https://github.com/ruanbekker/argocd-workshop
Experimenting with ArgoCD
https://github.com/ruanbekker/argocd-workshop
argocd devops gitops kubernetes workshop
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
Experimenting with ArgoCD
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/ruanbekker/argocd-workshop
- Owner: ruanbekker
- Created: 2023-03-17T19:20:43.000Z (about 2 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2023-04-01T11:01:34.000Z (about 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-23T06:31:11.879Z (about 2 months ago)
- Topics: argocd, devops, gitops, kubernetes, workshop
- Language: Smarty
- Homepage:
- Size: 19.5 KB
- Stars: 3
- Watchers: 2
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome - ruanbekker/argocd-workshop - Experimenting with ArgoCD (kubernetes)
README
# argocd-workshop
Experimenting with ArgoCD## TOC
- [About](#about)
- [Prerequisites](#prerequisites)
- [Docker](#docker)
- [Kubectl](#kubectl)
- [Helm](#helm)
- [Kind](#kind)
- [ArgoCD CLI](#argocd-cli)
- [Kubernetes Cluster](#kubernetes-cluster)
- [ArgoCD Setup](#argocd-setup)
- [Installation](#installation)
- [Access ArgoCD UI](#access-argocd-ui)
- [Authenticate ArgoCD CLI](#authenticate-argocd-cli)
- [ArgoCD Usage](#argocd-usage)
- [ArgoCD CLI](#argocd-cli-1)
- [ArgoCD UI](#argocd-ui)## About
This is a workshop / tutorial on my findings using ArgoCD. I will be deploying ArgoCD on Kubernetes using KinD.
From [their documentation](https://argo-cd.readthedocs.io/en/stable/):
> Argo CD is a declarative, GitOps continuous delivery tool for Kubernetes.
## Prerequisites
If you are following along, you will need the following:
- [KinD](https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/docs/user/quick-start/#installation) and [Docker](https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/)
- [Helm](https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/) and [Kubectl](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/)
- [ArgoCD CLI](https://argo-cd.readthedocs.io/en/stable/cli_installation/)If you don't have them installed, don't worry as we will be installing them from scratch. I will be using Linux as my operating system, if you are using something else, you can follow the links provided above.
### Docker
If you can run `docker ps` you have docker installed already. I am using this on Linux to install Docker, if you are using a different operating system you can view their [installation documentation](https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/ubuntu/)
Installation Steps
```bash
sudo apt update
sudo apt install ca-certificates curl gnupg lsb-release -y
sudo mkdir -m 0755 -p /etc/apt/keyrings
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg
echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/etc/apt/keyrings/docker.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu $(lsb_release -cs) stable" \
| sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
sudo apt update
sudo apt install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin -y
sudo usermod -aG docker $(whoami)
source ~/.bashrc
```### Kubectl
If you need to install kubectl on a operating system other than Linux, have a look at their [installation documentation](https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/tools/)
Due to [this argocd cli bug](https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/issues/8613), the workaround is to install kubectl 1.22.2.
Installation Steps (v1.22.2)
```bash
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/v1.22.2/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
rm -rf kubectl
```Once the bug has been resolved you can use the latest version.
Installation Steps (latest)
```bash
curl -LO "https://dl.k8s.io/release/$(curl -L -s https://dl.k8s.io/release/stable.txt)/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl"
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kubectl /usr/local/bin/kubectl
rm -rf kubectl
```### Helm
If you need to install kubectl on a operating system other than Linux, have a look at their [installation documentation](https://helm.sh/docs/intro/install/)
Installation Steps
```bash
curl -LO https://get.helm.sh/helm-v3.11.2-linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar -xf helm-v3.11.2-linux-amd64.tar.gz
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/helm
rm -rf helm-v3.11.2-linux-amd64.tar.gz linux-amd64
```### Kind
If you need to install kind on a operating system other than Linux, have a look at their [installation documentation](https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/docs/user/quick-start/#installation)
Installation Steps
```bash
curl -Lo kind https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/dl/v0.17.0/kind-linux-amd64
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 kind /usr/local/bin/kind
rm -rf kind
```### ArgoCD CLI
If you need to install argocd-cli on a operating system other than Linux, have a look at their [installation documentation](https://argo-cd.readthedocs.io/en/stable/cli_installation/)
Installation Steps
```bash
curl -sSL -o argocd-linux-amd64 https://github.com/argoproj/argo-cd/releases/latest/download/argocd-linux-amd64
sudo install -o root -g root -m 0755 argocd-linux-amd64 /usr/local/bin/argocd
rm argocd-linux-amd64
```## Kubernetes Cluster
Deploy a kubernetes cluster with [kind](https://kind.sigs.k8s.io/docs/user/quick-start/) and a list of images can be found on [github](https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kind/releases):
```bash
kind create cluster --name argocd --image kindest/node:v1.25.3
```You should be able to interact with your cluster using:
```bash
kubectl get nodes
# NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION
# argocd-control-plane Ready control-plane 45s v1.25.3
```If not you can use `kubectl config get-contexts` and switch to your context from the `NAME` column:
```bash
kubectl config get-contexts
# CURRENT NAME CLUSTER AUTHINFO NAMESPACE
# * kind-argocd kind-argocd kind-argocd
```And setting the context using:
```bash
kubectl config set-context kind-argocd
```## ArgoCD Setup
### Installation
We will be installing ArgoCD with helm, if you are looking for alternative methods, look at their [installation documentation](https://argo-cd.readthedocs.io/en/stable/operator-manual/installation/).
