https://github.com/rlgraph/rlgraph
RLgraph: Modular computation graphs for deep reinforcement learning
https://github.com/rlgraph/rlgraph
deep-learning deep-reinforcement-learning dqn machine-learning neural-networks ppo pytorch reinforcement-learning tensorflow
Last synced: about 1 month ago
JSON representation
RLgraph: Modular computation graphs for deep reinforcement learning
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/rlgraph/rlgraph
- Owner: rlgraph
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2018-05-04T19:19:19.000Z (over 7 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2019-11-05T16:33:55.000Z (about 6 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-18T14:50:21.956Z (8 months ago)
- Topics: deep-learning, deep-reinforcement-learning, dqn, machine-learning, neural-networks, ppo, pytorch, reinforcement-learning, tensorflow
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 7.86 MB
- Stars: 319
- Watchers: 21
- Forks: 40
- Open Issues: 23
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-deep-rl - RLgraph - Modular computation graphs for deep reinforcement learning. (Libraries)
- StarryDivineSky - rlgraph/rlgraph
README
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/rlgraph)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-356/)
[](https://github.com/rlgraph/rlgraph/blob/master/LICENSE)
[](https://rlgraph.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://travis-ci.org/rlgraph/rlgraph)
# RLgraph
Modular computation graphs for deep reinforcement learning.
RLgraph is a framework to quickly prototype, define and execute reinforcement learning
algorithms both in research and practice. RLgraph is different from most other libraries as it can support
TensorFlow (or static graphs in general) or eager/define-by run execution (PyTorch) through
a single component interface. An introductory blogpost can also be found here: [link](https://rlgraph.github.io/rlgraph/2019/01/04/introducing-rlgraph.html).
RLgraph exposes a well defined API for using agents, and offers a novel component concept
for testing and assembly of machine learning models. By separating graph definition, compilation and execution,
multiple distributed backends and device execution strategies can be accessed without modifying
agent definitions. This means it is especially suited for a smooth transition from applied use case prototypes
to large scale distributed training.
The current state of RLgraph in version 0.4.0 is alpha. The core engine is substantially complete
and works for TensorFlow and PyTorch (1.0). Distributed execution on Ray is exemplified via Distributed
Prioritized Experience Replay (Ape-X), which also supports multi-gpu mode and solves e.g. Atari-Pong in ~1 hour
on a single-node. Algorithms like Ape-X or PPO can be used both with PyTorch and TensorFlow. Distributed TensorFlow can
be tested via the IMPALA agent. Please create an issue to discuss improvements or contributions.
RLgraph currently implements the following algorithms:
- DQN - ```dqn_agent``` - [paper](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~vmnih/docs/dqn.pdf)
- Double-DQN - ```dqn_agent``` - via ```double_dqn``` flag - [paper](https://www.aaai.org/ocs/index.php/AAAI/AAAI16/paper/download/12389/11847)
- Dueling-DQN - ```dqn_agent``` - via ```dueling_dqn``` flag - [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1509.06461)
- Prioritized experience replay - via ```memory_spec``` option ```prioritized_replay``` - [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1511.05952)
- Deep-Q learning from demonstration ```dqfd_agent``` - [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.03732)
- Distributed prioritized experience replay (Ape-X) on Ray - via `apex_executor` - [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.00933)
- Importance-weighted actor-learner architecture (IMPALA) on distributed TF/Multi-threaded single-node - ```impala_agents``` - [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.01561)
- Proximal policy optimization with generalized advantage estimation - ```ppo_agent``` - [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1707.06347)
- Soft Actor-Critic / SAC ```sac_agent``` - [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1801.01290)
- Simple actor-critic for REINFORCE/A2C/A3C ```actor_critic_agent``` - [paper](https://arxiv.org/abs/1602.01783)
The ```SingleThreadedWorker``` implements high-performance environment vectorisation, and a ```RayWorker``` can execute
ray actor tasks in conjunction with a ```RayExecutor```. The ```examples``` folder contains simple scripts to
test these agents. There is also a very extensive test package including tests for virtually every component. Note
that we run tests on TensorFlow and have not reached full coverage/test compatibility with PyTorch.
For more detailed documentation on RLgraph and its API-reference, please visit
[our readthedocs page here](https://rlgraph.readthedocs.io).
