https://github.com/renggli/dart-xml
Lightweight library for parsing, traversing, and transforming XML in Dart.
https://github.com/renggli/dart-xml
dart flutter sax xml xml-builder xml-document xml-parser xml-parsing xml-queries xml-transformation xpath
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
Lightweight library for parsing, traversing, and transforming XML in Dart.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/renggli/dart-xml
- Owner: renggli
- License: mit
- Created: 2014-04-21T07:28:30.000Z (over 11 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-01-19T09:24:44.000Z (11 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-31T15:09:46.927Z (8 months ago)
- Topics: dart, flutter, sax, xml, xml-builder, xml-document, xml-parser, xml-parsing, xml-queries, xml-transformation, xpath
- Language: Dart
- Homepage: http://pub.dartlang.org/packages/xml
- Size: 1.23 MB
- Stars: 226
- Watchers: 7
- Forks: 51
- Open Issues: 3
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- License: LICENSE
- Authors: AUTHORS
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-dart - XML - Lightweight library for parsing, traversing, and querying XML in Dart.[<img src="https://travis-ci.org/renggli/dart-xml.svg?branch=master">](https://travis-ci.org/renggli/dart-xml) (Libraries / Parsers)
README
Dart XML
========
[](https://pub.dev/packages/xml)
[](https://github.com/renggli/dart-xml/actions/workflows/dart.yml)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/renggli/dart-xml)
[](https://github.com/renggli/dart-xml/issues)
[](https://github.com/renggli/dart-xml/network)
[](https://github.com/renggli/dart-xml/stargazers)
[](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/renggli/dart-xml/main/LICENSE)
Dart XML is a lightweight library for parsing, traversing, querying, transforming and building XML documents.
This library provides a [DOM-based](#Reading-and-Writing) object model for accessing and manipulating XML documents, as
well as an [event-based](#Event-driven) (comparable to SAX) for incremental reading and processing of XML streams.
Furthermore, it supports a large subset of [XPath](#XPath) to simplify the querying of large documents.
This library is open source, stable and well tested. Development happens
on [GitHub](https://github.com/renggli/dart-xml). Feel free to report issues or create a pull-request there. General
questions are best asked on [StackOverflow](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/xml+dart).
The package is hosted on [dart packages](https://pub.dev/packages/xml).
Up-to-date [class documentation](https://pub.dev/documentation/xml/latest/) is created with every release.
Tutorial
--------
### Installation
Follow the installation instructions on [dart packages](https://pub.dev/packages/xml/install).
Import the library into your Dart code using:
```dart
import 'package:xml/xml.dart';
```
:warning: This library makes extensive use of [static extension methods](https://dart.dev/guides/language/extension-methods). If you [import the library](https://dart.dev/guides/language/language-tour#using-libraries) using a _library prefix_ or only _selectively show classes_ you might miss some of its functionality. For historical reasons public classes have an `Xml` prefix, so conflicts with other code should be rare.
### Reading and Writing
To read XML input use the factory method `XmlDocument.parse(String input)`:
```dart
final bookshelfXml = '''
Growing a Language
29.99
Learning XML
39.95
132.00
''';
final document = XmlDocument.parse(bookshelfXml);
```
The resulting object is an instance of `XmlDocument`. In case the document cannot be parsed, a `XmlException` is thrown.
To write back the parsed XML document, simply call `toString()` or `toXmlString(...)` if you need more control:
```dart
print(document.toString());
print(document.toXmlString(pretty: true, indent: '\t'));
```
To read XML from a file use the [dart:io](https://api.dart.dev/dart-io/dart-io-library.html) library:
```dart
final file = new File('bookshelf.xml');
final document = XmlDocument.parse(file.readAsStringSync());
```
If your file is not _UTF-8_ encoded pass the correct encoding to `readAsStringSync`. It is the responsibility of the caller to provide a standard Dart [String] using the default UTF-16 encoding. To read and write large files you might want to use the [event-driven API](#event-driven) instead.
### Traversing and Querying
Accessors allow accessing nodes in the XML tree:
- `attributes` returns the attributes of the node.
- `children` returns the direct children of the node.
