https://github.com/salpreh/tablat
Print basic tables in python
https://github.com/salpreh/tablat
column-alignment pretty-print python tables
Last synced: 3 months ago
JSON representation
Print basic tables in python
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/salpreh/tablat
- Owner: salpreh
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-02-28T16:49:35.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2022-12-26T20:53:40.000Z (over 2 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-09T20:16:31.488Z (4 months ago)
- Topics: column-alignment, pretty-print, python, tables
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 898 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 4
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# tablat
[](https://badge.fury.io/py/tablat)
[](https://img.shields.io/github/license/salpreh/tablat.svg)
**A simple way to print output in a table**
---
## Basic usage
Just create a `Table` object and give it a headers list and the data. The number of columns will be calculated from the number of headers.
#### Code sample
```py
from pathlib import Path
from tablat import Table
folder_path = Path('./')
header = ['FILE_NAME', 'FOLDER', 'FILES_IN']
data = []
for file_path in folder_path.iterdir():
data.append(file_path.name)
if file_path.is_dir():
data.extend(['YES', len([f for f in file_path.iterdir()])])
else:
data.extend(['NO', 0])
my_table = Table(data, header)
my_table.print_table()
```
*Note: `print(my_table)` is also valid*
#### Output
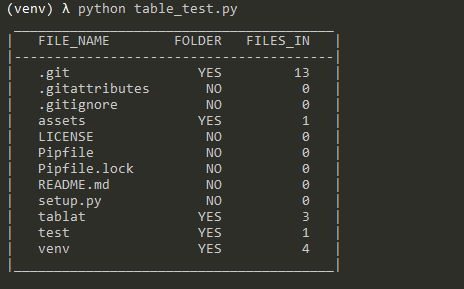
---
## Installation
You can intall the package using [pip](https://pip.pypa.io/en/stable/) (Python Package Installer)
```sh
pip install tablat
```
or
```sh
python -m pip install tablat
```
---
## Usage
### Creating and modifying `Table`
`Table` object can be initialized with the data or empty:
```py
my_table = Table(data=my_data, headers=my_headers)
```
If it is initialized empty it can be modified or updated later:
```py
my_table = Table()
my_table.headers = ['FILE_NAME', 'IS_DIR']
my_table.table_data = ['My docs', True, 'profile_pic.png', False]
```
Table data can be expanded anytime:
```py
for file_path in Path('./').iterdir():
my_table.add_data([file_path.name, file_path.is_dir()])
```
#### Loading `Table` data by column
You can use the method `set_column_content(column_dict)` to init the `Table` by columns.
This method expects a `dict` with the column names as **keys** and a list with the column data as **values**.
```json
{
"column_name1": ["item11", "item12", "item13"],
"column_name2": ["item21", "item21", "item23"],
.
.
.
}
```
Here is the example from the begining modified:
```py
from pathlib import Path
from tablat import Table
folder_path = Path('./')
column_data = {
'FILE_NAME': [],
'FOLDER': [],
'FILES_IN': []
}
for file_path in test_path.iterdir():
column_data['FILE_NAME'].append(file_path.name)
column_data['FOLDER'].append('Y' if file_path.is_dir() else 'N')
column_data['FILES_IN'].append(len([f for f in file_path.iterdir()]) if file_path.is_dir() else 0)
Table().set_column_content(column_data).print_table()
```
The method `get_column_conten()` returns a `dict` with the same structure even if you didn't initialized the table with `set_column_content(column_dict)`.
#### Loading `Table` data from _json_
The method `load_data(file_path)` initializes the table from a _json_ file. The _json_ file should
have the same structure that `set_column_content(column_dict)`, column name as **key** and column content list as **value**:
```json
{
"column_name1": ["item11", "item12", "item13"],
"column_name2": ["item21", "item21", "item23"],
.
.
.
}
```
### Modifying column alignment
By default first column will be aligned to left and the rest to right. The alignment
follows the same encoding as the string `format` function, a character can be passed to set the alignment:
- Right align: `>`
- Left align: `<`
- Center align: `^`
Column alignment can be changed with `alignment` attribute or `set_column_align()` method.
With `alignment` attribute you can provide a list with the alignment for each column:
```py
my_table.alignment = ['^', '^', '>']
```
With `set_column_align(index, align_char)` you can change a specific column alignment (_column index starts form 0)_:
```py
my_table.set_column_align(0, '<')
```
### Filtering columns to print
By default `print_table()` will print all columns in the table, but you can filter what columns should be printed.
`print_table()` have two optional arguments: `show_columns` and `hide_columns`. This arguments expects a list with the indexes of the columns to print or hide respectively. If the two arguments are used `hide_columns` will be ignored.
