Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/rlhflow/rlhf-reward-modeling
A recipe to train reward models for RLHF.
https://github.com/rlhflow/rlhf-reward-modeling
llm reward-functions rlhf
Last synced: 5 days ago
JSON representation
A recipe to train reward models for RLHF.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/rlhflow/rlhf-reward-modeling
- Owner: RLHFlow
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2024-03-21T05:13:27.000Z (8 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-05-16T16:38:50.000Z (6 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-05-16T17:48:35.296Z (6 months ago)
- Topics: llm, reward-functions, rlhf
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 143 KB
- Stars: 143
- Watchers: 6
- Forks: 7
- Open Issues: 6
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# RLHF-Reward-Modeling
## Structure
The initial release of tis project focus on the Bradley-Terry reward modeling and pairwise preference model. Since then, we have included more advanced techniques to construct preference model. The structure of this project is
- [`bradley-terry-rm`](./bradley-terry-rm/) to train the classic Bradley-Terry reward model;
- [`pair-pm`](./pair-pm/) to train the pairwise preference model, which takes a prompt and **two responses** as the input and directly predicts the probability of the first response is being preferred. We formulate the problem as a chat between the user and the model to leverage the next-token prediction ability of the model, which is referred to as generative RM in the subsequent literature.
- [`SSRM`](./pair-pm/SRRM/): the code of the paper [Semi-Supervised Reward Modeling via Iterative Self-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.06903)
- [`RRM`](./pair-pm/RRM/): to leverage casual inference to augment the preference dataset and mitigate the reward hacking. See https://arxiv.org/pdf/2409.13156v1
- [`armo-rm`](./armo-rm/) to train the ArmoRM, which starts with a multi-objective reward model and the reward vector is aggregated by a mixture-of-expert approach in a context-dependent way. See our technical report [[ArmoRM] Interpretable Preferences via Multi-Objective Reward Modeling and Mixture-of-Experts](https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.12845) for details.
