https://github.com/prprprus/gds
Implement Data Structures With Go.
https://github.com/prprprus/gds
datastructures go golang implement implementation
Last synced: 9 months ago
JSON representation
Implement Data Structures With Go.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/prprprus/gds
- Owner: prprprus
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-06-21T06:45:55.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2021-06-09T13:15:33.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-13T00:53:58.717Z (9 months ago)
- Topics: datastructures, go, golang, implement, implementation
- Language: Go
- Homepage:
- Size: 196 KB
- Stars: 4
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README-zh.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

[](https://goreportcard.com/report/github.com/prprprus/ds)
[](https://godoc.org/github.com/prprprus/ds)
[](https://github.com/prprprus/ds/blob/master/LICENSE)
[](./README.md)
## 介绍
用 Go 实现数据结构。
## 目录
- [Iterator](#iterator)
- [ValueIterator](#valueIterator)
- [ReverseValueIterator](#reverseValueIterator)
- [IndexIterator](#indexIterator)
- [ReverseIndexIterator](#reverseIndexIterator)
- [KeyIterator](#keyIterator)
- [ReverseKeyIterator](#reverseKeyIterator)
- [Container](#container)
- [List](#list)
- [SinglyLinkedList](#singlylinkedlist)
- [DoubleLinkedList](#DoubleLinkedList)
- [ArrayList](#ArrayList)
- [Stack](#Stack)
- [LinkedListStack](#LinkedListStack)
- [ArrayStack](#ArrayStack)
- [Queue](#Queue)
- [LinkedListQueue](#LinkedListQueue)
- [ArrayQueue](#ArrayQueue)
- [SkipList](#SkipList)
- [Map](#Map)
- [HashMap](#HashMap)
- [LinkedHashMap](#LinkedHashMap)
- [SkipMap](#SkipMap)
- [Set](#Set)
- [HashSet](#HashSet)
- [LinkedHashSet](#LinkedHashSet)
- [SkipSet](#SkipSet)
- [Util](#Util)
- [Comparator](#Comparator)
- [Benchmarking](#Benchmarking)
## Iterator
### ValueIterator
提供了 6 种迭代器,如下。
`ValueIterator` 向后遍历值。
```go
type ValueIterator interface {
Next() bool
Begin()
Value() interface{}
}
```
### ReverseValueIterator
`ReverseValueIterator` 可以向前或者向后遍历值。
```go
type ReverseValueIterator interface {
ValueIterator
Prev() bool
End()
}
```
### IndexIterator
`IndexIterator` 向后遍历索引和值。
```go
type IndexIterator interface {
ValueIterator
Index() int
}
```
### ReverseIndexIterator
`ReverseIndexIterator` 可以向前或者向后遍历索引和值。
```go
