https://github.com/seek-oss/capsize
Flipping how we define typography in CSS.
https://github.com/seek-oss/capsize
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
Flipping how we define typography in CSS.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/seek-oss/capsize
- Owner: seek-oss
- License: mit
- Created: 2020-06-03T22:57:36.000Z (almost 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: master
- Last Pushed: 2025-03-31T00:25:22.000Z (11 months ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-05-11T18:08:51.005Z (10 months ago)
- Language: TypeScript
- Homepage: https://seek-oss.github.io/capsize/
- Size: 42.2 MB
- Stars: 1,606
- Watchers: 10
- Forks: 42
- Open Issues: 9
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
- Codeowners: .github/CODEOWNERS
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-github-repos - seek-oss/capsize - Flipping how we define typography in CSS. (TypeScript)
README


> Capsize makes the sizing and layout of text as predictable as every other element on the screen.
>
> Using font metadata, text can now be sized according to the height of its capital letters while trimming the space above capital letters and below the baseline.
```bash
npm install @capsizecss/core
```
- [Usage](#usage)
- [createStyleObject](#createstyleobject)
- [createStyleString](#createstylestring)
- [Options](#options)
- [Text size](#text-size)
- [Line height](#line-height)
- [Font Metrics](#font-metrics)
- [Core](#core)
- [createFontStack](#createfontstack)
- [Usage in CSS stylesheet](#usage-in-css-stylesheet-or-a-style-tag)
- [Usage with CSS-in-JS frameworks](#usage-with-css-in-js-frameworks)
- [Additional `font-face` properties](#providing-additional-font-face-properties)
- [precomputeValues](#precomputevalues)
- [getCapHeight](#getcapheight)
- [Metrics](#metrics)
- [Unpack](#unpack)
- [Integrations](#integrations)
- [vanilla-extract](packages/vanilla-extract/README.md)
## Usage
### `createStyleObject`
Returns a CSS-in-JS style object.
1. Import `createStyleObject` passing the relevant [options](#options).
```ts
import { createStyleObject } from '@capsizecss/core';
const capsizeStyles = createStyleObject({
fontSize: 16,
leading: 24,
fontMetrics: {
capHeight: 700,
ascent: 1058,
descent: -291,
lineGap: 0,
unitsPerEm: 1000,
},
});
```
Note: It is recommended that you install the [@capsizecss/metrics](packages/metrics/README.md) package and import the metrics from there:
```ts
import { createStyleObject } from '@capsizecss/core';
import arialMetrics from '@capsizecss/metrics/arial';
const capsizeStyles = createStyleObject({
fontSize: 16,
leading: 24,
fontMetrics: arialMetrics,
});
```
See the [fontMetrics](#font-metrics) option documented below for more ways to obtain these metrics.
2. Apply styles to the text element, for example via the `css` prop.
```ts
My capsized text 🛶
```
> ⚠️ Note: It is not recommended to apply further layout-related styles to the same element, as this will risk interfering with the styles used for the trim. Instead consider using a nested element.
### `createStyleString`
Returns a CSS string that can be inserted into a `style` tag or appended to a stylesheet.
1. Import `createStyleString` passing the relevant [options](#options).
```ts
import { createStyleString } from '@capsizecss/core';
import arialMetrics from '@capsizecss/metrics/arial';
const capsizedStyleRule = createStyleString('capsizedText', {
fontSize: 16,
leading: 24,
fontMetrics: arialMetrics,
});
```
2. Add the styles into a stylesheet or `style` element and apply the specified class name.
```ts
document.write(`
${capsizedStyleRule}
My capsized text 🛶
`);
```
> ⚠️ Note: It is not recommended to apply further layout-related styles to the same element, as this will risk interfering with the styles used for the trim. Instead consider using a nested element.
## Options
### Text size
Capsize supports two methods of defining the size of text, `capHeight` and `fontSize`.
**NOTE: You should only ever pass one or the other, not both.**
#### `capHeight: `
Sets the height of the capital letters to the defined value. Defining typography in this way makes aligning to a grid or with other elements, e.g. icons, a breeze.

#### `fontSize: `
Setting the font size allows you to get all the benefits of the white space trimming, while still specifying an explicit `font-size` for your text. This can be useful when needed to match a concrete design spec or fitting into an existing product.

