Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/rektdeckard/kdim
Exploring mathematical types and data structures in TypeScript
https://github.com/rektdeckard/kdim
Last synced: 26 days ago
JSON representation
Exploring mathematical types and data structures in TypeScript
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/rektdeckard/kdim
- Owner: rektdeckard
- License: mit
- Created: 2022-05-22T22:14:34.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-05-01T21:12:11.000Z (6 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-09-14T03:27:49.068Z (about 2 months ago)
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage: https://rektdeckard.github.io/kdim
- Size: 56 MB
- Stars: 3
- Watchers: 4
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# kdim
A collection of interesting helpers, data structures, and utility types for messing around with mathematical things in Node/JS/TS. No guarantees are made here as to the speed, efficiency, or correctness of tools provided!
[](https://www.npmjs.com/package/kdim)

[](https://github.com/rektdeckard/kdim)
[](https://github.com/rektdeckard/kdim/fork)
[](https://github.com/rektdeckard/kdim)
[](https://github.com/rektdeckard)
## Contents
- [Installation](#installation)
- [Numerics](#numerics)
- [Constants](#constants)
- [Complex Number](#complex)
- [Rational Number](#rational)
- [Wrapping](#wrapping)
- [Saturating](#saturating)
- [Data Structures](#data-structures)
- [Matrix](#matrix)
- [Binary Search Tree](#bst)
- [K-dimensional Tree](#kdtree)
- [Bloom Filter](#bloomfilter)
- [Ring Buffer](#ringbuffer)
- [Generators](#generators)
- [Random](#random)
- [Range](#range)
- [Probability](#probability)
- [Noise](#noise)
- [Analysis](#analysis)
- [Comparator](#comparator)
- [Statistics](#statistics)
- [Fourier](#fourier)
- [Utils](#Utilities)
- [clamp](#clamp)
- [lerp](#lerp)
- [gcf](#gcf)
- [lcm](#lcm)
- [trailingZeros](#trailingzeros)
- [objectHash](#objecthash)
- [Assertions](#assertions)
- [castInteger](#castinteger)
- [assertInteger](#assertinteger)
- [assertNatural](#assertnatural)
- [assertCounting](#assertcounting)
- [assertValidRange](#assertvalidrange)
- [Types](#utility-types)
- [Tuple](#tuple)
- [Vec](#vec)
## Installation
```bash
npm install kdim
#^ Or whatever package manager you use
```
## Numerics
### Constants
Exported Constants
```ts
const U8_MAX = (1 << 8) - 1;
const U16_MAX = (1 << 16) - 1;
const U32_MAX = -1 >>> 0;
const I8_MAX = (1 << 7) - 1;
const I8_MIN = -I8_MAX - 1;
const I16_MAX = (1 << 15) - 1;
const I16_MIN = -I16_MAX - 1;
const I32_MAX = (U32_MAX + 1) / 2 - 1;
const I32_MIN = -I32_MAX - 1;
```
### Complex
A numeric type with real and imaginary components. An instance of the class is immutable, so arithmetic operations on it will always produce a new instance.
Class Signature
```ts
class Complex implements Number {
constructor(real?: number, imaginary?: number);
get real(): number;
get imaginary(): number;
static from(init: N): Complex;
add(addend: Number | Complex): Complex;
sub(subtrahend: Number | Complex): Complex;
mul(multiplicand: Number | Complex): Complex;
div(divisor: Number | Complex): Complex;
pow(exponent: Number): Complex;
eq(other: Number | Complex): boolean;
conjugate(): Complex;
valueOf(): number;
toFixed(fractionDigits?: number | undefined): string;
toExponential(fractionDigits?: number | undefined): string;
toPrecision(precision?: number | undefined): string;
toString(radix?: number | undefined): string;
toLocaleString(locales?: unknown, options?: unknown): string;
toLocaleString(
locales?: Intl.LocalesArgument,
options?: Intl.NumberFormatOptions | undefined
): string;
toLocaleString(
locales?: string | string[] | undefined,
options?: Intl.NumberFormatOptions | undefined
): string;
[Symbol.toPrimitive](hint: string): string | number;
get [Symbol.toStringTag](): string;
}
```
```ts
import { Complex } from "kdim";
const a = new Complex(-3, 5); // -3 + 5i
a.real; // -3
a.imaginary; // 5
const b = new Complex(7, -1); // 7 - i
a.add(b); // 4 + 4i
a.mul(b); // -16 + 38i
b.pow(2); // 48 - 14i
const c = Complex.from(b); // 7 - i
b.eq(c); // true
```
### Rational
A rational number class for fraction arithmetic without loss of precision. Operations are only guaranteed where numerator and denominator are within `Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER` and `Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER`.
Class Signature
```ts
class Rational implements Number {
constructor(numerator: number, denominator: number = 1);
get numerator(): number;
get denominator(): number;
static from(...input: RationalLike | [fraction: string]): Rational;
static parse(fraction: string): Rational;
recip(): Rational;
add(...addend: RationalLike): Rational;
sub(...subtrahend: RationalLike): Rational;
mul(...multiplicand: RationalLike): Rational;
div(...divisor: RationalLike): Rational;
pow(exponent: number): Rational;
mod(modulus: number): Rational;
abs(): Rational;
eq(...other: RationalLike): boolean;
gt(...other: RationalLike): boolean;
gte(...other: RationalLike): boolean;
lt(...other: RationalLike): boolean;
lte(...other: RationalLike): boolean;
toFraction(options?: RationalFormatOptions): string;
valueOf(): number;
toFixed(fractionDigits?: number | undefined): string;
toExponential(fractionDigits?: number | undefined): string;
toPrecision(precision?: number | undefined): string;
toString(radix?: number | undefined): string;
}
type RationalFormat = "space" | "nospace" | "unicode";
type RationalFormatOptions = {
mixed?: boolean;
format?: RationalFormat;
};
type RationalLike =
| [rational: Rational]
| [numerator: number]
| [numerator: number, denominator: number];
```
```ts
import { Rational } from "kdim";
const a = new Rational(5, 31); // construct from numerator, denominator
const b = Rational.parse("3 / 9"); // parse from string (spaces are not required)
const result = a
.add(b) // rationals as arguments
.mul(12) // integer arguments
.div(5, 4) // implicit rational arguments
.toFraction(); // "116/155"
Rational.parse("16 / 24").eq("2 / 3"); // true
```
Rationals are immutable, so arithmetic methods always produce new values. They will always simplify to their most reduced form upon construction.
