https://github.com/rodrigobdz/lrp
Explain Neural Networks using Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation and evaluate the explanations using Pixel-Flipping and Area Under the Curve.
https://github.com/rodrigobdz/lrp
activation-curve area-under-curve au-mse auac dataloader ilsvrc2012 imagenet-dataset layer-wise-relevance-propagation lrp pf pixel-flipping pruning-curve pytorch qualitative-evaluation quantitative-evaluation region-perturbation xai xai-library
Last synced: 5 months ago
JSON representation
Explain Neural Networks using Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation and evaluate the explanations using Pixel-Flipping and Area Under the Curve.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/rodrigobdz/lrp
- Owner: rodrigobdz
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-11-27T11:31:56.000Z (over 3 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2022-08-07T21:04:18.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2024-11-15T07:42:22.902Z (5 months ago)
- Topics: activation-curve, area-under-curve, au-mse, auac, dataloader, ilsvrc2012, imagenet-dataset, layer-wise-relevance-propagation, lrp, pf, pixel-flipping, pruning-curve, pytorch, qualitative-evaluation, quantitative-evaluation, region-perturbation, xai, xai-library
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://pypi.org/project/lrp-pf-auc/
- Size: 87.9 MB
- Stars: 13
- Watchers: 3
- Forks: 1
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: contributing.md
- License: license
- Code of conduct: CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
- Citation: CITATION.bib
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation
[](https://zenodo.org/badge/latestdoi/432443018)
[](https://pypi.org/project/lrp-pf-auc/)
[](license)
PyTorch implementation of Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP) algorithm together with quantitative evaluation metrics to compare heatmap explanations objectively part of master's thesis [_In-Depth Hyperparameter Selection For Layer-Wise Relevance Propagation_](https://zenodo.org/record/6972407#.YvAikS8Rr0o) at TU Berlin.
Special thanks to Dr. Grégoire Montavon for his insights, which shaped the development of this project.
## Features
Explainability:
- Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP)
Quantitative Evaluation:
- Pixel Flipping (PF), also known as Region Perturbation (RP)
- Perturbation modes:
- inpainting
- random
- Sort objectives:
- most relevant first (MoRF), also known as activation curve
- least relevant first (LRF), also known as pruning curve
- random
- AUC (Area Under the Curve), also known as AUAC (Area Under the Activation Curve) or AU-MSE (Area Under the Mean Squared Error Curve) depending on the sort objective
### Showcase
**LRP** ([lrp-tutorial](https://git.tu-berlin.de/gmontavon/lrp-tutorial) composite) and **PF** with **inpainting** perturbation mode and sort objective **MoRF**.
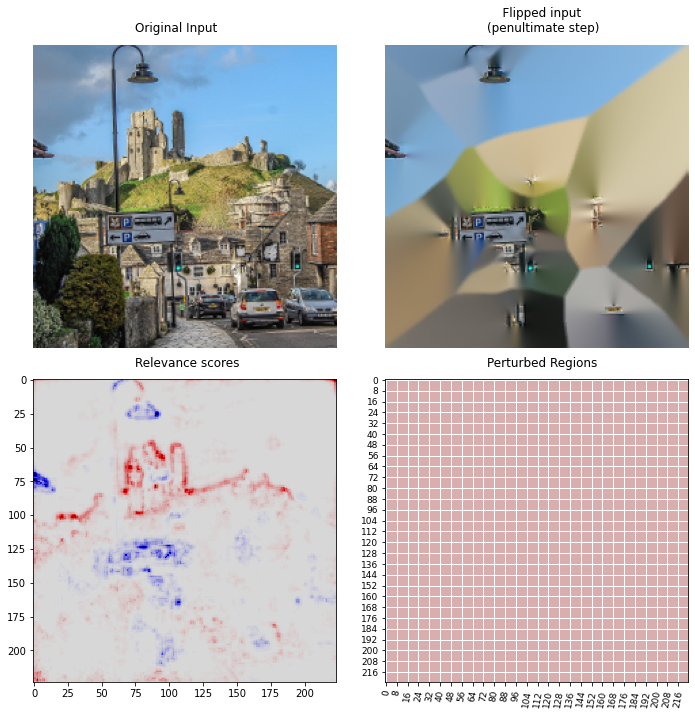
Classification scores of castle image with **inpainting** perturbation mode

Number of simultaneous flips per perturbation step during Pixel-Flipping.