### Line height
Capsize supports two mental models for specifying line height, `lineGap` and `leading`. If you pass neither the text will follow the default spacing of the specified font, e.g. `line-height: normal`.
**NOTE: You should only ever pass one or the other, not both.**
#### `lineGap: `
Sets the number of pixels between lines, as measured between the baseline and cap height of the next line.
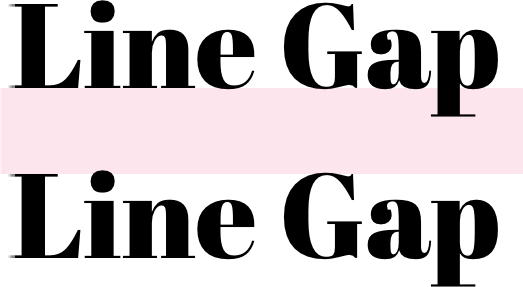
#### `leading: `
Sets the line height to the provided value as measured from the baseline of the text. This aligns the web with how typography is treated in design tools.

### Font Metrics
This metadata is extracted from the metrics tables inside the font itself. There are a number of ways to find this information:
- If using a Google Font or system font, install the [@capsizecss/metrics](packages/metrics/README.md) package and import the metrics by name. For example:
```ts
import arialMetrics from '@capsizecss/metrics/arial';
```
- If using a font from a file, install the [@capsizecss/unpack](packages/unpack/README.md) package and extract the metrics from the font file directly. For example:
```ts
import { fromFile } from '@capsizecss/unpack';
const metrics = await fromFile(filePath);
```
- Or, use [the Capsize website](https://seek-oss.github.io/capsize/) to find these by selecting a font and referencing `Metrics` tab in step 3.
## Core
The core package also provides a few other metrics-based features for improving typography on the web:
### createFontStack
Creates metrics-based `@font-face` declarations to improve the alignment of font family fallbacks, which can dramatically improve the [Cumulative Layout Shift](https://web.dev/cls/) metric for sites that depend on a web font.
#### Usage
Consider the following example, where the desired web font is [Lobster](https://fonts.google.com/specimen/Lobster), falling back to `Helvetica Neue` and then `Arial`, e.g. `font-family: Lobster, 'Helvetica Neue', Arial`.
1. Import `createFontStack` from the core package:
```ts
import { createFontStack } from '@capsizecss/core';
```
2. Import the font metrics for each of the desired fonts (see [Font Metrics](#font-metrics) above):
```ts
import lobster from '@capsizecss/metrics/lobster';
import helveticaNeue from '@capsizecss/metrics/helveticaNeue';
import arial from '@capsizecss/metrics/arial';
```
3. Create your font stack passing the metrics as an array, using the same order as you would via the `font-family` CSS property.
```ts
const { fontFamily, fontFaces } = createFontStack([
lobster,
helveticaNeue,
arial,
]);
```
The returned value contains the generated font face declarations as well as the computed `fontFamily` with the appropriately ordered font aliases.
#### Usage in CSS stylesheet or a style tag
The returned values can be templated into a stylesheet or a `style` block. Here is an example [handlebars](https://handlebarsjs.com/) template:
```html
.heading {
font-family: {{ fontFamily }}
}
{{ fontFaces }}
```
This will produce the following CSS:
```css
.heading {
font-family: Lobster, 'Lobster Fallback: Helvetica Neue',
'Lobster Fallback: Arial', 'Helvetica Neue', Arial;
}
@font-face {
font-family: 'Lobster Fallback: Helvetica Neue';
src: local('Helvetica Neue');
ascent-override: 115.1741%;
descent-override: 28.7935%;
size-adjust: 86.8251%;
}
@font-face {
font-family: 'Lobster Fallback: Arial';
src: local('Arial');
ascent-override: 113.5679%;
descent-override: 28.392%;
size-adjust: 88.053%;
}
```
#### Usage with CSS-in-JS frameworks
If working with a CSS-in-JS library, the returned `fontFaces` can be provided as a JavaScript style object by providing `styleObject` as a `fontFaceFormat` option.
Here is an example using [Emotion](https://emotion.sh/):
```tsx
import { Global } from '@emotion/core';
const { fontFaces, fontFamily } = createFontStack(
[lobster, helveticaNeue, arial],
{
fontFaceFormat: 'styleObject',
},
);
export const App = () => (
<>
...