Serializing a Rational by calling the `toFraction` allows to specify whether it should be in `mixed` number or irrational format (the default), as well as whether the unicode `FRACTION SLASH` (`\u2044`) character should be used instead of a typical forward slash (`/`), which produces small fractions on some platforms, E.G. `3⁄4`.
```ts
import { Rational } from "kdim";
Rational.from("3/4").toFraction({ format: "nospace" }); // "3/4"
Rational.from("3/4").toFraction({ format: "unicode" }); // "3⁄4"
```
### Wrapping
A wrapping integer class, allowing a value to be constrained to an arbitrary range, and wrapping around the range when arithmetic operations cause it to overflow or underflow Wrapping numbers are immutable, so arithmetic methods always produce new values.
Class Signature
```ts
abstract class Bounded {
abstract get value(): number;
abstract get min(): number;
abstract get max(): number;
}
type BoundedOptions = {
max: number;
min?: number;
};
class Wrapping implements Bounded, Number {
constructor({ max, min }: BoundedOptions, value?: number);
static from(bounded: Bounded): Wrapping;
add(n: N): Wrapping;
sub(n: N): Wrapping;
get value(): number;
get min(): number;
get max(): number;
valueOf(): number;
toFixed(fractionDigits?: number | undefined): string;
toExponential(fractionDigits?: number | undefined): string;
toPrecision(precision?: number | undefined): string;
toString(radix?: number | undefined): string;
toLocaleString(locales?: unknown, options?: unknown): string;
toLocaleString(
locales?: Intl.LocalesArgument,
options?: Intl.NumberFormatOptions | undefined
): string;
[Symbol.toPrimitive](hint: string): string | number;
get [Symbol.toStringTag](): string;
}
```
```ts
import { Wrapping } from "kdim";
let u16 = new Wrapping({ max: 0xffff }, 1); // default min = 0
u16 = u16.add(0xfffd); // (0xFFFE)
u16 = u16.add(1); // (0xFFFF)
u16 = u16.add(1); // (0x0000)
u16 = u16.add(1); // (0x0001)
```
Wrapping integers can have arbitrary `min` and `max` values (inclusive), and can be initialized with a starting value. Arithmetic operations can be performed with any numeric type, using the bounds of the reciever, and can be chained:
```ts
import { Wrapping } from "kdim";
let wk = new Wrapping({ min: 1, max: 7 }); // default value = min
let yr = new Wrapping({ min: 1, max: 365 }, 24);
wk = wk.add(yr); // (4)
yr = yr
.add(wk) // (28)
.sub(3) // (25)
.sub(30); // (361)
```
> **NOTE:** constructor throws a `RangeError` when `min >= max` or any of `min`, `max`, or `initial` have a fracitonal component, as will attempting to `add()` or `sub()` a number with a fractional component.
They can also be cloned from other Wrapping values, or other `Bounded` values like [Saturating](#saturating), copying their properties:
```ts
import { Wrapping, Saturating } from "kdim";
const vuMeter = new Saturating({ min: -20, max: 3 }, -3);
const clip = Wrapping.from(vuMeter);
```
### Saturating
A saturating (or clamping) integer class allowing a value to be constrained to an arbitrary range, and clamping it to the bounds when arithmetic operations would cause it to overflow or underflow. Saturating numbers are immutable, so arithmetic methods always produce new values.
Class Signature
```ts
class Saturating implements Bounded, Number {
constructor({ max, min }: BoundedOptions, value?: number);
static from(bounded: Bounded): Saturating;
add(n: N): Saturating;
sub(n: N): Saturating;
mul(n: N): Saturating;
div(n: N): Saturating;
get value(): number;
get min(): number;
get max(): number;
valueOf(): number;
toFixed(fractionDigits?: number | undefined): string;
toExponential(fractionDigits?: number | undefined): string;
toPrecision(precision?: number | undefined): string;
toString(radix?: number | undefined): string;
toLocaleString(locales?: unknown, options?: unknown): string;
toLocaleString(
locales?: Intl.LocalesArgument,
options?: Intl.NumberFormatOptions | undefined
): string;
[Symbol.toPrimitive](hint: string): string | number;
get [Symbol.toStringTag](): string;
}
```
```ts
import { Saturating } from "kdim";
let level = new Saturating({ min: 1, max: 99 });
level = level.add(50); // (51)
level = level.add(30); // (81)
level = level.add(30); // (99)
```
As with [Wrapping](#wrapping), Saturating types support arithmetic operations with any numeric type, using the receiver.
```ts
import { Saturating, Wrapping } from "kdim";
const s = new Saturating({ min: -1, max: 10 }, 1);
const w = new Wrapping({ max: 7 });
s.add(7); // (8)
w.add(5); // (5)
s.add(w); // (8)
```
> **NOTE:** constructor throws a `RangeError` when `min >= max` or any of `min`, `max`, or `initial` have a fracitonal component, as will attempting to `add()`, `sub()`, `mul()`, or `div()` a number with a fractional component or attempting to `div(0)`.