- [`odin-rm`](./odin/) to disentangle the reward modeling from length bias. See https://arxiv.org/pdf/2402.07319
- [`math-rm`](./math-rm/): the code to train process-supervised reward (PRM) and outcome-supervised reward (ORM) using the next-token prediction. We open-source the data, code, hyper-parameter, and model for a robust recipe that is easy to reproduce.
## News
🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥
🚀 **[Nov 2024]** PRM and ORM training code are released under the `math-rm/` folder!
🚀 **[Sep 2024]** ArmoRM training code is released under the `armo-rm/` folder!
🚀 **[Sep 2024]** Code for [Semi-Supervised Reward Modeling via Iterative Self-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.06903) is released under the `pair-pm/` folder
🚀 **[Jun 2024] Our [ArmoRM](https://huggingface.co/RLHFlow/ArmoRM-Llama3-8B-v0.1) is the Rank #1 8B model on RewardBench!**
🚀 **[May 2024] The top-3 open-source 8B reward models on RewardBench ([ArmoRM](https://huggingface.co/RLHFlow/ArmoRM-Llama3-8B-v0.1), [Pair Pref. Model](https://huggingface.co/RLHFlow/pair-preference-model-LLaMA3-8B), [BT RM](https://huggingface.co/sfairXC/FsfairX-LLaMA3-RM-v0.1)) are all trained with this repo!**
🚀 **[May 2024] The [pairwise preference model](https://huggingface.co/RLHFlow/pair-preference-model-LLaMA3-8B) training code is available (`pair-pm/`)!**
🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥🔥
+ **Tech Report**
+ [RLHF Workflow: From Reward Modeling to Online RLHF](https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.07863)
+ [[ArmoRM] Interpretable Preferences via Multi-Objective Reward Modeling and Mixture-of-Experts](https://arxiv.org/abs/2406.12845)
+ [Semi-Supervised Reward Modeling via Iterative Self-Training](https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.06903)
+ **Models**:
+ Absolute-Rating Multi-Objective Reward Model (ArmoRM): [ArmoRM-Llama3-8B-v0.1](https://huggingface.co/RLHFlow/ArmoRM-Llama3-8B-v0.1)
