https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec
https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec
module supported
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec
- Owner: puppetlabs
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2018-09-26T21:38:41.000Z (almost 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-02-19T00:21:12.000Z (4 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-29T18:06:56.220Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: module, supported
- Language: Ruby
- Homepage:
- Size: 703 KB
- Stars: 9
- Watchers: 18
- Forks: 25
- Open Issues: 2
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
- Codeowners: CODEOWNERS
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# splunk_hec
##### Table of Contents
1. [Overview](#overview)
2. [Requirements](#requirements)
3. [Installation](#installation)
4. [Custom Installation](#custom-installation)
5. [SSL Configuration](#ssl-configuration)
6. [Fact Configuration](#fact-configuration)
7. [Customized Reporting](#customized-reporting)
8. [Tasks](#tasks)
9. [Advanced Settings](#advanced-settings)
10. [FIPS Mode](#fips-mode)
11. [Advanced Topics](#advanced-topics)
12. [Known Issues](#known-issues)
13. [Breaking Changes](#breaking-changes)
14. [Release Process](#release-process)
## Overview
This module provides three services to Puppet and Splunk users.
1. A report processor to allow sending Puppet Agent run reports to Splunk. When a Puppet agent completes a run and submits some of the report data to Puppet, this module's processor can be invoked to send that report to Splunk. After this module is installed in your environment, to enable sending node reports to Splunk, do the following:
* Classify your Puppet Servers with the `splunk_hec` class.
* Set the `url` parameter which refers to your Splunk Hec url.
* Set the `token` parameter which will be the HEC token you create in Splunk.
* Set the `enable_reports` parameter to **true**.
For more advanced configuration options including sending reports based on specific conditions see the [Customized Reporting](#customized-reporting) section below.
2. A fact terminus to submit node facts to Splunk. See [Fact Terminus Support](https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec/blob/main/docs/fact_terminus_support.md) for details.
3. A PE Event Forwarding processor for sending data received from the [PE Event Forwarding](https://forge.puppet.com/modules/puppetlabs/pe_event_forwarding) module to Splunk. This data can include the details of Task and Plan executions that were initiated by the Puppet Orchestrator (clicking execute task|plan from the console or puppet command line), or it can be events from rbac, the node classifier, the console, or code-manager. To enable this feature, after the PE Event Forwarding module has been configured, set the `events_reporting_enabled` parameter on the `splunk_hec` class to **true**.
**Note**: This is a PE only feature and depends on the [PE Event Forwarding](https://forge.puppet.com/modules/puppetlabs/pe_event_forwarding) module being installed and classified on the Puppet Server nodes in your environment. Please see the documentation in that module for details on how to install and configure that module.
There is also the [Puppet Alert Actions](https://splunkbase.splunk.com/app/4928/) app, which contains the alert actions that were previously shipped in the Puppet Report Viewer:
> The Puppet Alert Actions app allows you to run custom Tasks in Puppet Enterprise or retrieve detailed Report information about a particular Puppet Event that would be sent to the Puppet Report Viewer. For additional information on configuring Puppet Alert Actions, please see our documentation located [here](https://github.com/puppetlabs/TA-puppet-alert-actions).
There are two Tasks included in this module, `splunk_hec:bolt_apply` and `splunk_hec:bolt_result`, that provide a pre-packaged way to compose Bolt Plans that submit data to Splunk every time they are run. Example plans are included which demonstrate task usage.
## Requirements
* Puppet Enterprise (PE) or Open Source Puppet
* Splunk
This was tested on the Puppet Enterprise LTS release, Puppet 7 and Puppet 8, using stock gems of `yaml`, `json`, and `net::https`.
* While most of this module is PE and Open Source, using the PE Event Forwarding processor is PE only because it gathers data from API's that exist only in Puppet Enterprise.
## Installation
Instructions assume you are using Puppet Enterprise. For Open Source Puppet installations please see the [Custom Installation](#custom-installation) section.
