https://github.com/riolaf05/spark-elasticsearch-recommendation
Recommendation system using Alternating Least Squares(ALS) and Cosine Similarity on PySpark and Elasticsearch
https://github.com/riolaf05/spark-elasticsearch-recommendation
collaborative-filtering docker elasticsearch machine-learning pyspark recommendation-system spark
Last synced: 4 months ago
JSON representation
Recommendation system using Alternating Least Squares(ALS) and Cosine Similarity on PySpark and Elasticsearch
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/riolaf05/spark-elasticsearch-recommendation
- Owner: riolaf05
- Created: 2021-10-15T15:04:39.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2021-10-15T16:16:52.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-21T14:27:44.400Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: collaborative-filtering, docker, elasticsearch, machine-learning, pyspark, recommendation-system, spark
- Language: Jupyter Notebook
- Homepage:
- Size: 8.79 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# spark-elasticsearch-recommendation
Recommendation system using Alternating Least Squares(ALS) and Cosine Similarity on PySpark and Elasticsearch
### Theory
There are basically three types of recommendation systems:
* Content-Based Filtering
* Collaborative Filtering
* Hybrid
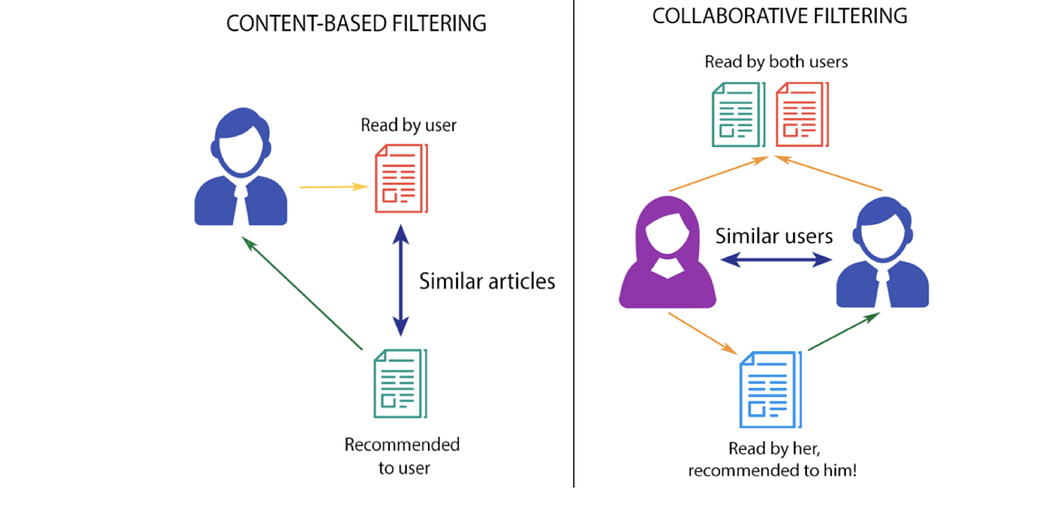
#### Content-Based Filtering
The attributes or characteristics of the items are taken into account to carry out the recommendation. For example, if we’re looking to recommend songs, we’ll look at the genre, duration, singer, and various other attributes that make up the item.
Pro:
- Requieres less data
- It is not necessary to identify users with similar preferences.
- It does not suffer from the *cold start problem*, a known issue in recommender systems that addresses the algorithm’s inability to recommend items or users for which it does not have enough information.
Cons:
- Suffer from a lack of diversity, that is, they can only recommend items that are strictly similar.
- Depend on the data filled in correctly and on the correct feeding of the systems.
- If items have the same characteristics, they will be treated as equal.
#### Collaborative Filtering
Analyze the preferences of other users to make recommendations, divided into two types:
##### Memory Based
Similarity matrices between all users or items. By identifying this similarity, it is possible to recommend new items.
There are several ways of computing similarity between vectors, such as euclidean, minkowski, jaccard etc., cosine similarity (which is a measure of similarity between two vectors).
