https://github.com/queeniecplusplus/bigquery_cloudsql
https://github.com/queeniecplusplus/bigquery_cloudsql
bigdata buckets cloudsql mysql-server sql
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/queeniecplusplus/bigquery_cloudsql
- Owner: QueenieCplusplus
- Created: 2020-11-06T05:23:05.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2020-11-07T09:52:33.000Z (about 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-06T04:26:10.430Z (12 months ago)
- Topics: bigdata, buckets, cloudsql, mysql-server, sql
- Homepage: https://github.com/QueenieCplusplus/QuickGoThru/blob/master/README.md#cloud-sql-big-data
- Size: 1.28 MB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# BigQuery_CloudSQL
SQL (Structured Query Language) is a standard language for Data Ops that allows DBA to query from structured datasets.
It's commonly used in DB mgmt and allows to perform tasks like transaction record writing into relational databases and do DA (petabyte-scale data analysis).
This is a data science topics. This lab is divided into two parts:
in the first half, you will learn how to export subsets of the London bikeshare dataset into CSV files, which you will then upload to Cloud SQL. From there you will learn how to use Cloud SQL to create and manage databases and tables. Towards the end, you will get hands-on practice with additional SQL keywords that manipulate and edit data.

In the second half, you will learn fundamental SQL querying keywords, which you will run in the BigQuery console on a public dataset that contains information on London bikeshares.

# Core Steps:
(1) uoload CSV data to Storage/Bucket.
(2) Create Cloud SQL instance, config AC.
(3) Create Connection between Storage/Bucket to SQL instance.
(4) as same as (1)
(5) util Google Big Data Production Tool called Big Query
--------------
# Storage Bucket
from step 1:
> upload Data to Storage Bucket
* 1.1, in cloud console, navigate to Storage >> Browser, click on "Create Bucket".
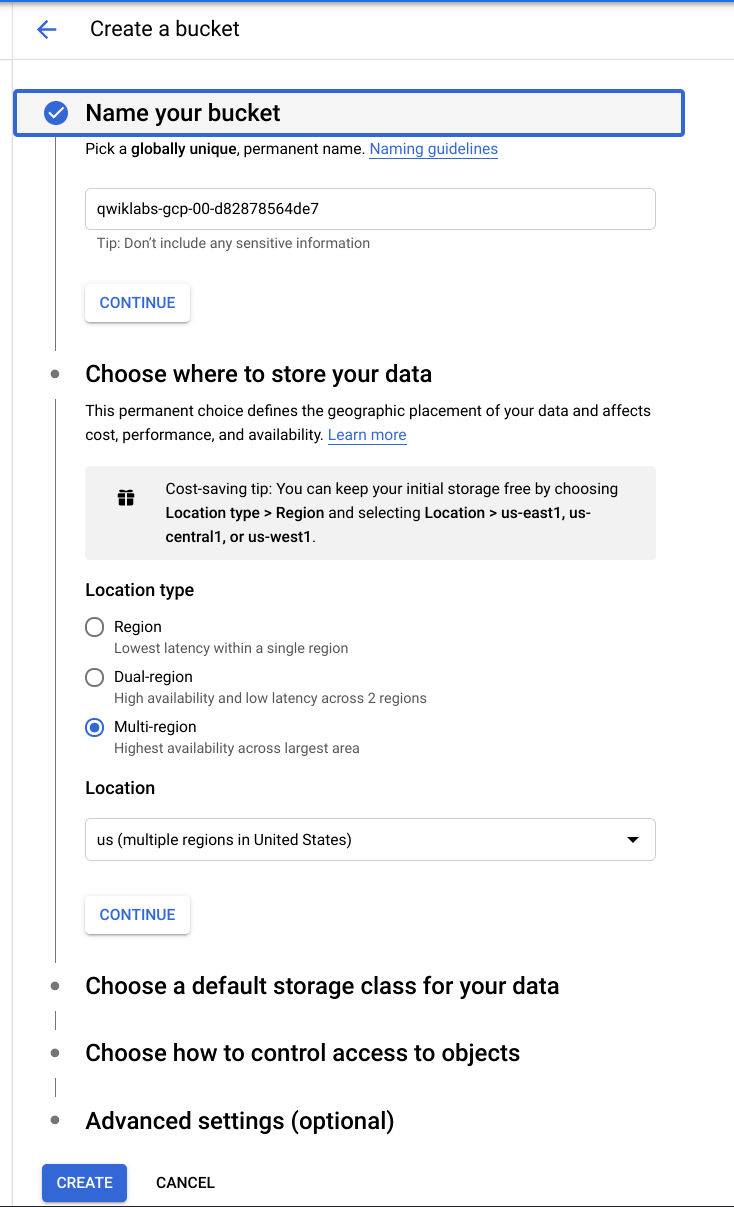
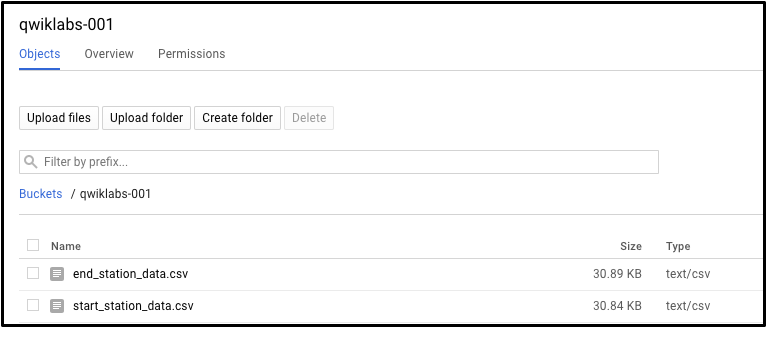
* 1.2, upload CSV data to the newly created Cloud Storage Bucket.
# Cloud SQL instance

from step 2:
> create Cloud SQL instance
* 2.1, navigate to Storage >> SQL, then click on "create Cloud SQL instance".
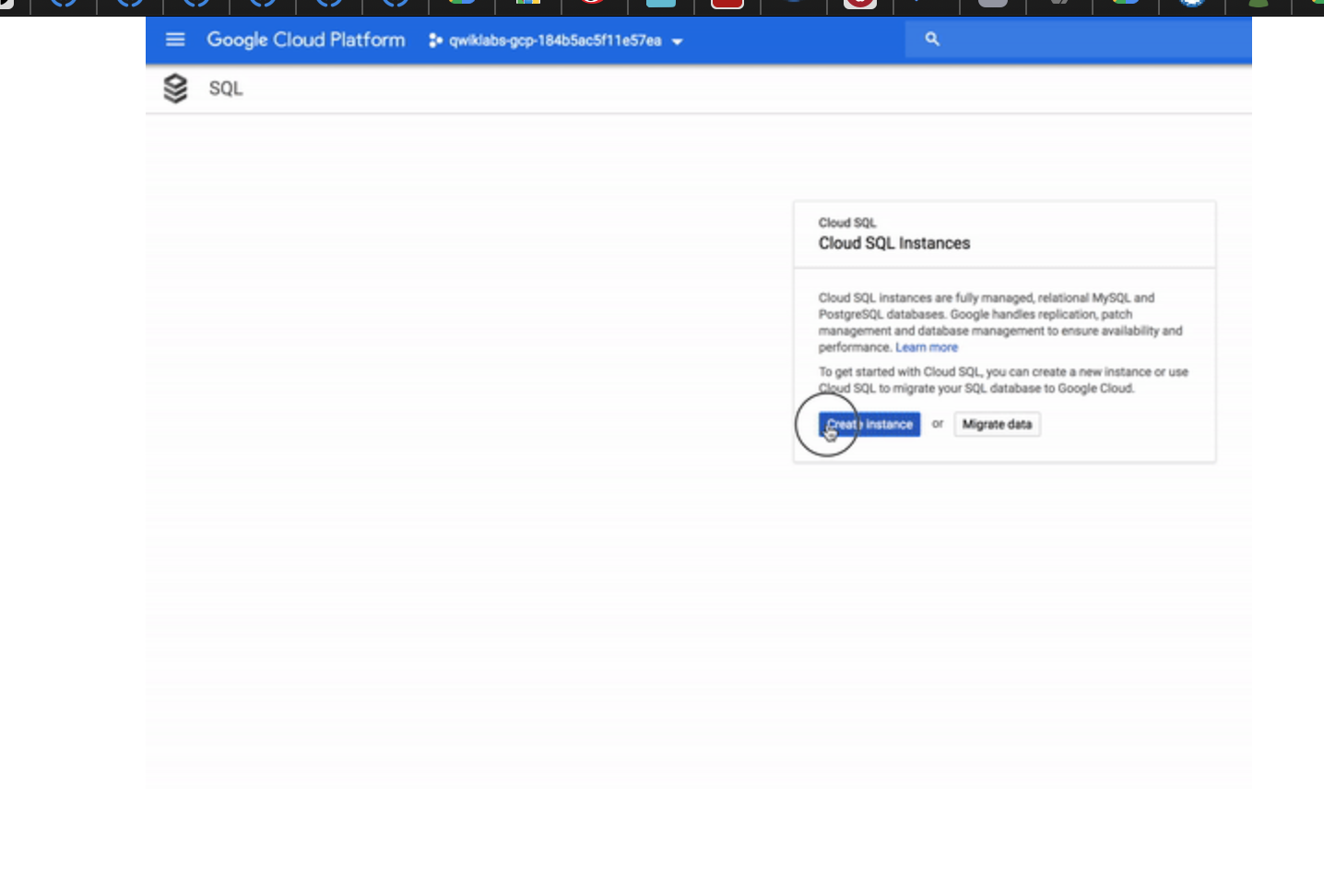
* 2.2, check the user & password to do Access Control to DB.

* 2.3, Cloud SQL Instance is created then.
# Connection using Cloud Shell
from step 3:
> activate Cloud Shell and type cmd line. (auth, project resource), then make it to connect with sql instance.
* 3.1, activate Cloud Shell.
* 3.2, type cmd line in shell, to check Project ID and auth Users Account.
gcloud auth list
[output]
Credentialed accounts: -@.com (active)
gcloud config list project
[output]
[Core]
Project=
[example output]
Project=kates-gcp-1234567890abcedee
// as above blue bar in step 1.5
* 3.3, make connection to sql.
gcloud sql connect [cloud sql instance name] --user=root
// the name is as same as pink bar in step 2.3
[output]
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MySQL connection id is 494
Server version: 5.7.14-google-log (Google)
Copyright (c) 2000, 2017, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
MySQL [(none)]>
* 3.4, execute SQL statement now.
CREATE DATABASE poupou;
USE poupou;
CREATE TABLE taiwanHome (start_station_name VARCHAR(255), num INT);
SELECT * FROM taiwanHome;
[output]
It says "empty set" because you haven't loaded in any data yet.
# Import Data to Cloud SQL instance
from step 4:
> upload csv data to table.
* 4.1, in the console for Cloud SQL Instance, click on "Import".
* 4.2, then browse the Storage Bucket File.
* 4.3, select the right file, and click on "Import".
* 4.4, CSV files uploaded to tables called taiwanHome in the poupou database.