1. Install the [Puppet Report Viewer](https://splunkbase.splunk.com/app/4413/) app in Splunk if not already installed.
* Please see [Splunk Installation](https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/SearchTutorial/InstallSplunk) if you need to install Splunk.
* Alternatively you can [install Splunk via Bolt](https://forge.puppet.com/configuration-management/puppetlabs/deploy-splunk-enterprise-in-minutes).
2. Create an HEC token in Splunk:
* Navigate to `Settings` > `Data Input` in your Splunk console.
* Add a new `HTTP Event Collector` with a name of your choice.
* Ensure `indexer acknowledgement` is not enabled.
* Click Next and set the source type to Automatic.
* Ensure the `App Context` is set to `Puppet Report Viewer`.
* Add the `main` index
* Set the **Default Index** to `main`.
* Click **Review** and then **Submit**.
* When complete the HEC token should look something like this:
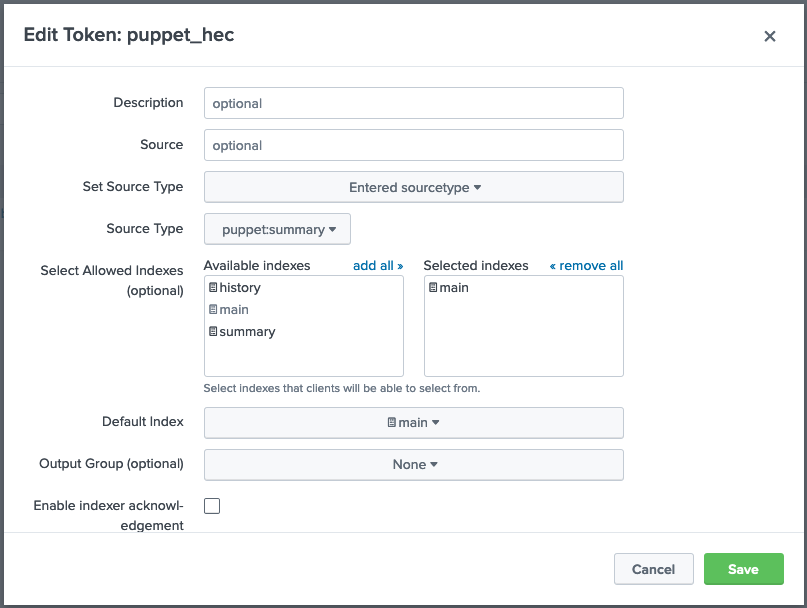
3. Install the module and add the `splunk_hec` class to the **PE Master** node group.
* Install the `splunk_hec` module on your Puppet Primary Server.
* `puppet module install puppetlabs-splunk_hec`
* In the PE console, navigate to `Node groups` and expand `PE Infrastructure`.
* Select `PE Master` and navigate to the `Classes` tab.
* Add the `splunk_hec` class.
* Configure the following parameters:
```
enable_reports = true
manage_routes = true
token =
url = something like https://splunk-8.splunk.internal:8088/services/collector
```
* Commit the changes.
* Run Puppet on the node group; this will cause a restart of the `pe-puppetserver` service.
4. Log into the Splunk console and search `index=* sourcetype=puppet:summary`, if everything was done properly you should see the reports from the systems in your Puppet environment.
## Source Types
1. `puppet:summary`
Puppet agent node reports.
2. `puppet:facts`
Node facts sent by the facts terminus enabled by setting `manage_routes` to true.
3. `puppet:jobs`
Events gathered from the [Puppet Jobs API](https://puppet.com/docs/pe/latest/orchestrator_api_jobs_endpoint.html#get_jobs)
The following source types all refer to different types of events gathered from the [Puppet Activities API](https://puppet.com/docs/pe/latest/activity_api_events.html#activity-api-v2-get-events)
4. `puppet:activities_rbac`
RBAC events such as creating and/or modifying users or groups, and user logins.
