https://github.com/rishibakshii/dsa-notes
https://github.com/rishibakshii/dsa-notes
Last synced: 7 months ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/rishibakshii/dsa-notes
- Owner: RishiBakshii
- Created: 2024-01-02T10:51:38.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: Intoduction-to-data-structure
- Last Pushed: 2024-01-02T15:12:12.000Z (almost 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-26T07:11:10.129Z (8 months ago)
- Size: 10.7 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
Data Structure
Data Structure can be defined as the group of data elements which provides an efficient way of storing and organising data in the computer so that it can be used efficiently.
- widely used
- Computer Science
- Operating System, Compiler Design, Artifical intelligence, Graphics and many more.
- handle the data in an efficient way.
- store and retrieve the user’s data as fast as possible
- building blocks of any program
## Baisic terminology
Data: Data can be defined as an elementary value or the collection of values, for example, student’s name and its id are the data about the student.
Group Items: Data items which have subordinate data items are called Group item, for example, name of a student can have first name and the last name. for example (dict)
Record: Record can be defined as the collection of various data items, for example, if we talk about the student entity, then its name, address, course and marks can be grouped together to form the record for the student.
File: A File is a collection of various records of one type of entity, for example, if there are 60 employees in the class, then there will be 20 records in the related file where each record contains the data about each employee.
Attribute and Entity: An entity represents the class of certain objects. it contains various attributes. Each attribute represents the particular property of that entity.
Field: Field is a single elementary unit of information representing the attribute of an entity
## Need of Data Structures
- Processor speed
- Data Search
- Multiple requests
## Advantages of Data Structures
- Efficiency - array not good as we to traverse the whole array so ordered array, binray search tree or hash tables
- Reusability - Implementation of data structures can be compiled into libraries which can be used by different clients
- Abstraction - The client program uses the data structure through interface only, without getting into the implementation details.
## Data Structure Classification
- 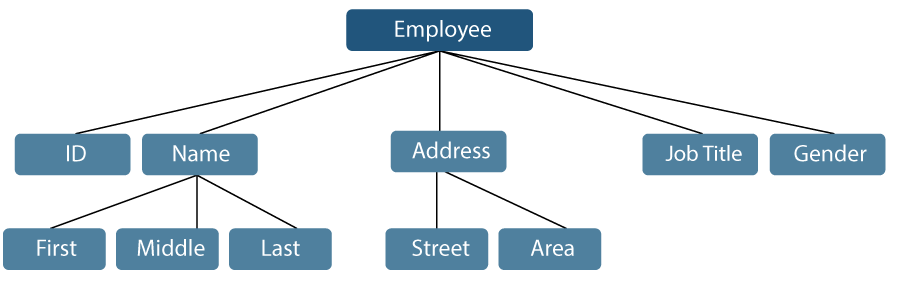
Linear Data Structures: A data structure is called linear if all of its elements are arranged in the linear order. In linear data structures, the elements are stored in non-hierarchical way where each element has the successors and predecessors except the first and last element. example (Arrays
- arrays :The elements of array share the same variable name but each one carries a different index number known as subscript. The array can be one dimensional, two dimensional or multidimensional.
- Linked List :Linked list is a linear data structure which is used to maintain a list in the memory. It can be seen as the collection of nodes stored at non-contiguous memory locations. Each node of the list contains a pointer to its adjacent node.
- Stack: Stack is a linear list in which insertion and deletions are allowed only at one end, called top.
- Queue: Queue is a linear list in which elements can be inserted only at one end called rear and deleted only at the other end called front.
## Non Linear Data Structures: This data structure does not form a sequence i.e. each item or element is connected with two or more other items in a non-linear arrangement. The data elements are not arranged in sequential structure.
- Trees: Trees are multilevel data structures with a hierarchical relationship among its elements known as nodes. The bottommost nodes in the herierchy are called leaf node while the topmost node is called root node. Each node contains pointers to point adjacent nodes.
- parent-child relationship
## Operations on data structure
- Traversing: ds mein ghumna
- Insertion: Insertion can be defined as the process of adding the elements to the data structure at any location.
