https://github.com/sherifabdlnaby/elastdocker
🐳 Elastic Stack (ELK) v8+ on Docker with Compose. Pre-configured out of the box to enable Logging, Metrics, APM, Alerting, ML, and SIEM features. Up with a Single Command.
https://github.com/sherifabdlnaby/elastdocker
docker docker-compos-template docker-compose elasticsearch elasticstack elk elk-stack kibana logstash observability siem
Last synced: 10 months ago
JSON representation
🐳 Elastic Stack (ELK) v8+ on Docker with Compose. Pre-configured out of the box to enable Logging, Metrics, APM, Alerting, ML, and SIEM features. Up with a Single Command.
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/sherifabdlnaby/elastdocker
- Owner: sherifabdlnaby
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-09-07T23:32:23.000Z (over 6 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2025-01-04T05:34:02.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-11T02:51:57.057Z (11 months ago)
- Topics: docker, docker-compos-template, docker-compose, elasticsearch, elasticstack, elk, elk-stack, kibana, logstash, observability, siem
- Language: Dockerfile
- Homepage: https://towardsdatascience.com/running-securing-and-deploying-elastic-stack-on-docker-f1a8ebf1dc5b
- Size: 145 KB
- Stars: 1,868
- Watchers: 36
- Forks: 325
- Open Issues: 7
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Contributing: .github/CONTRIBUTING.md
- Funding: .github/FUNDING.yml
- License: LICENSE
- Code of conduct: .github/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
- Security: .github/SECURITY.md
Awesome Lists containing this project
- awesome-starred - sherifabdlnaby/elastdocker - 🐳 Elastic Stack (ELK) v9+ on Docker with Compose. Pre-configured out of the box to enable Logging, Metrics, APM, Alerting, ML, and SIEM features. Up with a Single Command. (Dockerfile)
- awesome-hacking-lists - sherifabdlnaby/elastdocker - 🐳 Elastic Stack (ELK) v8+ on Docker with Compose. Pre-configured out of the box to enable Logging, Metrics, APM, Alerting, ML, and SIEM features. Up with a Single Command. (Dockerfile)
README

Elastic Stack on Docker
Preconfigured Security, Tools, and Self-Monitoring
Configured to be ready to be used for Log, Metrics, APM, Alerting, Machine Learning, and Security (SIEM) usecases.
# Introduction
Elastic Stack (**ELK**) Docker Composition, preconfigured with **Security**, **Monitoring**, and **Tools**; Up with a Single Command.
Suitable for Demoing, MVPs and small production deployments.
Stack Version: [8.10.2](https://www.elastic.co/blog/whats-new-elastic-8-10-0) 🎉 - Based on [Official Elastic Docker Images](https://www.docker.elastic.co/)
> You can change Elastic Stack version by setting `ELK_VERSION` in `.env` file and rebuild your images. Any version >= 8.0.0 is compatible with this template.
### Main Features 📜
- Configured as a Production Single Node Cluster. (With a multi-node cluster option for experimenting).
- Security Enabled By Default.
- Configured to Enable:
- Logging & Metrics Ingestion
- Option to collect logs of all Docker Containers running on the host. via `make collect-docker-logs`.
- APM
- Alerting
- Machine Learning
- Anomaly Detection
- SIEM (Security information and event management).
- Enabling Trial License
- Use Docker-Compose and `.env` to configure your entire stack parameters.
- Persist Elasticsearch's Keystore and SSL Certifications.
- Self-Monitoring Metrics Enabled.
- Prometheus Exporters for Stack Metrics.
- Embedded Container Healthchecks for Stack Images.
#### More points
And comparing Elastdocker and the popular [deviantony/docker-elk](https://github.com/deviantony/docker-elk)
Expand...
One of the most popular ELK on Docker repositories is the awesome [deviantony/docker-elk](https://github.com/deviantony/docker-elk).
Elastdocker differs from `deviantony/docker-elk` in the following points.
- Security enabled by default using Basic license, not Trial.
- Persisting data by default in a volume.
- Run in Production Mode (by enabling SSL on Transport Layer, and add initial master node settings).
- Persisting Generated Keystore, and create an extendable script that makes it easier to recreate it every-time the container is created.
- Parameterize credentials in .env instead of hardcoding `elastich:changeme` in every component config.
- Parameterize all other Config like Heap Size.
- Add recommended environment configurations as Ulimits and Swap disable to the docker-compose.
- Make it ready to be extended into a multinode cluster.
- Configuring the Self-Monitoring and the Filebeat agent that ship ELK logs to ELK itself. (as a step to shipping it to a monitoring cluster in the future).
- Configured Prometheus Exporters.
- The Makefile that simplifies everything into some simple commands.
-----
# Requirements
- [Docker 20.05 or higher](https://docs.docker.com/install/)
- [Docker-Compose 1.29 or higher](https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/)
- 4GB RAM (For Windows and MacOS make sure Docker's VM has more than 4GB+ memory.)
