https://github.com/qlishell/react-native-the-practical-guide
Use React Native and your React knowledge to build native iOS and Android Apps
https://github.com/qlishell/react-native-the-practical-guide
android-app ios-app react react-native stack-navigation
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Use React Native and your React knowledge to build native iOS and Android Apps
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/qlishell/react-native-the-practical-guide
- Owner: qlishell
- Created: 2024-08-09T13:21:14.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-08-20T04:41:51.000Z (over 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-30T17:24:07.767Z (12 months ago)
- Topics: android-app, ios-app, react, react-native, stack-navigation
- Language: JavaScript
- Homepage:
- Size: 18.1 MB
- Stars: 2
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# React Native Project Structure: A Best Practices Guide

- [React Native Learn once, write anywhere](https://reactnative.dev/)
- [7 Most Popular & Best React Native Apps in 2023](https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-most-popular-best-react-native-apps-2023-openxcell/)
## Initial Structure
To get started with this project, we'll use Expo. Open a terminal and run the following command inside a directory of your choice:
```bash
expo init rn-project-structure
```
Alternatively, you can use `create-expo-app` to set up a new Expo and React Native project:
```bash
yarn create expo-app --template blank AwesomeProject
cd AwesomeProject
yarn expo start
```
For more details on creating Expo projects, check out the [create-expo-app documentation](https://docs.expo.dev/more/create-expo/).
## Project Structure
Breaking down your project into manageable layers can help maintain a clean and organized codebase. Here is a common structure you can use:
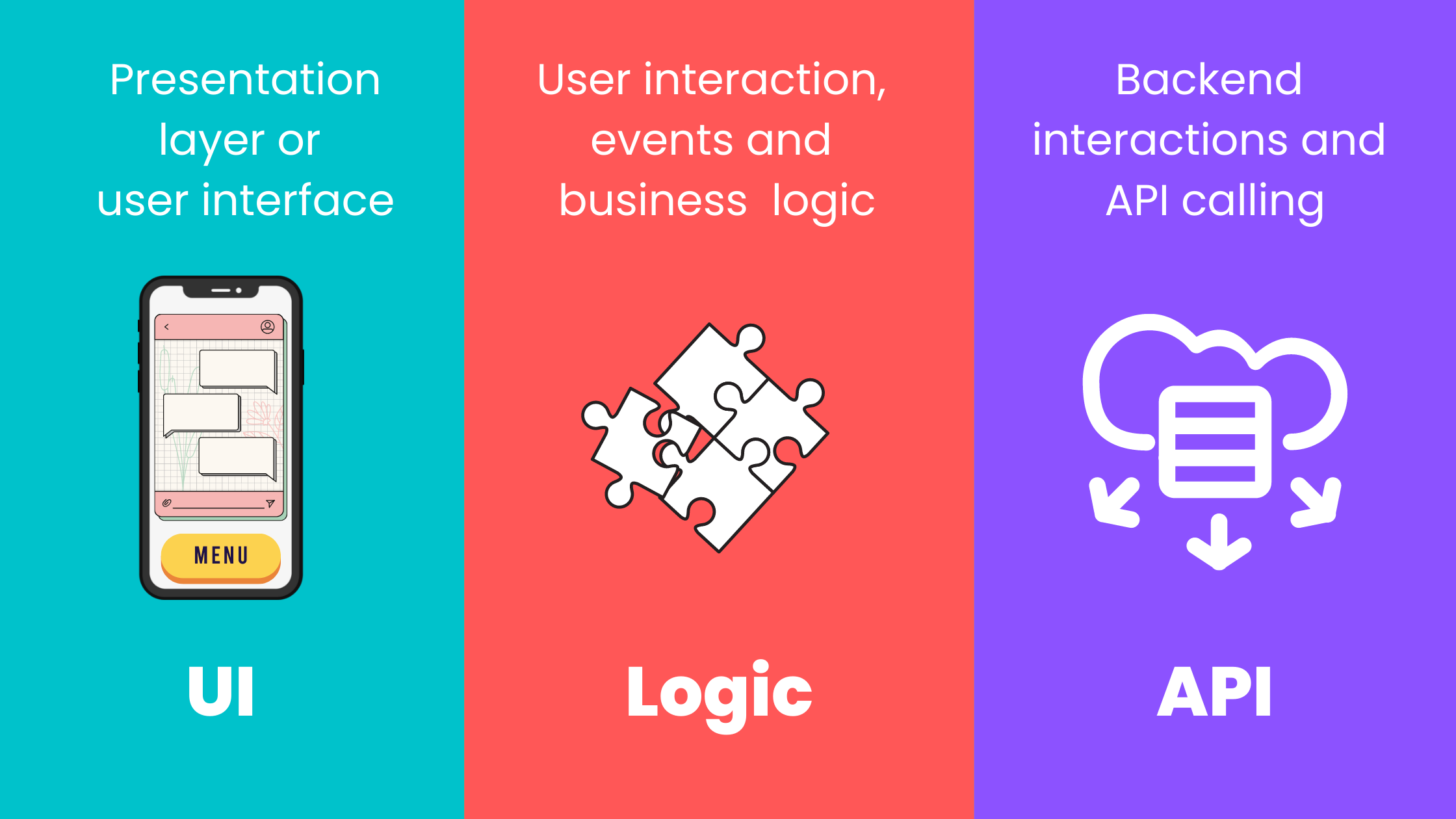
### 1. **UI or Presentation Layer**
This layer includes all the components and UI elements that the user interacts with. It covers elements like buttons, text, popups, and other visual components.
### 2. **Logic Layer**
The Logic Layer handles the core business logic of your application. It manages all the events, interactions, and operations that take place between the UI and the API layers.
### 3. **API Layer**
The API Layer is responsible for communication with back-end services. It handles API calls to servers or external web services and processes responses to be used by the Logic Layer.
## Folder Structure Example
Here’s a suggested folder structure for a React Native project:
```
/AwesomeProject
|--/assets
|--/components
| /Button
| /Header
|--/screens
| /Home
| /Details
|--/services
| /api
|--/utils
|--/hooks
|--/context
| App.js
| app.json
| package.json
```
- **/assets**: Contains static assets like images and fonts.
- **/components**: Reusable UI components.
- **/screens**: Different screens or views in the application.
- **/services**: API services and utilities.
- **/utils**: Utility functions and helpers.
- **/hooks**: Custom React hooks.
- **/context**: React context providers and state management.
## Best Practices
- **Modularity**: Keep components small and focused on a single responsibility.
- **Separation of Concerns**: Maintain a clear separation between UI, business logic, and API interactions.
- **Reusability**: Create reusable components and hooks to reduce code duplication.
- **Consistent Naming**: Use consistent naming conventions for files and folders to enhance readability.
By following these best practices, you'll create a well-organized and maintainable React Native project. Happy coding!