Both lists are mutable and support all common `List` methods, such as `add(XmlNode)`, `addAll(Iterable)`, `insert(int, XmlNode)`, and `insertAll(int, Iterable)`. Trying to add a `null` value or an unsupported node type throws an `XmlNodeTypeError` error. Nodes that are already part of a tree _are not_ automatically moved, you need to first create a copy as otherwise an `XmlParentError` is thrown. `XmlDocumentFragment` nodes are automatically expanded and copies of their children are added.
There are methods to traverse the XML tree along different axes:
- `siblings` returns an iterable over the nodes at the same level that proceed and follow this node in document order.
- `preceding` returns an iterable over nodes preceding the opening tag of the current node in document order.
- `descendants` returns an iterable over the descendants of the current node in document order. This includes the attributes of the current node, its children, the grandchildren, and so on.
- `following` the nodes following the closing tag of the current node in document order.
- `ancestors` returns an iterable over the ancestor nodes of the current node, that is the parent, the grandparent, and so on. Note that this is the only iterable that traverses nodes in reverse document order.
For example, the `descendants` iterator could be used to extract all textual contents from an XML tree:
```dart
final textual = document.descendants
.whereType()
.map((text) => text.value.trim())
.where((string) => string.isNotEmpty)
.join('\n');
print(textual); // prints 'Growing a Language', '29.99', 'Learning XML', '39.95', and '132.00'
```
There are convenience helpers to filter by element nodes only: `childElements`, `siblingElements`, `precedingElements`, `descendantElements`, `followingElements`, and `ancestorElements`.
Additionally, there are helpers to find elements with a specific tag:
- `getElement(String name)` finds the first direct child with the provided tag `name`, or `null`.
- `findElements(String name)` finds direct children of the current node with the provided tag `name`.
- `findAllElements(String name)` finds direct and indirect children of the current node with the provided tag `name`.
For example, to find all the nodes with the _<title>_ tag you could write:
```dart
final titles = document.findAllElements('title');
```
The above code returns a lazy iterator that recursively walks the XML document and yields all the element nodes with the requested tag name. To extract the textual contents of an element call `innerText`:
```dart
titles
.map((element) => element.innerText)
.forEach(print); // prints 'Growing a Language' and 'Learning XML'
```
This prints _Growing a Language_ and _Learning XML_.
Similarly, to compute the total price of all the books one could write the following expression:
```dart
final total = document.findAllElements('book')
.map((element) => double.parse(element
.findElements('price')
.single
.innerText))
.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
print(total); // prints 69.94
```
Note that this first finds all the books, and then extracts the price to avoid counting the price tag that is included
in the bookshelf.
#### XPath
To simplify accessing and extracting specific parts of a DOM document, this library supports the most commonly used
subset of [XPath 1.0](https://www.w3.org/TR/1999/REC-xpath-19991116/) expressions; a full XPath engine is outside the
scope of this library.
To get started import the XPath library:
```dart
import 'package:xml/xpath.dart';
```
This exposes the static extension method `XmlNode.xpath(String expression)` that can be used on documents, and any other
XML DOM node. The method returns an iterable over the matching XML DOM nodes. Using the `bookshelf` data defined above
we can write:
```dart
// Find all the books in the bookshelf.
print(document.xpath('/bookshelf/book'));
// Find the second book in the bookshelf.
print(document.xpath('/bookshelf/book[2]'));
// Find all the english titles anywhere in the document.
print(document.xpath('//title[@lang="en"]'));
// Find all the books with an english title.
print(document.xpath('//book[title/@lang="en"]'));
// Sum up the prices of all the books.
final total = document.xpath('//book/price/text()')
.map((node) => double.parse(node.value!))
.reduce((a, b) => a + b);
print(total); // prints 69.94
```
### Building
While it is possible to instantiate and compose `XmlDocument`, `XmlElement` and `XmlText` nodes manually,
the `XmlBuilder` provides a simple fluent API to build complete XML trees. To create the above bookshelf example one
would write:
```dart
final builder = XmlBuilder();
builder.processing('xml', 'version="1.0"');
builder.element('bookshelf', nest: () {
builder.element('book', nest: () {
builder.element('title', nest: () {
builder.attribute('lang', 'en');
builder.text('Growing a Language');
});
builder.element('price', nest: 29.99);
});
builder.element('book', nest: () {
builder.element('title', nest: () {
builder.attribute('lang', 'en');
builder.text('Learning XML');
});
builder.element('price', nest: 39.95);
});
builder.element('price', nest: '132.00');
});
final document = builder.buildDocument();
```
The `element` method supports optional named arguments:
- The most common is the `nest:` argument which is used to insert contents into the element. In most cases this will be a function that calls more methods on the builder to define attributes, declare namespaces and add child elements. However, the argument can also be a string or an arbitrary Dart object that is converted to a string and added as a text node.