+ Pairwise Preference Reward Model: [pair-preference-model-LLaMA3-8B](https://huggingface.co/RLHFlow/pair-preference-model-LLaMA3-8B)
+ Bradley-Terry Reward Model: [FsfairX-LLaMA3-RM-v0.1](https://huggingface.co/sfairXC/FsfairX-LLaMA3-RM-v0.1)
+ **Architectures**
+ Bradley-Terry (BT) Reward Model and Pairwise Preference Model
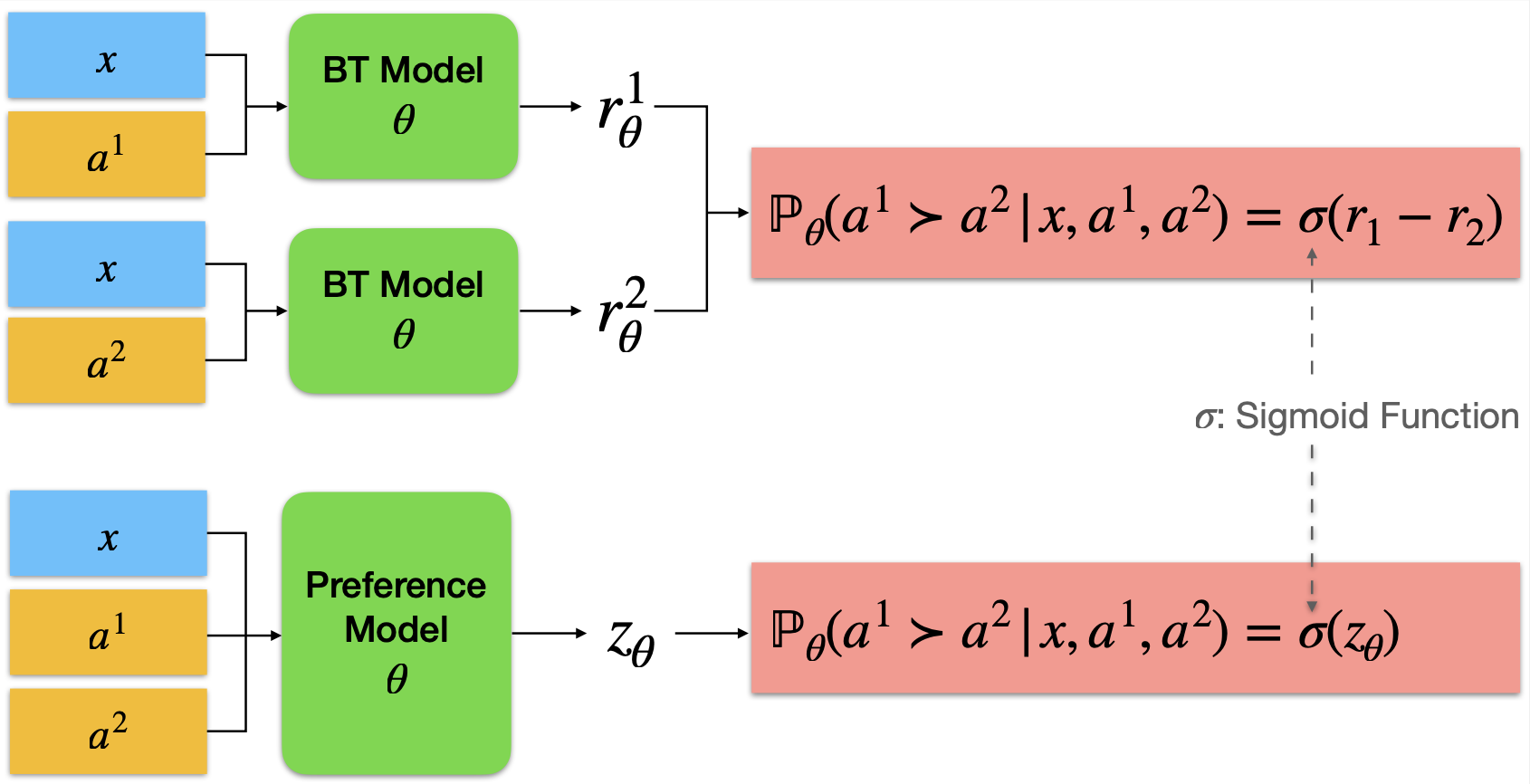
+ Absolute-Rating Multi-Objective Reward Model (ArmoRM)
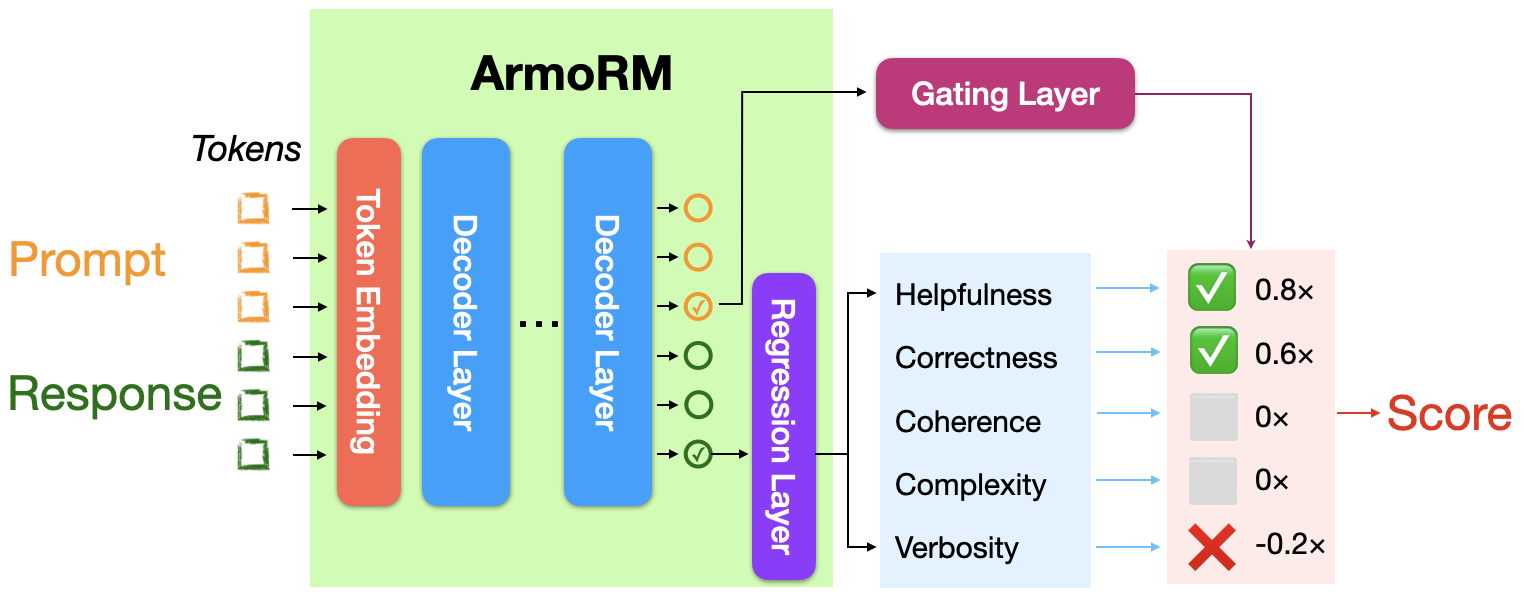
+ **[RewardBench LeaderBoard](https://huggingface.co/spaces/allenai/reward-bench)**

| Model | Base Model | Method | Score | Chat | Chat Hard | Safety | Reasoning | Prior Sets (0.5 weight) |
|:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:-----------------------------------------------------------------------|:-----:|:-----|:----------|:-------|:----------|:-----------------------|:------------------------|
| [ArmoRM-Llama3-8B-v0.1](https://huggingface.co/RLHFlow/ArmoRM-Llama3-8B-v0.1) (Ours) | Llama-3 8B | ArmoRM + MoE | **89.0** | 96.9 | **76.8** | **92.2** | **97.3** | 74.3 |
| Cohere May 2024 | Unknown | Unknown | 88.2 | 96.4 | 71.3 | **92.7** | **97.7** | **78.2** |
| [pair-preference-model](https://huggingface.co/RLHFlow/pair-preference-model-LLaMA3-8B) (Ours)| Llama-3 8B | [SliC-HF](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.10425) | 85.7 | 98.3 | 65.8 | 89.7 | 94.7 | 74.6 |
| GPT-4 Turbo (0125 version) | GPT-4 Turbo | LLM-as-a-Judge | 84.3 | 95.3 | 74.3 | 87.2 | 86.9 | 70.9 |
| [FsfairX-LLaMA3-RM-v0.1](https://huggingface.co/sfairXC/FsfairX-LLaMA3-RM-v0.1) (Ours) | Llama-3 8B | Bradley-Terry | 83.6 | **99.4** | 65.1 | 87.8 | 86.4 | 74.9 |
| [Starling-RM-34B](https://huggingface.co/Nexusflow/Starling-RM-34B) | Yi-34B | Bradley-Terry | 81.4 | 96.9 | 57.2 | 88.2 | 88.5 | 71.4 |
+ **Evaluation Results** (from [RLHF Workflow](https://arxiv.org/abs/2405.07863))

TL;DL: this is a repo for training the reward/preference model for [DRL-based RLHF (PPO)](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2203.02155.pdf), [Iterative SFT (Rejection sampling fine-tuning)](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2304.06767v4.pdf), and [iterative DPO](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.11456.pdf).
- 4 x A40 48G: we can train Gemma-7B-it with max_length 4096 by Deepspeed Zero-3 + gradient checkpoint;
- 4 x A100 80G: we can train Gemma-7B-it with max_length 4096 by gradient checkpoint;
- The resulting reward models achieve **SOTA performance** as open-source RMs in the leaderboard of [RewardBench](https://huggingface.co/spaces/allenai/reward-bench).
- Check out our [blog post](https://efficient-unicorn-451.notion.site/Reward-Modeling-for-RLHF-abe03f9afdac42b9a5bee746844518d0)!
## Installation instructions
It is recommeded to create separate environmnets for the Bradley-Terry reward model and pair wise preference model. The installation instructions are provided in the corresponding folders.
## Dataset Preparation
The dataset should be preprocessed as the standard format, where each of the sample consists of two conversations 'chosen' and 'rejected' and they share the same prompt. Here is an example of the rejected sample in the comparison pair.
```python
[
{ "content": "Please identify the top 5 rarest animals in the world.", "role": "user" },
{ "content": "Do you mean animals that are really rare, or rare relative to the size of the human population?", "role": "assistant" },
{ "content": "The ones that are really rare.", "role": "user" },
{ "content": "Alright, here’s what I found:", "role": "assistant" },
]
```
We preprocess many open-source preference datasets into the standard format and upload them to the hugginface hub. You can find them [HERE](https://huggingface.co/collections/RLHFlow/standard-format-preference-dataset-662eec0252e194d5d40c252a). We have also searched and found that some of the following mixture of preference dataset useful.
- [hendrydong/preference_700K](https://huggingface.co/datasets/hendrydong/preference_700K)
- [RLHFlow/UltraFeedback-preference-standard](https://huggingface.co/datasets/RLHFlow/UltraFeedback-preference-standard)
where the details can be found in the dataset card.
## Evaluation Results
You can evaluate the resulting reward model with the dataset provided by [benchmark](https://huggingface.co/datasets/allenai/reward-bench) by the following command.
