https://github.com/rancher-sandbox/rancher-desktop
Container Management and Kubernetes on the Desktop
https://github.com/rancher-sandbox/rancher-desktop
containers kubernetes linux macos windows
Last synced: 4 days ago
JSON representation
Container Management and Kubernetes on the Desktop
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/rancher-sandbox/rancher-desktop
- Owner: rancher-sandbox
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2020-10-23T17:20:58.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-05-08T16:21:47.000Z (8 days ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-08T17:23:12.877Z (8 days ago)
- Topics: containers, kubernetes, linux, macos, windows
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage: https://rancherdesktop.io
- Size: 80.9 MB
- Stars: 6,415
- Watchers: 54
- Forks: 317
- Open Issues: 1,208
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: CONTRIBUTING.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome - rancher-sandbox/rancher-desktop - Container Management and Kubernetes on the Desktop (TypeScript)
- awesome - rancher-sandbox/rancher-desktop - Container Management and Kubernetes on the Desktop (TypeScript)
- awesome - rancher-sandbox/rancher-desktop - Container Management and Kubernetes on the Desktop (TypeScript)
README
# Rancher Desktop
Rancher Desktop is an open-source project that brings Kubernetes and
container management to the desktop. It runs on Windows, macOS and
Linux. This README pertains to the development of Rancher Desktop.
For user-oriented information about Rancher Desktop, please see [rancherdesktop.io][home].
For user-oriented documentation, please see [docs.rancherdesktop.io][docs].
[home]: https://rancherdesktop.io
[docs]: https://docs.rancherdesktop.io
## Overview
Rancher Desktop is an Electron application that is mainly written in TypeScript.
It bundles a variety of other technologies in order to provide one cohesive application.
It includes a command line tool, `rdctl`, which is written in Go.
Most developer activities, such as running a development build, building/packaging
Rancher Desktop, running unit tests, and running end-to-end tests, are done through
`yarn` scripts. Some exceptions exist, such as running BATS tests.
## Setup
### Windows
There are two options for building from source on Windows: with a
[Development VM Setup](#development-vm-setup) or
[Manual Development Environment Setup](#manual-development-environment-setup)
with an existing Windows installation.
#### Development VM Setup
1. Download a Microsoft Windows 10 [development virtual machine].
All of the following steps should be done in that virtual machine.
2. Open a PowerShell prompt (hit Windows Key + `X` and open
`Windows PowerShell`).
3. Run the [automated setup script]:
```powershell
Set-ExecutionPolicy RemoteSigned -Scope CurrentUser
iwr -useb 'https://github.com/rancher-sandbox/rancher-desktop/raw/main/scripts/windows-setup.ps1' | iex
```
4. Close the privileged PowerShell prompt.
5. Ensure `msbuild_path` and `msvs_version` are configured correctly in `.npmrc` file. Run the following commands to set these properties:
```
npm config set msvs_version
npm config set msbuild_path
```
For example for Visual Studio 2022:
```
npm config set msvs_version 2022
npm config set msbuild_path "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\MSBuild\Current\Bin\MSBuild.exe"
```
If you get an error message when trying to run `npm config set...`, run `npm config edit` and then add lines like
```
msvs_version=2022
msbuild_path=C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\MSBuild\Current\Bin\MSBuild.exe
```
Do not quote the values to the right side of the equal sign. The quotes aren't needed, and it's possible that some
processors will treat them as literal parts of the path, and then fail.
7. Configure `git` to work with linux- and macos-originated files:
```
git config --global --replace-all core.autocrlf false
git config --global --replace-all core.eol lf
```
If you find the `lint:go` tests are failing mysteriously, it's possible that the line-endings are incorrect.
You can now clone the repository and run `yarn`.
[development virtual machine]: https://developer.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/downloads/virtual-machines/
[automated setup script]: ./scripts/windows-setup.ps1
#### Manual Development Environment Setup
1. Install [Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)] on your machine. Skip this step, if WSL is already installed.
