https://github.com/privet-kitty/dufy
Colorimetry library for Common Lisp
https://github.com/privet-kitty/dufy
color colorimetry common-lisp munsell
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Colorimetry library for Common Lisp
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/privet-kitty/dufy
- Owner: privet-kitty
- License: mit
- Created: 2017-12-01T19:43:31.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2023-10-22T11:36:40.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-19T23:49:06.353Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: color, colorimetry, common-lisp, munsell
- Language: Common Lisp
- Homepage:
- Size: 2.37 MB
- Stars: 45
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 4
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-cl - dufy - exact color manipulation and conversion in various color models. [MIT][200]. (Miscellaneous ##)
README
Dufy - Color Library for Common Lisp
====
[](https://github.com/privet-kitty/dufy/actions)
[](http://quickdocs.org/dufy/)
Dufy is a library for exact color manipulation and conversion in various color spaces, which supports the following color models:
* RGB
* XYZ and xyY
* CIELAB and LChab
* CIELUV and LChuv
* HSV and HSL
* HSLuv and HPLuv
* Munsell Color System
* LMS
* spectrum (as spectral power distribution function)
Dufy can deal with the following concepts:
* Illuminant: A, B, C, D series, F series, etc. A new illuminant can be defined by white point or SPD.
* RGB space: sRGB, Adobe RGB, scRGB, etc. A new RGB space can be defined by primary coordinates, illuminant, method of gamma correction, bit per channel and other encoding characteristics.
* Observer (Color Matching Functions): CIE 1931 2° Standard Observer, CIE 1964 10°. Other observer model can be defined by color matching data.
* Color difference: ΔE*ab, CIE94, CIEDE2000, CMC l:c.
* Chromatic adaptaion transform: Bradford, Von Kries, etc. User-defined CAT is also available.
## Documentation
Besides this README file, most of the documentation is written as docstrings in the source code. [Quickdocs](http://quickdocs.org/dufy/) will be helpful to overview them. Some other information (e.g. changes between versions) is in [github wiki](https://github.com/privet-kitty/dufy/wiki).
## Dependencies
* alexandria
* cl-ppcre
You can install all of the dependent libraries via quicklisp.
## Install
The easiest way to install dufy is to use [quicklisp](https://www.quicklisp.org/beta/):
* (ql:quickload :dufy)
The latest version in this repository can also be loaded with quicklisp:
$ cd ~/quicklisp/local-projects # the path is held in ql:*local-project-directories*
$ git clone [email protected]:privet-kitty/dufy.git
$ sbcl # , ccl, etc.
* (ql:register-local-projects)
* (ql:quickload :dufy)
If you want to load the ASDF system directly without quicklisp, you should put the directory of dufy to an appropriate location (e.g. `~/common-lisp/dufy/`) and do `(asdf:load-system :dufy)`.
Note that the `master` branch always coincides with the latest stable release. The `develop` branch is usually where development happens.
## Basic Usage
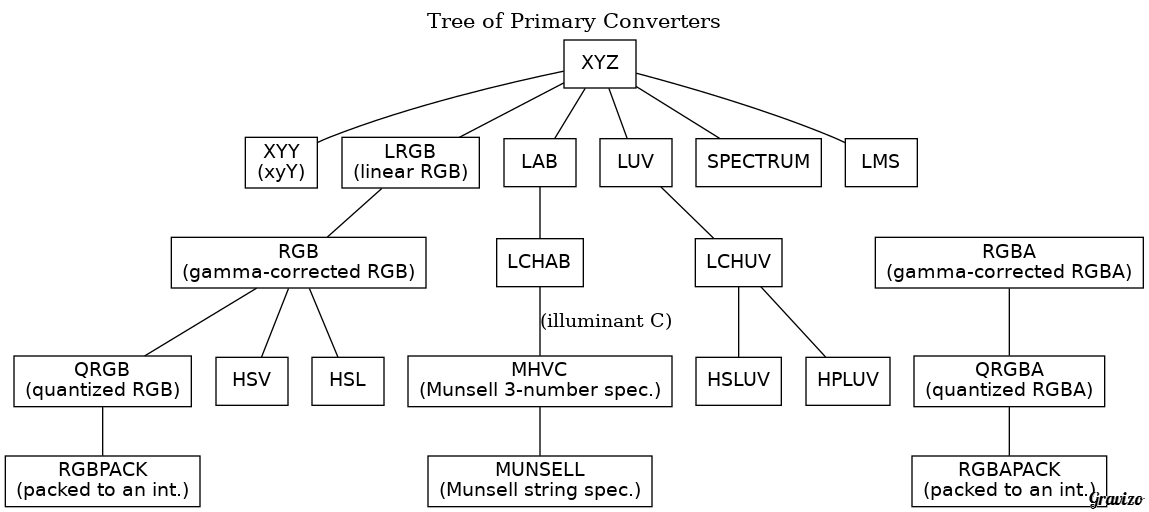
converter_tree
graph G {
graph [
labelloc = "t",
label = "Tree of Primary Converters",
fontsize = 16
];
node [
shape = "box",
fontname = "helvetica",
fontsize = 14
];
xyz [ label = "XYZ" ]