```bash
helm repo add argo https://argoproj.github.io/argo-helm
helm repo update
helm install argocd argo/argo-cd --version 5.27.1 --namespace kube-system --set "configs.params.server\.insecure=true"
```### Access ArgoCD UI
Once the installation process has been completed, you should be able to get the initial admin password from this secret:
```bash
kubectl -n kube-system get secret argocd-initial-admin-secret -o jsonpath="{.data.password}" | base64 -d
```Once you have copied the password, create a port forward to access the argocd ui:
```bash
kubectl -n kube-system port-forward svc/argocd-server 8080:80
```Head over to `http://localhost:8080` and the homepage will look like this:
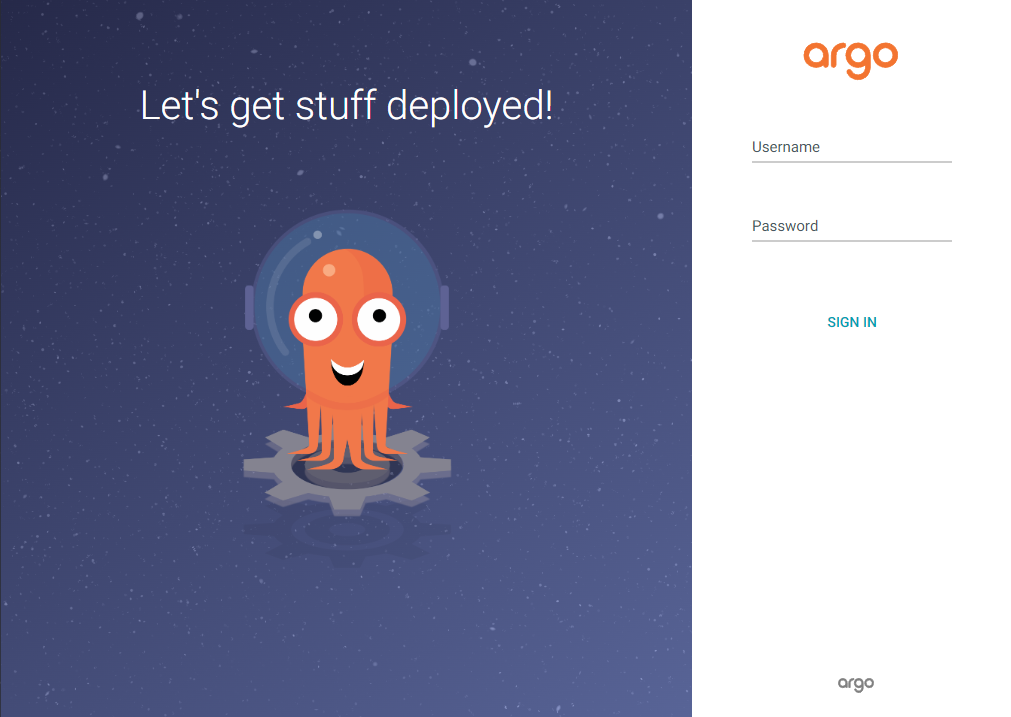