type ReverseIndexIterator interface {
IndexIterator
Prev() bool
End()
}
```
### KeyIterator
`KeyIterator` 向后遍历键值对。
```go
type KeyIterator interface {
ValueIterator
Key() interface{}
}
```
### ReverseKeyIterator
`ReverseKeyIterator` 可以向前或者向后遍历键值对。
```go
type ReverseKeyIterator interface {
KeyIterator
Prev() bool
End()
}
```
不同的数据结构对迭代器的支持是不同的,如下。
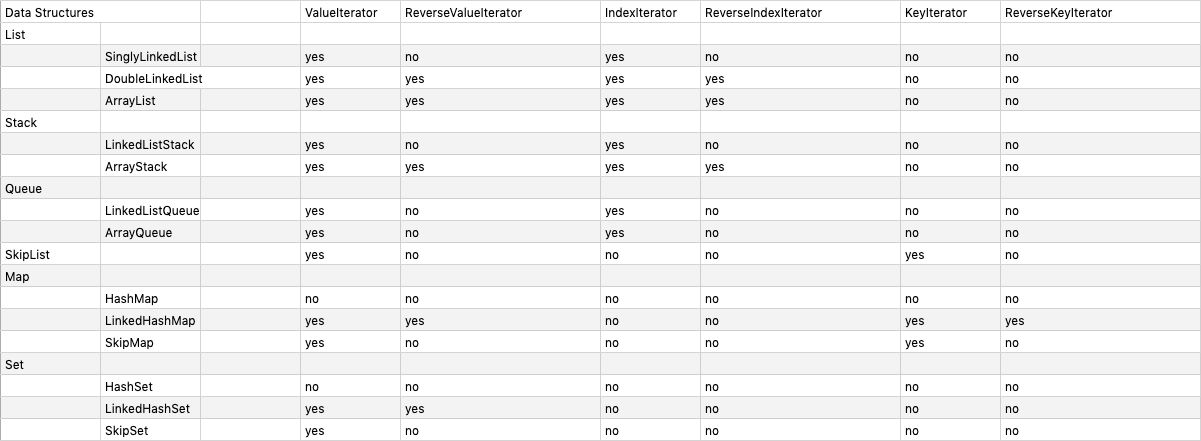
## Container
所有的数据结构都会实现 Container 接口。
```go
type Container interface {
Empty() bool
Size() int
Clear()
Values() []interface{}
}
```
### List
`List` 是有序的,而且值可以重复。
实现了 [Container](#container) 接口。
```go
type List interface {
Append(values ...interface{})
Get(index int) (interface{}, error)
Remove(index int) error
Contains(values ...interface{}) bool
Swap(i, j int) error
Insert(index int, values ...interface{}) error
Set(index int, value interface{}) error
IndexOf(value interface{}) (int, error)
container.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
}
```
#### SinglyLinkedList
`SinglyLinkedList` 的当前元素会指向下一个元素。
实现了 [List](#list), [ValueIterator](#ValueIterator) and [IndexIterator](#indexIterator) 接口。

```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/list/singlylinkedlist"
)
func main() {
list := singlylinkedlist.New() // []
list.Append(1) // [1]
list.Append(2) // [1, 2]
list.Append(3) // [1, 2, 3]
list.PreAppend(4) // [4, 1, 2, 3]
_, _ = list.Get(0) // 4, nil
_, _ = list.Get(999) // nil, ErrIndex
_ = list.Remove(2) // [4, 1, 3]
_ = list.Contains() // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 1) // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 3) // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 1, 3, 5) // false
_ = list.Swap(0, 1) // [1, 4, 3]
_ = list.Insert(1, 5, 6, 7, 8) // [1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 3]
_ = list.Set(3, -1) // [1, 4, 5, -1, 7, 8, 3]
// iterator
it := list.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 1
// 1 4
// 2 5
// 3 -1
// 4 7
// 5 8
// 6 3
_, _ = list.IndexOf(1) // 0, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(8) // 5, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(100) // -1, ErrIndexOf
list.Reverse() // [3, 8, 7, -1, 5, 4, 1]
_ = list.Empty() // false
_ = list.Size() // 7
_ = list.Values() // [3 8 7 -1 5 4 1]
list.Clear() // []
}
```
#### DoubleLinkedList
`DoubleLinkedList` 的当前元素和下一个元素之间相互指向。
