https://github.com/rafsaf/tw-complex
Algorithms for TW
https://github.com/rafsaf/tw-complex
mit numpy poetry pypi-package python scipy sklearn
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Algorithms for TW
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/rafsaf/tw-complex
- Owner: rafsaf
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-05-10T22:48:51.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2022-10-26T18:50:34.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-10-13T08:43:44.014Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: mit, numpy, poetry, pypi-package, python, scipy, sklearn
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://pypi.org/project/tw-complex/
- Size: 3.4 MB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README



# TW Complex
Repo with algorithms to divide ally villages into front and back in TW.
Underneath it is a problem of dividing a set of 2D points **A** according to the `min_radius` and `max_radius` distances from a set of other 2D points **B**, which can be solved most simply by counting the distances from each point in the first set **A** to all points in the second set **B** one by one.
- [Instalation](#instalation)
- [Basic usage](#basic-usage)
- [Examples](#examples-before---after)
- [Running locally](#running-locally)
# Instalation
```bash
pip install tw_complex
```
# Basic usage
```python
from tw_complex import CDistBrute
import numpy as np
# The code for Example 1 below
points1 = np.random.rand(10000, 2) + [2, 0]
points2 = np.random.rand(15000, 2)
min_radius = 1.4
max_radius = 2
precise_front, precise_back = CDistBrute(
ally_villages=points1,