- While attributes can be defined from within the element, for simplicity there is also an argument `attributes:` that takes a map to define simple name-value pairs.
- Furthermore, we can provide a URI as the namespace of the element using `namespace:` and declare new namespace prefixes using `namespaces:`. For details see the documentation of the method.
The builder pattern allows you to easily extract repeated parts into specific methods. In the example above, one could put the part writing a book into a separate method as follows:
```dart
void buildBook(XmlBuilder builder, String title, String language, num price) {
builder.element('book', nest: () {
builder.element('title', nest: () {
builder.attribute('lang', language);
builder.text(title);
});
builder.element('price', nest: price);
});
}
```
The above `buildDocument()` method returns the built document. To attach built nodes into an existing XML document, use `buildFragment()`. Once the builder returns the built node, its internal state is reset.
```dart
final builder = XmlBuilder();
buildBook(builder, 'The War of the Worlds', 'en', 12.50);
buildBook(builder, 'Voyages extraordinaries', 'fr', 18.20);
document.rootElement.children.add(builder.buildFragment());
```
### Event-driven
Reading large XML files and instantiating their DOM into the memory can be expensive. As an alternative this library provides the possibility to read and transform XML documents as a sequence of events using Dart Iterables or [Streams](https://dart.dev/tutorials/language/streams). These approaches are comparable to event-driven SAX parsing known from other libraries.
```dart
import 'package:xml/xml_events.dart';
```
#### Iterables
In the simplest case you can get a `Iterable` over the input string using the following code. This parses the input lazily, and only parses input when requested:
```dart
parseEvents(bookshelfXml)
.whereType()
.map((event) => event.value.trim())
.where((text) => text.isNotEmpty)
.forEach(print);
```
The function `parseEvents` supports various other options, see [its documentation](https://pub.dev/documentation/xml/latest/xml_events/parseEvents.html) for further examples.
This approach requires the whole input to be available at the beginning and does not work if the data itself is only available asynchronous, such as coming from a slow network connection. A more flexible, but also more complicated API is provided with [Dart Streams](https://dart.dev/tutorials/language/streams).
#### Streams
To asynchronously parse and process events directly from a file or HTTP stream use the provided extension methods on `Stream` to convert between streams of strings, events and DOM tree nodes:
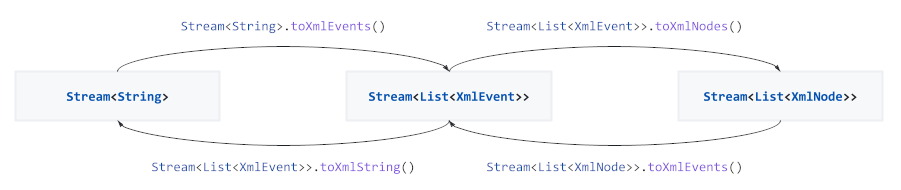
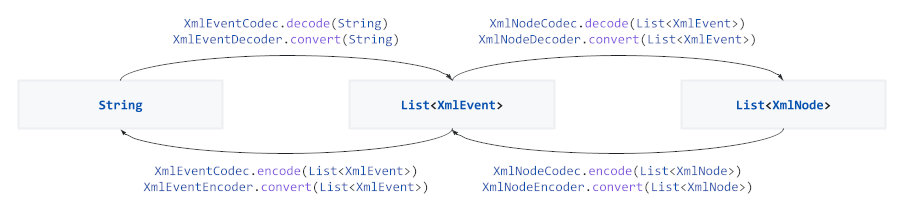
For more control the underlying `Codec` and `Converter` implementations can be used:
Various other transformations are provided to simplify processing complex streams:
- Normalizes a sequence of `XmlEvent` objects by removing empty and combining adjacent text events. \
`Stream> normalizeEvents()` on `Stream>`
- Annotates `XmlEvent` objects with their parent events that is thereafter accessible through `XmlParented.parentEvent`. Validates the nesting and throws an exception if it is invalid. \
`Stream> withParentEvents()` on `Stream>`
- From a sequence of `XmlEvent` objects filter the event sequences that form sub-trees for which a predicate returns `true`. \
`Stream> selectSubtreeEvents(Predicate)` on `Stream>`
- Flattens a chunked stream of objects to a stream of objects. \
`Stream flatten()` on `Stream>`
- Executes the provided callbacks on each event of this stream. \
`Future forEachEvent({onText: ...})` on `Stream`.