[Wrapping](#wrapping) and [Saturating](#saturating) values may also be used with mathematical operators for convenience, though they will be cast to a primitive in doing so, and will not be modified:
```ts
import { Saturating } from "kdim";
const s = new Saturating({ max: 50 }, 40);
const primitiveSum = s + 20; // 60
s; // Still (40)
s.add(20); // 50
```
## Data Structures
### Matrix
A concrete Matrix class for simple linear algebra, currently only supporting simple numbers, but with plans to add support for complex numbers.
Class Signature
```ts
class Matrix
implements Iterable>
{
constructor(data: MatrixLike);
static zero(n: N): Matrix;
static identity(n: N): Matrix;
static withSize(
rows: M,
cols: N,
fillValue?: number
): Matrix;
static fromDiagonal(
diagonal: Tuple | number[]
): Matrix;
static fromMTX(
data: string,
options?: MTXOptions
): Matrix;
static isMatrixLike(
arg: unknown,
...dimensions: [m: M, n: N] | []
): arg is MatrixLike;
get rows(): M;
get cols(): N;
get size(): number;
get data(): MatrixLike;
isSquare(): boolean;
isOrthogonal(): boolean;
at(i: number, j: number): number | undefined;
row(i: number): Tuple | undefined;
col(j: number): Tuple | undefined;
clone(): Matrix;
submatrix(
options: SubmatrixOptions
): Matrix;
augment(
other: MatrixOperand
): Matrix;
trace(): number;
determinant(): number | undefined;
inverse(tolerance?: number): Matrix | undefined;
transpose(): Matrix;
add(other: MatrixOperand): Matrix;
sub(other: MatrixOperand): Matrix;
mul | number>(
other: I
): MatrixResult;
pow(k: number): Matrix;
eq(other: MatrixOperand, tolerance?: number): boolean;
dot(other: MatrixOperand): number;
[Symbol.iterator](): Iterator>;
}
```
```ts
import { Matrix } from "kdim";
const mtx = new Matrix<3, 3>([
[5, 2, 10],
[-1, 7, 7],
[3, -3, 9],
]);
mtx.rows; // 3
mtx.cols; // 3
mtx.col(2); // [10, 7, 9]
mtx.mul(2);
// [
// [10, 4, 20],
// [-2, 14, 14],
// [6, -6, 18],
// ]
mtx.mul(Matrix.identity(3)).eq(mtx); // true
```
### BST
A simple binary search tree for time-efficient search or arbitrary data.
Class Signature
```ts
class BSTNode {
constructor(data: V, parent?: BSTNode);
asBST(): BST;
}
class BST implements Iterable {
constructor(compareFn?: CompareFunction);
static fromNode(node: BSTNode): BST;
search(value: V): BSTNode | null;
insert(value: V): boolean;
has(value: V): boolean;
delete(valueOrNode: V | BSTNode): boolean;
max(node?: BSTNode): BSTNode | null;
min(node?: BSTNode): BSTNode | null;
successor(node: BSTNode): BSTNode | null;
predecessor(node: BSTNode): BSTNode | null;
asOrdered(): V[];
asPreOrdered(): V[];
asPostOrdered(): V[];
*[Symbol.iterator](): IterableIterator;
}
```
```ts
import { BST, CompareFunction } from "kdim";
type Person = { name: string; age: number };
const comp: CompareFunction = (a, b) =>
a.name === b.name ? a.age - b.age : a > b ? 1 : -1;
const tree = new BST(comp);
tree.insert({ name: "Cillian Murphy", age: 47 });
tree.insert({ name: "Emily Blunt", age: 40 });
```
### KDTree
A time-efficient data structure for searching higher-dimensional datasets. Inspired by Mike Pound's [Computerphile Video](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BK5x7IUTIyU).
Class Signature
```ts
class Node {
parent: Node | null;
point: T;
left: Node | null;
right: Node | null;
constructor(point: T);
}
type KDTreeOptions = {
clone?: boolean;
};
class KDTree implements Iterable> {
constructor(data?: Vec[], options?: KDTreeOptions);
get dimensions(): number;
get tree(): Node> | null;
[Symbol.iterator](): Iterator>;
insert(point: Vec): void;
remove(point: Vec): Vec | null | void;
has(point: Vec): boolean;
nearestNeighbor(point: Vec): {
point: Vec | null;
distance: number;
};
}
```
```ts
import { Vec, KDTree } from "kdim";
const data: Vec<5>[] = [
[0, 1, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
];
const tree = new KDTree<5>(data);
const testPoint: Vec<5> = [1, 0, 1, 1, 1];
tree.has(testPoint); // false
const { point, distance } = tree.nearestNeighbor(testPoint);
// { point: [1, 1, 1, 1, 1], distance: 1 }
tree.insert(testPoint);
tree.has(testPoint); // true
tree.remove(testPoint);
tree.has(testPoint); // false
```
> **NOTE:** by default, input datasets are shallowly copied during tree construction, and retained within the data structure. If desired, the underlying dataset may be used without copying, using the option `copy: false`;
### BloomFilter
A probabalistic data structure used to test for membership of a large set in which storage of all set elements is unfeasible. False positives are possible, but false negatives are not, so that the structure will tell you if an element is either "probably in the set" or "definitely not in the set".
Class Signature
```ts
type HashFunction = (data: T) => Promise | string;
type BloomFilterOptions = {
size?: number;
hashFunctions?: Array>;
};
class BloomFilter {
constructor(options?: BloomFilterOptions);
static DEFAULT_HASH_FUNCTIONS: HashFunction[]:
async add(element: T): void;
async test(element: T): boolean;
}
```
```ts
import { BloomFilter } from "kdim";
const filter = new BloomFilter<{ name: string }>();
await filter.add({ name: "Julien Baker" });
await filter.add({ name: "Phoebe Bridgers" });
await filter.add({ name: "Lucy Dacus" });
await filter.test({ name: "Phoebe Bridgers" }); // true
await filter.test({ name: "Julia Jacklin" }); // false
```
> **NOTE:** by default, `BloomFilter` uses a set of object hashers that considers two objects to have the same hash if all their properties are equal, therefore will consider structurally identical objects equal.