xyy [ label = "XYY\n(xyY)" ]
lrgb [ label = "LRGB\n(linear RGB)" ]
rgb [ label = "RGB\n(gamma-corrected RGB)" ]
qrgb [ label = "QRGB\n(quantized RGB)" ]
rgbpack [ label = "RGBPACK\n(packed to an int.)" ]
rgba [ label = "RGBA\n(gamma-corrected RGBA)" ]
qrgba [ label = "QRGBA\n(quantized RGBA)" ]
rgbapack [ label = "RGBAPACK\n(packed to an int.)" ]
lab [ label = "LAB" ]
lchab [ label = "LCHAB" ]
luv [ label = "LUV" ]
lchuv [ label = "LCHUV" ]
mhvc [ label = "MHVC\n(Munsell 3-number spec.)" ]
munsell [ label = "MUNSELL\n(Munsell string spec.)" ]
hsv [ label = "HSV" ]
hsl [ label = "HSL" ]
hsluv [ label = "HSLUV" ]
hpluv [ label = "HPLUV" ]
spectrum [ label = "SPECTRUM" ]
lms [ label = "LMS" ]
xyz -- xyy
xyz -- lms
xyz -- spectrum
xyz -- lrgb
lrgb -- rgb
rgb -- qrgb
qrgb -- rgbpack
rgba -- qrgba
qrgba -- rgbapack
xyz -- lab
lab -- lchab
xyz -- luv
luv -- lchuv
lchuv -- hsluv
lchuv -- hpluv
rgb -- hsv
rgb -- hsl
lchab -- mhvc [ label = "(illuminant C)" ]
mhvc -- munsell
{ rank=same; rgb rgba }
}
converter_tree
The fundamental color space of dufy is CIE XYZ (Illuminant D65): There are `xyz-to-` and `-to-xyz` converters for all other (connected) color spaces. Every converter function just receives numbers and returns multiple numbers:
```lisp
(dufy:lab-to-xyz 87.07 -78.15 -20.51) ; L*=87.07, a*=-78.15, b*=-20.51
;; => 0.3731544163010862d0 ; X
;; 0.701492216468595d0 ; Y
;; 1.0600774614243746d0 ; Z
(multiple-value-call #'dufy:xyz-to-qrgb
(dufy:lab-to-xyz 87.07 -78.15 -20.51)
:clamp nil)
;; => -169 ; R
;; 255 ; G
;; 255 ; B
(multiple-value-call #'dufy:xyz-to-qrgb
(dufy:lab-to-xyz 87.07 -78.15 -20.51))
;; => 0 ; R
;; 255 ; G
;; 255 ; B
```
In the second example, a conversion from CIELAB to quantized RGB, `xyz-to-qrgb` returns a negative R value, which means the color is out of gamut; it is clamped in the third example.
Out of which gamut, however? By default, `xyz-to-qrgb` (and all other RGB converters) regard it as sRGB (D65). You can specify the RGB space explicitly:
```lisp
(dufy:xyz-to-qrgb 0.37314 0.70144 1.0601 :rgbspace dufy:+srgb+ :clamp nil) ; sRGB
;; => -169
;; 255
;; 255
(dufy:xyz-to-qrgb 0.37314 0.70144 1.0601 :rgbspace dufy:+adobe+ :clamp nil) ; Adobe RGB
;; => 2
;; 255
;; 255
(dufy:xyz-to-qrgb 0.37314 0.70144 1.0601 :rgbspace dufy:+bg-srgb-10+ :clamp nil) ; bg-sRGB (10 bit)
;; => 47
;; 893
;; 893
;; In the Adobe RGB space and bg-sRGB space the color is within gamut.
```
Likewise most converters regard the implicit illuminant as D65. You can also specify it explicitly:
```lisp
(dufy:luv-to-xyz 100 0 0) ; Illuminant D65
(dufy:luv-to-xyz 100 0 0 :illuminant dufy:+illum-d65+) ; Illuminant D65
;; => 0.9504692366968726d0
;; 1.0d0
;; 1.0889440678362423d0
;; the white point of standard illuminant D65
(dufy:luv-to-xyz 100 0 0 :illuminant dufy:+illum-e+) ; Illuminant E
;; => 1.0d0
;; 1.0d0
;; 1.0000000000000004d0
```
## Modules
Dufy consists of several independent modules:
- dufy
- dufy/core
- dufy/hsluv (HSLuv and HPLuv color spaces)
- dufy/munsell (Munsell Color System)
- dufy/extra-data
- dufy/examples
Since the main package `dufy` contains slightly large colorimetric data, you may want to load `dufy/core` instead of `dufy` in some cases.
As of dufy 0.3.0, both the system names and the package names use the separator `/` instead of `-`, though the old package prefixes like `dufy-core` are left as nicknames.