**Note**: RBAC events can be disabled from the pe_event_forwarding module for performance reasons. Ensure the `disable_rbac` parameter is set to false in the pe_event_forwarding module if you wish to send RBAC events to Splunk.
5. `puppet:activities_classifier`
Classifier events such as creating node groups, or modifying the properties of node groups.
6. `puppet:activities_console`
Console events such as requesting Task or Plan runs via the console.
7. `puppet:activities_code_manager`
Code manager events.
## Custom Installation
> **Please Note**: If you are installing this module using a [`control-repo`](https://puppet.com/docs/pe/latest/control_repo.html) you must have `splunk_hec` in your production environment's [`Puppetfile`](https://puppet.com/docs/pe/latest/puppetfile.html) so the Puppet Server process can properly load the required libraries. You can then create a feature branch to enable them and test the configuration, but the libraries **must be** in `production`; otherwise the feature branch won't work as expected. If your Puppet Server is in a different environment, please add this module to the `Puppetfile` in that environment as well.
The steps below will help install and troubleshoot the report processor on a standard Puppet Primary Server; including manual steps to configure compilers (Puppet Servers), and to use the included `splunk_hec` class. Because one is modifying production machines, these steps allow you to validate your settings before deploying the changes live.
1. Install the Puppet Report Viewer app in Splunk. This will import the needed source types to configure Splunk's HTTP Endpoint Collector (HEC) and provide a dashboard that will show the reports once they are sent to Splunk.
2. Create a Splunk HEC Token or use an existing one that sends to `main` index and **does not** have acknowledgement enabled. Follow the steps provided by Splunk's [Getting Data In Guide](http://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/Data/UsetheHTTPEventCollector) if you are new to HTTP Endpoint Collectors.
3. [Install this Puppet module](https://puppet.com/docs/puppet/latest/modules_installing.html) in the environment that your Puppet Servers are using (e.g. `production`).
4. Run `puppet plugin download` on your Puppet Servers to sync the content. Some users with strict permissions may need to run `umask 022` first.
* **Please Note**: If permissions are too restrictive you may see the following error in the Puppet Server logs:
```
Could not find terminus splunk_hec for indirection facts
```
5. Create `/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/splunk_hec.yaml` (see the [examples directory](https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec/blob/main/examples/splunk_hec.yaml)), adding your Splunk Server URL to the `url` parameter (e.g. `https://splunk-dev:8088/services/collector`) and HEC Token created during step 2 to the `splunk_token` parameter.
* You can add `timeout` as an optional parameter. The **default value** is `1` second for both open and read sessions, so take value x2 for real world use.
* **PE Only**: Provide the `pe_console` parameter value. This is the FQDN for the PE console, which Splunk can use to lookup further information if the installation utilizes compilers (it is best practice to set this if you're anticipating scaling the installation in the future).
```
---
"url" : "https://splunk-dev.testing.local:8088/services/collector"
"token" : "13311780-EC29-4DD0-A796-9F0CDC56F2AD"
```
(**Note**: If [Disaster Recovery](https://puppet.com/docs/pe/latest/dr_overview.html) is enabled you will need to ensure these settings exist on the Replica node as well. This is often done through the `PE HA Replica` node group.)
6. Run `puppet apply -e 'notify { "hello world": }' --reports=splunk_hec` from the Puppet Server, this will load the report processor and test your configuration settings without actually modifying your Puppet Server's running configuration. If you are using the Puppet Report Viewer app in Splunk then you will see the page update with new data. If not, perform a search by the `sourcetype` you provided with your HEC configuration.
7. If configured properly the Puppet Report Viewer app in Splunk will show 1 node in the `Overview` tab.
8. Now it is time to roll these settings out to the fleet of Puppet Servers in the installation. For PE users:
* In the [PE console](https://puppet.com/docs/pe/latest/console_accessing.html), navigate to `Node groups` and expand `PE Infrastructure`.
* Select `PE Master` and navigate to the `Classes` tab.