### RingBuffer
A fixed-capacity FIFO queue that overwrites earliest entries when its capacity is exceeded.
Class Signature
```ts
type Constructor = { new (capacity: number): RingBuffer };
class RingBuffer implements Iterable {
constructor(capacity: number);
static from(this: Constructor>, data: T[]): RingBuffer;
get capacity(): number;
get data(): (T | null)[];
get isEmpty(): boolean;
get isFull(): boolean;
get [Symbol.toStringTag](): string;
toString(): string;
[Symbol.iterator](): IterableIterator;
peek(index: number = 0): T | null;
enqueue(element: T): void;
dequeue(): T | null;
drain(): T[];
}
```
```ts
import { RingBuffer } from "kdim";
// Initialized with capacity
const buff = new RingBuffer(10);
buff.enqueue("age");
buff.enqueue("quod");
buff.enqueue("agis");
buff.isFull; // false
buff.isEmpty; // false
buff.dequeue(); // "age"
buff.peek(); // "quod"
buff.drain(); // ["quod", "agis"]
buff.isEmpty; // true
// Initialized with data
const buff2 = RingBuffer.from([12, 24, 36, 48]);
buff.capacity; // 4
buff.enqueue(1);
buff.peek(); // 1
buff.peek(2); // 36
buff.dequeue(); // 1
buff.dequeue(); // 24
buff.drain(); // [36, 48];
```
## Generators
### Random
Produce random values of common numeric and other types (E.G. `u8`, `integer`, `bool`), sample and shuffle `Array`s and `Set`s of values, and determine characteristics of those sets.
Class Signature
```ts
class Random {
static bool(): boolean;
static natural(max?: number): number;
static counting(max?: number): number;
static integer(opts?: { min?: number; max?: number }): number;
static float(opts?: { min?: number; max?: number }): number;
static dice(sides: number): number;
static u8(): number;
static u16(): number;
static u32(): number;
static i8(): number;
static i16(): number;
static i32(): number;
static unitVector(n: N): Vec;
static sample(options: T[] | Set): T | undefined;
static take(options: T[] | Set): T | undefined;
static permute(array: T[]): void;
static permutation(array: T[]): T[];
static permutationsOf(set: number | Array | Set): number;
static derange(array: T[]): void;
static derangement(array: T[]): T[];
static derangementsOf(set: number | Array | Set): number;
static Seedable = Mulberry32;
static SFC32 = SFC32;
static JSF32B = JSF32B;
static SplitMix32 = SplitMix32;
static Mulberry32 = Mulberry32;
static GJRand32 = GJRand32;
}
```
```ts
import { Random } from "kdim";
// Generate values
const trueOrFalse = Random.bool();
const volume = Random.integer({ max: 11 });
const attackRoll = Random.dice(20);
// Sample lists and sets
const adjectives = ["harder", "better", "faster", "stronger"];
const doIt = Random.sample(adjectives);
const cookieJar = new Set(["chocolate chip", "oatmeal", "macadamia"]);
const eaten = Random.take(cookieJar); // "macadamia" maybe?
cookieJar.has(eaten); // false
// Shuffle lists
const code = [13, 17, 29, 42];
const shuf = Random.permutation(code); // [29, 17, 13, 42] maybe?
const friends = ["alice", "bob", "carlos", "dan", "erin"];
const secretSantas = Random.derangement(friends); // Shuffled with no fixed points
Random.derangementsOf(friends); // 44: ways to match 5 people for secret santa
```
> **NOTE:** Generators that take numeric arguments will throw if range is invalid (E.G. `min > max`), values are invalid (decimal number passed to integer generator), or other.
#### Seedable PRNGs
In addition to the default, static random generator functions, there are a number of constructable, seedable PRNGs, each with slightly different characteristics:
- `Seedable`: the default seedable PRNG, currently `Mulberry32`
- `Mulberry32`: a fast, well-distributed PRNG with 32 bits of internal state and a reasonable period of ~4 billion
- `SFC32`: a fast, chaotic PRNG with 128 bits of internal state and a large period
- `GJRand32`: a chaotic PRNG with 128 bits of internal state and a massive period, with pretty good performance
- `JSF32B`: yet another fast, chaotic PRNG with overall good characteristics
- `SplitMix32`: the fastest PRNG here, with overall great characteristics, if relatively small seed and period
```ts
const m32 = new Random.Mulberry32(69);
const sfc = new Random.SFC32(69, 420, 0, 42);
const gjr = new Random.GJRand32(69, 420, 0, 42);
const jsf = new Random.JSF32B(69, 420, 0, 42);
const smx = new Random.SplitMix32(69);
[m32, sfc, gjr, jsf, smx].map((rng) => rng.dice(20));
// [ 16, 1, 1, 18, 10 ]
```
> **NOTE:** remember to construct these PRNGs! Unlike the `Random` singleton itself, each of these needs an initial seed, which can be chosen as a constant if predictable results are desired, or from another source of entropy, like `Math.random()`.
### Range
Produce values over numeric ranges, including infinite ranges, descending ranges, and custom step sizes. The `Range.of` static method will produce an array, while the `Range.lazy` static method returns a Generator which can be iterated, producing values on demand.
Class Signature
```ts
type RangeOptions = { from?: number; to: number; step?: number };
type Constructor> = {
new (...args: A): T;
};
type Factory> = (...args: A) => T;
class Range {
static of(
where: number | RangeOptions,
factory?: Constructor | Factory
): N[];
static *lazy(
where: number | RangeOptions,
factory?: Constructor | Factory
): Generator;
}
```
#### Simple numeric ranges
```ts
import { Range } from "kdim";
// Produce simple numeric ranges
const zeroToFive = Range.of(5); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4]
// Produce ranges with custom bounds and step sizes
const oddNumbers = Range.of({ from: 1, to: 9, step: 2 }); // [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
const descending = Range.of({ from: 43, to: 40 }); // [43, 42, 41, 40]
```
By default, `from = 0` and `step = 1`, unless specified.