Logon with the user `admin` and the password that you received from the secret, then it should look like this:
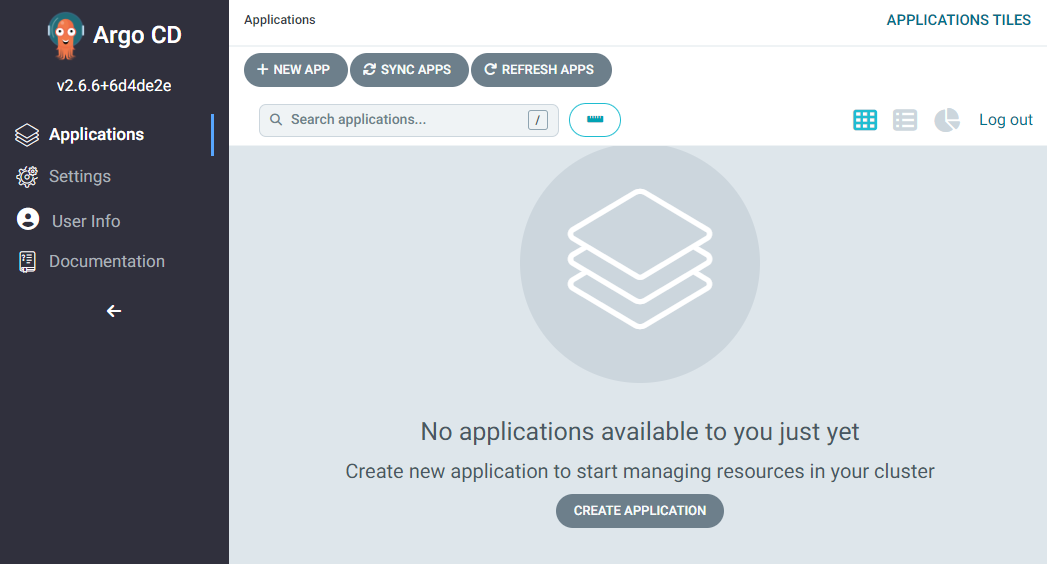
### Authenticate ArgoCD CLI
Ensure that you have a port-forward open to the server:
```bash
kubectl -n kube-system port-forward svc/argocd-server 8080:80
```Use the argocd cli to logon to the server:
```bash
argocd login --insecure localhost:8080
# WARNING: server is not configured with TLS. Proceed (y/n)? y
# Username: admin
# Password:
# 'admin:login' logged in successfully
# Context 'localhost:8080' updated
```Since we are here I'm going to update my password:
```bash
argocd account update-password
```Then authenticate again to your server:
```bash
argocd login --insecure localhost:8080
```## ArgoCD Usage