* Click **Refresh** to ensure that the `splunk_hec` class is loaded.
* Add new class `splunk_hec`.
* From the `Parameter` drop down list you will need to configure at least `url` and `token`, providing the same values from the testing configuration file.
* Optionally set `enable_reports` to `true` if there isn't another component managing the servers reports setting. Otherwise manually add `splunk_hec` to the settings as described in the [manual steps](#manual-steps) below.
* Commit changes and run Puppet. It is best to navigate to the `PE Certificate Authority` node group and run Puppet there first, before running Puppet on the remaining nodes.
9. For Inventory support in the Puppet Report Viewer, see [Fact Terminus Support](https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec/blob/main/docs/fact_terminus_support.md).
#### Manual Steps:
* Add `splunk_hec` to `reports` under the `[master]` configuration block in `/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/puppet.conf`:
```
[master]
node_terminus = classifier
storeconfigs = true
storeconfigs_backend = puppetdb
reports = puppetdb,splunk_hec
```
* [Restart the `pe-puppetserver`](https://puppet.com/docs/puppetserver/latest/restarting.html) process (`puppet-server` for Open Source Puppet) for it to reload the configuration and the plugin.
* Run `puppet agent -t` on an agent; if you are using the suggested name, use `source="http:puppet-report-summary"` in your Splunk search field to show the reports as they arrive.
## SSL Configuration
Configuring SSL support for this report processor and tasks requires that the Splunk HEC service being used has a [properly configured SSL certificate](https://docs.splunk.com/Documentation/Splunk/latest/Security/AboutsecuringyourSplunkconfigurationwithSSL). Once the HEC service has a valid SSL certificate, the CA will need to be made available to the report processor to load. The supported path is to install a copy of the Splunk CA to a directory called `/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/splunk_hec/` and provide the file name to `splunk_hec` class.
You can manually update the `splunk_hec.yaml` file with these settings:
```
"ssl_ca" : "splunk_ca.cert"
```
Alternatively, you can create a [profile class](https://puppet.com/docs/pe/latest/osp/the_roles_and_profiles_method.html) that copies the `splunk_ca.cert` as part of invoking the splunk_hec class:
```
class profile::splunk_hec {
file { '/etc/puppetlabs/puppet/splunk_hec/splunk_ca.cert':
ensure => file,
owner => 'pe-puppet',
group => 'pe-puppet',
mode => '0644',
source => 'puppet:///modules/profile/splunk_hec/splunk_ca.cert',
}
}
```
**Note**: When `splunk_hec::ssl_ca` is configured it takes precendence over the system certificate store. The report processor will build its own cert store with the provided CA certificate to validate requests against the Splunk HEC endpoint. Alternatively, you can add the Splunk HEC CA to the system certificate store and set `splunk_hec::include_system_cert_store` to `true`. This will allow the code to ONLY use the system default store to perform certificate validation.
## Fact Configuration
The following parameters are utilized to configure which facts (including custom facts) you would like to send to Splunk:
* `facts_allowlist`
* `facts_blocklist` (**Optional**)
To configure which facts to collect add the `facts_allowlist` parameter to the `splunk_hec` class and modify the array of facts presented.
* To collect **all facts** available at the time of the Puppet run, add the special value `all.facts` to the `facts_allowlist` array.
* When collecting **all facts**, you can configure the optional parameter `facts_blocklist` with an array of facts that should not be collected.
## PE Event Forwarding
PE Customers can install the [`puppetlabs-pe_event_forwarding`](https://forge.puppet.com/modules/puppetlabs/pe_event_forwarding) module to gather events from the Puppet Orchestrator API and from the Activities API, and then use this module to process that data and send it to Splunk. To enable this feature in a standard installation where this module is already classified to a Puppet Server node and sending reports to Splunk:
1. See the documenation for [`puppetlabs-pe_event_forwarding`](https://forge.puppet.com/modules/puppetlabs/pe_event_forwarding) for details on installing and configuring that module. That module will need to be installed and configured before moving on to the next step.
