https://github.com/ricardofalasca/deep-pages
Django's database stored web content processor
https://github.com/ricardofalasca/deep-pages
database deep-pages django middleware pageview signal template-tags templates
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
Django's database stored web content processor
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ricardofalasca/deep-pages
- Owner: ricardofalasca
- License: mit
- Created: 2018-03-20T22:58:45.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2019-10-18T16:23:39.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-12T20:23:59.024Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: database, deep-pages, django, middleware, pageview, signal, template-tags, templates
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 85 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# deep-pages
Django's database stored web content processor
## About
My motivation to create this small package raises when I was needing to create some small pages with static URL and want to use some template tags. So, unfortunatelly Django's Flat Pages wasn't enough in my case.
Ok, so what the DeepPages does? With DeepPages you can store a page (or any other text-based content) into your database using the `Page` Model, set a static URL to that and get it rendered. Simple.
## How it works?
DeepPages provides two ways to being used into your Django's project:
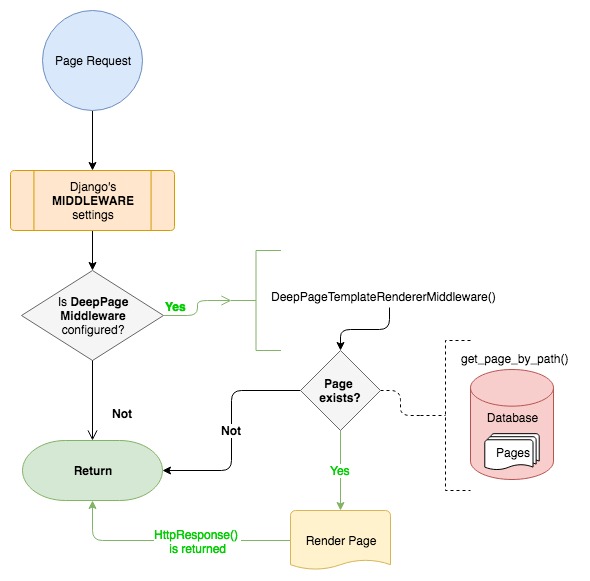
### 1. As Middleware
All you need is add `DeepPageTemplateRendererMiddleware` as a middleware in your `settings`. I really do recommend to insert this middleware in the end of MIDDLEWARE's list.
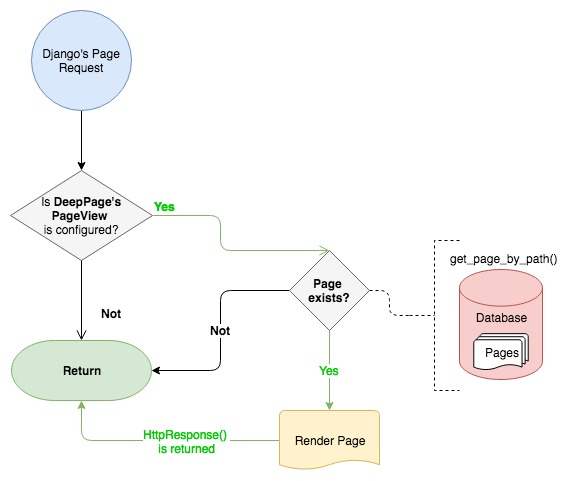
### 2. As PageView (TemplateView's inheritance)
Actually it was the first way that I've created. You need to include DeepPage's url patterns into your project (see Install).
## Signals
DeepPages has three signals that you can connect to workaround. You can import those from `signals.py`.
They are: `page_requested`, `page_found` and `page_not_found`.
```
from django.dispatch import receiver
from deeppages.signals import page_requested, page_found, page_not_found
@receiver(page_requested)
def page_requested_callback(sender, path, request):
# do something here
pass
@receiver(page_not_found)
def page_not_found_callback(sender, path, request):
# do something here
pass
@receiver(page_found)
def page_found_callback(sender, path, request, page, content, context):
# do something here
```
In `page_found` signal's receiver you can change the arguments `content` and `context` to get rendered by Middleware or PageView (depending how you've configured in your project).
## Programmatically DeepPages Rendering
You can get a DeepPage rendered programmatically. To do this you just need to import `get_page_by_name` function from `utils.py`.
Function statement:
```
def get_page_by_name(name, context=None, callback=None)
```
Where:
- name = Page name
- context (optional) = A dictionary with context for template processing
- callback (optional) = A function to be called with arguments `page` and `context` before rendering and should return the new page content.
So, assuming that you've created a page named as `test-page`, do it:
```
from deeppages.utils import get_page_by_name
def render():
rendered_page = get_page_by_name('test-page', ctx)
# do something
```
## Install
```
pip install deeppages
```
After package install, add `deeppages` in your INSTALLED_APPS list.
```
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'deeppages.apps.DeepPagesConfig',
...
]
```
If you want to use the `Middleware way` (personally, it's my preferred btw), open your settings file and look for MIDDLEWARE list.
```
MIDDLEWARE = [
...
'deeppages.middleware.DeepPageTemplateRendererMiddleware',
]
```
Or, if you want to use the `PageView way`, you just need to open your project's URL patterns file (`urls.py`) and configure DeepPage as an URL Pattern:
```
from deeppages.views import PageView
urlpatterns = [
...
url(r'^deeppages/', include(deeppages.urls, namespace='deeppages')),
...
]
```
This way, you can create a page with URL `/test-page/` and it will be found at: `/deeppages/test-page/`.
Of course that you can use as default URL seeker, maybe for small projects it can work fine. For example:
```
urlpatterns = [
...
url(r'', include(deeppages.urls, namespace='deeppages')),
...
]
```
Or, if you want to make your own View, you can import the `PageView` class and inherite from that:
```
from deeppages.view import PageView
class YourNewView(PageView):
# do something
```
And your `/test-page/` will be found at `/test-page/` as well.
I'm using this package in a project that I'm developing and isn't under production environment. So, be careful to use this in production.
Feel free to make it better and send your updates/suggestions.
Enjoy.