2. Open a PowerShell prompt (hit Windows Key + `X` and open `Windows PowerShell`).
3. Install [Scoop] via `iwr -useb get.scoop.sh | iex`.
4. Install 7zip, git, go, mingw, nvm, and unzip via `scoop install 7zip git go mingw nvm python unzip`.
Check node version with `nvm list`. If node v22 is not installed or set as the current version, then install using `nvm install 22` and set as current using `nvm use 22.xx.xx`.
5. Install the yarn package manager via `npm install --global yarn`
6. Install Visual Studio 2017 or higher. As of this writing the latest version is available at [https://visualstudio.microsoft.com/downloads/]; if that's changed, a good search engine should find it.
7. Make sure you have the `Windows SDK` component installed. This [Visual Studio docs] describes steps to install components.
The [Desktop development with C++] workload needs to be selected, too.
8. Configure `git` to work with linux- and macos-originated files:
```
git config --global --replace-all core.autocrlf false
git config --global --replace-all core.eol lf
```
If you find the `lint:go` tests are failing mysteriously, it's possible that the line-endings are incorrect.
9. Ensure `msbuild_path` and `msvs_version` are configured correctly in `.npmrc` file. Run the following commands to set these properties:
```
npm config set msvs_version
npm config set msbuild_path
```
For example for Visual Studio 2022:
```
npm config set msvs_version 2022
npm config set msbuild_path "C:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\MSBuild\Current\Bin\MSBuild.exe"
```
If you get an error message when trying to run `npm config set...`, run `npm config edit` and then add lines like
```
msvs_version=2022
msbuild_path=C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2022\Community\MSBuild\Current\Bin\MSBuild.exe
```
Do not quote the values to the right side of the equal sign. They aren't needed, and it's possible that some
processor will treat them as literal parts of the path, and then fail.
You can now clone the repository and run `yarn`.
[Scoop]: https://scoop.sh/
[Visual Studio docs]: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/install/modify-visual-studio?view=vs-2022
[Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL)]: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/wsl/install
[Desktop development with C++]: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/visualstudio/install/modify-visual-studio?view=vs-2022#change-workloads-or-individual-components
### macOS
Install `nvm` to get Node.js and npm:
See https://github.com/nvm-sh/nvm#installing-and-updating and run the `curl` or `wget`
command to install nvm.
Note that this script adds code dealing with `nvm` to a profile file
(like `~/.bash_profile`). To add access to `nvm` to a current shell session,
you'll need to `source` that file.
Currently we build Rancher Desktop with Node 22. To install it, run:
```
nvm install 22.14
```
Next, you'll need to install the yarn package manager:
```
npm install --global yarn
```
You'll also need to run `brew install go` if you haven't installed go.
Then you can install dependencies with:
```
yarn
```
> ### ⚠️ Working on a mac with an M1 chip?
>
> You will need to set the `M1` environment variable before installing dependencies and running any npm scripts:
>
> ```
> export M1=1
> yarn
> ```
>
> You will want to run `git clean -fdx` to clean out any cached assets and re-downloaded with the correct arch before running `yarn` if you previously installed dependencies without setting `M1` first.
### Linux
Ensure you have the following installed:
- [Node.js][Node.js] v22. **Make sure you have any development packages
installed.** For example, on openSUSE Leap 15.6 you would need to install
`nodejs22` and `nodejs22-devel`.
- [yarn classic][yarn-classic]
- Go 1.22 or later.
- Dependencies described in the [`node-gyp` docs][node-gyp] installation.
This is required to install the [`ffi-napi`][ffi-napi] npm package. These docs mention
"a proper C/C++ compiler toolchain". You can install `gcc` and `g++` for this.
Then you can install dependencies with:
```
yarn
```
You can then run Rancher Desktop as described below. It may fail on the first run -
if this happens, try doing a factory reset and re-running, which has been known
to solve this issue.