2. Set the `events_reporting_enabled` parameter to `true`.
By default the `event_types` parameter is configured to send all event types. You can choose which event types to send by setting this parameter to one or more of `orchestrator`, `rbac`, `classifier`, `pe-console`, or `code-manager`.
### Filtering Event Data
To filter the event data, one can set the following parameters:
* `orchestrator_data_filter`
* `rbac_data_filter`
* `classifier_data_filter`
* `pe_console_data_filter`
* `code_manager_data_filter`
The default (no filter set) will send all the data received from the event type. The filters must begin with the top level keys of the event data. One can look at the data in Splunk to see/determine what the top level keys are in the event data.
The format of setting these filters is an array of strings and within the string, you separate the different properties of a single path with a dot `.` and continue till the desired value.
Here's an example of a correctly constructed filter:
`['options.scope.nodes', 'report.id', 'environment.name']`
**NOTE:**
* You cannot step into arrays. The result of attempting this will return the selected key containing the array as a key of an empty hash.
* If a key selected does not exist (ie. `['options.foo']`), it will return the key with a `null` value.
* If there are two incorrect keys such as `['options.foo.baz']`, it will query only up until the first invalid key and return the first incorrect key as an empty hash.
### Sending from Non Server Nodes
This feature can be configured to send these events from non server nodes if needed. To do this, on the chosen server:
1. Classify and configure the [`puppetlabs-pe_event_forwarding`](https://forge.puppet.com/modules/puppetlabs/pe_event_forwarding) according to that module's documentation.
2. Classify this module with the following parameter values:
```puppet
class {'splunk_hec':
events_reporting_enabled => true,
url => "http://:8088/services/collector/event",
token => ''
}
```
Note: This manifest shows an end point with no SSL protection. To do SSL validation with this module you will have to do all of the steps detailed in the [SSL Configuration](#ssl-configuration) section, but ensuring you copy the certificate to the correct location on the chosen server where you are classifying `splunk_hec` and `pe_event_forwarding`, not the Puppet Server.
### Supported Puppet Versions For Event Forwarding
The `puppetlabs-pe_event_forwarding` module that this feature depends on requires PE versions **2021.2** and above to access the API methods for the module to function properly.
## Customized Reporting
As of `0.8.0` and later the report processor can be configured to include [**Logs**](https://puppet.com/docs/puppet/latest/format_report.html#puppet::util::log) and [**Resource Events**](https://puppet.com/docs/puppet/latest/format_report.html#puppet::resource::status) along with the existing summary data. Because this data varies between runs and agents in Puppet, it is difficult to predict how much data you will use in Splunk as a result. However, this removes the need for configuring the **Detailed Report Generation** alerts in Splunk to retrieve that information; which may be useful for large installations that need to retrieve a large amount of data. You can now just send the information from Puppet directly.
Add one or more of these parameters based on the desired outcome, these apply to the state of the puppet runs. You cannot filter by facts on which nodes these are in effect for. As such, you can get ***logs when a puppet run fails***, but not *logs when a `windows` server puppet run fails*.
By default this type of reporting is not enabled.
**Parameters**:
##### event_types (Requires `puppetlabs-pe_event_forwarding` module)
`Array`: Determines which event types should be forwarded to Splunk. Default value includes all event types. This can be one, or any of the following:
* `classifier`
* `code-manager`
* `orchestrator`
* `pe-console`
* `rbac`
##### include_logs_status
`Array`: Determines if [logs](https://puppet.com/docs/puppet/latest/format_report.html#puppet::util::log) should be included based on the return status of the puppet agent run. This can be none, one, or any of the following:
* `failed`
* `changed`
* `unchanged`
##### include_logs_catalog_failure
`Boolean`: Include logs if a [catalog](https://puppet.com/docs/puppet/latest/subsystem_catalog_compilation.html) fails to compile. This is a more specific type of failure that indicates a server-side issue.