实现了 [List](#list), [ValueIterator](#ValueIterator), [ReverseValueIterator](#ReverseValueIterator), [IndexIterator](#IndexIterator) and [ReverseIndexIterator](#ReverseIndexIterator) 接口。

```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/list/doublelinkedlist"
)
func main() {
list := doublelinkedlist.New() // []
list.Append(1) // [1]
list.Append(2) // [1 2]
list.Append(3) // [1 2 3]
list.PreAppend(4) // [4 1 2 3]
_, _ = list.Get(0) // 4, nil
_, _ = list.Get(999) // nil, ErrIndex
_ = list.Remove(2) // [4 1 3]
_ = list.Contains() // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 1) // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 3) // true
_ = list.Contains(4, 1, 3, 5) // false
_ = list.Swap(0, 1) // [1 4 3]
_ = list.Insert(1, 5, 6, 7, 8) // [1 4 5 6 7 8 3]
_ = list.Set(3, -1) // [1 4 5 -1 7 8 3]
// iterator
it := list.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 1
// 1 4
// 2 5
// 3 -1
// 4 7
// 5 8
// 6 3
it.End()
for it.Prev() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 6 3
// 5 8
// 4 7
// 3 -1
// 2 5
// 1 4
// 0 1
_, _ = list.IndexOf(1) // 0, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(8) // 5, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(100) // -1, ErrIndexOf
list.Reverse() // [3 8 7 -1 5 4 1]
_ = list.Empty() // false
_ = list.Size() // 7
_ = list.Values() // [3 8 7 -1 5 4 1]
list.Clear() // []
}
```
#### ArrayList
`ArrayList` 是一种动态数组,可以根据容量和元素个数之间的比例动态伸缩。
实现了 [List](#list), [ValueIterator](#ValueIterator), [ReverseValueIterator](#ReverseValueIterator), [IndexIterator](#IndexIterator) and [ReverseIndexIterator](#ReverseIndexIterator) 接口。

```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/list/arraylist"
)
func main() {
list := arraylist.New() // []
list.Append(1) // [1]
list.Append(2) // [1 2]
list.Append(3) // [1 2 3]
_, _ = list.Get(0) // 1, nil
_, _ = list.Get(999) // nil, ErrIndex
_ = list.Remove(2) // [1 2]
_ = list.Contains() // true
_ = list.Contains(1, 2) // true
_ = list.Contains(2) // true
_ = list.Contains(1, 2, 3) // false
_ = list.Swap(0, 1) // [2 1]
_ = list.Insert(1, 5, 6, 7, 8) // [2 1 5 6 7 8]
_ = list.Set(3, -1) // [2 1 5 -1 7 8]
// iterator
it := list.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 2
// 1 1
// 2 5
// 3 -1
// 4 7
// 5 8
it.End()
for it.Prev() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 5 8
// 4 7