- Deletion: to delete data , and random location deletion is also possible
- If we try to delete an element from an empty data structure then underflow occurs
- Searching: kisi bhi elemtn ko dhundna (linear seach, binary search)
- Sorting: process of rearranging the data (nsertion sort, selection sort, bubble sort, merge sort, heap sort)
- Merging: When two lists List A and List B of size M and N respectively, of similar type of elements, clubbed or joined to produce the third list, List C of size (M+N), then this process is called merging
## Array ( Advantages of Array, Need of using Array)
- similar type of data items
- contiguous memory locations
- derived data type in C programming language
- primitive type of data such as int, char, double, float, etc.
- randomly accessed by using its index number
- we just need to know the base address of the array in order to visit each element one by one.
## Memory Allocation of the array
- types of index
- 0 (zero – based indexing) : The first element of the array will be arr[0].
- 1 (one – based indexing) : The first element of the array will be arr[1].
- n (n – based indexing) : The first element of the array can reside at any random index number.
## Accessing Elements of an array
- base address
- size of element in bytes
- which type of indexing array follows
## 2d array ( array ke andar array)
- collection of arrays/rows&columns
- organised as matrices
- relational database look alike data structure.
- **syntax:** : int arr[max_rows][max_columns];
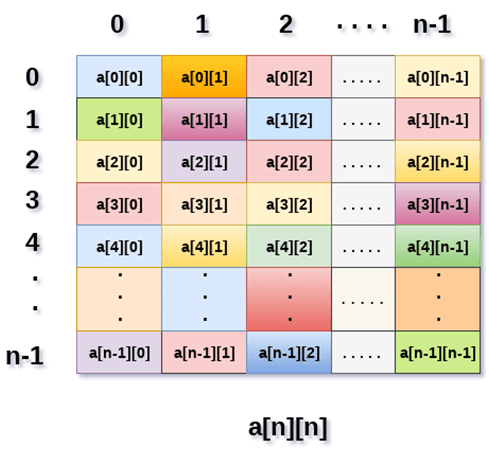
## How do we access data in a 2D array
- arr[row][column]
- int x = a[i][j]; // to store the array element
- to make everyting in 2d array zero
- ```cpp
for ( int i=0; i
using namespace std;
int main() {
int arr[3][3], i, j;
// Input elements
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
cout << "Enter a[" << i << "][" << j << "]: ";
cin >> arr[i][j];
}
}
// Print elements
cout << "\nPrinting the elements:\n";
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << endl;
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << "\t";
}
}
return 0;
}
```
## Sparse matrix example
- Here is an example of a 4 x 4 matrix containing 12 zero values and 4 non-zero values, giving it a sparsity of 3:
```cpp
[[5, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 11, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 25, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 7]]
```
- Representing a sparse matrix by a 2D array leads to wastage of lots of memory as zeroes in the matrix are of no use in most of the cases. So, instead of storing zeroes with non-zero elements, we only store non-zero elements. This means storing non-zero elements with triples- (Row, Column, value).
- Sparse Matrix Representations can be done in many ways following are two common representations:
- Array representation
- Linked list representation
Method 1: Using Arrays
- 2D array is used to represent a sparse matrix in which there are three rows named as
- Row: Index of row, where non-zero element is located
- Column: Index of column, where non-zero element is located
- Value: Value of the non zero element located at index – (row,column)
- 
Method 2: Using Linked Lists
In linked list, each node has four fields. These four fields are defined as:
- Row: Index of row, where non-zero element is located
- Column: Index of column, where non-zero element is located
- Value: Value of the non zero element located at index – (row,column)
- Next node: Address of the next node

## sparse ( upper and lower triangular matrics)
- An upper triangular matrix is a square matrix in which all entries below the main diagonal are zero (only nonzero entries are found above the main diagonal – in the upper triangle).
- A lower triangular matrix is a square matrix in which all entries above the main diagonal are zero
(only nonzero entries are found below the main diagonal – in the lower triangle). See the picture
below.
- ***– Notation: An upper triangular matrix is typically denoted with U and a lower triangular matrix***