This section will demonstrate how to create an application on ArgoCD which will reference and monitor our github repository for content and any changes that is being made.
I have a basic helm chart that resides in `deployment/helm/simple-chart` and once we connected our repository, argocd will monitor the repository and if it detects changes or that it doesn't exist in our cluster it will sync down our changes.
### ArgoCD CLI
First create the application named `simple-app` and connect the github repository `argocd-workshop` and point the path to where our helm chart resides:
```bash
argocd app create simple-app \
--repo https://github.com/ruanbekker/argocd-workshop.git \
--path deployment/helm/simple-chart \
--dest-server https://kubernetes.default.svc \
--dest-namespace default \
--sync-policy automated \
--auto-prune# application 'simple-app' created
```Now that our application inside argocd has been created we can head back to the ArgoCD UI under applications:
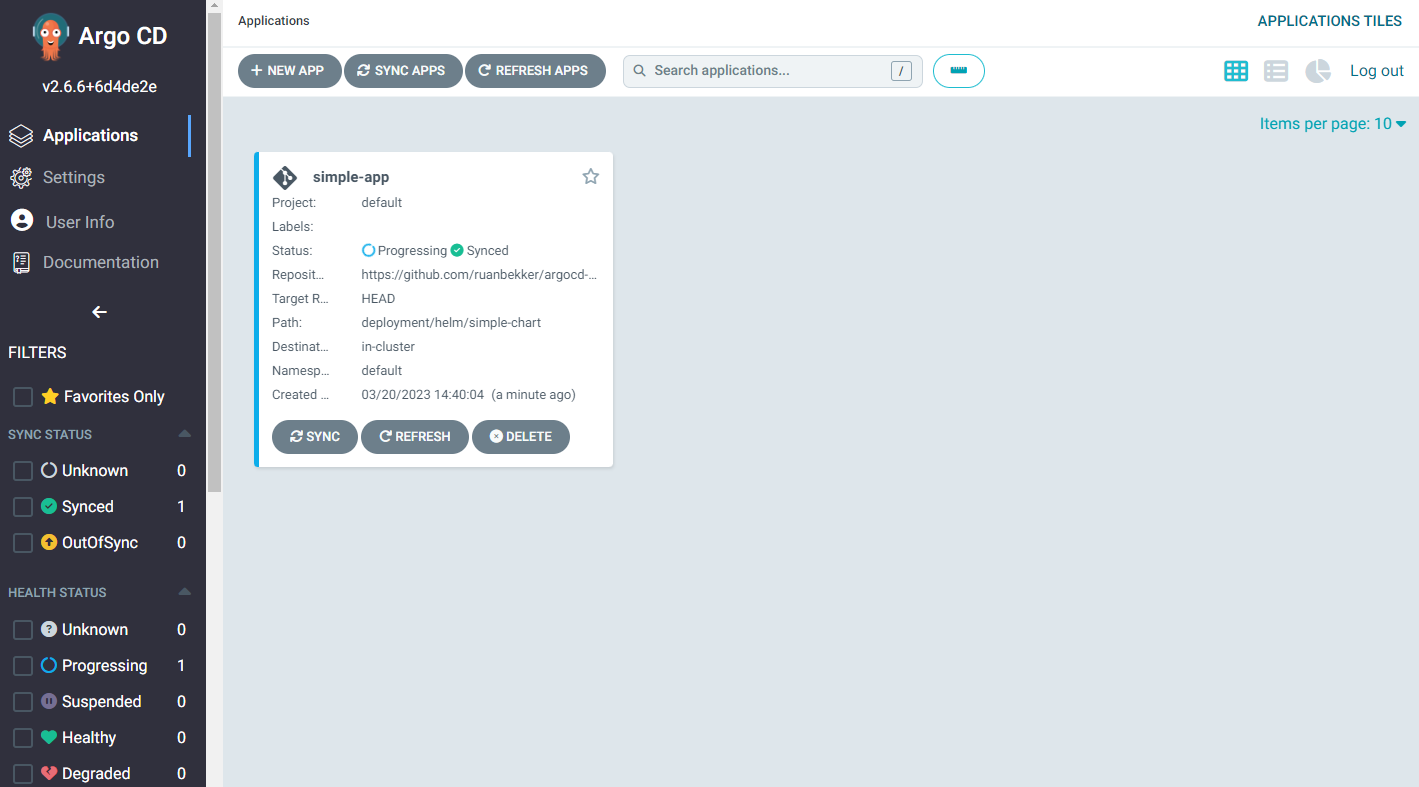
When we select the application we can see all our resources:
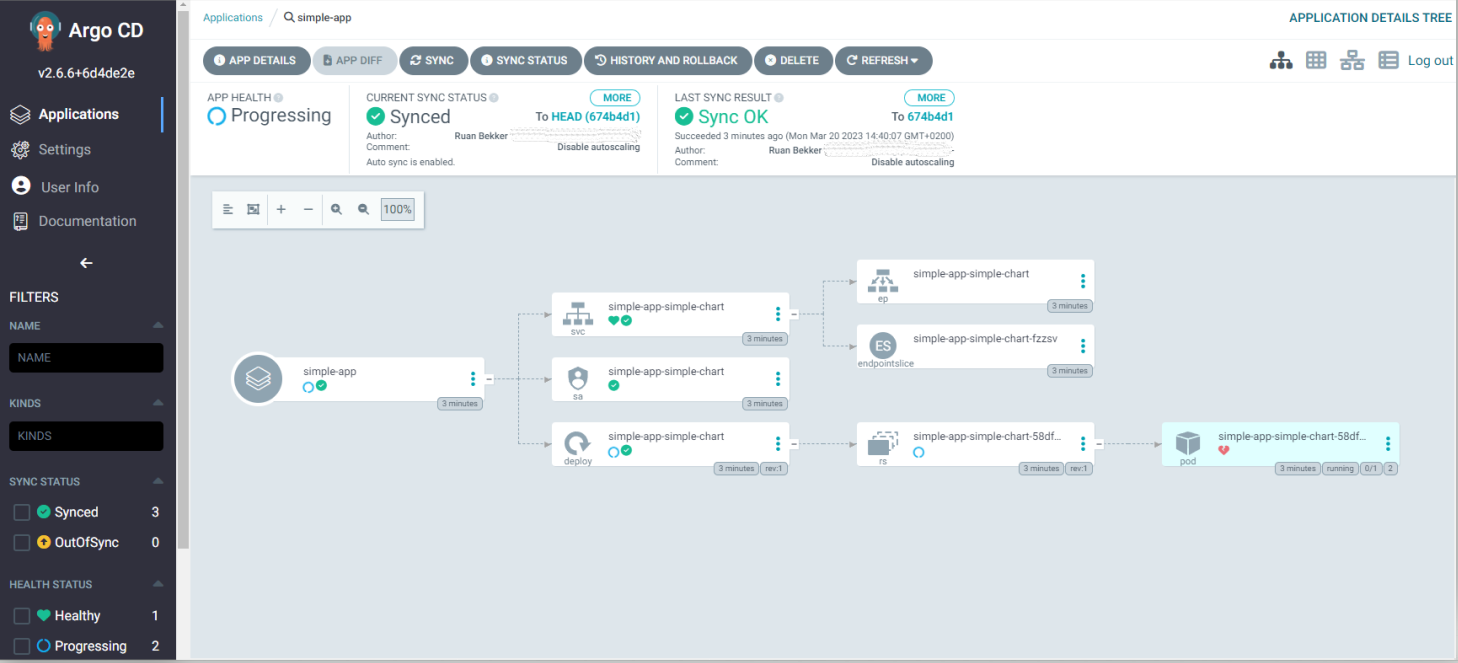
While we are here, we can see the pod is unhealthy, when we select the pod we can see the health is degraded:
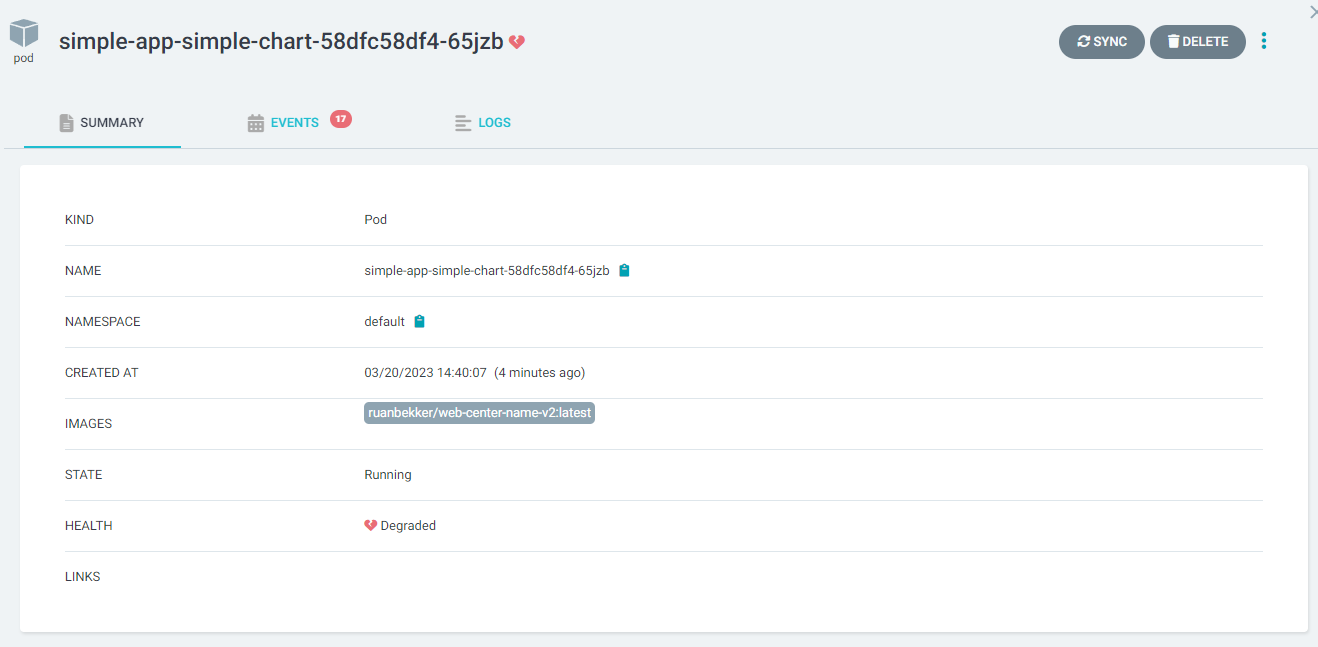
When we select the events tab:
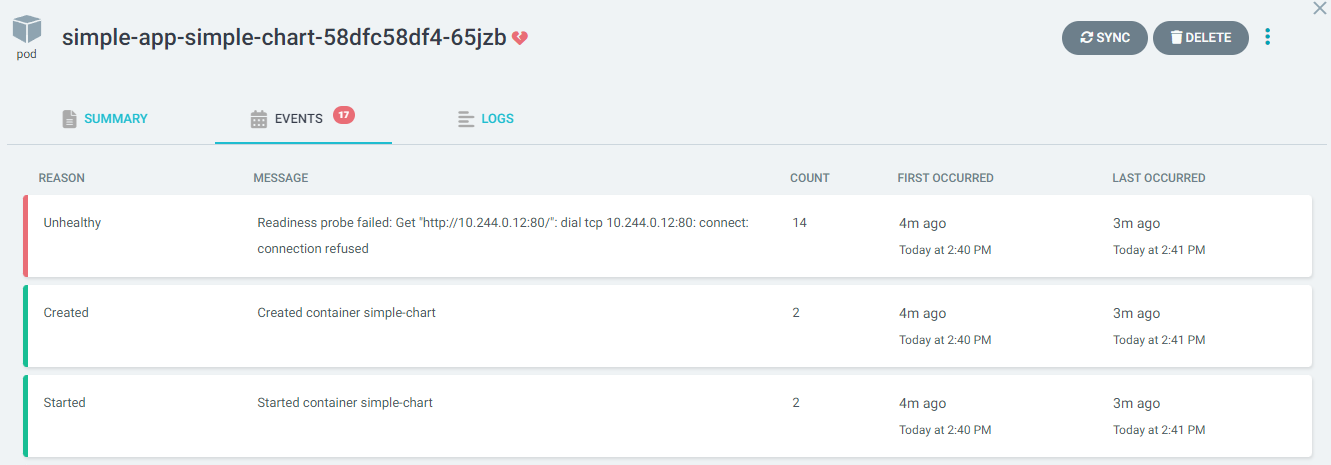
We can see that its failing due to the health checks being done against port 80 and the container listens on port 5000, lets fix that in `deployment/helm/simple-chart/values.yaml` and push it up to github.
About a minute after I've pushed up [this commit](https://github.com/ruanbekker/argocd-workshop/commit/694a94e2601275fb229d66bbfb3aab480e43a674) we can see that our application is now health:
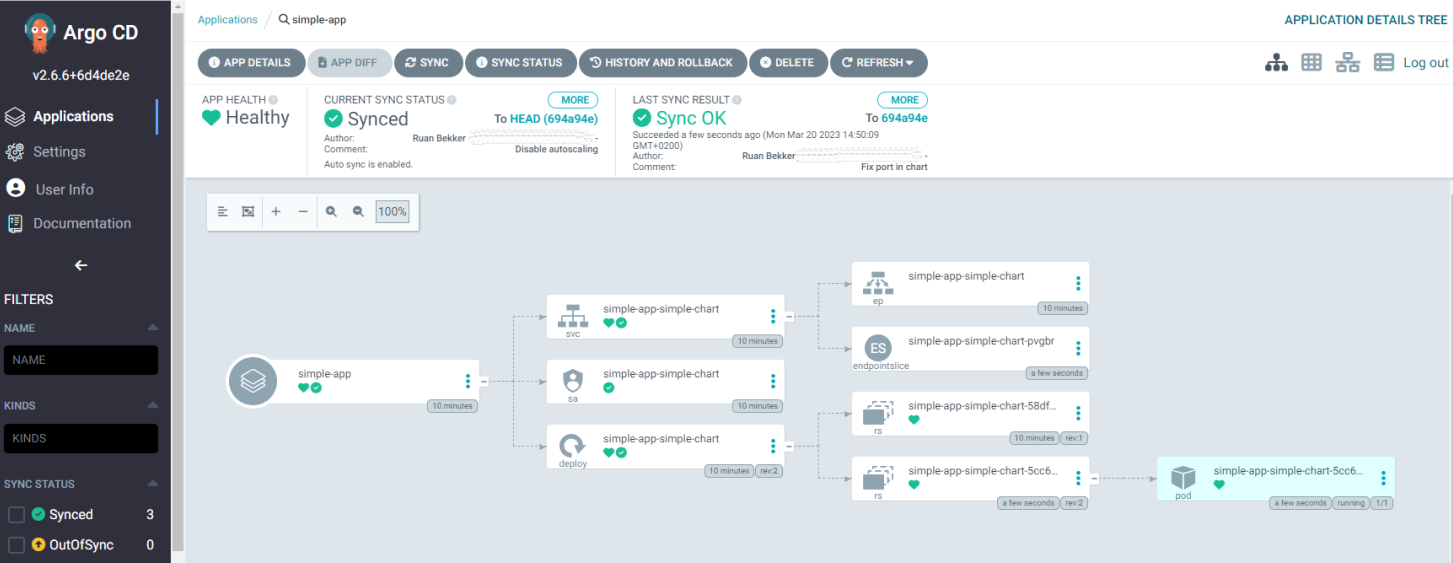
If we look at our resources using kubectl:
```bash
kubectl get all -n default
# NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
# pod/simple-app-simple-chart-5cc6bc5bf-cmd6s 1/1 Running 0 3m48s# NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
# service/kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 443/TCP 87m
# service/simple-app-simple-chart ClusterIP 10.96.244.107 80/TCP 13m# NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
# deployment.apps/simple-app-simple-chart 1/1 1 1 13m# NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
# replicaset.apps/simple-app-simple-chart-58dfc58df4 