// 3 -1
// 2 5
// 1 1
// 0 2
_, _ = list.IndexOf(1) // 1, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(8) // 5, nil
_, _ = list.IndexOf(100) // -1, ErrIndexOf
_ = list.Empty() // false
_ = list.Size() // 6
_ = list.Values() // [2 1 5 -1 7 8]
list.Clear() // []
}
```
### Stack
`Stack` 是一种先进后出的数据结构。
实现了 [Container](#container) 接口。

```go
type Stack interface {
Push(value interface{})
Pop() (interface{}, error)
Peek() (interface{}, error)
container.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
}
```
#### LinkedListStack
`LinkedListStack` 是基于 [SinglyLinkedList](#SinglyLinkedList) 实现的栈。
实现了 [Stack](#Stack), [ValueIterator](#ValueIterator) and [IndexIterator](#IndexIterator) 接口。
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/stack/linkedliststack"
)
func main() {
stack := linkedliststack.New() // []
stack.Push(1) // [1]
stack.Push(2) // [2 1]
stack.Push(3) // [3 2 1]
// iterator
it := stack.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 3
// 1 2
// 2 1
_, _ = stack.Peek() // 3, nil
_, _ = stack.Pop() // 3, nil
_, _ = stack.Peek() // 2, nil
_ = stack.Empty() // false
_ = stack.Size() // 2
_ = stack.Values() // [2 1]
stack.Clear() // []
}
```
#### ArrayStack
`ArrayStack` 是基于 [ArrayList](#ArrayList) 实现的栈。
实现了 [Stack](#Stack), [ValueIterator](#ValueIterator), [ReverseValueIterator](#ReverseValueIterator), [IndexIterator](#IndexIterator) and [ReverseIndexIterator](#ReverseIndexIterator) 接口。
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/stack/arraystack"
)
func main() {
stack := arraystack.New() // []
stack.Push(1) // [1]
stack.Push(2) // [2 1]
stack.Push(3) // [3 2 1]
// iterator
it := stack.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 3
// 1 2
// 2 1
_, _ = stack.Peek() // 3, nil
_, _ = stack.Pop() // 3, nil
_, _ = stack.Peek() // 2, nil
_ = stack.Empty() // false
_ = stack.Size() // 2
_ = stack.Values() // [2 1]
stack.Clear() // []
}
```
### Queue
`Queue` 是一种先进先出的数据结构。
实现了 [Container](#container) 接口。

```go
type Queue interface {
Put(value interface{})
Get() (interface{}, error)
container.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
}
```
#### LinkedListQueue
`LinkedListQueue` 是基于 [SinglyLinkedList](#SinglyLinkedList) 实现的队列。
实现了 [Queue](#Queue), [ValueIterator](#ValueIterator) and [IndexIterator](#IndexIterator) 接口。
