https://github.com/sandysanthosh/msa-book
https://github.com/sandysanthosh/msa-book
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/sandysanthosh/msa-book
- Owner: sandysanthosh
- License: apache-2.0
- Created: 2021-11-06T18:27:12.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2021-11-06T18:42:49.000Z (about 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-06-13T00:05:00.939Z (7 months ago)
- Size: 19.5 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# SpringBoot:
### SPRING-BOOT-MICROSERVICES Annotations:
#### No beans.xml
* **@Required:** It applies to the bean setter method. It indicates that the annotated bean must be populated at configuration time with the required property, else it throws an exception BeanInitilizationException.
* **@Autowired:** Spring provides annotation-based auto-wiring by providing @Autowired annotation. It is used to autowire spring bean on setter methods, instance variable, and constructor. When we use @Autowired annotation, the spring container auto-wires the bean by matching data-type.
* **@Configuration:** It is a class-level annotation. The class annotated with @Configuration used by Spring Containers as a source of bean definitions.
* **@ComponentScan:** It is used when we want to scan a package for beans. It is used with the annotation @Configuration. We can also specify the base packages to scan for Spring Components.
* **@Bean:** It is a method-level annotation. It is an alternative of XML tag. It tells the method to produce a bean to be managed by Spring Container.
* **@Component:** It is a class-level annotation. It is used to mark a Java class as a bean. A Java class annotated with @Component is found during the classpath. The Spring Framework pick it up and configure it in the application context as a Spring Bean.
* **@Controller:** The @Controller is a class-level annotation. It is a specialization of @Component. It marks a class as a web request handler. It is often used to serve web pages. By default, it returns a string that indicates which route to redirect. It is mostly used with @RequestMapping annotation.
* **@Service:** It is also used at class level. It tells the Spring that class contains the business logic.
* **@Repository:** It is a class-level annotation. The repository is a DAOs (Data Access Object) that access the database directly. The repository does all the operations related to the database.
* **@SpringBootApplication:** It is a combination of three annotations @EnableAutoConfiguration, @ComponentScan, and @Configuration.
### Spring MVC and REST Annotations:
* **@RequestMapping:** It is used to map the web requests. It has many optional elements like consumes, header, method, name, params, path, produces, and value. We use it with the class as well as the method.
* **@GetMapping:** It maps the HTTP GET requests on the specific handler method. It is used to create a web service endpoint that fetches It is used instead of using: @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
* **@PostMapping:** It maps the HTTP POST requests on the specific handler method. It is used to create a web service endpoint that creates It is used instead of using: @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
* **@PutMapping**: It maps the HTTP PUT requests on the specific handler method. It is used to create a web service endpoint that creates or updates It is used instead of using: @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
* **@DeleteMapping:** It maps the HTTP DELETE requests on the specific handler method. It is used to create a web service endpoint that deletes a resource. It is used instead of using: @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
* **@PatchMapping:** It maps the HTTP PATCH requests on the specific handler method. It is used instead of using: @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PATCH)
* **@RequestBody:** It is used to bind HTTP request with an object in a method parameter. Internally it uses HTTP MessageConverters to convert the body of the request. When we annotate a method parameter with @RequestBody, the Spring framework binds the incoming HTTP request body to that parameter.
* **@ResponseBody:** It binds the method return value to the response body. It tells the Spring Boot Framework to serialize a return an object into JSON and XML format.
* **@PathVariable:** It is used to extract the values from the URI. It is most suitable for the RESTful web service, where the URL contains a path variable. We can define multiple @PathVariable in a method.
* **@RequestParam:** It is used to extract the query parameters form the URL. It is also known as a query parameter. It is most suitable for web applications. It can specify default values if the query parameter is not present in the URL.
* **@RequestHeader:** It is used to get the details about the HTTP request headers. We use this annotation as a method parameter. The optional elements of the annotation are name, required, value, defaultValue. For each detail in the header, we should specify separate annotations. We can use it multiple time in a method
* **@RestController:** It can be considered as a combination of @Controller and @ResponseBody annotations. The @RestController annotation is itself annotated with the @ResponseBody annotation. It eliminates the need for annotating each method with @ResponseBody.