> **NOTE:** throws an Error when given a negative `step` size; the sign of the step is determined by the direction of the range, E.G. `Math.sign(to - from)`.
#### Ranges of custom values via factory function
```ts
// Produce a range of custom values with a factory function
type Foo = { bar: number };
const foos = Range.of(4, (n) => ({
bar: n ** n,
}));
// [{ bar: 0 }, { bar: 1 }, { bar: 4 }, { bar: 27 }]
```
#### Ranges of class instances
```ts
// Produce instances of a class with a constructor of type
// { new (n: number): T }
class Baz {
n: number;
s: number;
constructor(n: number) {
this.n = n;
this.s = n * n;
}
}
const bazzes = Range.of({ from: 2, to: 4 }, Baz);
// [Baz { n: 2, s: 4 }, Baz { n: 3, s: 9 }, Baz { n: 4, s: 16 }]
```
#### Lazy ranges
```ts
// Iterating an infinite range
const gen = Range.lazy({ from: 1, to: Infinity });
for (const i of gen) {
if (i >= 99) break;
}
gen.next(); // 100
// Using a lazy range to defer producing values until needed
const deferred = Range.lazy({ to: 20 }, (n) => new Complex(-n, n - 5));
// Some time later...
const complexes = Array.from(deferred); // Only now are values produced
```
> **NOTE:** Generators over infinite ranges _will_ lock up resources and crash the process if you attempt to convert them to an Array via `Array.from(gen)`, `[...gen]`, or other means.
### Noise
Generate structured mathematical noise patterns like Perlin and Simplex, in both 2D and 3D spaces. Layer patterns for fractal noise fields. Efficiently fill `TypedArray` and `ImageData` buffers for use in graphics applications. These can be parametrized with [Seedable PRNGs](#seedable-prngs), or use the default (unseedable) PRNG based on `Math.random()`.
Abstract Class Signature
```ts
abstract class NoiseGenerator {
abstract seed(seed: number): this;
abstract xy(x: number, y: number): number;
abstract xyz(x: number, y: number, z: number): number;
abstract fill(target: NoiseTarget, options?: NoiseFillOptions): void;
}
type NoiseTarget = ImageData | number[][] | TypedArrayNoiseTarget;
type TypedArrayNoiseTarget = {
data: Uint8ClampedArray;
width: number;
stride: number;
};
type NoiseFillOptions = {
freq?: number;
set?: (cell: { x: number; y: number; z: number; v: number }) => void;
} & (Noise2DFillOptions | Noise3DFillOptions);
type Noise2DFillOptions = {
z?: never;
};
type Noise3DFillOptions = {
z: number;
};
```
| Type | Description | Image |
| -------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- | ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
| Perlin | `freq = 5` |  |
| Simplex | `freq = 5` | 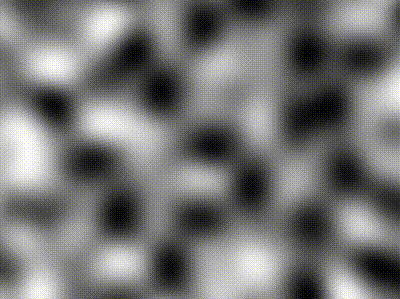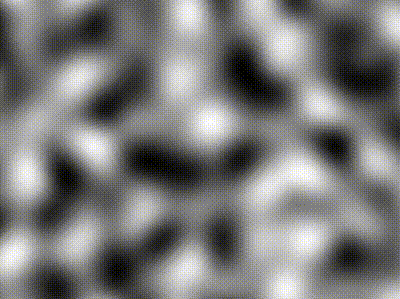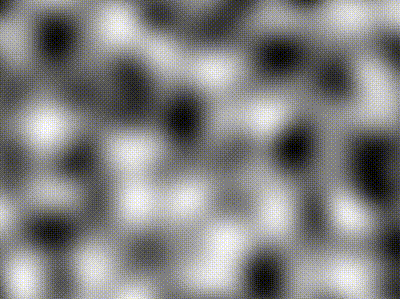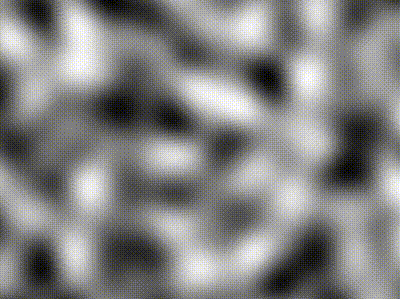 |
| Compound noise | Perlin of `freq = 5` added pixel-wise with Simplex of `freq = 40` contribution scaled by `0.25` | 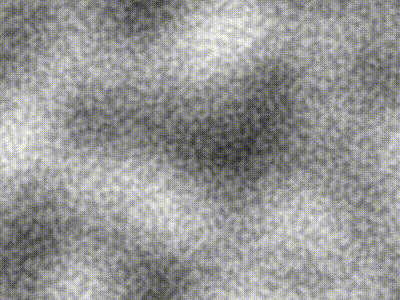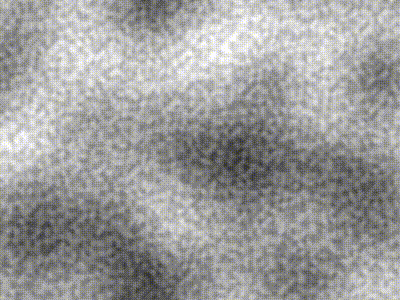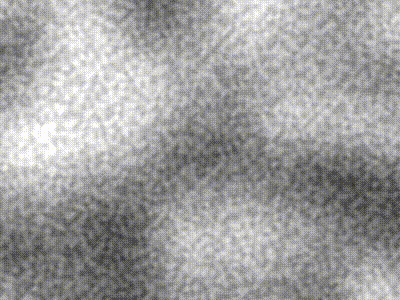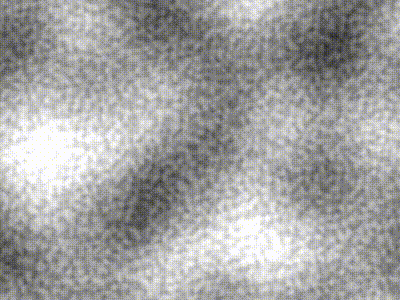 |
The `Noise` module contains various classes implementing `NoiseGenerator`:
#### Perlin
[Perlin noise](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Perlin_noise) is a type of gradient noise with smoothly-varying texture in 2 and 3 dimensions.