[Node.js]: https://nodejs.org/
[ffi-napi]: https://www.npmjs.com/package/ffi-napi
[node-gyp]: https://github.com/nodejs/node-gyp#on-unix
[yarn-classic]: https://classic.yarnpkg.com/lang/en/docs/install/#debian-stable
## Running
Once you have your dependencies installed you can run a development version
of Rancher Desktop with:
```
yarn dev
```
## Tests
To run the unit tests:
```
yarn test
```
To run the integration tests:
```
yarn test:e2e
```
## Building
Rancher can be built from source on Windows, macOS or Linux.
Cross-compilation is currently not supported. To run a build do:
```
yarn build
yarn package
```
The build output goes to `dist/`.
### Debugging builds with the Chrome remote debugger
The Chrome remote debugger allows you to debug Electron apps using Chrome Developer Tools. You can use it to access log messages that might output to the developer console of the renderer process. This is especially helpful for getting additional debug information in production builds of Rancher Desktop.
#### Starting Rancher Desktop with Remote Debugging Enabled
To enable remote debugging, start Rancher Desktop with the `--remote-debugging-port` argument.
On Linux, start Rancher Desktop with the following command:
``` bash
rancher-desktop --remote-debugging-port="8315" --remote-allow-origins=http://localhost:8315
```
On macOS, start Rancher Desktop with the following command:
```
/Applications/Rancher\ Desktop.app/Contents/MacOS/Rancher\ Desktop --remote-debugging-port="8315" --remote-allow-origins=http://localhost:8315
```
On Windows, start Rancher Desktop with the following command:
``` powershell
cd 'C:\Program Files\Rancher Desktop\'
& '.\Rancher Desktop.exe' --remote-debugging-port="8315" --remote-allow-origins=http://localhost:8315
```
After Rancher Desktop starts, open Chrome and navigate to `http://localhost:8315/`. Select the available target to start remote debugging Rancher Desktop.
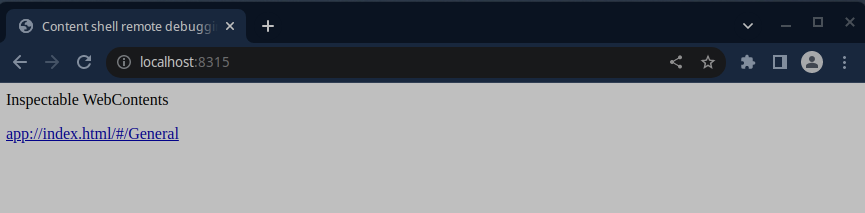
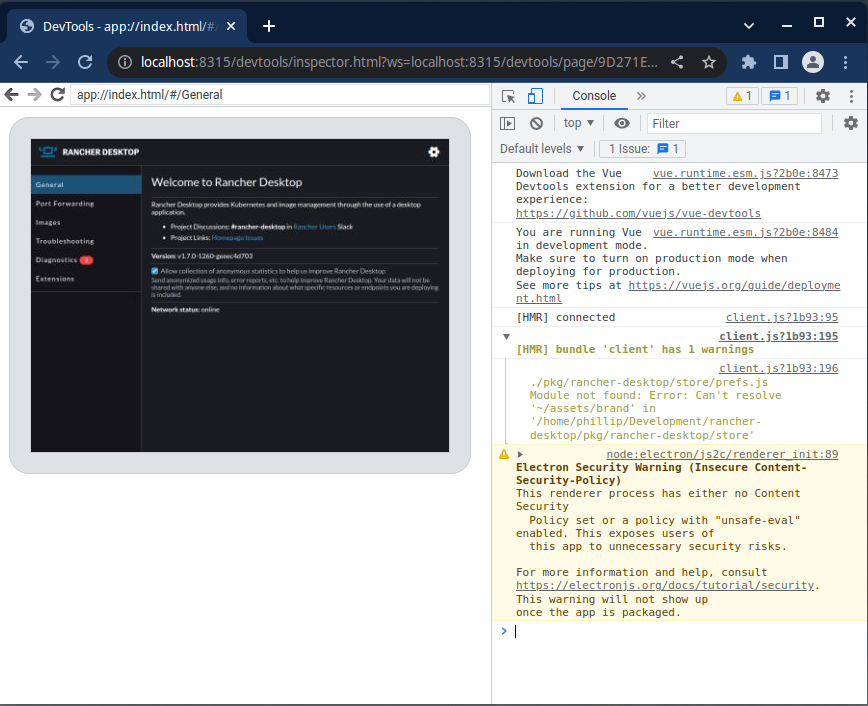
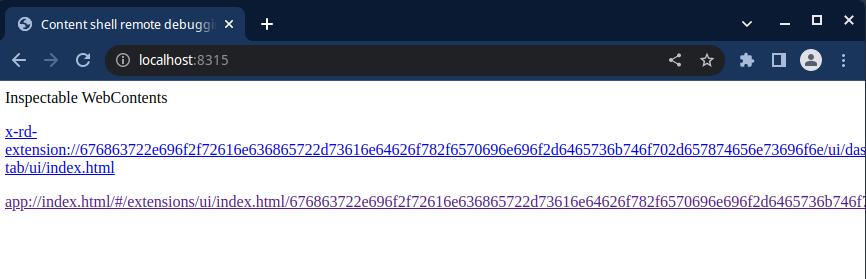
#### Remote Debugging an Extension
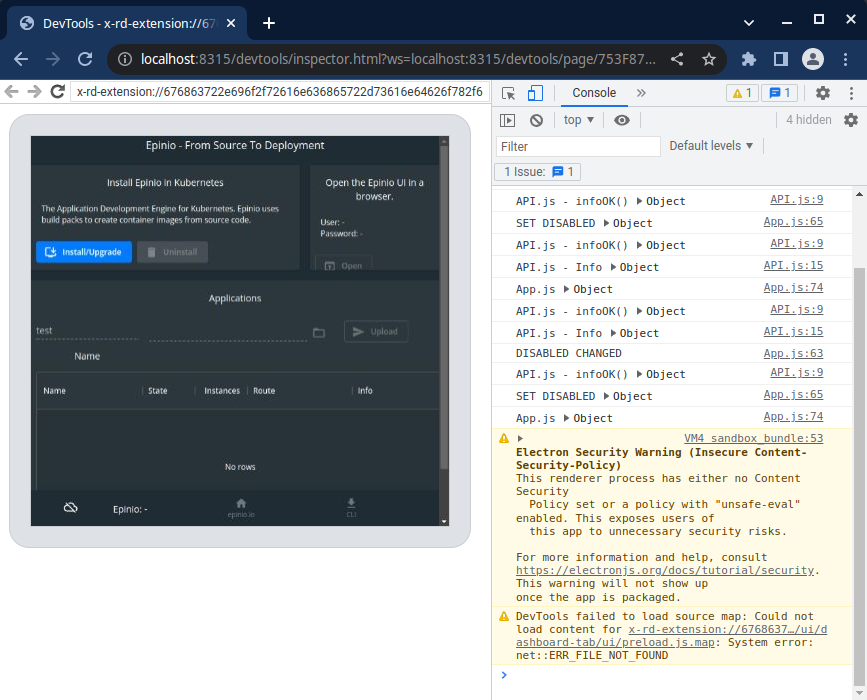
To remote debug an extension, follow the same process as remote debugging a build. However, you will need to load an extension before navigating to `http://localhost:8315/`. Both Rancher Desktop and the loaded extension should be listed as available targets.
### Debugging dev env with GoLand
The following steps have been tested with GoLand on Linux but might work for other
JetBrains IDEs in a similar way.