* **@RequestAttribute:** It binds a method parameter to request attribute. It provides convenient access to the request attributes from a controller method. With the help of @RequestAttribute annotation, we can access objects that are populated on the server-side.
* **@EnableSwagger2:** Mainly used for documentation the Restful we-service
* **@EnableOAuth2Sso:** Oauth Authentication
# Boot-starter-logging:
* internal Logger -> Apache Commons Logging
* private final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
* spring.output.ansi.enabled - always, detect or never
* LOGGER.info("Simple log statement with inputs {}, {} and {}", 1,2,3);
* Types -> logging, log4j, logback
LOGGER.debug("This is a debug message");
LOGGER.info("This is an info message");
LOGGER.warn("This is a warn message");
LOGGER.error("This is an error message");
# REST request validation annotations:
@AssertFalse -> The annotated element must be false.
@AssertTrue -> The annotated element must be true.
@DecimalMax -> The annotated element must be a number whose value must be lower or equal to the specified maximum.
@DecimalMin -> The annotated element must be a number whose value must be higher or equal to the specified minimum.
@Future -> The annotated element must be an instant, date or time in the future.
@Max -> The annotated element must be a number whose value must be lower or equal to the specified maximum.
@Min -> The annotated element must be a number whose value must be higher or equal to the specified minimum.
@Negative -> The annotated element must be a strictly negative number.
@NotBlank -> The annotated element must not be null and must contain at least one non-whitespace character.
@NotEmpty -> The annotated element must not be null nor empty.
@NotNull -> The annotated element must not be null.
@Null -> The annotated element must be null.
@Pattern -> The annotated CharSequence must match the specified regular expression.
@Positive -> The annotated element must be a strictly positive number.
@Size -> The annotated element size must be between the specified boundaries (included).
#### AOP annotation:
* @Advice
* @before
* @order(0)
* @after
* @afterAdvice
* @beforeReturningAdvice
#### Junit Test annotation:
* @BeforeClass
* @Before
* @Test
* @After
* @AfterClass
#### arious Assest Statement:
```
Void equals(boolean exptation, boolean Actual)
Void Notequals(boolean exptation, boolean Actual)
Void assertTrue(boolean condition)
Void assertFalse(boolean condition)
Void assertNull(Object object)
Void assertNotNull(Object object)
Void assertSame(Object object1,Object object 2)
Void assertNotSame(Object object1,Object object 2)
void assertArrayEquals(expectedArray, resultArray);
```
#### @data in Lombok
* Will add all getter and setters
* To string
* Equal and barcode
@NOTnull
#### Web App:
* request
* response
* get
* post
* jsp
* jstl
* bootstrap
#### Spring mvc:
* dispatcher servlet
* view resolver
* model
* view
* validation
* form tags
#### Spring Boot:
* starterss
* Autoconfiguration
* Initializr
* actuator
* embedded servers
#### External config:
#### MSA:
* Collection of small autonomous
* Small multiple services
* All component seperate module
* Stateless communication
#### Advantage:
* easy to maintain
* Continuous Delivery
* Hybrid Technology -java csharp mysql
* Cross Team coordination
* Higher Quality code
* Smarter Scaling
* Risk Reduction -Seperation of services allowed for localized changes
* Promote Big Data Best Practises
* Improved ROI with Reduced TCO
## Microservices:
* Client Side load balancer - Ribbon
* Distributed Tracking - Sluth and Zipkin
* Fault Tolerance using Hystrix
* Feign Client
* Router and ZUUL
* Service Registry using Eureka
* Spring Cloud BUS
* Spring Cloud Config
### 12FactorAPP-Microservices
* Codebase = One codebase tracked in revision control, many deploys - SVN
* Dependencies = Explicitly declare and isolate dependencies - pom.xml
* Config = Store config in the environment - DEV ,FET , ACC
* Backing services = Treat backing services as attached resources
* Build, release, run = Strictly separate build and run stages
* Processes = Execute the app as one or more stateless processes
* Port binding = Export services via port binding
* Concurrency = Scale out via the process model
* Disposability = Maximize robustness with fast startup and graceful shutdown
* Dev/prod parity = Keep development, staging, and production as similar as possibe
* Logs = Treat logs as event streams
* Admin processes = Run admin/management tasks as one-off processes