* `true`
* `false`
##### include_logs_corrective_change
`Boolean`: Include logs if a there is a [corrective change](https://puppet.com/docs/pe/latest/analyze_changes_across_runs.html) (a PE only feature) - indicating drift was detected from the last time puppet ran on the system.
* `true`
* `false`
##### include_resources_status
`Array`: Determines if [resource events](https://puppet.com/docs/puppet/latest/format_report.html#puppet::resource::status) should be included based on the return status of the puppet agent run. **Note**: This only includes resources whose status is not `unchanged` - not the entire catalog. The can be none, one, or any of the following:
* `failed`
* `changed`
* `unchanged`
##### include_resources_corrective_change
`Boolean`: Include resource events if a there is a corrective change (a **PE only** feature) - indicating drift was detected from the last time puppet ran on the system.
* `true`
* `false`
##### only_changes
`Boolean`: Only process reports when the report status indicates there were [changes](https://puppet.com/docs/puppet/latest/format_report.html#format_report-puppet-transaction-report).
* `true`
* `false` :: **Default Value**
##### summary_resources_format
`String`: If `include_resources_corrective_change` or `include_resources_status` is set and therefore `resource_events` are being sent as part of `puppet:summary` events, we can choose what format they should be sent in. Depending on your usage within Splunk, different formats may be preferable. The possible values are:
* `hash` :: **Default Value**
* `array`
Here is an example of the data that will be forwarded to Splunk in each instance:
**`hash`**:
```json
{
"resource_events": {
"File[/etc/something.conf]": {
"resource": "File[/etc/something.conf]",
"failed": false,
"out_of_sync": true
}
}
}
```
**`array`**:
```json
{
"resource_events": [
{
"resource": "File[/etc/something.conf]",
"failed": false,
"out_of_sync": true
}
]
}
```
## Tasks
Two tasks are provided for submitting data from a Bolt [plan](https://puppet.com/docs/bolt/latest/plans.html) to Splunk. For clarity, we recommend using a different HEC token to distinguish between events from Puppet runs and those generated by Bolt. The Puppet Report Viewer app includes a `puppet:bolt` sourcetype to faciltate this. Currently SSL validation for Bolt communications to Splunk is not supported.
* `splunk_hec::bolt_apply`: A task that uses the remote task option to submit a Bolt Apply report in a similar format to the `puppet:summary`. Unlike the summary, this includes the facts from a target because those are available to bolt at execution time and added to the report data before submission to Splunk.
* `splunk_hec::bolt_result`: A task that sends the result of a function to Splunk. Since the format is freeform and dependent on the individual function/tasks being called, formatting of the data is best done in the plan itself prior to submitting the result hash to the task.
To setup, add the `splunk_hec` endpoint as a remote target in your `inventory.yaml` file:
```
---
nodes:
- name: splunk_bolt_hec
config:
transport: remote
remote:
hostname:
token:
port: 8088
```
See the [`plans`](https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec/tree/main/plans) directory for working examples of apply and result usage.
## Advanced Settings
The `splunk_hec` module also supports customizing the `fact_terminus` and `facts_cache_terminus` names in the custom `splunk_routes.yaml` it deploys. If you are using a different `facts_terminus` (i.e. not PuppetDB), you will want to set that parameter.
If you are already using a custom `splunk_routes.yaml`, these are the equivalent instructions of what the `splunk_hec` module does. The most important setting is configuring `cache: splunk_hec`.
* Create a custom `splunk_routes.yaml` file to override where facts are cached:
```
---
master:
facts:
terminus: puppetdb
cache: splunk_hec
```
* Set this routes file instead of the default one by running the following commmand:
```
puppet config set route_file /etc/puppetlabs/puppet/splunk_routes.yaml --section master
```
## FIPS Mode
This module has some limitations in a FIPS environment. In particular, the SSL configuration steps and the available parameters are different under FIPS.