0 0 0 13m
# replicaset.apps/simple-app-simple-chart-5cc6bc5bf 1 1 1 3m48s
```Let's delete our application from the CLI, first list our applications
```bash
argocd app list --output name
# kube-system/simple-app
```Then delete the application:
```bash
argocd app delete simple-app
# Are you sure you want to delete 'simple-app' and all its resources? [y/n] y
# application 'simple-app' deleted
```### ArgoCD UI
From the UI you will notice that our application has been deleted:
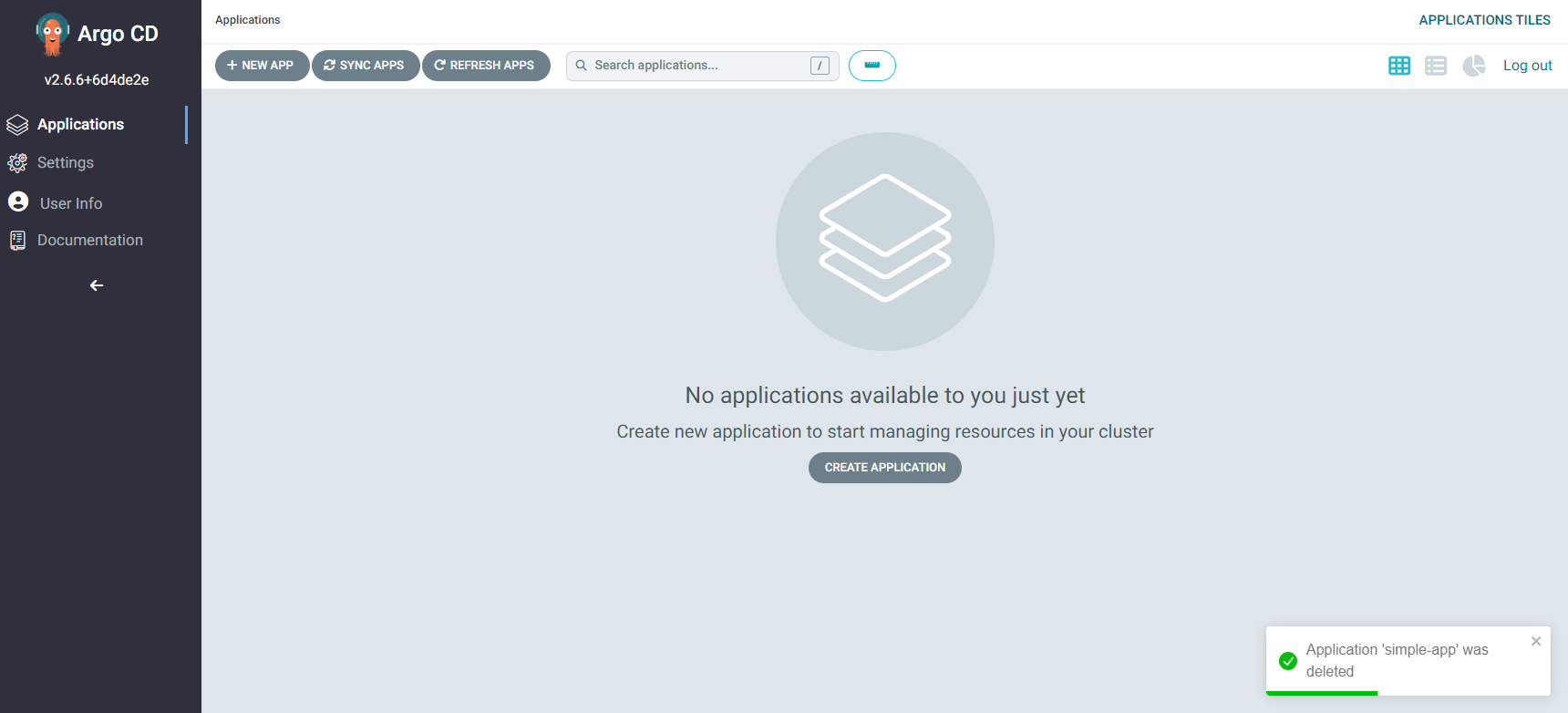
Now to do the same that we did in the CLI against the UI, we will head over to "New App", then we should get a screen like the following:
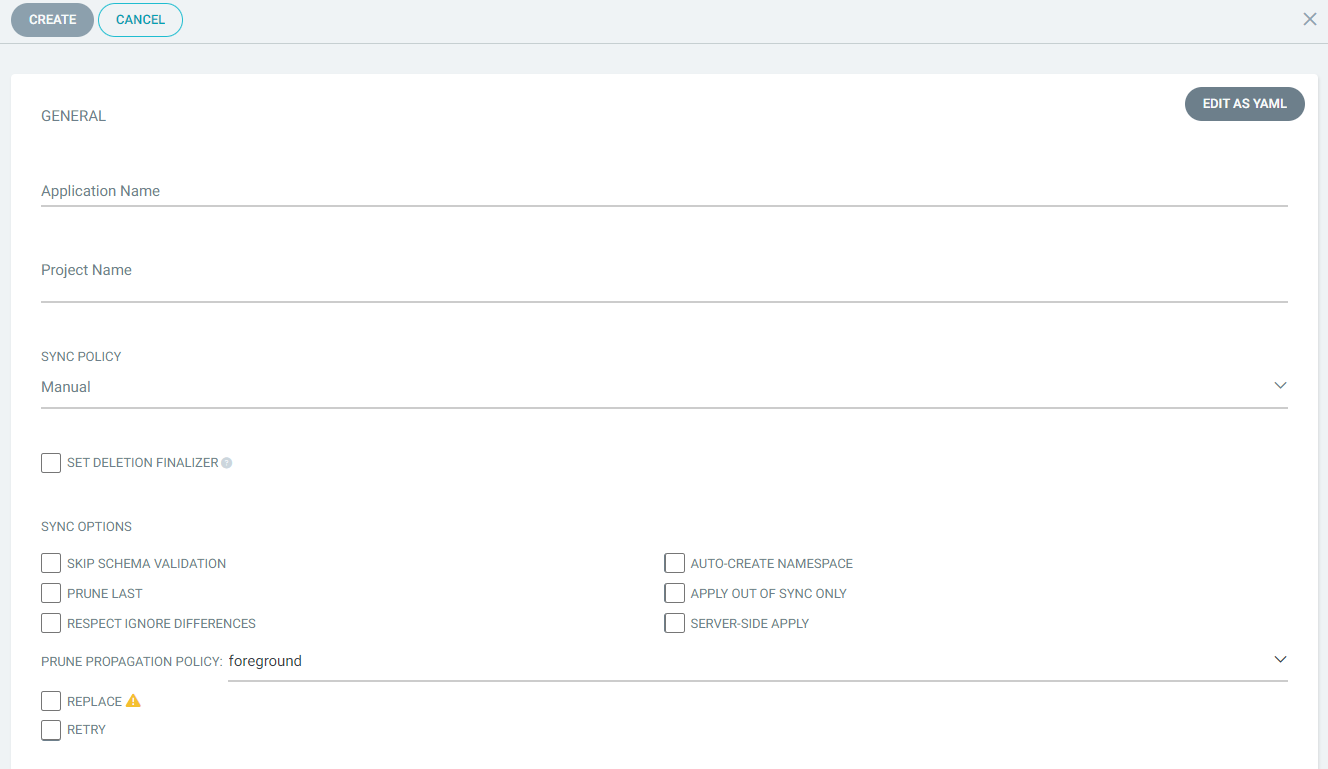
Which we can populate the same fields:
- Application Name: `simple-app`
- Project Name: `default`
- Sync Policy: `Automatic`, `Prune Resources`
- Repository URL: `https://github.com/ruanbekker/argocd-workshop.git`
- Revision: `HEAD`
- Path: `deployment/helm/simple-chart`
- Destination Cluster URL: `https://kubernetes.default.svc`
- Destination Namespace: `default`
- Helm values should be populatedThen select "Create" and a couple of seconds after that you should see your application running:
```bash
kubectl get pods -n default
# NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
# simple-app-simple-chart-5cc6bc5bf-f2dqx 1/1 Running 0 17s
```## Credit
Thanks to [Anais Urlichs ](https://anaisurl.com/) and [TheDevOpsToolkit](https://www.devopstoolkitseries.com/) for the awesome content as I've learned a lot from them.