---
PF perturbation mode random
**LRP** ([lrp-tutorial](https://git.tu-berlin.de/gmontavon/lrp-tutorial) composite) and **PF** with **random** perturbation mode and sort objective **MoRF**.
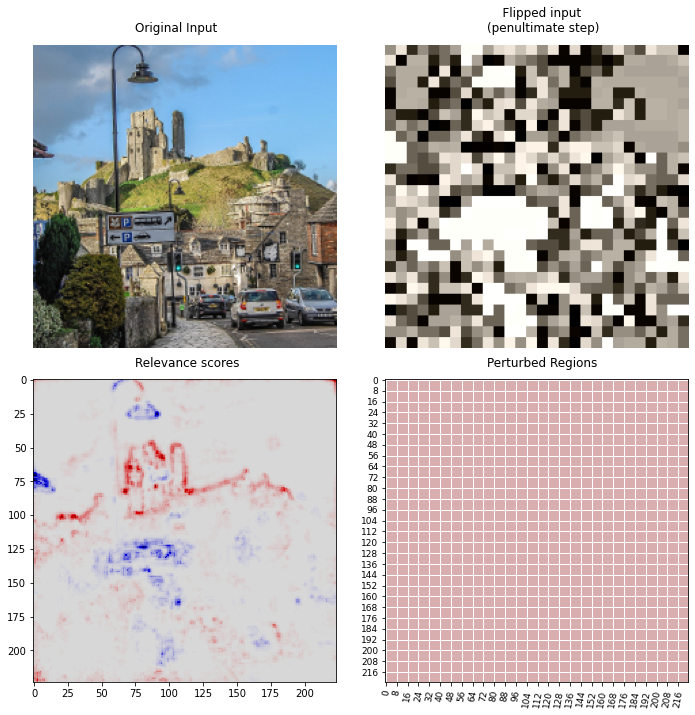
Classification scores of castle image with random perturbation mode

## Requirements
- `python3` >= 3.9
## Installation
```sh
python3 -m pip install lrp-pf-auc
```
The PyPI distribution `lrp-pf-auc` provides the following two packages: `lrp` and `pf`.
The name `lrp-pf-auc` stands for Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP), Pixel Flipping (PF), and Area Under the Curve (AUC) respectively.
## Usage
Refer to [demo.ipynb](https://github.com/rodrigobdz/lrp/blob/main/demo.ipynb) for an example of Layer-wise Relevance Propagation (LRP), Pixel-Flipping (PF) and Area under the Curve (AUC).
Feel free to check out the Jupyter notebooks under [experiments/notebooks](https://github.com/rodrigobdz/lrp/tree/main/experiments/notebooks) for a chronological overview of the project.
## Related Projects
- Sequential LRP implementation: [gmontavon/lrp-tutorial](https://git.tu-berlin.de/gmontavon/lrp-tutorial)
> Tutorial on how to implement LRP
- Updated version of `gmontavon/lrp-tutorial`: [rodrigobdz/lrp-tutorial](https://git.tu-berlin.de/rodrigobdz/lrp-tutorial)
- Forward-hook LRP implementation: [chr5tphr/zennit](https://github.com/chr5tphr/zennit)
> Implementation of LRP-based methods in PyTorch
- [`innvestigate`](https://github.com/albermax/innvestigate)-based LRP implementation: [moboehle/Pytorch-LRP](https://github.com/moboehle/Pytorch-LRP)
- Caffe-based LRP implementation: [`lrp_toolbox`](https://github.com/sebastian-lapuschkin/lrp_toolbox)
- Pixel-Flipping and Region Perturbation implementation: [understandable-machine-intelligence-lab/Quantus](https://github.com/understandable-machine-intelligence-lab/Quantus)
## Citation
Cite as:
- Plaintext:
> Rodrigo Bermúdez Schettino. (2022). rodrigobdz/lrp: v0.1.6 (v0.1.6). Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6821295
- BibTeX:
```text
@software{rodrigo_bermudez_schettino_2022_6821295,
author = {Rodrigo Bermúdez Schettino},
title = {rodrigobdz/lrp: v0.1.6},
month = jul,
year = 2022,
publisher = {Zenodo},
version = {v0.1.6},
doi = {10.5281/zenodo.6821295},
url = {https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6821295}
}
```
## Credits
- The structure of this readme is based on [minimal-readme](https://github.com/rodrigobdz/minimal-readme)
- Scripts follow [Personal Shell Style Guide](https://github.com/rodrigobdz/styleguide-sh)
- The `lrp` package uses [two customized files](https://github.com/rodrigobdz/lrp/tree/main/lrp/zennit) originally from [chr5tphr/zennit](https://github.com/chr5tphr/zennit).
- The syntax for defining custom composites is inspired by [this discussion](https://github.com/chr5tphr/zennit/issues/76) on `zennit`'s repo.
This implementation is based on insights from:
- LRP overview paper
> G. Montavon, A. Binder, S. Lapuschkin, W. Samek, K.-R. Müller
> [Layer-wise Relevance Propagation: An Overview](https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-28954-6_10)
> in Explainable AI: Interpreting, Explaining and Visualizing Deep Learning, Springer LNCS, vol. 11700, 2019
- Original LRP paper
> S. Bach, A. Binder, G. Montavon, F. Klauschen, K.-R. Müller, W. Samek
> [On pixel-wise explanations for non-linear classifier decisions by layer-wise relevance propagation](https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0130140)
> PloS ONE 10 (7), e0130140, 2015
- [ECML/PKDD 2020 Tutorial: Explainable AI for Deep Networks: Basics and Extensions (Part 3)](http://heatmapping.org/slides/2020_ECML_3.pdf)
## License
[MIT](LICENSE) © [rodrigobdz](https://github.com/rodrigobdz/)