Ecosyste.ms: Awesome
An open API service indexing awesome lists of open source software.
https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats
Statistics tools and utilities.
https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats
hep hep-ex python python3 scikit-hep statistical-inference statistics
Last synced: 5 days ago
JSON representation
Statistics tools and utilities.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats
- Owner: scikit-hep
- Created: 2019-06-11T15:14:27.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-01-28T15:07:19.000Z (13 days ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-01-29T16:36:09.189Z (12 days ago)
- Topics: hep, hep-ex, python, python3, scikit-hep, statistical-inference, statistics
- Language: Python
- Homepage: https://scikit-hep.org/hepstats/
- Size: 64.8 MB
- Stars: 74
- Watchers: 5
- Forks: 15
- Open Issues: 6
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.rst
- License: LICENSES/LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README

# `hepstats` package: statistics tools and utilities
[![Scikit-HEP][sk-badge]](https://scikit-hep.org/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
[](https://pypi.org/project/hepstats/)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/hepstats)
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3519200)

[](https://codecov.io/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master)
hepstats is a library for statistical inference aiming to cover the needs High Energy Physics.
It is part of the [Scikit-HEP project](https://scikit-hep.org/).
**Questions**: for usage questions, use [StackOverflow with the hepstats tag](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/ask?tags=hepstats)
**Bugs and odd behavior**: open [an issue with hepstats](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/issues/new)
## Installation
Install `hepstats` like any other Python package:
```
pip install hepstats
```
or similar (use e.g. `virtualenv` if you wish).
## Changelog
See the [changelog](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/master/CHANGELOG.md) for a history of notable changes.
## Getting Started
The `hepstats` module includes `modeling`, `hypotests` and `splot` submodules. This a quick user guide to each submodule. The [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master) examples are also a good way to get started.
### modeling
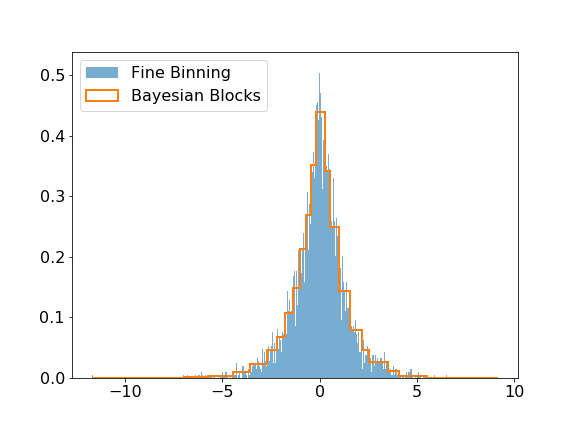
The modeling submodule includes the [Bayesian Block algorithm](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1207.5578.pdf) that can be used to improve the binning of histograms. The visual improvement can be dramatic, and more importantly, this algorithm produces histograms that accurately represent the underlying distribution while being robust to statistical fluctuations. Here is a small example of the algorithm applied on Laplacian sampled data, compared to a histogram of this sample with a fine binning.