- Executes the provided callbacks on each event of this stream as a side-effect. \
`Stream tapEachEvent({onText: ...})` on `Stream`.
For example, the following snippet downloads data from the Internet, converts the UTF-8 input to a Dart `String`, decodes the stream of characters to `XmlEvent`s, and finally normalizes and prints the events:
```dart
final url = Uri.parse('http://ip-api.com/xml/');
final request = await HttpClient().getUrl(url);
final response = await request.close();
await response
.transform(utf8.decoder)
.toXmlEvents()
.normalizeEvents()
.forEachEvent(onText: (event) => print(event.value));
```
Similarly, the following snippet extracts sub-trees with location information from a `sitemap.xml` file, converts the XML events to XML nodes, and finally prints out the containing text:
```dart
final file = File('sitemap.xml');
await file.openRead()
.transform(utf8.decoder)
.toXmlEvents()
.normalizeEvents()
.selectSubtreeEvents((event) => event.name == 'loc')
.toXmlNodes()
.expand((nodes) => nodes)
.forEach((node) => print(node.innerText));
```
A common challenge when processing XML event streams is the lack of hierarchical information, thus it is very hard to figure out parent dependencies such as looking up a namespace URI. The `.withParentEvents()` transformation validates the hierarchy and annotates the events with their parent event. This enables features (such as `parentEvent` and the `namespaceUri` accessor) and makes mapping and selecting events considerably simpler. For example:
```dart
await Stream.fromIterable([shiporderXsd])
.toXmlEvents()
.normalizeEvents()
.withParentEvents()
.selectSubtreeEvents((event) =>
event.localName == 'element' &&
event.namespaceUri == 'http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema')
.toXmlNodes()
.expand((nodes) => nodes)
.forEach((node) => print(node.toXmlString(pretty: true)));
```
Misc
----
### Examples
This package comes with several [examples](https://github.com/renggli/dart-xml/tree/main/example), as well as a [web demo](https://petitparser.github.io/examples/xml/xml.html).
Furthermore, there are [numerous packages](https://pub.dev/packages?q=dependency%3Axml) depending on this package.
### Supports
- ☑ Standard well-formed XML (and HTML).
- ☑ Reading documents using an event based API (SAX).
- ☑ Decodes and encodes commonly used character entities.
- ☑ Querying, traversing, and mutating API using Dart principles.
- ☑ Querying the DOM using a subset of XPath.
- ☑ Building XML trees using a builder API.
### Limitations
- ☐ Doesn't validate namespace declarations.
- ☐ Doesn't validate schema declarations.
- ☐ Doesn't parse, apply or enforce the DTD.
- ☐ Doesn't support XSL or XSLT.
### Standards
- [Extensible Markup Language (XML) 1.0](https://www.w3.org/TR/xml/)
- [Namespaces in XML 1.0](https://www.w3.org/TR/xml-names/)
- [XPath 1.0](https://www.w3.org/TR/1999/REC-xpath-19991116/)
- [W3C DOM4](https://www.w3.org/TR/domcore/)
### History
This library started as an example of the [PetitParser](https://github.com/renggli/PetitParserDart) library. To my own surprise various people started to use it to read XML files. In April 2014 I was asked to replace the original [dart-xml](https://github.com/prujohn/dart-xml) library from John Evans.
### License
The MIT License, see [LICENSE](https://github.com/renggli/dart-xml/raw/main/LICENSE).