[output UI]
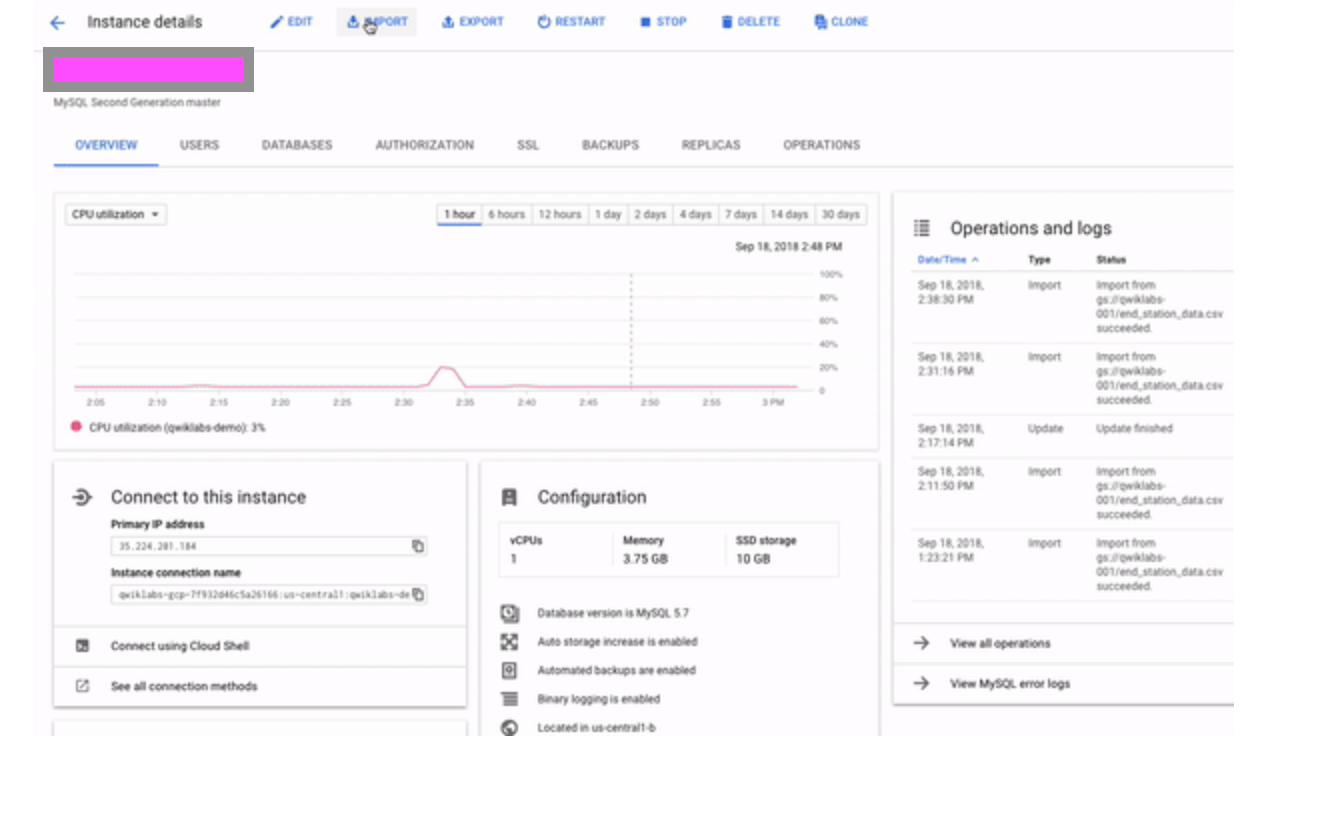
* 4.5, do Big Query now!
Return to your Cloud Shell session and run the following command at the MySQL server prompt to inspect the contents of table called taiwanHome, run sql cmd at the sql server prompt (we choose hereby the MySQL server. see step 2.1)
SELECT * FROM taiwanHome;
SELECT * FROM chinaHome;
DELETE FROM taiwanHome WHERE num=0;
INSERT INTO taiwanHome (start_station_name, num) VALUES ("test destination", 1);
SELECT start_station_name AS top_stations, num FROM london1 WHERE num>100000
UNION
SELECT end_station_name, num FROM london2 WHERE num>100000
ORDER BY top_stations DESC;
# Big Query

from step 5:
> util Big Query
* 5.1, in cloud console, navigate to BigData > BigQuery, and both of the BigQuery Console and the Message Box are opened.
* 5.2. check project id, then add data, and check DB & table.
check the project → dataset → table of the console, you can load up some queryable data.
* tips & attentions:
It's important to note that you are still working out of your "main project" in this left-hands tab.
All you did was pull a publicly accessible project that contains datasets and tables into BigQuery for analysis.It means you didn't switch over to that "main project". (see green bar in step 5.2)
All of your jobs and services are still tied to your account. You can see this for yourself by inspecting the project field near the top of the console.
# Ref Code
2802, 3642(trouble shoot)