The CA certificate PEM file must be appended to the end of the `localcacert` file. Find the path to the file by running [`puppet config print localcacert`](https://puppet.com/docs/puppet/latest/configuration.html#localcacert). Keep in mind that this file will be overwritten any time the puppetserver is upgraded to a new version and this step will have to be done again. Consider copying a backup of this file to a safe location before attempting to add content to it until correct functioning of the Puppet Server and this module can be validated.
```
ca_file=$(puppet config print localcacert)
cp $ca_file ~/$ca_file
cat my_splunk_hec_ca.pem >> $ca_file
```
The module must use a different FIPS compliant HTTP client. This client currently lacks support for a number of configurable options. For example, none of the timeout parameters will have any effect. Additionally, ignoring the system certificate store is the default behavior, so there is no need to use the `ignore_system_certificate_store` parameter. When running in a FIPS environment the following optional parameters are available:
**Note**: These parameters only have an effect on metrics and will be ignored by the report processor when sending reports and facts.
##### fips_crl_check
`Boolean`: In FIPS mode, the HTTP Client will attempt to check the Splunk CA against the Splunk CRL. Unless the Splunk HEC endpoint is configured with a certificate generated by the Puppet CA, set this parameter to `false` to allow metrics to successfully send.
* `true` :: **Default Value**
* `false`
##### fips_verify_peer
`Boolean`: In FIPS mode, the HTTP Client will attempt peer verfication by default. When utilizing a self-signed certificate set this parameter to `false` to allow metrics to successfully send.
* `true` :: **Default Value**
* `false`
**NOTE**
To set up a testing environment with FIPS enabled, run the following command: `PROVISION_LIST=fips_acceptance bundle exec rake acceptance:setup`
## Advanced Topics
* [Advanced Puppet Configuration](https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec/blob/main/docs/advanced_puppet_configuration.md)
* [Advanced Splunk Configuration](https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec/blob/main/docs/advanced_splunk_configuration.md)
* [Fact Terminus Support](https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec/blob/main/docs/fact_terminus_support.md)
* [Puppet Metrics Collection](https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec/blob/main/docs/puppet_metrics_collector_support.md)
* [Troubleshooting and Verification](https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec/blob/main/docs/troubleshooting_and_verification.md)
## Known Issues
* Integration with the `puppet_metrics_collection` requires version `>= 6.0.0`.
* SSL Validation is under active development and behavior may change.
* Automated testing could use work.
* `>= 0.9.0` With the deprecated `reports` parameter set to an empty string, any values in the reports settings in `puppet.conf` are removed.
## Breaking Changes
* `>= 0.5.0` The `splunk_hec::url` parameter now expects a full URI of **https://servername:8088/services/collector**.
* `0.5.0` -> `0.6.0` Switches to the fact terminus cache setting via `splunk_hec_routes.yaml` to ensure compatibility with [CD4PE](https://puppet.com/docs/continuous-delivery/4.x/cd_user_guide.html). See [Fact Terminus Support](https://github.com/puppetlabs/puppetlabs-splunk_hec/blob/main/docs/fact_terminus_support.md) for guides on how to change it. Prior to deploying this module, remove the setting `facts_terminus` from the `puppet_enterprise::profile::master` class in the `PE Master` node group in your environment if you set it in previous versions of this module (`0.6.0 <`). It will prevent PE from operating normally if left on.
## Release Process
This module is hooked up with an automatic release process using Github actions. To provoke a release simply check the module out locally, tag with the new release version, then github will promote the build to the forge.
Full process to prepare for a release:
Update `metadata.json` to reflect new module release version (0.8.1).
Run `bundle exec rake changelog` to update the `CHANGELOG` automatically.
Submit PR for changes.
Create Tag on target version:
```
git tag -a v0.8.1 -m "0.8.1 Feature Release"
git push upstream --tags
```
## Authors
P.I.E. Team
P. uppet\
I. ntegrations\
E. ngineering
---