```ts
import { Noise } from "kdim";
const perlin = new Noise.Perlin();
// Iteratively create noise over a 2D plane
for (let x = 0; x < 100; x++) {
for (let y = 0; y < 100; y++) {
// Generates a number between [-1, 1] that smoothly varies with x and y.
// Since we scale the coordinates down to [0, 1], the final texture
// will have a frequency of 1 (one "cell" of a pattern).
const value = perlin.xy(x / 100, y / 100);
doSomething(value);
}
}
// Fill a canvas with Perlin noise, animating smoothly as we take
// different slices of the 3D volume.
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
const img = ctx.createImageData(canvas.width, canvas.height);
let z = 0;
(function loop() {
// Fill the underlying buffer with a 2D slice of 3D noise, which
// has a frequncy of 5x5 "cells". The `fill` method will detect
// the buffer size and stride automatically.
perlin.fill(img, { freq: 5, z });
ctx.putImageData(img, 0, 0);
z += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(loop);
})();
```
#### Simplex
[Simplex noise](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Simplex_noise) is a type of gradient noise with with fewer dimensional artifacts than [Perlin noise](#perlin). It is visually more isotropic, and less computationally expensive in higher dimensions.
```ts
import { Noise } from "kdim";
const simplex = new Noise.Simplex();
// Iteratively create noise over a 2D plane
for (let x = 0; x < 100; x++) {
for (let y = 0; y < 100; y++) {
// Generates a number between [-1, 1] that smoothly varies with x and y.
// Since we scale the coordinates down to [0, 1], the final texture
// will have a frequency of 1 (one "cell" of a pattern).
const value = simplex.xy(x / 100, y / 100);
doSomething(value);
}
}
// Fill a canvas with Simplex noise, animating smoothly as we take
// different slices of the 3D volume.
const canvas = document.querySelector("canvas");
const ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
const img = ctx.createImageData(canvas.width, canvas.height);
let z = 0;
(function loop() {
// Fill the underlying buffer with a 2D slice of 3D noise, which
// has a frequncy of 5x5 "cells". The `fill` method will detect
// the buffer size and stride automatically.
simplex.fill(img, { freq: 5, z });
ctx.putImageData(img, 0, 0);
z += 0.01;
requestAnimationFrame(loop);
})();
```
### Probability
Sample weighted collections of elements to emulate complex probabilities, unfair dice, etc. These can be parametrized with [Seedable PRNGs](#seedable-prngs), or use the default (unseedable) PRNG based on `Math.random()`.
Class Signature
```ts
class Probability {
constructor(events: ProbabilityEvent[] = [], rng?: PRNG | null);
event(event: ProbabilityEvent): this;
sample(): ProbabilityEvent;
take(): ProbabilityEvent;
}
type ProbabilityEvent = {
value: T;
p?: number;
};
```
```ts
import { Probability } from "kdim";
const events = [
{ value: "common", p: 0.65 },
{ value: "uncommon", p: 0.25 },
{ value: "rare", p: 0.1 },
];
const d1 = new Probability(events);
d1.sample().value; // "common", probably?
const rng = new Random.Mulberry32(42);
const d2 = new Probability(events, new Random.Seedable(42));
d2.sample().value; // "uncommon", definitely.
```
## Analysis
### Comparator
A class used to determine ordering and equality of values of arbitrary types. A `Comparator` implements custom equality (`eq`) and ordering (`gt`, `gte`, `lt`, `lte`) for values based on the provided `CompareFunction`. If no function is provided, it defaults to the same lexical comparison used by `Array.prototype.sort`.
Class Signature
```ts
type CompareFunction = (a: V, b: V) => number;
class Comparator {
constructor(compareFn?: CompareFunction);
static lexicalCompare(a: V, b: V): 0 | 1 | -1;
static reverseLexicalCompare(a: V, b: V): 0 | 1 | -1;
static numericCompare(a: V, b: V): number;
static reverseNumericCompare(a: V, b: V): number;
eq(a: V, b: V): boolean;
gt(a: V, b: V): boolean;
gte(a: V, b: V): boolean;
lt(a: V, b: V): boolean;
lte(a: V, b: V): boolean;
}
```
#### CompareFunction
The `CompareFunction` type is similar to the callback passed to `Array.prototype.sort`, in that it is called with two arguments `a` and `b`, and returns a number determining if `a` should be sorted before `b` (negative number), after `b` (positive number), or equal to `b` (0). The `Comparator` class has a number of built-in static `CompareFunction`s for ordering primitives.