# Setup
1. Clone the Repository
```bash
git clone https://github.com/sherifabdlnaby/elastdocker.git
```
2. Initialize Elasticsearch Keystore and TLS Self-Signed Certificates
```bash
$ make setup
```
> **For Linux's docker hosts only**. By default virtual memory [is not enough](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/vm-max-map-count.html) so run the next command as root `sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144`
3. Start Elastic Stack
```bash
$ make elk $ docker-compose up -d $ docker compose up -d
```
4. Visit Kibana at [https://localhost:5601](https://localhost:5601) or `https://:5601`
Default Username: `elastic`, Password: `changeme`
> - Notice that Kibana is configured to use HTTPS, so you'll need to write `https://` before `localhost:5601` in the browser.
> - Modify `.env` file for your needs, most importantly `ELASTIC_PASSWORD` that setup your superuser `elastic`'s password, `ELASTICSEARCH_HEAP` & `LOGSTASH_HEAP` for Elasticsearch & Logstash Heap Size.
> Whatever your Host (e.g AWS EC2, Azure, DigitalOcean, or on-premise server), once you expose your host to the network, ELK component will be accessible on their respective ports. Since the enabled TLS uses a self-signed certificate, it is recommended to SSL-Terminate public traffic using your signed certificates.
> 🏃🏻♂️ To start ingesting logs, you can start by running `make collect-docker-logs` which will collect your host's container logs.
## Additional Commands
Expand
#### To Start Monitoring and Prometheus Exporters
```shell
$ make monitoring
```
#### To Ship Docker Container Logs to ELK
```shell
$ make collect-docker-logs
```
#### To Start **Elastic Stack, Tools and Monitoring**
```
$ make all
```
#### To Start 2 Extra Elasticsearch nodes (recommended for experimenting only)
```shell
$ make nodes
```
#### To Rebuild Images
```shell
$ make build
```
#### Bring down the stack.
```shell
$ make down
```
#### Reset everything, Remove all containers, and delete **DATA**!
```shell
$ make prune
```
# Configuration
* Some Configuration are parameterized in the `.env` file.
* `ELASTIC_PASSWORD`, user `elastic`'s password (default: `changeme` _pls_).
* `ELK_VERSION` Elastic Stack Version (default: `8.10.2`)
* `ELASTICSEARCH_HEAP`, how much Elasticsearch allocate from memory (default: 1GB -good for development only-)
* `LOGSTASH_HEAP`, how much Logstash allocate from memory.
* Other configurations which their such as cluster name, and node name, etc.
* Elasticsearch Configuration in `elasticsearch.yml` at `./elasticsearch/config`.
* Logstash Configuration in `logstash.yml` at `./logstash/config/logstash.yml`.
* Logstash Pipeline in `main.conf` at `./logstash/pipeline/main.conf`.
* Kibana Configuration in `kibana.yml` at `./kibana/config`.
### Setting Up Keystore
You can extend the Keystore generation script by adding keys to `./setup/keystore.sh` script. (e.g Add S3 Snapshot Repository Credentials)
To Re-generate Keystore:
```
make keystore
```
### Notes
- ⚠️ Elasticsearch HTTP layer is using SSL, thus mean you need to configure your elasticsearch clients with the `CA` in `secrets/certs/ca/ca.crt`, or configure client to ignore SSL Certificate Verification (e.g `--insecure` in `curl`).
- Adding Two Extra Nodes to the cluster will make the cluster depending on them and won't start without them again.
- Makefile is a wrapper around `Docker-Compose` commands, use `make help` to know every command.
- Elasticsearch will save its data to a volume named `elasticsearch-data`
- Elasticsearch Keystore (that contains passwords and credentials) and SSL Certificate are generated in the `./secrets` directory by the setup command.
- Make sure to run `make setup` if you changed `ELASTIC_PASSWORD` and to restart the stack afterwards.
- For Linux Users it's recommended to set the following configuration (run as `root`)
```
sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
```
By default, Virtual Memory [is not enough](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/vm-max-map-count.html).
---------------------------




# Working with Elastic APM
After completing the setup step, you will notice a container named apm-server which gives you deeper visibility into your applications and can help you to identify and resolve root cause issues with correlated traces, logs, and metrics.
## Authenticating with Elastic APM
In order to authenticate with Elastic APM, you will need the following:
- The value of `ELASTIC_APM_SECRET_TOKEN` defined in `.env` file as we have [secret token](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/apm/guide/master/secret-token.html) enabled by default
- The ability to reach port `8200`
- Install elastic apm client in your application e.g. for NodeJS based applications you need to install [elastic-apm-node](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/apm/agent/nodejs/master/typescript.html)
- Import the package in your application and call the start function, In case of NodeJS based application you can do the following:
```
const apm = require('elastic-apm-node').start({
serviceName: 'foobar',
secretToken: process.env.ELASTIC_APM_SECRET_TOKEN,
// https is enabled by default as per elastdocker configuration
serverUrl: 'https://localhost:8200',
})
```
> Make sure that the agent is started before you require any other modules in your Node.js application - i.e. before express, http, etc. as mentioned in [Elastic APM Agent - NodeJS initialization](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/apm/agent/nodejs/master/express.html#express-initialization)
For more details or other languages you can check the following:
- [APM Agents in different languages](https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/apm/agent/index.html)
# Monitoring The Cluster
### Via Self-Monitoring
Head to Stack Monitoring tab in Kibana to see cluster metrics for all stack components.