```py
# Shows first and third column
my_table.print_table(show_columns=[0, 2])
# Hide third column and shows the rest
my_table.print_table(hide_columns=[2])
```
### Additional Notes
You can retrieve data form the table using indices
```py
# Get first row data
my_table[0]
# Get third row, second column
my_table[2][1]
```
---
## `Table` style
### Syling the table with `TabStyle`
`TabStyle` class is used to encapsulate style options for the table. Current values are:
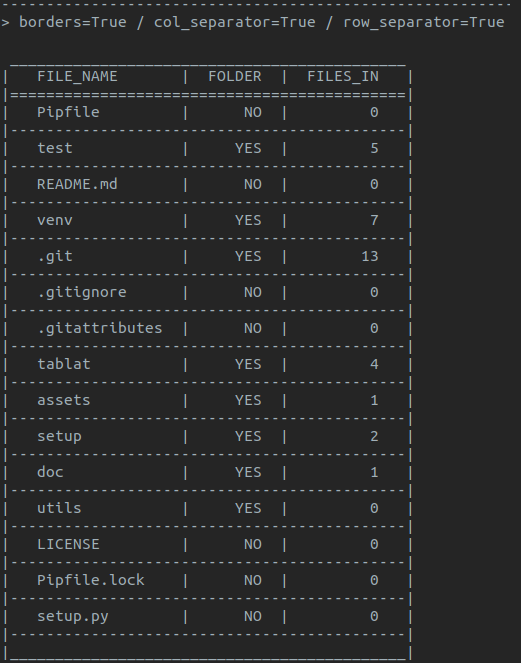
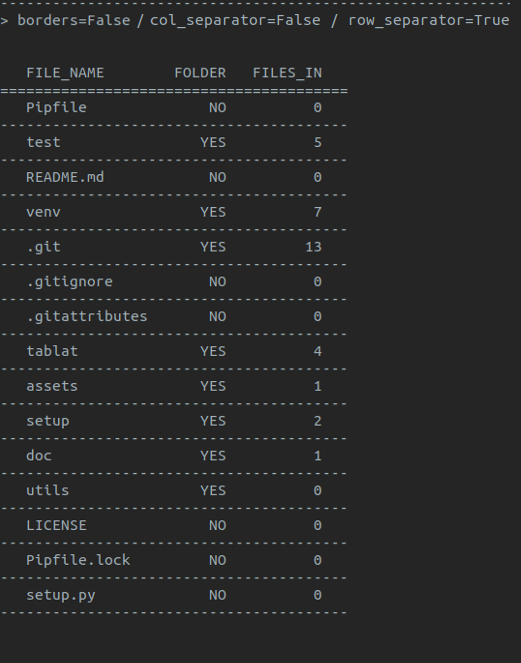
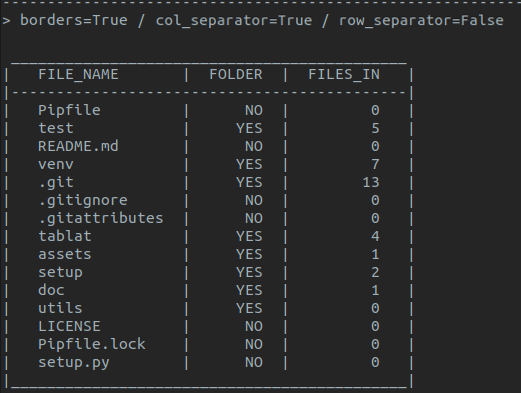
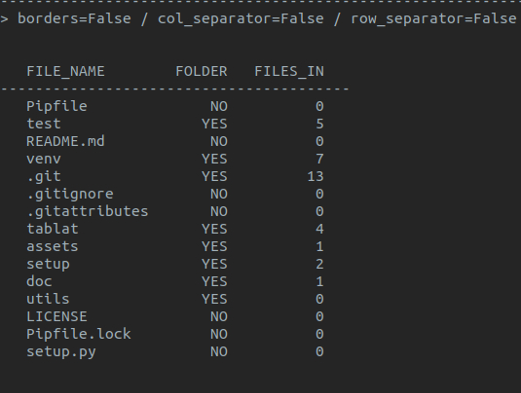
- Table borders
- Row separators
- Column separators
*Note: default style is **with borders** and **no separators** for rows and columns*
Using `TabStyle` to configure the style:
```py
form tablat import Table, TabStyle
# Style object with no borders and row separators
pref_style = TabStyle(borders=False, row_sep=True)
.
.
.
# Initializing Table with our prefered style
some_tab = Table(data, headers, pref_style)
.
.
.
# Restoring Table default style
some_tab.style = TabStyle()
```
`Table` objects are initialized with a default `TabStyle` that can be modified
```py
my_table = Table()
# Disabling borders
my_table.syle.borders = False
# Modifying style properties at once
my_table.style.update(col_sep=True, row_sep=True)
```
### Sample table with style modifications