https://github.com/santiagoenriquega/maze_path_finder
This project implements algorithms for maze path finding in 2D using curses and 3D using ursina.
https://github.com/santiagoenriquega/maze_path_finder
curses pathfinding python ursina
Last synced: about 2 months ago
JSON representation
This project implements algorithms for maze path finding in 2D using curses and 3D using ursina.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/santiagoenriquega/maze_path_finder
- Owner: SantiagoEnriqueGA
- Created: 2024-10-11T15:00:10.000Z (7 months ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-10-17T19:42:05.000Z (7 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-23T05:22:07.614Z (3 months ago)
- Topics: curses, pathfinding, python, ursina
- Language: Python
- Homepage:
- Size: 344 KB
- Stars: 0
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 0
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Maze Path Finder
This project, **maze_path_finder**, implements multiple algorithms for maze path finding. There are two implementations, one for path finding in 2D, on a square grid, and in 3D, on a cubical grid.
For our 2D path finding the visualization are done using the curses library and the 3D path finding visuals are done using the ursina library.
## Project Structure
- **pathfinding/path_finder.py**: The main script that implements the path finding algorithms and visualization.
- **pathfinding/maze.csv**: Contains the maze data in CSV format.
- **pathfinding_3d/main.py**: The main script for 3D path finding algorithms.
- **pathfinding_3d/pathfinding.py**: Implements 3D path finding methods and handles the relationship of cells across cube faces.
- **requirements.txt**: Packages required
## Features
- **2D Path Finding**:
- Visualization of the maze and the path finding process using the curses library.
- Multiple path finding algorithms.
- **3D Path Finding**:
- Visualization of the maze and the path finding process using the ursina library.
- Interactive, user controllable camera view.
## 2D Path Finding Visualized
The visualization is done using the curses library, which provides a terminal-based interface to display the maze and the path finding process.
### `python pathfinding/path_finder.py --maze_type 0`

### `python pathfinding/path_finder.py --maze_type 4 --rows 20 --cols 20`

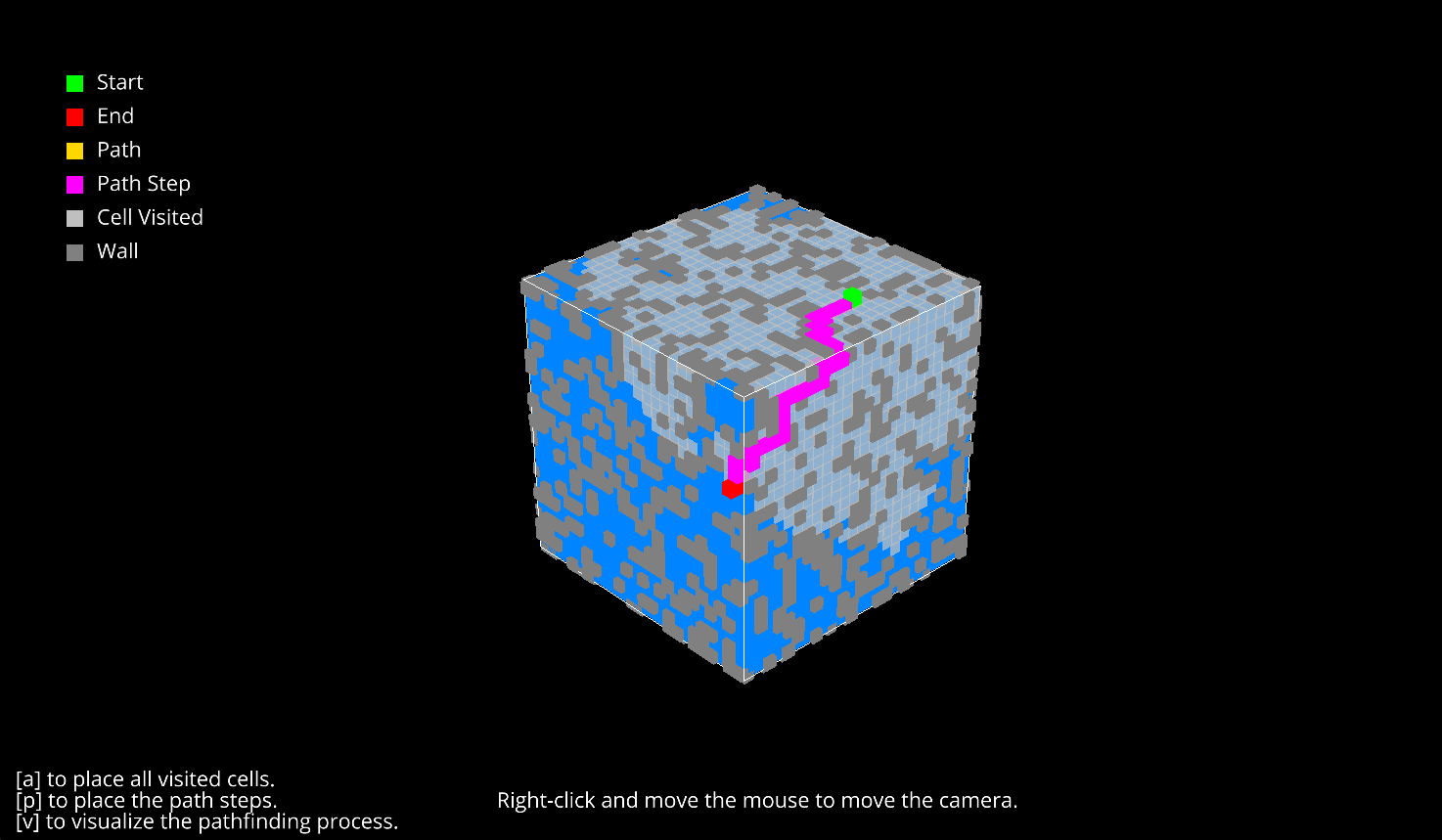
## 3D Path Finding Visualized
The visualization is done using the ursina library.