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/queue/linkedlistqueue"
)
func main() {
queue := linkedlistqueue.New() // []
queue.Put(1) // [1]
queue.Put(2) // [1 2]
queue.Put(3) // [1 2 3]
queue.Put(4) // [1 2 3 4]
// iterator
it := queue.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 1
// 1 2
// 2 3
// 3 4
_, _ = queue.Get() // 1, nil
_, _ = queue.Get() // 2, nil
_ = queue.Empty() // false
_ = queue.Size() // 2
_ = queue.Values() // [3 4]
queue.Clear() // []
}
```
#### ArrayQueue
`ArrayQueue` 是基于 [ArrayList](#ArrayList) 实现的队列。
实现了 [Queue](#Queue), [ValueIterator](#ValueIterator) and [IndexIterator](#IndexIterator) 接口。
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/queue/arrayqueue"
)
func main() {
queue := arrayqueue.New() // []
queue.Put(1) // [1]
queue.Put(2) // [1 2]
queue.Put(3) // [1 2 3]
queue.Put(4) // [1 2 3 4]
// iterator
it := queue.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Index(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 0 1
// 1 2
// 2 3
// 3 4
_, _ = queue.Get() // 1, nil
_, _ = queue.Get() // 2, nil
_ = queue.Empty() // false
_ = queue.Size() // 2
_ = queue.Values() // [3 4]
queue.Clear() // []
}
```
### SkipList
`SkipList` 是一种带有随机性的数据结构,它的性能可以和红黑树媲美。需要注意的是,键必须是可以比较的类型。
实现了 [Container](#container), [ValueIterator](#ValueIterator) and [KeyIterator](#KeyIterator) 接口。

```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/skiplist"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/util"
)
func main() {
skiplist := skiplist.New(util.IntComparator) // []
skiplist.Set(1, "a") // [{1: "a"}]
skiplist.Set(2, "b") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"}]
skiplist.Set(3, "c") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"}]
skiplist.Set(4, "d") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"} {4: "d"}]
// iterator
it := skiplist.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Key(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 1 a
// 2 b
// 3 c
// 4 d
_ = skiplist.Exists(1) // true
_ = skiplist.Exists(9) // false
_, _ = skiplist.Get(1) // "a", nil
_, _ = skiplist.Get(3) // "c", nil
_ = skiplist.Remove(2) // nil
_ = skiplist.Keys() // [1 3 4]
_ = skiplist.Empty() // false
_ = skiplist.Size() // 3
_ = skiplist.Values() // [a c d]
skiplist.Clear() // []
}
```
### Map
`Map` 用于存储键值对,拥有出色的性能。需要注意的是,键必须是可以比较的类型。
实现了 [Container](#container) 接口。