#### Properties in Spring Boot:
```
#MYSQL DB Properties
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/dbname
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#JPA Properties
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.generate-ddl=true
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.format_sql=true
#Eureka Properties
eureka.client.register-with-eureka=true
eureka.client.fetch-registry=true
eureak.instance.hostnam=localhost
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone = http://localhost:8761/eureka
spring.cloud.config.uri=http://localhost:8888
spring.rabbitmq.addresses=amqps://ailhzrhf:pnHKsJmZxwUZwUh_P7wEBiiD37BrfCnQ@finch.rmq.cloudamqp.com/ailhzrhf
Server:
Jetty
Spring jpa mysql security
security:
oauth2:
client:
clientId: a48f56f893775afb1912
clientSecret: c91036f105c04d0666655f411f716c43b606d373
accessTokenUri: https://github.com/login/oauth/access_token
userAuthorizationUri: https://github.com/login/oauth/authorize
clientAuthenticationScheme: form
resource:
user-info-uri: https://api.github.com/user
prefer-token-info: false
```
### Microservies-MSA
### Springboot with Microservies
#### N-Tier and monolithic applications used to be the de facto standard. In one single binary web artifact, like an EAR or WAR file, there would be a layered architecture with the decomposition of code into more functional components.
* Presentation Layer
* Business Process Layer/Service Layer
* Data Access Layer
#### There are several disadvantages to the n-tier monolithic application architecture:
* Tight coupling of code which makes changes hard.
* A single deployment with multiple layers that causes long testing, building, and deployment cycles.
* A big monolithic application that makes code reuse and sharing of components difficult.
* The Microservices Architecture (MSA) decomposes systems into discrete, individual, standalone components that can communicate amongst themselves, working together or with external systems.
** MSA is a more agile framework that fits well with the cloud-based world and lends itself well to web application development and web service development.**
#### MSA Features:
* MSA is very flexible because it supports any language that can communicate via a RESTful endpoint and leverages REST over HTTP.
* MSA offers agility and systems that are easier to write, test, deploy, and share.
* MSA provides systems that can better scale to load and demand.
* MSA provides systems that are resilient because failures are isolated and don’t cascade through the infrastructure.
#### Eureka:
* Eureka, created by Netflix, is responsible for the registration and discovery microservices. Spring has incorporated Eureka into Spring Cloud, making it even easier to stand up a Eureka server.
* Eureka consists of a server and a client-side component. The server component will be the registry in which all the microservices register their availability. The microservices use the Eureka client to register; once the registration is complete, it notifies the server of its existence.
#### What make a microservice different from a normal RESTful service?
A microservice must register itself with a discovery service
#### Eureka server to load:
#### pom.xml:
* spring cloud starter config
* spring cloud netfli eureka server
javax.xml.bind
jaxb-api
2.4.0-b180725.0427
#### application.properties:
```
spring.appliation.name=eurela-server
server.port=8761
#dont register itself as client
eureka.client.regiser-with-eureka = false
eureka.client.fetch-registry= false
logging.level.com.netflix.eureka=ON
logging.level.com.netflix.discovery = ON
```
##### Starter:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableEurekaServer
##### login:
https://localhost:8761
##### Eureka dashboard:
* system status
* current time -> uptime
* general Info -> total memory, enviroment, cpus
* DS replicas
instane currently registered with Eureka
##### Spring Data REST makes it easy to expose microservices.
##### Spring Data REST builds on top of Spring Data repositories and automatically exports those as REST resources.
#### So how does Spring Data Rest work?
* At application startup, Spring Data Rest finds all of the spring data repositories
* Then, Spring Data Rest creates an endpoint that matches the entity name
* Next, Spring Data Rest appends an S to the entity name in the endpoint
* Lastly, Spring Data Rest exposes CRUD (Create, Read, Update, and Delete) operations as RESTful APIs over HTTP
* There is no need to create a controller or service layer!