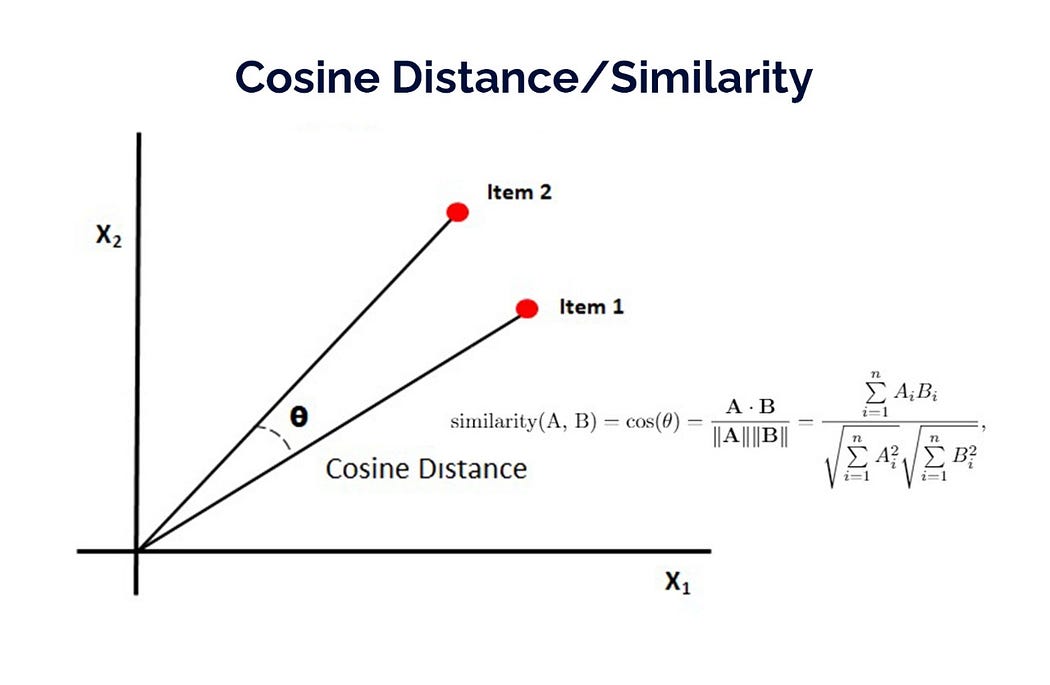
the most similar a vector can be to the other is when the angle between them is 0º, where the cosine has a value of 1.
For instance, user-movie (or movie-user) interaction matrix (where each entry records an interaction of a user i and a movie j), in a real world setting because the vast majority of movies receive very few or even no ratings at all by users, is an extremely sparse matrix:
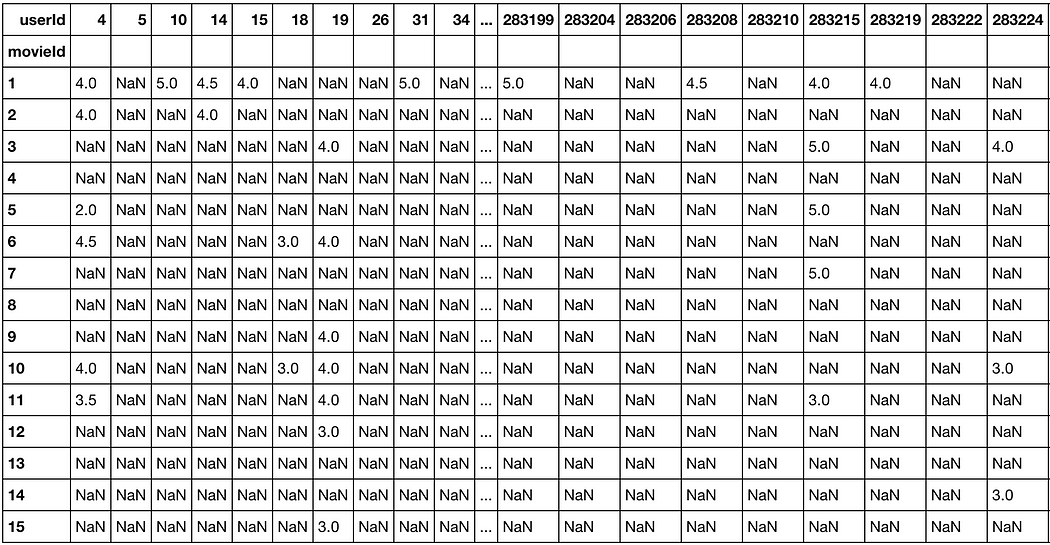
With such a sparse matrix, what ML algorithms can be trained and reliable to make inference? To find solutions we use **Matrix factorization**.