enemy_villages=points2,
min_radius=min_radius,
max_radius=max_radius,
).result()
```
# Examples (before -> after)
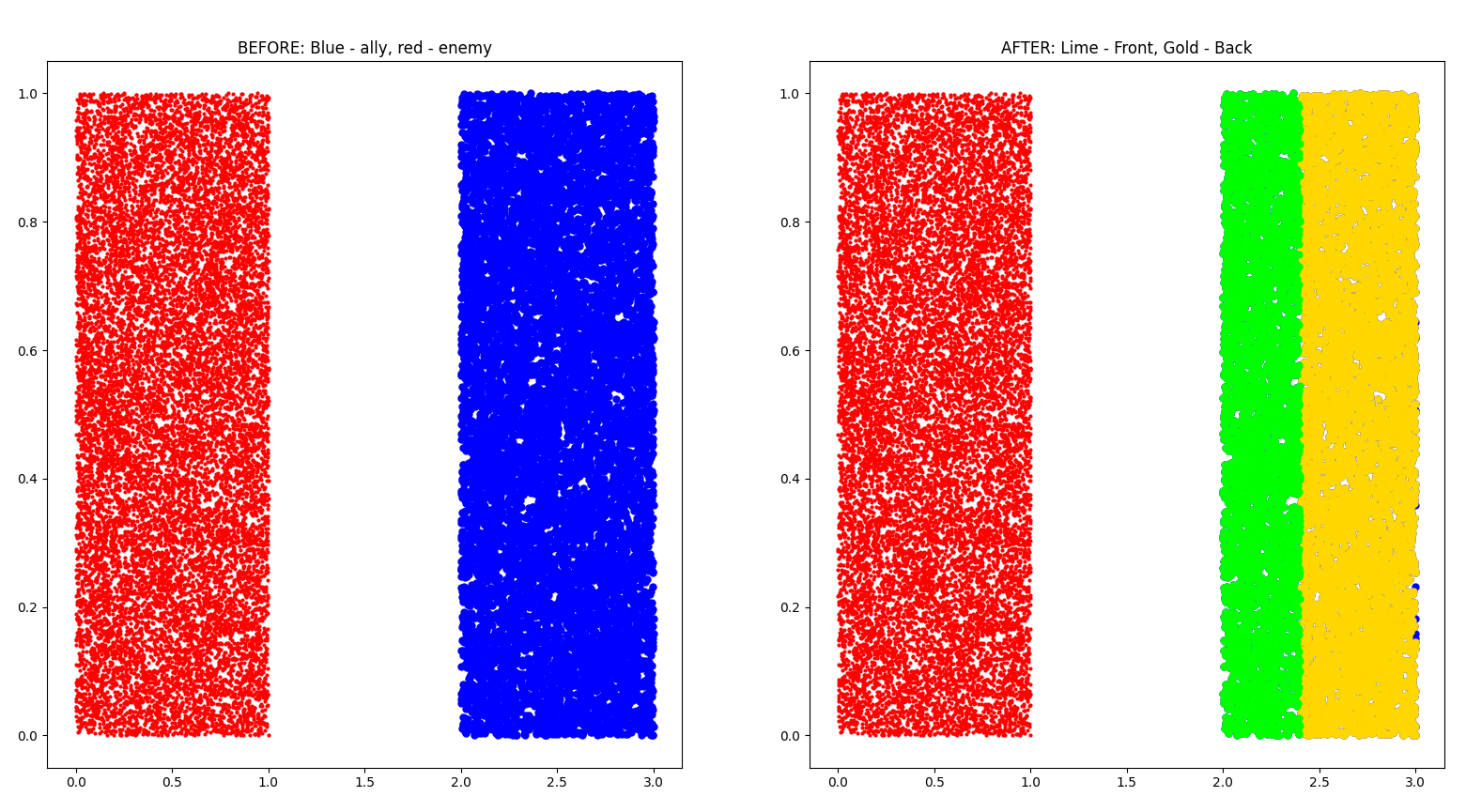
### Example 1
```bash
Ally: 10000 points
Enemy: 15000 points
min_radius: 1.4
max_radius: 2
```
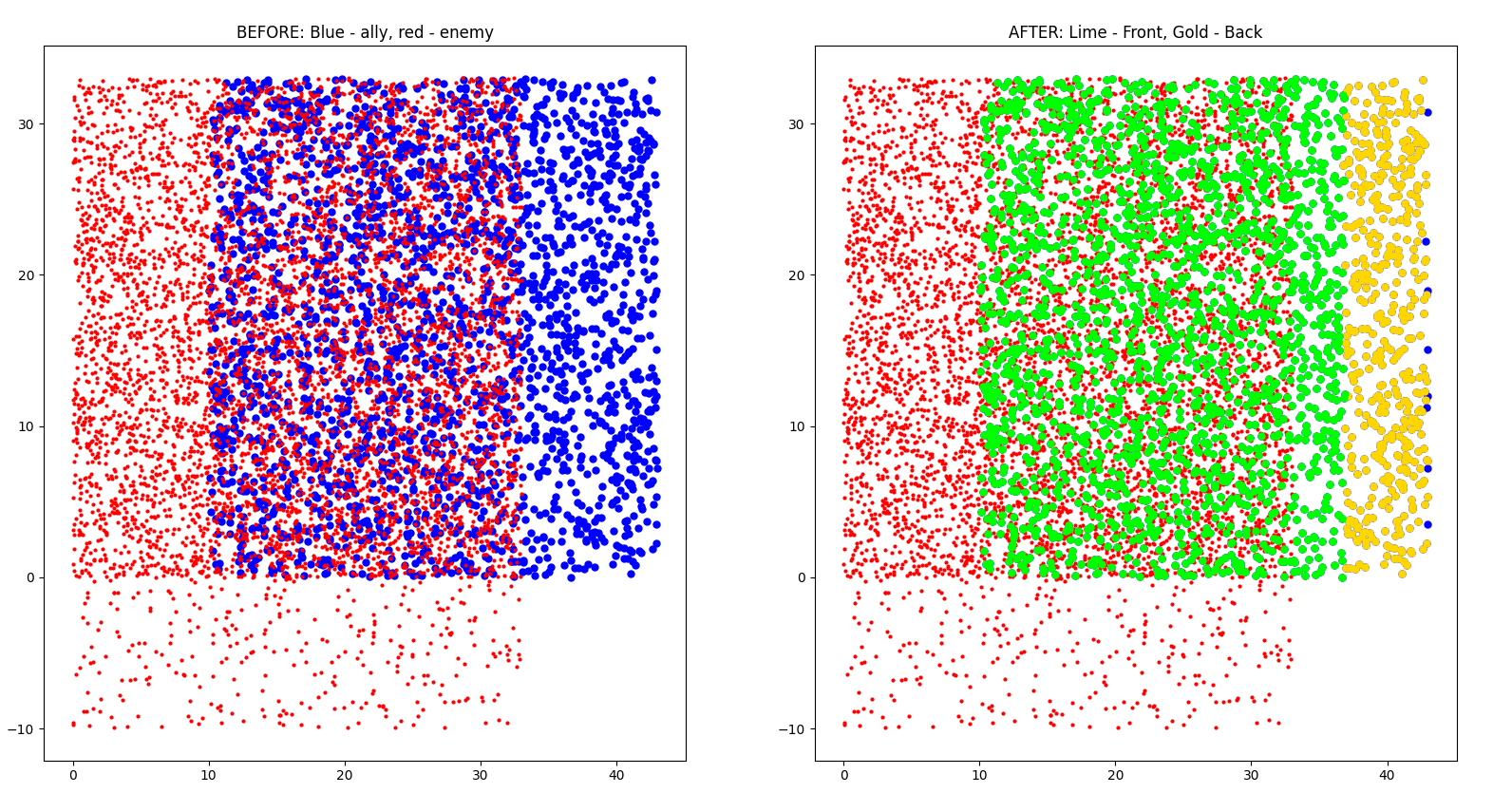
### Example 2
```bash
Ally: 2500 points
Enemy: 6000 points
min_radius: 4
max_radius: 10
```
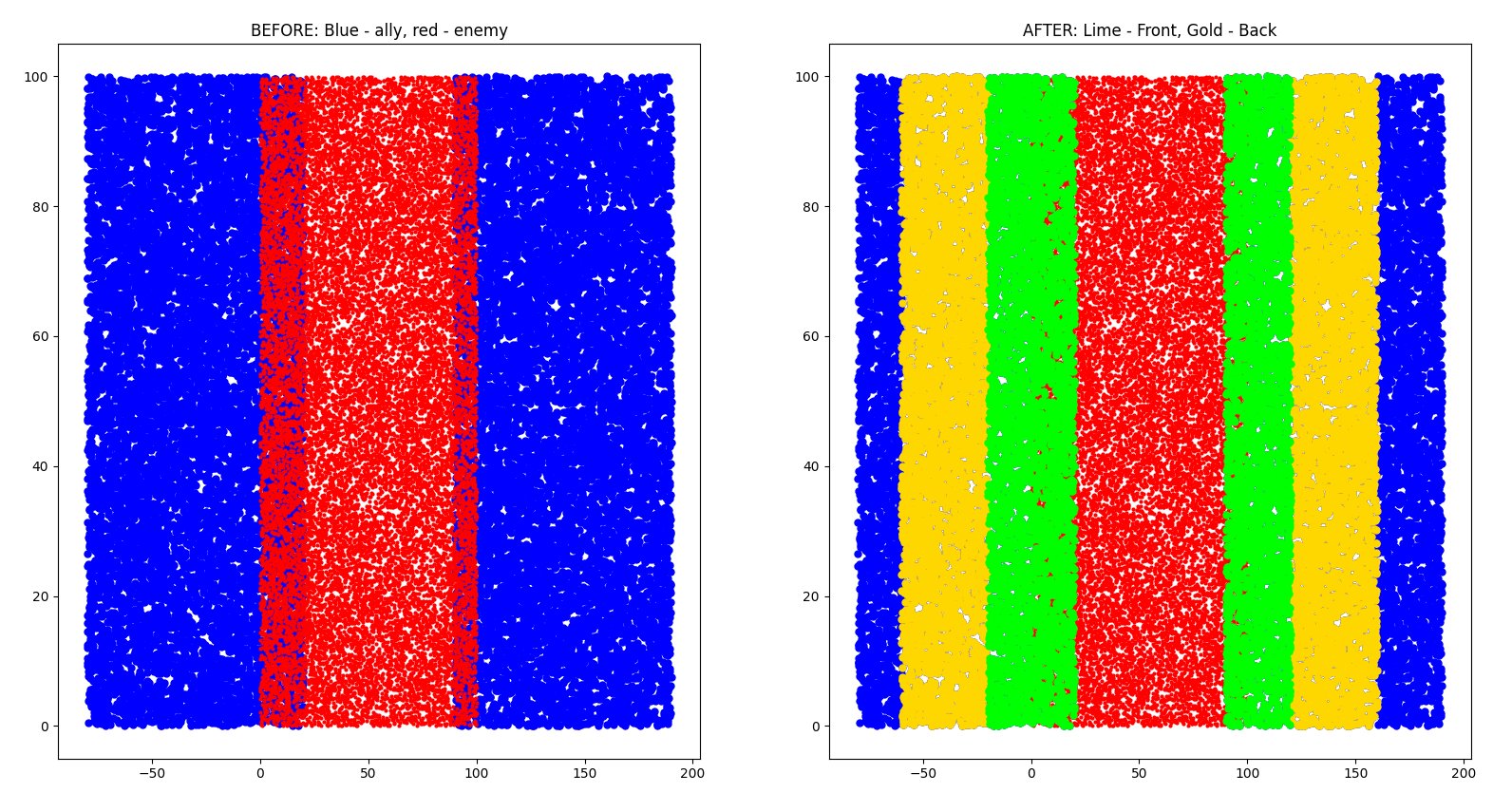
### Example 3
```bash
Ally: 20000 points
Enemy: 20000 points
min_radius: 20
max_radius: 60
```
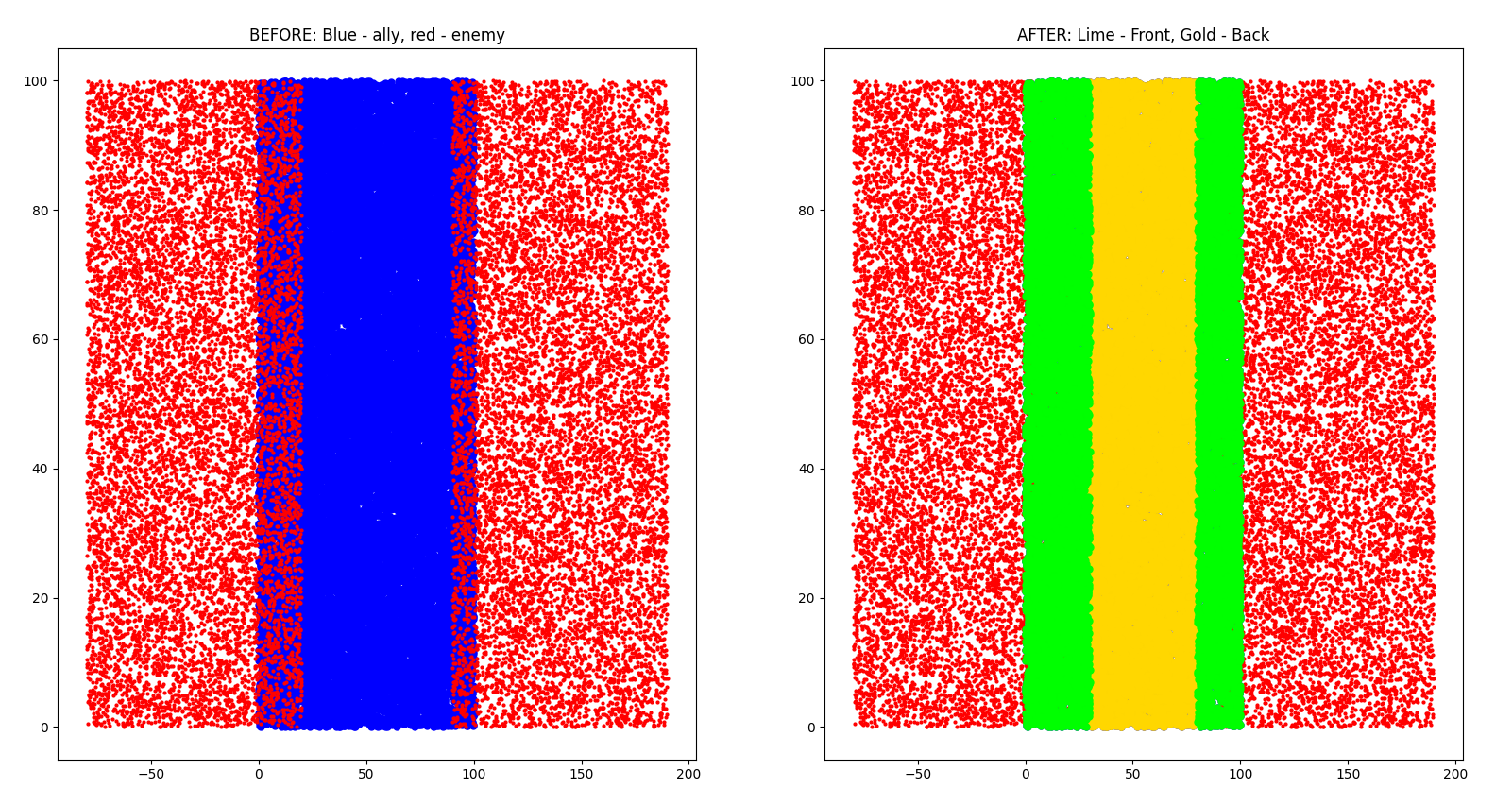
### Example 4
```bash
Ally: 20000 points
Enemy: 20000 points
min_radius: 10
max_radius: 120
```
# Running locally
You will need to have [poetry](https://python-poetry.org/) installed.
```
git clone https://github.com/rafsaf/tw-complex.git
cd tw-complex
poetry install
```
Code lives in `tw-complex` folder, and you may also test algorithms running in main folder
```
# In main folder
# eg. ~/Desktop/tw-complex
pytest
```
For CDistAndKNN it looks like
```python
# tests/test_cdist.py
from tw_complex import CDistAndKNN
import tests.utils as utils
def test_CDistAndKNN():
utils.run_all_tests(CDistAndKNN, "CDistAndKNN", _precision=0.8, draw=True)
# Go with `draw=False` if you do not want to use pyplot to show diagrams
```
Some hardcoded tests are located in `tests/utils.py`, it uses brute force for calculating exact result, then compare it to given algorithm using basic maths. You can even compare it to brute force itself (eg. using diffrent `_precision`). For new test there should be another file in `tests/test_name_of_file_in_tw_complex_folder.py` with pretty much the same content as above.