```go
type Map interface {
Put(key, value interface{})
Get(key interface{}) (interface{}, error)
Remove(key interface{})
container.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
}
```
#### HashMap
`HashMap` 是基于哈希表实现的 map。
实现了 [Map](#Map) 接口。

```go
package main
import (
"github.com/prprprus/ds/maps/hashmap"
)
func main() {
m := hashmap.New() // []
m.Put(1, "a") // [{1: "a"}]
m.Put(2, "b") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"}]
m.Put(3, "c") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"}]
m.Put(4, "d") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"} {4: "d"}]
_ = m.Keys() // [1 2 3 4] (Note: order of random)
_, _ = m.Get(1) // "a", nil
_, _ = m.Get(3) // "c", nil
_ = m.Remove(2) // nil
_ = m.Keys() // [1 3 4]
_ = m.Empty() // false
_ = m.Size() // 3
_ = m.Values() // [a c d] (Note: order of random)
m.Clear() // []
}
```
#### LinkedHashMap
`LinkedHashMap` 是基于哈希表和 [DoubleLinkedList](#DoubleLinkedList) 实现的 map,它提供了额外的有序键值对。
实现了 [Map](#Map), [ValueIterator](#ValueIterator), [ReverseValueIterator](#ReverseValueIterator), [KeyIterator](#KeyIterator) and [ReverseKeyIterator](#ReverseKeyIterator) 接口。
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/maps/linkedhashmap"
)
func main() {
m := linkedhashmap.New() // []
m.Put(1, "a") // [{1: "a"}]
m.Put(2, "b") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"}]
m.Put(3, "c") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"}]
m.Put(4, "d") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"} {4: "d"}]
// iterator
it := m.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Key(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 1 a
// 2 b
// 3 c
// 4 d
it.End()
for it.Prev() {
fmt.Println(it.Key(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 4 d
// 3 c
// 2 b
// 1 a
_ = m.Keys() // [1 2 3 4]
_, _ = m.Get(1) // "a", nil
_, _ = m.Get(3) // "c", nil
_ = m.Remove(2) // nil
_ = m.Keys() // [1 3 4]
_ = m.Empty() // false
_ = m.Size() // 3
_ = m.Values() // [a c d]
m.Clear() // []
}
```
#### SkipMap
`SkipMap` 是基于 [SkipList](#SkipList) 实现的 map。
实现了 [Map](#Map), [ValueIterator](#ValueIterator) and [KeyIterator](#KeyIterator) 接口。
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/maps/linkedhashmap"
)
func main() {
m := linkedhashmap.New() // []
m.Put(1, "a") // [{1: "a"}]