Matrix factorization is a factorization of a matrix into a product of matrices:
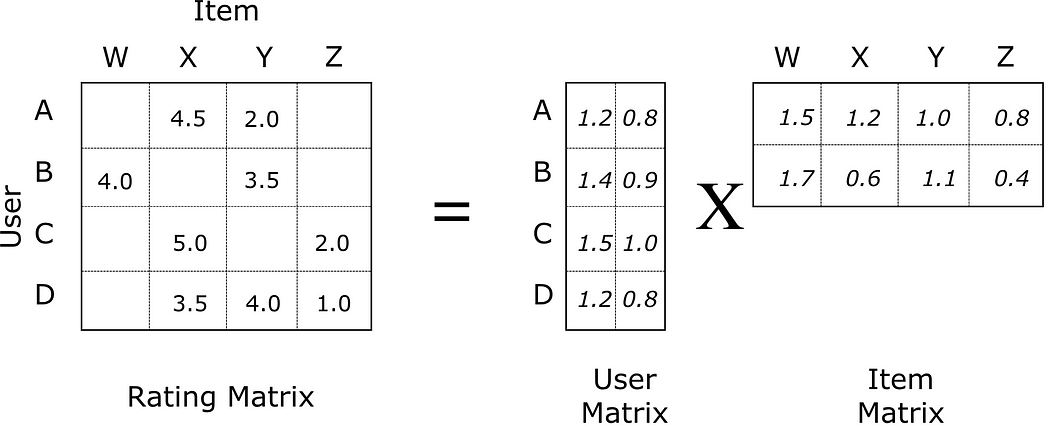
One matrix can be seen as the user matrix where rows represent users and columns are attributes or characteristics (latent factor). The other matrix is the item matrix where rows are attributes or characteristics and columns represent items.
This allows model to predict better personalized movie ratings for users, e.g. less-known movies can have rich latent representations as much as popular movies.
**TODO: [Alternating Least Square (ALS) with Spark ML](https://towardsdatascience.com/prototyping-a-recommender-system-step-by-step-part-2-alternating-least-square-als-matrix-4a76c58714a1)**
### Setup
Setup 3-node Spark cluster and single node Elasticsearch with:
`docker-compose up -d --build`
Then run Jupyter notebook.
### References
* [Building a Recommendation System with Spark ML and Elasticsearch](https://towardsdatascience.com/building-a-recommendation-system-with-spark-ml-and-elasticsearch-abbd0fb59454)
* [Collaborative Filtering](https://spark.apache.org/docs/3.0.0/ml-collaborative-filtering.html)
* [Notebook](https://github.com/lijoabraham/spark-playground/blob/master/recommendation_system_spark_es/ES_Spark_Recommendation.ipynb)
### Tutorials
* [Understanding recommender systems](https://medium.com/codex/understanding-recommender-systems-1077f4215516)
* [Prototyping a Recommender System Step by Step Part 1: KNN Item-Based Collaborative Filtering](https://towardsdatascience.com/prototyping-a-recommender-system-step-by-step-part-1-knn-item-based-collaborative-filtering-637969614ea)
* [Prototyping a Recommender System Step by Step Part 2: Alternating Least Square (ALS) Matrix Factorization in Collaborative Filtering](https://towardsdatascience.com/prototyping-a-recommender-system-step-by-step-part-2-alternating-least-square-als-matrix-4a76c58714a1)