```shell
CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=1 python ./useful_code/eval_reward_bench_bt.py --reward_name_or_path ./models/gemma_2b_mixture2_last_checkpoint --record_dir ./bench_mark_eval.txt
```
## To Do
- [x] Bradley-Terry Reward Model
- [x] Preference model
- [x] Multi-Objective Reward Model
- [ ] LLM-as-a-judge
Our models and codes have contributed to many academic research projects, e.g.,
1. Xu Zhangchen, et al. "Magpie: Alignment Data Synthesis from Scratch by Prompting Aligned LLMs with Nothing."
2. Chen, Lichang, et al. "OPTune: Efficient Online Preference Tuning."
3. Xie, Tengyang, et al. "Exploratory Preference Optimization: Harnessing Implicit Q*-Approximation for Sample-Efficient RLHF." arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.21046 (2024).
4. Zhong, Han, et al. "Dpo meets ppo: Reinforced token optimization for rlhf." arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.18922 (2024).
5. Zheng, Chujie, et al. "Weak-to-strong extrapolation expedites alignment." arXiv preprint arXiv:2404.16792 (2024).
6. Ye, Chenlu, et al. "A theoretical analysis of nash learning from human feedback under general kl-regularized preference." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.07314 (2024).
7. Chen, Ruijun, et al. "Self-Evolution Fine-Tuning for Policy Optimization"
8. Li Bolian, et al., Cascade Reward Sampling for Efficient Decoding-Time Alignment
9. Zhang, Yuheng, et al. "Iterative Nash Policy Optimization: Aligning LLMs with General Preferences via No-Regret Learning"
10. Lin Tzu-Han, et al., "DogeRM: Equipping Reward Models with Domain Knowledge through Model Merging",
11. Yang Rui, et al., "Regularizing Hidden States Enables Learning Generalizable Reward Model for LLMs"
12. Junsoo Park, et al., "OffsetBias: Leveraging Debiased Data for Tuning Evaluators"
13. Meng Yu, et al., "SimPO: Simple Preference Optimization with a Reference-Free Reward"
14. Song Yifan, et al., "The Good, The Bad, and The Greedy: Evaluation of LLMs Should Not Ignore Non-Determinism"
15. Wenxuan Zhou et al., "WPO: Enhancing RLHF with Weighted Preference Optimization"
16. Han Xia et al., "Inverse-Q*: Token Level Reinforcement Learning for Aligning Large Language Models Without Preference Data"
17. Wang Haoyu et al., "Probing the Safety Response Boundary of Large Language Models via Unsafe Decoding Path Generation"
18. He Yifei et al., "Semi-Supervised Reward Modeling via Iterative Self-Training"
19. Tao leitian et al., "Your Weak LLM is Secretly a Strong Teacher for Alignment"
20. Guijin Son et al., "LLM-as-a-Judge & Reward Model: What They Can and Cannot Do"
21. Nicolai Dorka et al., "Quantile Regression for Distributional Reward Models in RLHF"
22. Zhaolin Gao et al., "Rebel: Reinforcement learning via regressing relative rewards"
## Contributors
Thanks to all of our contributors to date (Made with [contrib.rocks](https://contrib.rocks)).
## Citation
If you find the content of this repo useful in your work, please consider citing:
```bibtex
@article{dong2024rlhf,
title={RLHF Workflow: From Reward Modeling to Online RLHF},
author={Dong, Hanze and Xiong, Wei and Pang, Bo and Wang, Haoxiang and Zhao, Han and Zhou, Yingbo and Jiang, Nan and Sahoo, Doyen and Xiong, Caiming and Zhang, Tong},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2405.07863},
year={2024}
}
@inproceedings{ArmoRM,
title={Interpretable Preferences via Multi-Objective Reward Modeling and Mixture-of-Experts},
author={Haoxiang Wang and Wei Xiong and Tengyang Xie and Han Zhao and Tong Zhang},
booktitle={The 2024 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing},
year={2024}
}
@article{xiong2024iterative,
title={Iterative Preference Learning from Human Feedback: Bridging Theory and Practice for RLHF under KL-Constraint},
author={Wei Xiong and Hanze Dong and Chenlu Ye and Ziqi Wang and Han Zhong and Heng Ji and Nan Jiang and Tong Zhang},
year={2024},
journal={ICML}
}
```