```ts
import { Comparator } from "kdim";
// Using built-in CompareFunctions for sorting
const ns = [12, 5, 80, 3, -1];
const descendingOrder = ns.sort(Comparator.reverseNumericCompare);
// [80, 12, 5, 3, -1]
const words = ["hi", "there", "friends"];
const descendingWordOrder = words.sort(Comparator.reverseLexicalCompare);
// ["there", "friends", "hi"]
```
#### Comparator of a complex type
```ts
// Compare non-primitive values by comparing their primitive properties
const quzComp = new Comparator<{ quz: number }>((a, b) => {
return Comparator.numericCompare(a.quz, b.quz);
});
quzComp.eq({ quz: 7 }, { quz: 7 }); // true
quzComp.lt({ quz: 7 }, { quz: 3 }); // true
quzComp.gte({ quz: 1 }, { quz: -20 }); // false
```
#### Comparator for values of multiple types
```ts
type A = { id: number; tag: string };
type B = { id: number; foo: string };
// As and Bs are considered equal if their ids and string part match,
// otherwise they are ordered first by id then by string part.
const abComp = new Comparator((first, second) => {
if (first.id === second.id) {
const firstStr = (first as A).tag || (first as B).foo;
const secondStr = (second as A).tag || (second as B).foo;
return Comparator.lexicalCompare(firstStr, secondStr);
} else {
return first.id - second.id;
}
});
abComp.eq({ id: 1, tag: "cool" }, { id: 1, foo: "bad" }); // false
abComp.eq({ id: 1, tag: "cool" }, { id: 1, foo: "cool" }); // true
abComp.gt({ id: 1, tag: "cool" }, { id: 1, tag: "neat" }); // true
abComp.lte({ id: 5, tag: "ok" }, { id: 99, tag: "neat" }); // false
```
### Statistics
Perform common statistical analyses on discrete numeric data. These data are typically `number[]`, but can also be object number types like [Complex](#complex) and [Rational](#rational), or your own custom number types that implement the `ArithmeticObject` interface listed in the class signature below.
Class Signature
```ts
class Statistics {
static min>(data: T[]): T | undefined;
static max>(data: T[]): T | undefined;
static mean>(data: T[]): T | undefined;
static median>(data: T[]): T | undefined;
static mode>(
data: T[]
): number[] | undefined;
static variance>(data: T[]): T | undefined;
static sd>(data: T[]): T | undefined;
static sem>(data: T[]): T | undefined;
static range>(data: T[]): T | undefined;
static iqr>(
data: T[],
options?: SummaryOptions
): T | undefined;
static mad>(data: T[]): T | undefined;
static percentiles>(
data: T[],
options?: PercentileOptions | number[]
): T[] | undefined;
static summary>(
data: T[],
options?: SummaryOptions
): FiveNumberSummary | undefined;
}
type ArithmethicObject = Add<[T] | [number], T> &
Sub<[T] | [number], T> &
Mul<[T] | [number], T> &
Div<[T] | [number], T> &
Pow<[T] | [number], T> &
Eq<[T] | [number]> &
Abs;
type Arithmetic = number | ArithmethicObject;
type FiveNumberSummary = {
q0: T;
q1: T;
q2: T;
q3: T;
q4: T;
};
type InterpolationMethod =
| "midpoint"
| "nearest"
| "hrank"
| "lrank"
| "weighted"
| "outer";
type SummaryOptions = {
method?: InterpolationMethod;
};
type PercentileOptions = SummaryOptions & {
p: number[];
};
const QUARTILES = [0, 0.25, 0.5, 0.75, 1];
```
#### Central tendency
Calculate common measures of centrality, including `mean`, `median`, `mode`.
```ts
import { Statistics } from "kdim";
const data = [3, 2, 2, 9, 4, 7, 1]; // data does not need to be pre-sorted
Statistics.mean(data); // 6
Statistics.median(data); // 5
Statistics.mode(data); // [2] (returned as an array for cases of multimodal data)
```
#### Dispersion
Calculate common measures of statistical dispersion.
```ts
import { Statistics } from "kdim";
const data = [2, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 7, 9];
Statistics.sd(data); // Standard Deviation = 2
Statistics.variance(data); // Variance = 4
Statistics.sem(data); // Standard Error of Mean = 0.7071067811865475
Statistics.range(data); // Range = 7
Statistics.mad(data); // Mean Absolute Deviation = 0.5
Statistics.iqr(data); // Inter-Quartile Range = 2
```
#### Interpolation methods
Many of the statistical methods offer multiple `InterpolationMethod` strategies for interpolating between discrete data points.
```ts
import { Statistics } from "kdim";
const data = [6, 7, 15, 36, 39, 40, 41, 42, 43, 47, 49];
// Five-Number Summary using different interpolation strategies
Statistics.summary(data); // default "midpoint"
// { q0: 6, q1: 25.5, q2: 40, q3: 42.5, q4: 49 }
Statistics.summary(data, { method: "nearest" });
// { q0: 6, q1: 36, q2: 40, q3: 43, q4: 49 }
Statistics.summary(data, { method: "lrank" });
// { q0: 6, q1: 15, q2: 40, q3: 42, q4: 49 }
```
### Fourier
Perform Fourier analysis on discrete numeric data.
Class Signature
```ts
class Fourier {
static dft(input: (Number | Complex)[]): Complex[];
}
```
```ts
import { Fourier } from "kdim";
const samples = [1, 1, 0, 0];
const d = Fourier.dft(sample);
// [
// Complex { real: 2, imaginary: 0 },
// Complex { real: 1, imaginary: -1 },
// Complex { real: 0, imaginary: 0 },
// Complex { real: 1, imaginary: 1 },
// ]
```
## Utilities
### clamp
Constrain a value to within a given range `[min, max]`.
Function Signature
```ts
function clamp(min: number, max: number, value: number): number;
```
```ts
import { clamp } from "kdim";
// Clamp values to [0, 255]
const a = 32;
const b = 300;
clamp(0, 255, a); // 32
clamp(0, 255, b); // 255
```
> **NOTE:** throws a RangeError when the range is invalid, E.G. `min > max`.
### lerp
Linear interpolation of a value in the range `[0, 1]` to a value in the range `[from, to]`.
