https://github.com/shravan20/unravel-spring-boot
Exploring Basics of Spring Boot
https://github.com/shravan20/unravel-spring-boot
Last synced: 6 months ago
JSON representation
Exploring Basics of Spring Boot
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/shravan20/unravel-spring-boot
- Owner: shravan20
- License: mit
- Created: 2021-03-19T09:05:15.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2021-04-08T19:22:30.000Z (over 4 years ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-02-09T19:17:34.037Z (8 months ago)
- Language: Java
- Size: 102 KB
- Stars: 4
- Watchers: 1
- Forks: 0
- Open Issues: 1
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# unravel-spring-boot
Spring Boot is a Spring module that provides the RAD (Rapid Application Development) feature to the Spring framework.
Spring Boot is an opinionated, convention-over-configuration focused addition to the Spring platform – highly useful to get started with minimum effort and create stand-alone, production-grade applications.
## What is Spring Boot?
Spring Boot is a project that is built on the top of the Spring Framework. It provides an easier and faster way to set up, configure, and run both simple and web-based applications.
It is a Spring module that provides the RAD (Rapid Application Development) feature to the Spring Framework. It is used to create a stand-alone Spring-based application that you can just run because it needs minimal Spring configuration.
```
@----------@ @----------@ @--------------@ @----------@
| | |Embedded | |XML | | |
|Spring | + | HTTP | - |Configuration/| = | Spring |
| Framework| | Servers| |@Configuration| | Boot |
@----------@ @----------@ @--------------@ @----------@
```
In short, Spring Boot is the combination of Spring Framework and Embedded Servers.
In Spring Boot, there is no requirement for XML configuration (deployment descriptor). It uses convention over configuration software design paradigm that means it decreases the effort of the developer.
We can use Spring STS IDE or Spring Initializr to develop Spring Boot Java applications.
## Why should we use Spring Boot Framework?
- The dependency injection approach is used in Spring Boot.
- It contains powerful database transaction management capabilities.
- It simplifies integration with other Java frameworks like JPA/Hibernate ORM, Struts, etc.
- It reduces the cost and development time of the application.
Along with the Spring Boot Framework, many other Spring sister projects help to build applications addressing modern business needs. There are the following Spring sister projects are as follows:
- **Spring Data**: It simplifies data access from the relational and NoSQL databases.
- **Spring Batch**: It provides powerful batch processing.
- **Spring Security**: It is a security framework that provides robust security to applications.
- **Spring Social**: It supports integration with social networking like LinkedIn.
- **Spring Integration**: It is an implementation of Enterprise Integration Patterns. It facilitates integration with other enterprise applications using lightweight messaging and declarative adapters.
## Goals of Spring Boot
- Provides Opinionated Development approach
- Avoids defining more Annotation Configuration
- Avoids writing lots of import statements
- Avoids XML Configuration.
## Advantages of Spring Boot
- Stand-alone Spring applications that can be started using Java -jar.
- Tests web applications easily with the help of different Embedded HTTP servers such as Tomcat, Jetty, etc. We don't need to deploy WAR files.
- Provides opinionated 'starter' POMs to simplify our Maven configuration.
- Provides production-ready features such as metrics, health checks, and externalized configuration.
- No requirement for XML configuration.
- Offers a CLI tool for developing and testing the Spring Boot application.
- Offers the number of plug-ins.
- Minimizes writing multiple boilerplate codes (the code that has to be included in many places with little or no alteration), XML configuration, and annotations.
- Increases productivity and reduces development time.
## Features of Spring Boot
- Web Development
- SpringApplication
- Application events and listeners
- Admin features
- Externalized Configuration
- Properties Files
- YAML Support
- Type-safe Configuration
- Logging
- Security
## What's up with Spring Boot 2.0?
- **What's New**
- Infrastructure Upgrade
- Spring Framework 5
- **What's Changed**
- Configuration Properties
- Gradle Plugin
- Actuators endpoints
- **What's Evolving**
- Security
- Metrics
## Performance Improvements
In Spring Boot 2.2.1 the following performance has been improved:
- **Lazy Initialization**: In Spring Boot 2.2.1, we can enable global lazy initialization by using the property spring.main.lazy-initialization property. It reduces the application startup time.
- **Java 13 Support**: Spring Boot 2.2.1 now supports the latest version of Java that is Java 13.
- **Immutable Binding**: In the newer version of Spring Boot, Configuration properties support constructor-based binding. The class annotates with @ConfigurationProperties annotation is to be immutable. It can be enabled by adding an annotation @ConfugurationProperties to a class or one of its constructors with @ConstructorBinding.
- **RSocket Support**: It is a part of Spring Security. RSocket integration is auto-configured when an application finds spring-security-rsocket is present on the classpath.
## Spring Boot v/s Spring
- **Spring**: Spring Framework is the most popular application development framework of Java. The main feature of the Spring Framework is dependency Injection or Inversion of Control (IoC). With the help of Spring Framework, we can develop a loosely coupled application. It is better to use if application type or characteristics are purely defined.
- **Spring Boot**: Spring Boot is a module of Spring Framework. It allows us to build a stand-alone application with minimal or zero configurations. It is better to use if we want to develop a simple Spring-based application or RESTful services.
## Spring Boot Architecture
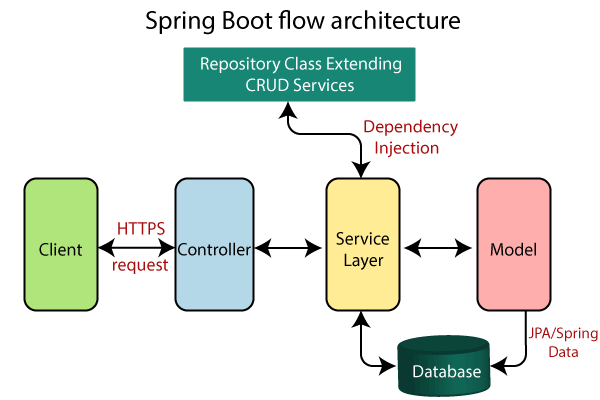
- Now we have validator classes, view classes, and utility classes.
- Spring Boot uses all the modules of Spring-like Spring MVC, Spring Data, etc. The architecture of Spring Boot is the same as the architecture of Spring MVC, except one thing: there is no need for DAO and DAOImpl classes in Spring boot.
- Creates a data access layer and performs CRUD operation.
- The client makes the HTTP requests (PUT or GET).
- The request goes to the controller, and the controller maps that request and handles it. After that, it calls the service logic if required.
- In the service layer, all the business logic performs. It performs the logic on the data that is mapped to JPA with model classes.
- A JSP page is returned to the user if no error occurred.