Eureka client
#### pom.xml:
* spring data
* JPA Item Repository
* Spring DATA REST
* For a @SpringBootApplication to be discovery-aware, all that's needed is the Spring Discovery Client (i.e., spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client dependency) in the classpath.
* The next step is to annotate the main Spring application class with the @EnableEurekaClient annotation.
* @EnableEurekaClient is optional if the spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client dependency is on the classpath.

# Devops
Devops Tools:
#### GIT-> for version control for tracking changes in code files
#### Maven -> for software packaging
#### Jenkins -> For continuous integration and continuous deployment
#### Docker -> for container image which is lightweight, executable package of software which Includes everything to run the image(eg. Code, libraries)
#### Puppet -> open source software configuration management tool
#### Nagios -> Application Monitoring tool
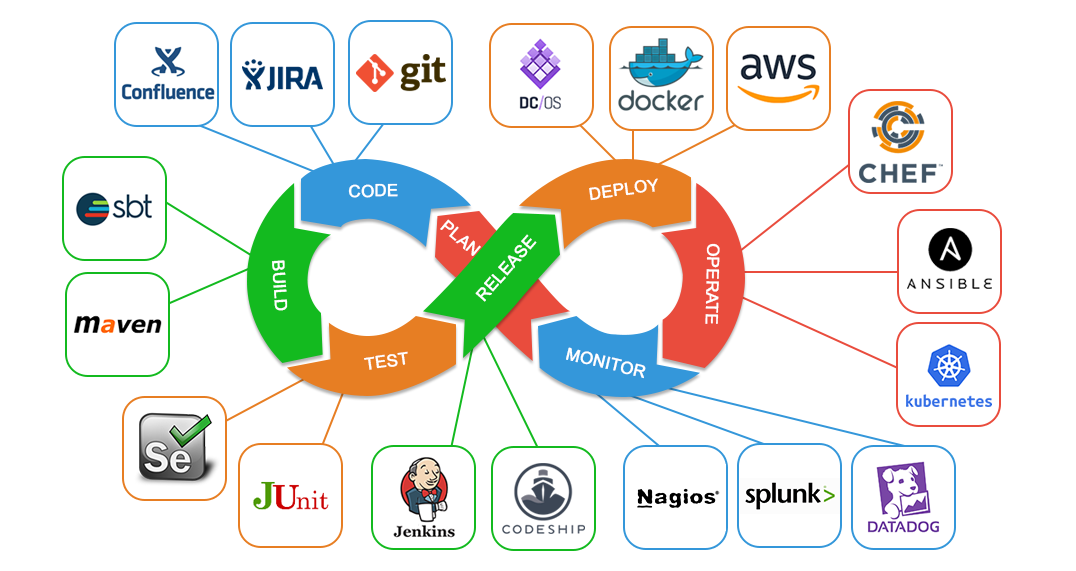
# CI-CD-Pipeline
CI/CD pipeline

* GIT
* DOCKER
* AWS
* JENKINS
#### Devops:
* Version Control - SVN, GIT
* Continuous Integration - compile, Validate, code review, unit test, integration testing
* Continuous Delivery - Deployment the build application to test servers. Performing UAT
* Continuous Deploy - Deploying the tested application on the prod server for release.
#### Docker:
* A container is a standard unit of software that packages up code and all its dependencies so the application runs quickly and reliably from one computing environment to another.
* A Docker container image is a lightweight, standalone, executable package of software that includes everything needed to run an application:
code,
runtime,
system tools,
system libraries and settings.
#### AWS:
* Amazon Web Services (AWS) provides cloud computing platforms on a pay-as-you-go basis.
# Maven
powerful project management tool that is based on POM
#### maven:
aache software foundation
build automation tool
roet automation tool
handles comlete build Proess
#### advantage of maven:
making the build proess easy
provide a unifrom build system
provide guidelines for best pratises
allow transparent migration
#### pom.xml:
project
modelversion
grou-id- Com.sandy
version - 0.0.1 snapshot
name- dummyproject
jdk 12.0.1
#### mvn package command completes the build life cycle of the maven project such as:
validate
compile
test
package
integration-test
verify
install