Function Signature
```ts
function lerp(from: number, to: number, value: number): number;
```
```ts
import { lerp } from "kdim";
// Interpolate 0.4 in range [0,1] to range [1,99]
const value = 0.4;
const interpolated = lerp(1, 99, value); // 40.2
```
> **NOTE:** throws a RangeError when the value is outside of `[0, 1]`
### gcf
Find the Greatest Common Factor of two integers.
Function Signature
```ts
function gcf(a: number, b: number): number;
```
```ts
import { gcf } from "kdim";
gcf(45, 420); // 15
```
> **NOTE:** throws a RangeError when `a` or `b` are non-integral.
### lcm
Find the Least Common Multiple of two integers.
Function Signature
```ts
function lcm(a: number, b: number): number;
```
```ts
import { lcm } from "kdim";
lcm(6, 20); // 60
```
> **NOTE:** throws a RangeError when `a` or `b` are non-integral.
### trailingZeros
Compute the number of trailing zeros in a number's 32-bit representation, equivalent to its largest power-of-two divisor.
Function Signature
```ts
function trailingZeros(n: number): number;
```
```ts
import { trailingZeros } from "kdim";
trailingZeros(24); // 3
```
> **NOTE:** throws a RangeError when `n` is non-integral.
### objectHash
A hashing function for arbitrary objects and primitives that digests the value into a pseudo-unique base-16 hash string. Uses structural hashing, such that objects of identical structure will produce the same hash.
Function Signature
```ts
type ObjectHashAlgorithm = "SHA-1" | "SHA-256" | "SHA-384" | "SHA-512";
type ObjectHashOptions = {
algorithm?: ObjectHashAlgorithm;
};
async function objectHash(
obj: T,
options?: ObjectHashOptions
): Promise;
```
```ts
import { objectHash } from "kdim";
const hash = await objectHash({ foo: 7, bar: [] }, { algorithm: "SHA-1" });
// "1448bf86764e7ff7f9df0cb61b2d77c946ba854"
```
## Assertions
### castInteger
Assert that a number (or object convertible to number) has no fractional part and is within the safe integer range, and cast it to a primitive number.
Function Signature
```ts
function castInteger(n: N): number;
```
```ts
import { castInteger, Wrapping } from "kdim";
const i = 300;
const u8 = new Wrapping({ max: 7 }, 5);
const f = 29.7;
const safeI = castInteger(i); // 300
const safeU8 = castInteger(u8); // 5
const errF = castInteger(f); // Error: Values must be safe integers
```
> **NOTE:** throws a RangeError if `n` has a fractional part, is not in safe integer range, or cannot be coerced from/to a number via `Number(n)` and `n.valueOf()`.
### assertInteger
Assert that number(s) have no fractional part and are within the safe integer range.
Function Signature
```ts
function assertInteger(...numbers: number[]): void;
```
```ts
import { assertInteger } from "kdim";
assertInteger(-300); // ok
assertInteger(1, 2, 10); // ok
assertInteger(7.89); // Error: Arguments must be integers
```
> **NOTE:** throws a RangeError if any `number` has a fractional part, or is not in safe integer range.
### assertNatural
Assert that number(s) have no fractional part and are zero or greater.
Function Signature
```ts
function assertNatural(...numbers: number[]): void;
```
```ts
import { assertNatural } from "kdim";
assertNatural(300); // ok
assertNatural(1, 2, 10); // ok
assertNatural(-1); // Error: Arguments must be natural numbers
```
> **NOTE:** throws a RangeError if any `number` has a fractional part, or is not zero or greater.
### assertCounting
Assert that number(s) have no fractional part and are greater than zero.
Function Signature
```ts
function assertCounting(...numbers: number[]): void;
```
```ts
import { assertCounting } from "kdim";
assertCounting(300); // ok
assertCounting(1, 2, 10); // ok
assertCounting(0); // Error: Arguments must be counting numbers
```
> **NOTE:** throws a RangeError if any `number` has a fractional part, or is not greater than zero.
### assertValidRange
Assert that the arguments constitute a valid range, in which `min < max`, and, if present, `min <= value && value <= max`.
Function Signature
```ts
function assertValidRange(min: number, max: number, value?: number): void;
```
```ts
assertValidRange(0, 5);
assertValidRange(0, 5, 1);
assertValidRange(5, 0); // Error: Minimum must be less than maximum
assertValidRange(0, 5, 9); // Error: Value must be between minimum and maximum
```
## Utility Types
### Tuple
A typed tuple of generic length.
```ts
import { Tuple } from "kdim";
const threeBoolTuple: Tuple = [true, false, false];
const wrongBoolTuple: Tuple = [false, true]; // Error: Source has 2 element(s) but target requires 3
```
This also composes to allow for strongly-typed multidimensional arrays, such as a chess board:
```ts
import { Tuple } from "kdim";
type Piece = "pawn" | "rook" | "knight" | "bishop" | "queen" | "king";
type Board = Tuple, 8>;
const board: Board = [
["rook", "knight", "bishop", "queen", "king", "bishop", "knight", "rook"],
["pawn", "pawn", "pawn", "pawn", "pawn", "pawn", "pawn", "pawn"],
[null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null],
[null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null],
[null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null],
[null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null],
["pawn", "pawn", "pawn", "pawn", "pawn", "pawn", "pawn", "pawn"],
["rook", "knight", "bishop", "queen", "king", "bishop", "knight", "rook"],
];
```
### Vec
A convenience type equivalent to `Tuple`, useful for mathematical computation and data structures.
```ts
import { Vec } from "kdim";
const position: Vec<3> = [1.0, 69, 420];
const speed: Vec<3> = [-1, 3, 11];
const accel: Vec<3> = [0, 0, "no"]; // Error: type 'string' is not assignable to type 'number'
```
## License
MIT © [Tobias Fried](https://github.com/rektdeckard)