https://github.com/s-will/locarna
Alignment of RNAs
https://github.com/s-will/locarna
alignment rna-structural-analysis rna-structure-prediction
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
Alignment of RNAs
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/s-will/locarna
- Owner: s-will
- License: gpl-3.0
- Created: 2015-12-15T17:36:51.000Z (over 9 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2024-07-31T10:05:22.000Z (10 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-03-17T03:51:14.141Z (2 months ago)
- Topics: alignment, rna-structural-analysis, rna-structure-prediction
- Language: C++
- Homepage: https://s-will.github.io/LocARNA
- Size: 20.8 MB
- Stars: 24
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 4
- Open Issues: 12
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README
- Changelog: ChangeLog.md
- License: COPYING
- Authors: AUTHORS
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
[TOC]
LocARNA: Alignment of RNAs
==========================
The LocARNA package provides several tools for the structural analysis of
RNA. LocARNA's main functionality is to align a set of a priori unaligned
RNAs sequences and at the same time predict their common structure. In
this way, LocARNA performs simultaneous alignment and folding in the spirit
of the classical Sankoff algorithm, but implements strategies to perform
this computationally challenging task efficiently and comparably fast.
Due to the central ability to simultaneously assess sequence similarity and
the similarity of predicted structure, LocARNA is recommends itself for the
analysis of RNAs in the twilight zone (around or below 60% sequence
identity), where alignments based on only sequence similarity are
unreliable. Thus, it could be sometimes easier and typically faster to align highly
similar RNAs using pure sequence alignment tools; similarily, RNAs with existing trusted
alignments can be more efficiently analyzed based on specialized tools like
RNAalifold, R-scape, or Infernal.
### Example of standard usage
Most of the package's functionality is accessible via the command-line tool [`mlocarna`](https://s-will.github.io/LocARNA/md_src_Utils_mlocarna.html)
through its various options. In the simplest case, we provide the input
sequences in a fasta file.
```
$ mlocarna archaea.fa
```
yields text output and writes results (and intermediary results) to disk; here to folder ```archaea.out```.
As main result, it produces the alignment of the seven short RNA sequences in [`archaea.fa`](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/s-will/LocARNA/master/Data/Examples/archaea.fa) together with a consensus structure:
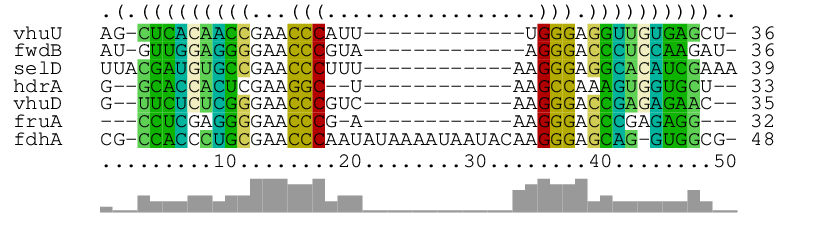
The graphical RNAalifold-generated output shows the aligned RNAs (with
gaps), the consensus structure as dot-bracket string on top, and the column
similarities by bars at the bottom. In the way of alifold, columns are
color-coded to visualize compensatory and incompatible mutations at
predicted base pairs.
### More on features and alignment variants
LocARNA distinguishes itself from many other Sankoff-style multiple
alignment programs by its high performance (strongly improved in the 2.x
line) and low memory complexity, high accuracy, and a broad set of features.
As unique features, it offers structure-local alignment,
flexible structure constraints and anchor constraints, specialized
realignment modes for refining existing alignments, and provides efficient
computation of reliabilities in sequence-structure alignment.
The package offers a robust core of
features and is used as experimental platform for new RNA alignment related methods.
Multiple alignment can be performed in one of several different ways:
* progressive alignment using sequence-structure alignment of profiles
* progressive alignment after consistency transformation using
T-Coffee
* progressive alignment using probabilistic consistency transformation
and sequence-structure profile alignments, optionally followed by
iterative refinement.
Besides of global alignment, LocARNA supports two kinds of
locality. Local alignment as it is known from sequence alignment,
identifies and aligns the best matching subsequences. This form of
locality is called sequence local to distinguish it from structural
locality. When performing structure local alignment, LocARNA
identifies and aligns the best matching substructures in the RNAs. The
sequences of those substructures can be discontinuous on the sequence
level, but remain connected via structural bonds.