m.Put(2, "b") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"}]
m.Put(3, "c") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"}]
m.Put(4, "d") // [{1: "a"} {2: "b"} {3: "c"} {4: "d"}]
// iterator
it := m.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Key(), it.Value())
}
// output:
// 1 a
// 2 b
// 3 c
// 4 d
_ = m.Keys() // [1 2 3 4]
_, _ = m.Get(1) // "a", nil
_, _ = m.Get(3) // "c", nil
_ = m.Remove(2) // nil
_ = m.Keys() // [1 3 4]
_ = m.Empty() // false
_ = m.Size() // 3
_ = m.Values() // [a c d]
m.Clear() // []
}
```
### Set
`Set` 用于存储不可重复的值,通常也拥有出色的性能。
实现了 [Container](#container) 接口。
```go
type Set interface {
Add(values ...interface{})
Remove(values ...interface{}) error
Contains(values ...interface{}) bool
container.Container
// Empty() bool
// Size() int
// Clear()
// Values() []interface{}
}
```
#### HashSet
`HashSet` 是基于哈希表实现的 set。
实现了 [Set](#Set) 接口。
```go
package main
import (
"github.com/prprprus/ds/set/hashset"
)
func main() {
s := hashset.New() // []
s.Add(1) // [1]
s.Add(2) // [1 2]
s.Add(3) // [1 2 3]
_ = s.Contains() // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 2, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(2, 3, 4) // false
_ = s.Remove(2) // nil
_ = s.Empty() // false
_ = s.Size() // 2
_ = s.Values() // [1 3]
s.Clear() // []
}
```
#### LinkedHashSet
`LinkedHashSet` 是基于哈希表和 [DoubleLinkedList](#DoubleLinkedList) 实现的 set,它保证了值是有序的。
实现了 [Set](#Set), [ValueIterator](#valueIterator) and [ReverseValueIterator](#reverseValueIterator) 接口。
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/set/linkedhashset"
)
func main() {
s := linkedhashset.New() // []
s.Add(1) // [1]
s.Add(2) // [1 2]
s.Add(3) // [1 2 3]
// iterator
it := s.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Value())
}
// output:
// 1
// 2
// 3
it.End()
for it.Prev() {
fmt.Println(it.Value())
}
// output:
// 3
// 2
// 1
_ = s.Contains() // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 2, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(2, 3, 4) // false
_ = s.Remove(2) // nil
_ = s.Empty() // false
_ = s.Size() // 2
_ = s.Values() // [1 3]
s.Clear() // []
}
```
#### SkipSet
`SkipSet` 是基于 [SkipList](#SkipList) 实现的 set。
实现了 [Set](#Set) and [ValueIterator](#valueIterator) 接口。
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/set/skipset"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/util"