1. Install the Node.js plugin (via `File > Settings > Plugins`)

2. Go to the "Run/Debug Configurations" dialog (via `Run > Edit Configurations...`)
3. Add a new Node.js configuration with the following settings:
- Name: a name for the debug configuration, e.g. `rancher desktop`
- Node interpreter: choose your installed node interpreter, e.g. `/usr/bin/node`
- Node parameters: `scripts/ts-wrapper.js scripts/dev.ts`
- Working directory: choose the working directory of your project, e.g.
`~/src/rancher-desktop`

4. Save the configuration
5. You can now set a breakpoint and click "Debug 'rancher desktop'" to start debugging

## Development Builds
### Windows and macOS
Each commit triggers a GitHub Actions run that results in application bundles
(`.exe`s and `.dmg`s) being uploaded as artifacts. This can be useful if you
want to test the latest build of Rancher Desktop as built by the build system.
You can download these artifacts from the Summary page of completed `package`
actions.
### Linux
Similar to Windows and macOS, Linux builds of Rancher Desktop are made from each
commit. However on Linux, only part of the process is done by GitHub Actions.
The final part of it is done by [Open Build Service][OBS].
There are two channels of the Rancher Desktop repositories: `dev` and `stable`.
`stable` is the channel that most users use. It is the one that users are
instructed to add in the official [documentation][docs], and the one that contains
builds that are created from official releases. `dev` is the channel that we are
interested in here: it contains builds created from the latest commit made on
the `main` branch, and on any branches that match the format `release-*`. To
learn how to install the development repositories, see below.
When using the `dev` repositories, it is important to understand the format of
the versions of Rancher Desktop available from the `dev` repositories.
The versions are in the format:
```
...
```
where:
`priority` is a meaningless number that exists to give versions built from the `main`
branch priority over versions built from the `release-*` branches when updating.
`branch` is the branch name; dashes are removed due to constraints imposed by
package formats.
`commit_time` is the UNIX timestamp of the commit used to make the build.
`commit` is the shortened hash of the commit used to make the build.
[docs]: https://docs.rancherdesktop.io
[OBS]: https://build.opensuse.org/
#### `.deb` Development Repository
You can add the repo with the following steps:
```
curl -s https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/isv:/Rancher:/dev/deb/Release.key | gpg --dearmor | sudo dd status=none of=/usr/share/keyrings/isv-rancher-dev-archive-keyring.gpg
echo 'deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/isv-rancher-dev-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/isv:/Rancher:/dev/deb/ ./' | sudo dd status=none of=/etc/apt/sources.list.d/isv-rancher-dev.list
sudo apt update
```
You can see available versions with:
```
apt list -a rancher-desktop
```
Once you find the version you want to install you can install it with:
```
sudo apt install rancher-desktop=
```
This works even if you already have a version of Rancher Desktop installed.
#### `.rpm` Development Repository
You can add the repo with:
```
sudo zypper addrepo https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/isv:/Rancher:/dev/rpm/isv:Rancher:dev.repo
sudo zypper refresh
```
You can see available versions with:
```
zypper search -s rancher-desktop
```
Finally, install the version you want with:
```
zypper install --oldpackage rancher-desktop=
```
This works even if you already have a version of Rancher Desktop installed.
#### Development AppImages
There are no repositories for AppImages, but you can access the latest development
AppImage builds [here](https://download.opensuse.org/repositories/isv:/Rancher:/dev/AppImage/).
## API
Rancher Desktop supports a limited HTTP-based API. The API is defined in
`pkg/rancher-desktop/assets/specs/command-api.yaml`, and you can see examples of how it's
invoked in the client code at `go/src/rdctl`.
### Stability
The API is currently at version 1, but is still considered internal and experimental, and
is subject to change without any advance notice. At some point we expect that necessary
changes to the API will go through a warning and deprecation notice.
## Contributing
Please see [the document about contributing](CONTRIBUTING.md).
## Further Reading
Please see the [docs](docs/development/) directory for further developer documentation.