Alignment Reliabilities (LocARNA-P). In this special, probabilistic
mode of operation LocARNA supports the efficient computation of match
probabilities, probabilistic consistency transformation for more
accurate multiple alignment, and generates reliability profiles of
multiple alignments.
------------
Installation
------------
The software can be installed on recent Linux or MacOSX systems; Windows
is untested but should be supported via WSL.
### Installation from Conda package (recommended)
On Mac/Linux, LocARNA is installed most easily via Conda from a pre-compiled
package. For this purpose, install Conda and run from the command line:
```
conda install -c conda-forge -c bioconda locarna
```
### Alternative installation from source
Installing from source requires a C++ compiler (GNU C++,
Clang, ...) and Autotools. Moreover, it depends on the Vienna RNA package.
#### Installation from source distribution
Obtain the tar.gz source distribution, e.g. from Github
[https://github.com/s-will/LocARNA/releases](https://github.com/s-will/LocARNA/releases)
Then, build and install like
```
tar xzf locarna-xxx.tar.gz
cd locarna-xxx
./configure --prefix=/usr/local
make
make install
```
Is Vienna RNA installed in a non-standard location, this has to be
specified by configure option ```--with-vrna=path-to-vrna``.
Installing from source furthermore allows testing via
```
make check
```
and building documentation locally by
```
make doxygen-doc
```
Building documentation requires additional tools: doxygen, pod2markdown and pandoc.
#### Installation from the git repository
Installing from repository is possible after cloning and setting up the
autotools suite. This is most easily achieved by running
```
autoreconf -i
```
in the cloned repository. Then, the installation essentially works like
installing from source distribution. Note that, we will however require
additional tools to build the documentation: help2man, pod2man.
-----
Usage
-----
For instructions on the use of the tools, please see the documentation / man pages of
the single tools
* [mlocarna](https://s-will.github.io/LocARNA/md_src_Utils_mlocarna.html) --- for multiple alignment of
RNAs. This program supports most of the functionality of the package via
a high level interface.
* [locarna](https://s-will.github.io/LocARNA/md__build_Doc_man_locarna.html) --- for pairwise alignment
* [locarna_p](https://s-will.github.io/LocARNA/md__build_Doc_man_locarna_p.html) --- for pairwise computation of alignment partition function
and (sequence and structure) match probabilities
* [sparse](https://s-will.github.io/LocARNA/md__build_Doc_man_sparse.html) --- for structurally stronger sparsified pairwise alignment
For additional functionality and special purposes, see
* [exparna_p](https://s-will.github.io/LocARNA/md__build_Doc_man_exparna_p.html) --- for generating exact matches from the ensembles of two RNAs
* [locarnate](https://s-will.github.io/LocARNA/md_src_Utils_locarnate.html) --- for multiple alignment of
RNAs via T-Coffee. This script offers multiple alignment of RNAs that is
performed by sequence-structurally aligning all pairs of RNAs and then
using T-Coffee to construct a common multiple alignment out of all
pairwise ones.
----------
Web server
----------
The core functionality of the package is accessible through a web
interface at
http://rna.informatik.uni-freiburg.de
-------
Contact
-------
Main author and contact: Sebastian Will sebastian.will (at) polytechnique.edu
------------
References
------------
* Sebastian Will, Kristin Reiche, Ivo L. Hofacker, Peter F. Stadler, and Rolf Backofen. Inferring non-coding RNA families and classes by means of genome-scale structure-based clustering. PLOS Computational Biology, 3 no. 4 pp. e65, 2007. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.0030065
* Sebastian Will, Tejal Joshi, Ivo L. Hofacker, Peter F. Stadler, and Rolf Backofen. LocARNA-P: Accurate boundary prediction and improved detection of structural RNAs. RNA, 18 no. 5 pp. 900-914, 2012. doi:10.1261/rna.029041.111
* Sebastian Will, Michael Yu, and Bonnie Berger. Structure-based Whole Genome Realignment Reveals Many Novel Non-coding RNAs. Genome Research, no. 23 pp. 1018-1027, 2013. doi:10.1101/gr.137091.111
* Sebastian Will, Christina Otto, Milad Miladi, Mathias Mohl, and Rolf Backofen. SPARSE: quadratic time simultaneous alignment and folding of RNAs without sequence-based heuristics. Bioinformatics, 31(15):2489–2496, 2015. doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv185