinates (N_P x 2/3)
T: Triangle indices (N_T x 3)
STAT: Mesh generation statistics (struct)
Examples
--------
To automatically run the collection of basic mesh generation examples
described below, type
[distmesh_demo](https://github.com/precise-simulation/distmesh/blob/master/distmesh_demo.m)
into the MATLAB or Octave CLI command prompts from the directory where
the _distmesh_ files can be found.
- Example 1: Uniform mesh on unit circle
fd = @(p) sqrt(sum(p.^2,2)) - 1;
fh = @(p) ones(size(p,1),1);
[p,t] = distmesh( fd, fh, 0.2, [-1,-1;1,1] );
patch( 'vertices', p, 'faces', t, 'facecolor', [.9, .9, .9] )
- Example 2: Uniform mesh on ellipse
fd = @(p) p(:,1).^2/2^2 + p(:,2).^2/1^2 - 1;
fh = @(p) ones(size(p,1),1);
[p,t] = distmesh( fd, fh, 0.2, [-2,-1;2,1] );
patch( 'vertices', p, 'faces', t, 'facecolor', [.9, .9, .9] )
- Example 3: Uniform mesh on unit square
fd = @(p) -min(min(min(1+p(:,2),1-p(:,2)),1+p(:,1)),1-p(:,1));
fh = @(p) ones(size(p,1),1);
[p,t] = distmesh( fd, fh, 0.2, [-1,-1;1,1], [-1,-1;-1,1;1,-1;1,1] );
patch( 'vertices', p, 'faces', t, 'facecolor', [.9, .9, .9] )
- Example 4: Uniform mesh on complex polygon
pv = [-0.4 -0.5;0.4 -0.2;0.4 -0.7;1.5 -0.4;0.9 0.1;
1.6 0.8;0.5 0.5;0.2 1;0.1 0.4;-0.7 0.7;-0.4 -0.5];
fd = { 'l_dpolygon', [], pv };
fh = @(p) ones(size(p,1),1);
[p,t] = distmesh( fd, fh, 0.1, [-1,-1; 2,1], pv );
patch( 'vertices', p, 'faces', t, 'facecolor', [.9, .9, .9] )
- Example 5: Rectangle with circular hole, refined at circle boundary
drectangle = @(p,x1,x2,y1,y2) -min(min(min(-y1+p(:,2),y2-p(:,2)),-x1+p(:,1)),x2-p(:,1));
fd = @(p) max( drectangle(p,-1,1,-1,1), -(sqrt(sum(p.^2,2))-0.5) );
fh = @(p) 0.05 + 0.3*(sqrt(sum(p.^2,2))-0.5);
[p,t] = distmesh( fd, fh, 0.05, [-1,-1;1,1], [-1,-1;-1,1;1,-1;1,1] );
patch( 'vertices', p, 'faces', t, 'facecolor', [.9, .9, .9] )
- Example 6: Square, with size function point and line sources
dcircle = @(p,xc,yc,r) sqrt((p(:,1)-xc).^2+(p(:,2)-yc).^2)-r;
fd = @(p) -min(min(min(p(:,2),1-p(:,2)),p(:,1)),1-p(:,1));
dpolygon = @(p,v) feval('l_dpolygon',p,v);
fh = @(p) min(min(0.01+0.3*abs(dcircle(p,0,0,0)), ...
0.025+0.3*abs(dpolygon(p,[0.3,0.7;0.7,0.5;0.3,0.7]))),0.15);
[p,t] = distmesh( fd, fh, 0.01, [0,0;1,1], [0,0;1,0;0,1;1,1] );
patch( 'vertices', p, 'faces', t, 'facecolor', [.9, .9, .9] )
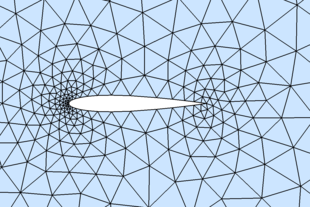
- Example 7: NACA0012 airfoil
hlead = 0.01; htrail = 0.04; hmax = 2; circx = 2; circr = 4;
a = 0.12/0.2*[0.2969,-0.126,-0.3516,0.2843,-0.1036];
fd = @(p) max( dcircle(p,circx,0,circr), ...
-((abs(p(:,2))-polyval([a(5:-1:2),0],p(:,1))).^2-a(1)^2*p(:,1)) );
fh = @(p) min(min(hlead+0.3*dcircle(p,0,0,0),htrail+0.3*dcircle(p,1,0,0)),hmax);
fixx = 1 - htrail*cumsum(1.3.^(0:4)');
fixy = a(1)*sqrt(fixx) + polyval([a(5:-1:2),0],fixx);
pfix = [[circx+[-1,1,0,0]*circr; 0,0,circr*[-1,1]]'; 0,0; 1,0; fixx,fixy; fixx,-fixy];
bbox = [circx-circr,-circr; circx+circr,circr];
h0 = min([hlead,htrail,hmax]);
[p,t] = distmesh( fd, fh, h0, bbox, pfix );
patch( 'vertices', p, 'faces', t, 'facecolor', [.9, .9, .9] )
- Example 8: Uniform mesh on unit sphere
fd = @(p) sqrt(sum(p.^2,2)) - 1;
fh = @(p) ones(size(p,1),1);
[p,t] = distmesh( fd, fh, 0.2, [-1,-1,-1;1,1,1] );
f = [t(:,[1:3]); t(:,[1,2,4]); t(:,[2,3,4]); t(:,[3,1,4])];
patch( 'vertices', p, 'faces', f, 'facecolor', [.9, .9, .9] )
- Example 9: Uniform mesh on unit cube
fd = @(p) -min(min(min(min(min(p(:,3),1-p(:,3) ),p(:,2)),1-p(:,2)),p(:,1)),1-p(:,1));
fh = @(p) ones(size(p,1),1);
pfix = [-1,-1,-1;-1,1,-1;1,-1,-1;1,1,-1; -1,-1,1;-1,1,1;1,-1,1;1,1,1];
[p,t] = distmesh( fd, fh, 0.2, [-1,-1,-1;1,1,1], pfix );
f = [t(:,[1:3]); t(:,[1,2,4]); t(:,[2,3,4]); t(:,[3,1,4])];
patch( 'vertices', p, 'faces', f, 'facecolor', [.9, .9, .9] ), view(3)
- Example 10: Uniform mesh on cylinder
fd = @(p) -min(min(p(:,3),4-p(:,3)),1-sqrt(sum(p(:,1:2).^2,2)));
fh = @(p) ones(size(p,1),1);
pfix = [-1,-1,-1;-1,1,-1;1,-1,-1;1,1,-1; -1,-1,1;-1,1,1;1,-1,1;1,1,1];
[p,t] = distmesh( fd, fh, 0.5, [-1,-1,0;1,1,4], [] );
f = [t(:,[1:3]); t(:,[1,2,4]); t(:,[2,3,4]); t(:,[3,1,4])];
patch( 'vertices', p, 'faces', f, 'facecolor', [.9, .9, .9] ), view(3)
References
----------
[1] [P.-O. Persson, G. Strang, A Simple Mesh Generator in MATLAB. SIAM Review, Volume 46 (2), pp. 329-345, June 2004.](http://persson.berkeley.edu/distmesh/persson04mesh.pdf)
[2] [P.-O. Persson, Mesh Generation for Implicit Geometries. Ph.D. thesis, Department of Mathematics, MIT, Dec 2004.](http://persson.berkeley.edu/thesis/persson-thesis-color.pdf)
[3] [P.-O. Persson's DistMesh website](http://persson.berkeley.edu/distmesh/)
[4] [FEATool Multiphysics grid generation documentation](https://www.featool.com/doc/grid.html)
Alternative Implementations
---------------------------
[5] [libDistMesh: A Simple Mesh Generator in C++](https://github.com/pgebhardt/libdistmesh)
[6] [DistMesh-Julia - Julia Mesh Generation with DistMesh](https://github.com/precise-simulation/distmesh-julia)
[7] [PyDistMesh - A Simple Mesh Generator in Python](https://github.com/bfroehle/pydistmesh)
[8] [Mesh generator - Java implementation of DistMesh](https://github.com/plichjan/jDistMesh)
[9] [DistMesh - Wolfram Language Implementation](https://github.com/WolframResearch/DistMesh)
[10] [J. Burkardt's DistMesh repository](http://people.sc.fsu.edu/~jburkardt/m_src/distmesh/distmesh.html)
[11] [KOKO Mesh Generator](http://fc.isima.fr/~jkoko/codes.html)
License
-------
DistMesh is distributed for free under the GNU GPL; see the License
and Copyright notice for more information.
Modifications made to the original DistMesh code are copyrighted by
Precise Simulation Limited and licensed under the GNU GPL License.