> In Production, cluster metrics should be shipped to another dedicated monitoring cluster.
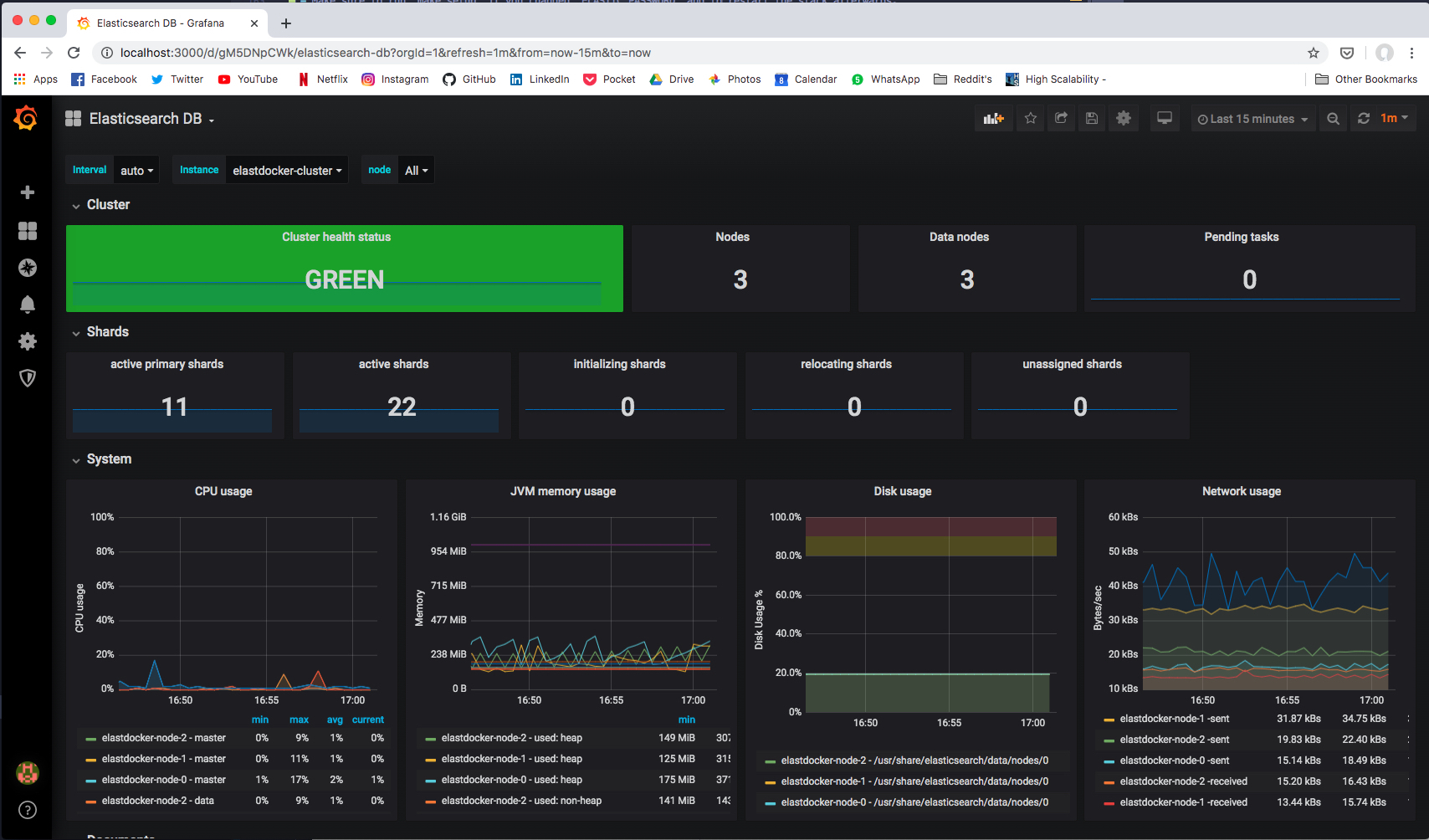
### Via Prometheus Exporters
If you started Prometheus Exporters using `make monitoring` command. Prometheus Exporters will expose metrics at the following ports.
| **Prometheus Exporter** | **Port** | **Recommended Grafana Dashboard** |
|-------------------------- |---------- |------------------------------------------------ |
| `elasticsearch-exporter` | `9114` | [Elasticsearch by Kristian Jensen](https://grafana.com/grafana/dashboards/4358) |
| `logstash-exporter` | `9304` | [logstash-monitoring by dpavlos](https://github.com/dpavlos/logstash-monitoring) |
# License
[MIT License](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/sherifabdlnaby/elastdocker/master/LICENSE)
Copyright (c) 2022 Sherif Abdel-Naby
# Contribution
PR(s) are Open and Welcomed.