>
);
```
> Also useful as a source for further manipulation given it is a data structure that can be iterated over or extended.
#### Providing additional `font-face` properties
Additional properties can be added to the generated `@font-face` declarations via the `fontFaceProperties` option:
```ts
const { fontFamily, fontFaces } = createFontStack(
[lobster, helveticaNeue, arial],
{
fontFaceProperties: {
fontDisplay: 'swap',
},
},
);
```
This will result in the following additions to the declarations:
```diff
@font-face {
font-family: 'Lobster Fallback: Helvetica Neue';
src: local('Helvetica Neue');
ascent-override: 115.1741%;
descent-override: 28.7935%;
size-adjust: 86.8251%;
+ font-display: swap;
}
@font-face {
font-family: 'Lobster Fallback: Arial';
src: local('Arial');
ascent-override: 113.5679%;
descent-override: 28.392%;
size-adjust: 88.053%;
+ font-display: swap;
}
```
> [!NOTE]
> Passing any of the metric override CSS properties will be ignored as they are calculated by Capsize.
> However, the `size-adjust` property is accepted to support fine-tuning the override for particular use cases.
> This can be used to finesse the adjustment for specific text, or to disable the adjustment by setting it to `100%`.
#### Scaling for different character subsets
For languages that use different unicode subsets, e.g. Thai, the fallbacks need to be scaled accordingly, as the scaling is [based on character frequency in written language].
A fallback font stack can be generated for a supported subset by specifying `subset` as an option:
```ts
const { fontFamily, fontFaces } = createFontStack([lobster, arial], {
subset: 'thai',
});
```
> [!TIP]
> Need support for a different unicode subset?
> Either create an issue or follow the steps outlined in the [`generate-weightings` script] and open a PR.
[based on character frequency in written language]: packages/metrics/README.md#how-xwidthavg-is-calculated
[`generate-weightings` script]: packages/unpack/scripts/generate-weightings.ts
### precomputeValues
Returns all the information required to create leading trim styles for a specific font size given the provided font metrics. This is useful for integrations with different styling solutions.
Accepts the same [options](#options) as [createStyleObject](#createstyleobject) and [createStyleString](#createstylestring).
```ts
import { precomputeValues } from '@capsizecss/core';
import arialMetrics from '@capsizecss/metrics/arial';
const capsizeValues = precomputeValues({
fontSize: 16,
leading: 24,
fontMetrics: arialMetrics,
});
// => {
// fontSize: string,
// lineHeight: string,
// capHeightTrim: string,
// baselineTrim: string,
//}
```
### getCapHeight
Return the rendered cap height for a specific font size given the provided font metrics.
```ts
import { getCapHeight } from '@capsizecss/core';
import arialMetrics from '@capsizecss/metrics/arial';
const actualCapHeight = getCapHeight({
fontSize: 24,
fontMetrics: arialMetrics,
});
// => number
```
## Metrics
To make the retrieval of font metrics easy, Capsize provides the `@capsizecss/metrics` package containing all the required data for both system and Google fonts.
```bash
npm install @capsizecss/metrics
```
See the [package](packages/metrics/README.md) for documentation.
## Unpack
If you are using a custom font or one not included in the `@capsizecss/metrics` package, Capsize provides the `@capsizecss/unpack` package to extract the required data either via a URL or from a local file.
```bash
npm install @capsizecss/unpack
```
See the [package](packages/unpack/README.md) for documentation.
## Integrations
- [vanilla-extract](https://vanilla-extract.style) integration via [@capsizecss/vanilla-extract](packages/vanilla-extract/README.md)
## Thanks
- [Vincent De Oliveira](https://twitter.com/iamvdo) for writing [Deep dive CSS: font metrics, line-height and vertical-align](https://iamvdo.me/en/blog/css-font-metrics-line-height-and-vertical-align), which provided the research needed to build all this.
- [Devon Govett](https://github.com/devongovett) for creating [Fontkit](https://github.com/foliojs/fontkit), which does all the heavy lifting of extracting the font metrics under the covers.
- [SEEK](https://www.seek.com.au) for giving us the space to do interesting work.
## License
MIT.