```python
>>> import numpy as np
>>> import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
>>> from hepstats.modeling import bayesian_blocks
>>> data = np.random.laplace(size=10000)
>>> blocks = bayesian_blocks(data)
>>> plt.hist(data, bins=1000, label='Fine Binning', density=True, alpha=0.6)
>>> plt.hist(data, bins=blocks, label='Bayesian Blocks', histtype='step', density=True, linewidth=2)
>>> plt.legend(loc=2)
```
### hypotests
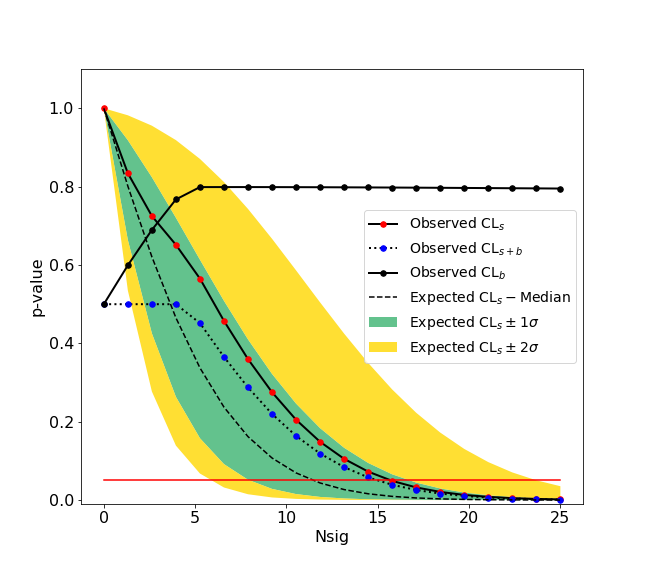
This submodule provides tools to do hypothesis tests such as discovery test and computations of upper limits or confidence intervals. hepstats needs a fitting backend to perform computations such as [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit). Any fitting library can be used if their API is compatible with hepstats (see [api checks](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/blob/master/hepstats/hypotests/utils/fit/api_check.py)).
We give here a simple example of an upper limit calculation of the yield of a Gaussian signal with known mean and sigma over an exponential background. The fitting backend used is the [zfit](https://github.com/zfit/zfit) package. An example with a **counting experiment** analysis is also given in the [binder](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/scikit-hep/hepstats/master) examples.
```python
>>> import zfit
>>> from zfit.loss import ExtendedUnbinnedNLL
>>> from zfit.minimize import Minuit
>>> bounds = (0.1, 3.0)
>>> obs = zfit.Space('x', limits=bounds)
>>> bkg = np.random.exponential(0.5, 300)
>>> peak = np.random.normal(1.2, 0.1, 10)
>>> data = np.concatenate((bkg, peak))
>>> data = data[(data > bounds[0]) & (data < bounds[1])]
>>> N = data.size
>>> data = zfit.Data.from_numpy(obs=obs, array=data)
>>> lambda_ = zfit.Parameter("lambda", -2.0, -4.0, -1.0)
>>> Nsig = zfit.Parameter("Nsig", 1., -20., N)
>>> Nbkg = zfit.Parameter("Nbkg", N, 0., N*1.1)
>>> signal = zfit.pdf.Gauss(obs=obs, mu=1.2, sigma=0.1).create_extended(Nsig)
>>> background = zfit.pdf.Exponential(obs=obs, lambda_=lambda_).create_extended(Nbkg)
>>> total = zfit.pdf.SumPDF([signal, background])
>>> loss = ExtendedUnbinnedNLL(model=total, data=data)
>>> from hepstats.hypotests.calculators import AsymptoticCalculator
>>> from hepstats.hypotests import UpperLimit
>>> from hepstats.hypotests.parameters import POI, POIarray
>>> calculator = AsymptoticCalculator(loss, Minuit(), asimov_bins=100)
>>> poinull = POIarray(Nsig, np.linspace(0.0, 25, 20))
>>> poialt = POI(Nsig, 0)
>>> ul = UpperLimit(calculator, poinull, poialt)
>>> ul.upperlimit(alpha=0.05, CLs=True)
Observed upper limit: Nsig = 15.725784747406346
Expected upper limit: Nsig = 11.927442041887158
Expected upper limit +1 sigma: Nsig = 16.596396280677116
Expected upper limit -1 sigma: Nsig = 8.592750403611896
Expected upper limit +2 sigma: Nsig = 22.24864429383046
Expected upper limit -2 sigma: Nsig = 6.400549971360598
```
### splots
A full example using the **sPlot** algorithm can be found [here](https://github.com/scikit-hep/hepstats/tree/master/notebooks/splots/splot_example.ipynb). **sWeights** for different components in a data sample, modeled with a sum of extended probability density functions, are derived using the `compute_sweights` function:
```python
>>> from hepstats.splot import compute_sweights
# using same model as above for illustration
>>> sweights = compute_sweights(zfit.pdf.SumPDF([signal, background]), data)
>>> bkg_sweights = sweights[Nbkg]
>>> sig_sweights = sweights[Nsig]
```
The model needs to be fitted to the data for the computation of the **sWeights**, if not an error is raised.