)
func main() {
s := skipset.New(util.IntComparator) // []
s.Add(1) // [1]
s.Add(2) // [1 2]
s.Add(3) // [1 2 3]
// iterator
it := s.Iterator()
it.Begin()
for it.Next() {
fmt.Println(it.Value())
}
// output:
// 1
// 2
// 3
_ = s.Contains() // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 2, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(1, 3) // true
_ = s.Contains(2, 3, 4) // false
_ = s.Remove(2) // nil
_ = s.Empty() // false
_ = s.Size() // 2
_ = s.Values() // [1 3]
s.Clear() // []
}
```
## Util
包含一些辅助函数。
### Comparator
提供了用于内置类型的比较器,如下。
```go
func IntComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int8Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int16Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int32Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Int64Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UIntComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt8Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt16Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt32Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func UInt64Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Float32Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func Float64Comparator(a, b interface{}) int
func ByteComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func RuneComparator(a, b interface{}) int
func StringComparator(a, b interface{}) int
```
返回值的意义如下。
```
-1 => a < b
0 => a == b
1 => a > b
```
对于自定义类型,也可以创建相对应的比较器。
```go
package main
import (
"fmt"
"github.com/prprprus/ds/set/skipset"
)
type People struct {
name string
age int
}
func AgeComparator(a, b interface{}) int {
c1 := a.(People)
c2 := b.(People)
switch {
case c1.age < c2.age:
return -1
case c1.age > c2.age:
return 1
default:
return 0
}
}
func main() {
s := skipset.New(AgeComparator)
s.Add(People{"Wade", 35})
s.Add(People{"Simon", 32})
s.Add(People{"yiyi", 22})
fmt.Println(s.Values()) // [{"yiyi", 22}, {"Simon", 32}, {"Wade", 35}]
}
```
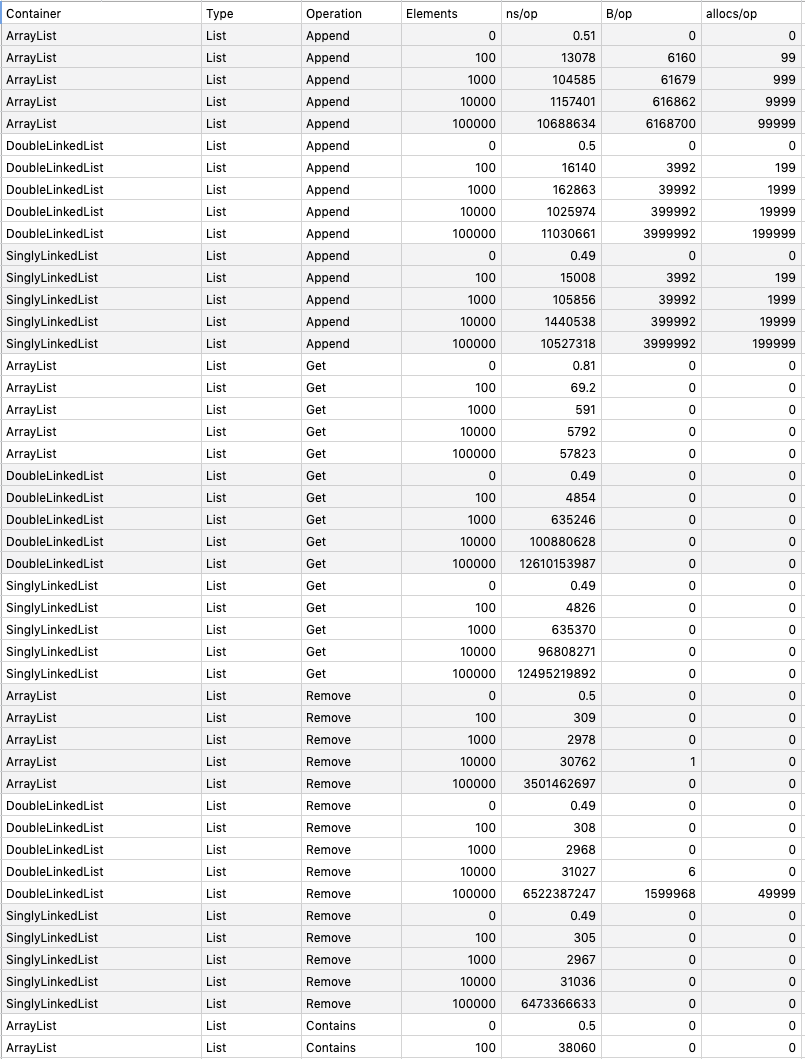
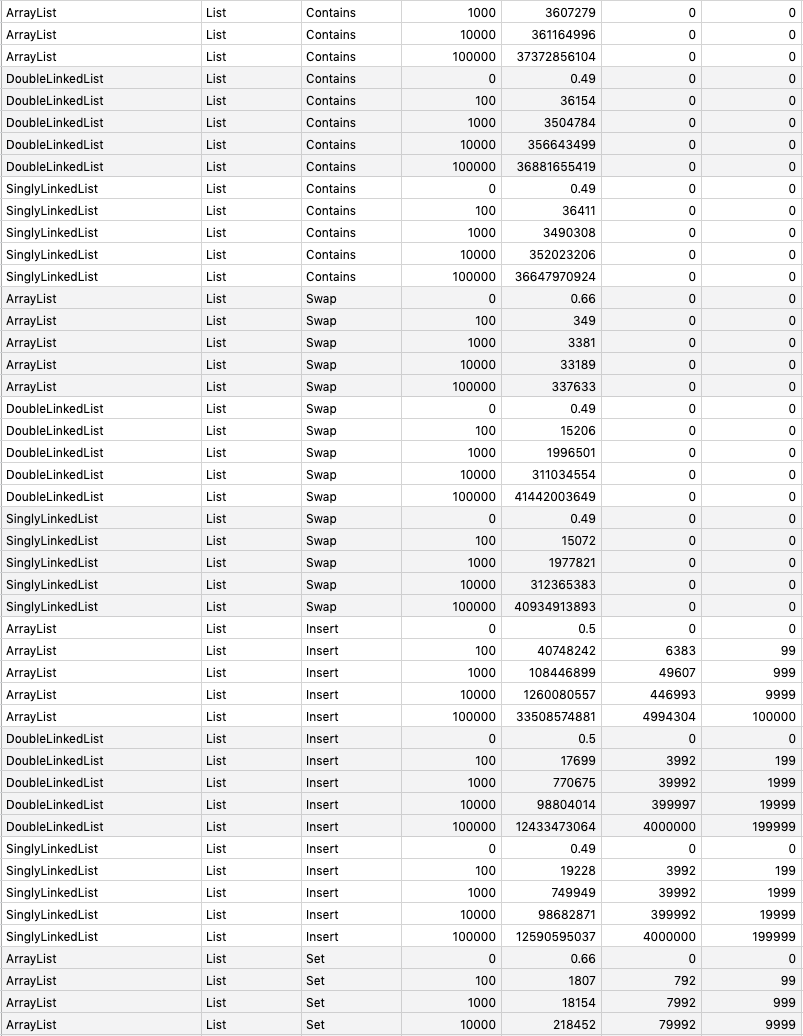
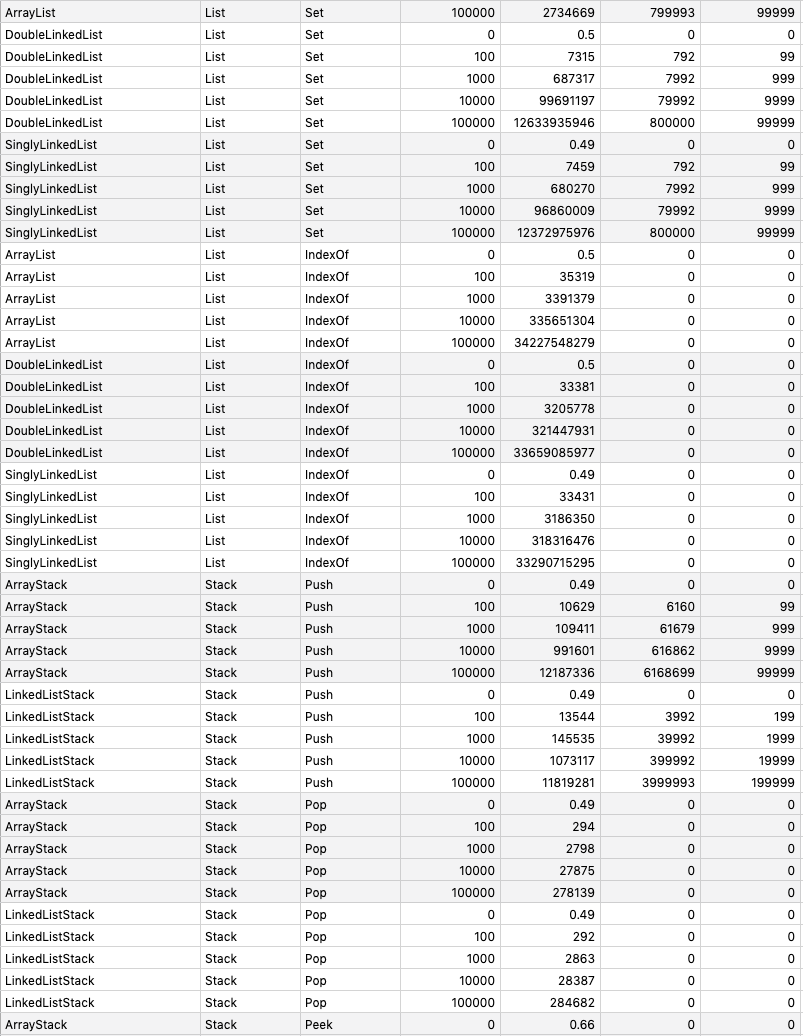
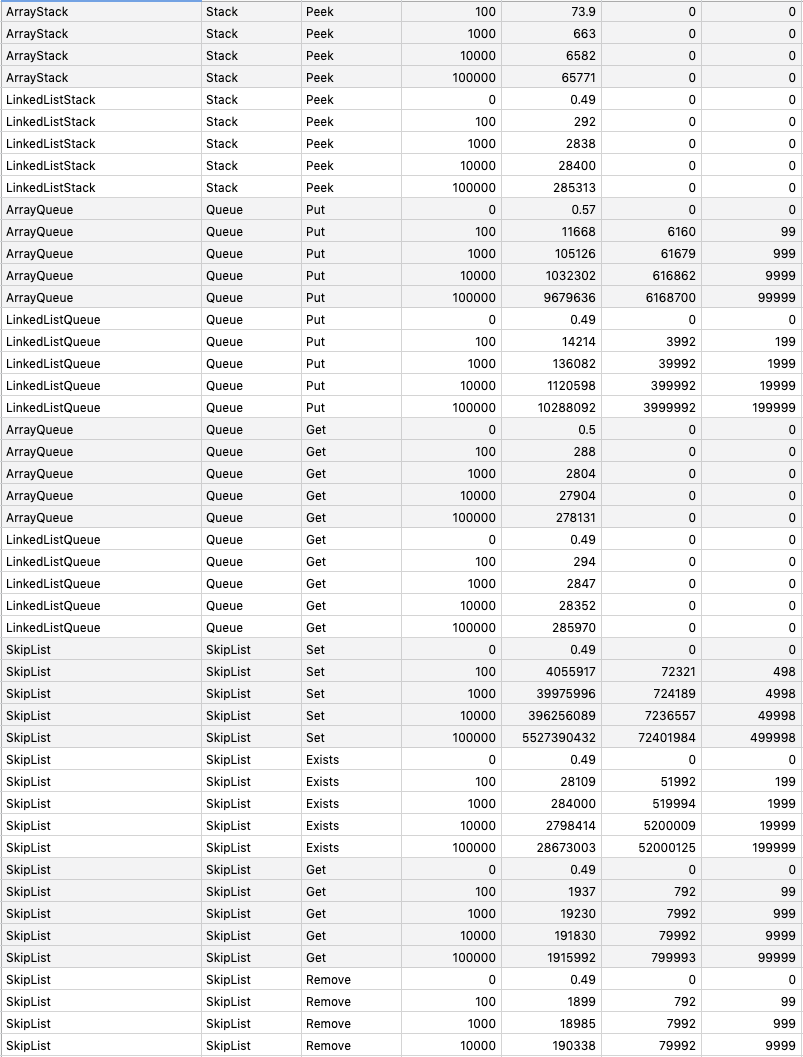
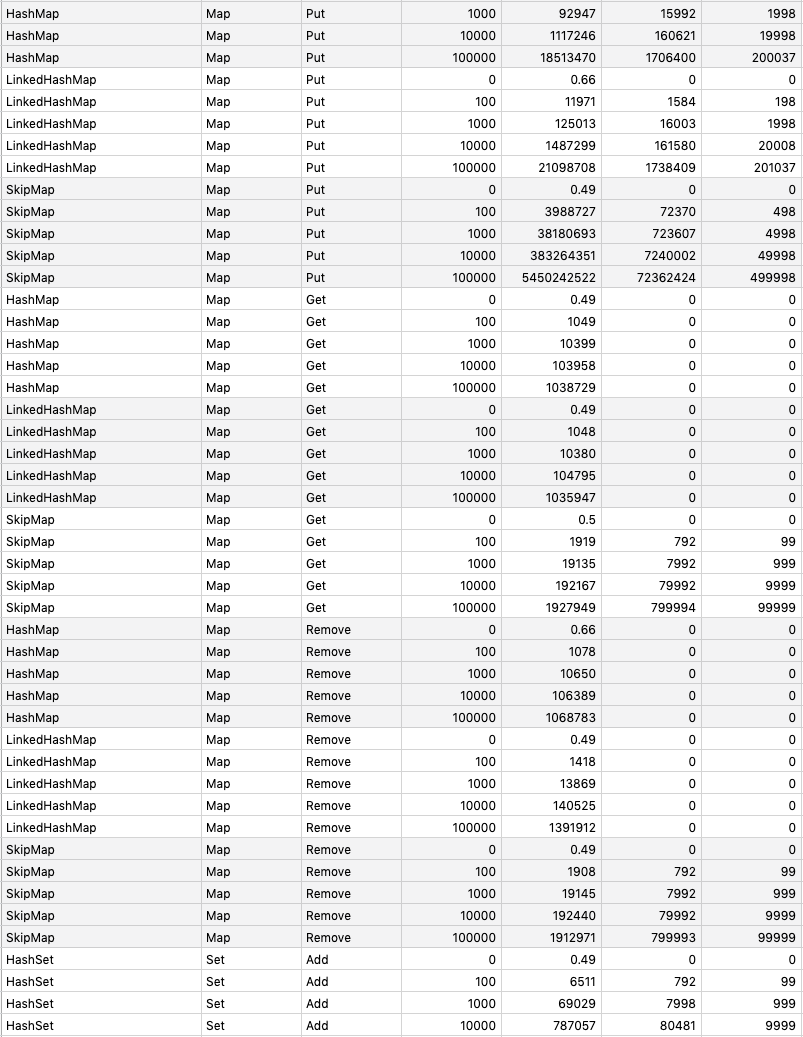
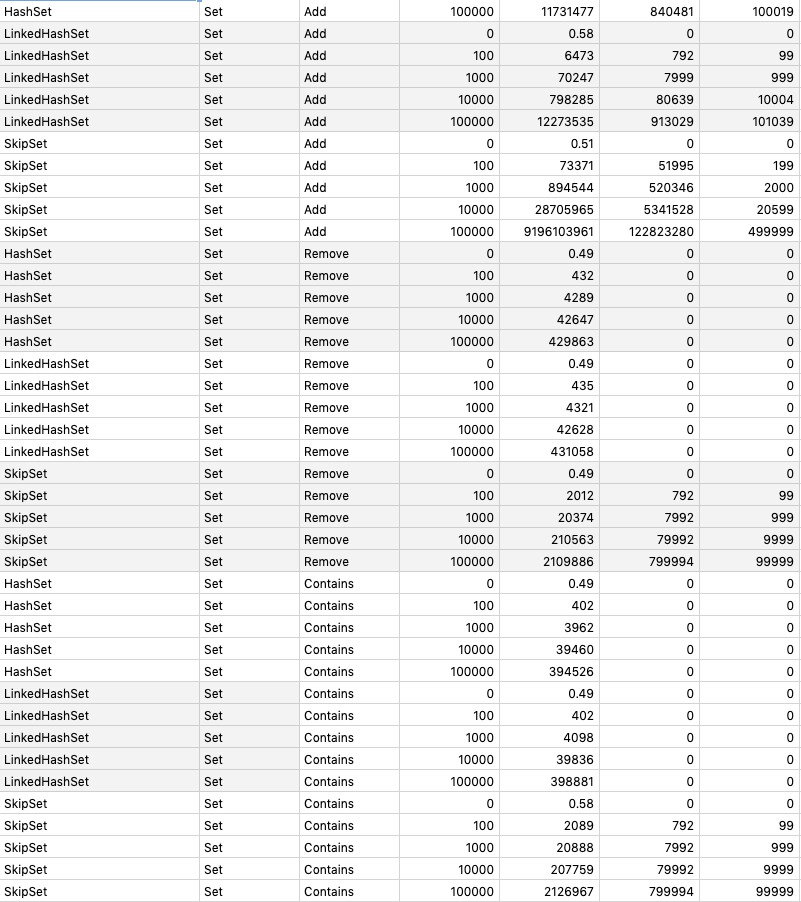
## Benchmarking
`go test -run=NO_TEST -bench=. -benchmem -benchtime 1s github.com/prprprus/ds/...`