Below we show some training results on gym tasks:
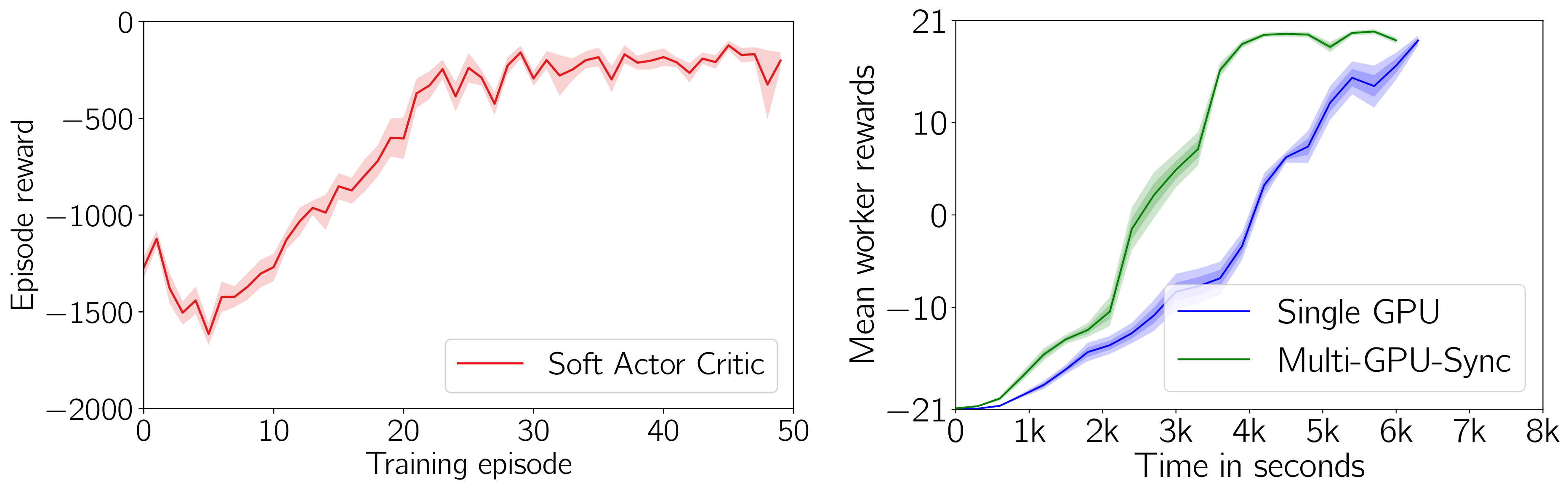
**Left:** Soft Actor Critic on Pendulum-v0 (10 seeds). **Right:** Multi-GPU Ape-X on Pong-v0 (10 seeds).
## Install
The simplest way to install RLgraph is from pip:
```pip install rlgraph```
Note that some backends (e.g. ray) need additional dependencies (see setup.py).
For example, to install dependencies for the distributed backend ray, enter:
```pip install rlgraph[ray]```
To successfully run tests, please also install OpenAI gym, e.g.
```pip install gym[all]```
Upon calling RLgraph, a config JSON is created under ~.rlgraph/rlgraph.json
which can be used to change backend settings. The current default stable
backend is TensorFlow ("tf"). The PyTorch backend ("pytorch") does not support
all utilities available in TF yet. Namely, device handling for PyTorch is incomplete,
and we will likely wait until a stable PyTorch 1.0 release in the coming weeks.
### Quickstart / example usage
We provide an example script for training the Ape-X algorithm on ALE using Ray in the [examples](examples) folder.
First, you'll have to ensure, that Ray is used as the distributed backend. RLgraph checks the file
`~/.rlgraph/rlgraph.json` for this configuration. You can use this command to
configure RLgraph to use TensorFlow as the backend and Ray as the distributed backend:
```bash
echo '{"BACKEND":"tf","DISTRIBUTED_BACKEND":"ray"}' > $HOME/.rlgraph/rlgraph.json
```
Then you can run our Ape-X example:
```bash
# Start ray on the head machine
ray start --head --redis-port 6379
# Optionally join to this cluster from other machines with ray start --redis-address=...
# Run script
python apex_pong.py
```
You can also train a simple DQN agent locally on OpenAI gym environments such as CartPole (this doesn't require Ray).
The following example script also contains a simple tf-summary switch for adding neural net variables to
your tensorboard reports (specify those Component by Perl-RegExp, whose variables you would like to see):
```bash
python dqn_cartpole_with_tf_summaries.py
```
## Import and use agents
Agents can be imported and used as follows:
```python
from rlgraph.agents import DQNAgent
from rlgraph.environments import OpenAIGymEnv
environment = OpenAIGymEnv('CartPole-v0')
# Create from .json file or dict, see agent API for all
# possible configuration parameters.
agent = DQNAgent.from_file(
"configs/dqn_cartpole.json",
state_space=environment.state_space,
action_space=environment.action_space
)
# Get an action, take a step, observe reward.
state = environment.reset()
action, preprocessed_state = agent.get_action(
states=state,
extra_returns="preprocessed_states"
)
# Execute step in environment.
next_state, reward, terminal, info = environment.step(action)
# Observe result.
agent.observe(
preprocessed_states=preprocessed_state,
actions=action,
internals=[],
next_states=next_state,
rewards=reward,
terminals=terminal
)
# Call update when desired:
loss = agent.update()
```
Full examples can be found in the examples folder.
## Cite
If you use RLgraph in your research, please cite the following paper: [link](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.09028)
```
@InProceedings{Schaarschmidt2019,
author = {Schaarschmidt, Michael and Mika, Sven and Fricke, Kai and Yoneki, Eiko},
title = {{RLgraph: Modular Computation Graphs for Deep Reinforcement Learning}},
booktitle = {{Proceedings of the 2nd Conference on Systems and Machine Learning (SysML)}},
year = {2019},
month = apr,
}
```