Ursina is a game engine for Python built on top of the Panda3D engine, designed to make it easier to develop games and visualizations. It provides an API for creating 3D applications, handling input, and managing game logic.
### `python pathfinding_3d/main.py `
## Usage 2D path finding:
1. Ensure you have Python installed on your system.
2. Install the required dependencies:
**Note**: `curses` is a built-in module in Unix-based systems and does not need to be installed via pip. If you are using Windows, need to install requirements.txt wich includes `windows-curses`.
```sh
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
3. Run the 2D path finder script:
```sh
python pathfinding/path_finder.py
```
### Command Line Arguments
**Usage**: path_finder.py [-h] [--rows ROWS] [--cols COLS] [--maze_type MAZE_TYPE]
**Defaults**: [--rows 10] [--cols 10] [--maze_type MAZE_TYPE]
```
-h, --help: Show this help message and exit
--rows ROWS: Number of rows in the maze
--cols COLS: Number of columns in the maze
--maze_type MAZE_TYPE: Type of maze to generate: Maze type small: 0, Maze type large: 1, Maze type csv: 2, Random grid maze: 3, Random maze: 4
```
**Note**: [--rows ROWS] and [--cols COLS] arguments will only apply to Maze types Random grid maze: 3 and Random maze: 4
## Usage 3D path finding:
1. Ensure you have Python installed on your system.
2. Install the required dependencies:
```sh
pip install -r requirements.txt
```
3. Run the 3D main script:
```sh
python pathfinding_3d/main.py
```
## Algorithms Implemented
1. Breadth-First Search (BFS)
2. Depth-First Search (DFS)
3. A* Search (with four heuristics: Manhattan, Euclidean, Chebyshev, and Octile)
4. Greedy Best-First Search
5. Dijkstra
6. Bidirectional Search
### Algorithms Explained
#### 1. Breadth-First Search (BFS)
Breadth-First Search is an algorithm that explores all the nodes at the present depth level before moving on to the nodes at the next depth level. It uses a queue to keep track of the nodes to be explored next. The implementation can be found in the [`bfs`](path_finder.py) function.
#### 2. Depth-First Search (DFS)
Depth-First Search is an algorithm that explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking. It uses a stack (or recursion) to keep track of the nodes to be explored next. The implementation can be found in the [`dfs`](path_finder.py) function.
#### 3. A* Search
A* Search is an algorithm that finds the shortest path by combining the cost to reach the current node and a heuristic estimate of the cost to reach the goal. It uses a priority queue to expand the node with the lowest combined cost. The implementation can be found in the [`a_star`](path_finder.py) function.
#### 4. Greedy Best-First Search (GBFS)
GBFS is an algorithm that expands the most promising node chosen according to a specified rule. It uses a heuristic to estimate the cost to reach the goal from the current node and always expands the node with the lowest estimated cost. The implementation can be found in the [`gbfs`](path_finder.py) function.
#### 5. Dijkstra's Algorithm
Dijkstra's Algorithm finds the shortest path from the start position to the end position in a weighted graph. It uses a priority queue to explore the node with the lowest cost first and updates the cost of reaching its neighbors. The implementation can be found in the [`dijkstra`](path_finder.py) function.
#### 6. Bidirectional Search
Bidirectional Search is an algorithm that simultaneously searches from the start and end positions until the two searches meet. This can significantly reduce the search space and time compared to unidirectional search. The implementation can be found in the [`bidirectional`](path_finder.py) function.
### Heuristics
#### 1. Manhattan Distance
The Manhattan distance between two points is the sum of the absolute differences of their Cartesian coordinates. It is used in grid-based path finding where movement is restricted to horizontal and vertical directions. The implementation can be found in the [`heuristic`](path_finder.py) function with the type `"manhattan"`.
#### 2. Euclidean Distance
The Euclidean distance between two points is the straight-line distance between them. It is used in scenarios where movement can occur in any direction. The implementation can be found in the [`heuristic`](path_finder.py) function with the type `"euclidean"`.
#### 3. Chebyshev Distance
The Chebyshev distance between two points is the maximum of the absolute differences of their Cartesian coordinates. It is used in grid-based path finding where movement can occur in any direction, including diagonally. The implementation can be found in the [`heuristic`](path_finder.py) function with the type `"chebyshev"`.
#### 4. Octile Distance
The Octile distance is a combination of Manhattan and diagonal distances. It is used in grid-based path finding where diagonal movement is allowed but has a different cost than horizontal and vertical movement. The implementation can be found in the [`heuristic`](path_finder.py) function with the type `"octile"`.