[sk-badge]: https://img.shields.io/badge/Scikit--HEP-Project-blue?logo=data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAABoAAAAcCAYAAAB/E6/TAAAACXBIWXMAAAEZAAABGQHyCY1sAAAAGXRFWHRTb2Z0d2FyZQB3d3cuaW5rc2NhcGUub3Jnm+48GgAAA6dJREFUSImdlktonFUUx/930kQ0nYo2JX5NUqSghSq2oIgvcCFaC0EEH2AXUh9FEV1UUaGIC924qY8igo+FQi26sWp8gDS24qOgCOIiKCVomLlnZpxk7Dh2GjMz389F7tgv4zfNJGdzh/M/5/zuud/ch9MKDFgnaUjSnHOu2kuOmb0h6brMMoVHgceBY8ApSVVJ05JOAnXga+BJ4OK0fO/9PZL2AL91AwwBLwLz9GYLwKvAcLtGLpcbMbM5MyuXy+UoDXI14BNFcsABYBy4DLgojDvDZH5PxJaAG4CM937SzCgUCnemQcaB0yFpDngMGFhmefuBh4E/Qt4/tVrtoJlhZq+nJWwHaiH4F2DL2QAp+SPA9wBxHDM7O5svl8vZzqBzgOkAOQGsXwmkbbVabUOj0Wh/1xIw+J+Yy+UuBJ4O4jywdTUQSSoUCgdKpRJxHC+Ees8mxVKr1WoGYf9qId77m80sNrNvgedDvb+A8yQpMzg4OJHJZPoAVavVQ6uBmNmQc+4dSfVWq7Vb0n5JC5KyknZIUiabzdYlqdFoqF6vTxSLxctXwXpNUuSce3RsbOyEc+6kpKNBG5ekjKRLguMTSUNxHE/m8/ntvRK89w9IukvS4SiK3k5Ix8N4aRu0UZIGBgaOAHdIWpfJZI56769fDlIqlTY7515yzlkcx3s65xDGjW1Qf3A0R0ZGJpxzOyX1Oee+MLMd3SDAmjiOD0paK+nB0dHRuY6QhTD2t0EWHJEkRVF0zDl3k6TTkj5OPUIkmdkzwLWSXomi6POUkNFkZxlJM8GxrR0RRdEPzrkbnXOzwHve+/s7IFc55/ZJmmq1Wvu6NH1FGGfaS3B3YrMuOTJKpdJmM5sO+2OvJBWLxUEz+9XM5vP5/DalWDhpqqHu7rYzmzhI96Ys0aZQmEKh8IKZvRV+P9GlEwEPhXoNYCgpvByE2SXCmc6GzeyncCLjvZ8EUi9N4HygEOq92SmuB/4M4pdAf2eBmZmZC7z3lQDb1AXSB3wW6vwNpF54twOtEPQBsLYzplgsfmhmpHUDnAscCvkxsCttMu3gpzhjPwNLNq2ZHU4DsXgr/5jIfa4rJJF0H0vfCp8C9wLDSRCwAdgFfBQ6gMW3wyPLQhKwK4Gv+L81m80mwKkU7Tvgmp4hHcBbgXcTf5ROqwLvA7cBblWQDmA/sLVSqXxTqVQAbmHxJXTWh0vS1vQS5JxrSJoys3JwHXHOxSuZbE+ghE1J2rJSiCT9CxJT5EBIY81lAAAAAElFTkSuQmCC