https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid
A grid-based layout system for Flutter, inspired by CSS Grid Layout
https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid
dart flutter grid-layout layout
Last synced: 2 months ago
JSON representation
A grid-based layout system for Flutter, inspired by CSS Grid Layout
- Host: GitHub
- URL: https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid
- Owner: shyndman
- License: mit
- Created: 2019-11-12T03:09:46.000Z (over 5 years ago)
- Default Branch: main
- Last Pushed: 2024-05-20T03:23:25.000Z (about 1 year ago)
- Last Synced: 2025-04-02T01:35:48.492Z (2 months ago)
- Topics: dart, flutter, grid-layout, layout
- Language: Dart
- Homepage:
- Size: 1.36 MB
- Stars: 448
- Watchers: 8
- Forks: 44
- Open Issues: 22
-
Metadata Files:
- Readme: README.md
- Changelog: CHANGELOG.md
- License: LICENSE
Awesome Lists containing this project
README
# Flutter Layout Grid
[](https://pub.dev/packages/flutter_layout_grid)
[](https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid/actions?query=workflow%3Atest)
A powerful grid layout system for Flutter, optimized for complex user interface
design.
_Click images to see their code_
---
✨Featuring:✨
- 📐 Fixed, flexible, and content-sized rows and columns
([docs](#sizing-of-columns-and-rows))
- 👇 Precise control over placement of items, including the ability to span
rows, columns, and overlap items
([docs](#positioning-child-widgets-in-the-layoutgrid))
- 💬 Named grid areas for descriptive positioning of children
([docs](#naming-areas-of-the-grid))
- 🦾 A configurable automatic grid item placement algorithm, capable of sparse
and dense packing across rows and columns ([docs](#automatic-child-placement))
- 🔚 Right-to-left support, driven by ambient `Directionality` or configuration
- ♿ Accessibility considerations (**this is your responsibility** as a frontend
developer, so please read [docs](#accessibility-and-placement) and learn
related technologies)
- 🩳 Extension methods and helper functions for descriptive, and short, layout
code
- 🐛 Debugging aids, including widget property listings in
[DevTools](https://flutter.dev/docs/development/tools/devtools/overview),
Debug Painting, and visual indication of child overflow
Inspired by (and largely based on), the excellent [CSS Grid
Layout](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/CSS_Grid_Layout) spec.
## Getting Started
All the terminology used in this library is shared with the CSS Grid Layout
spec. If youʼre unfamiliar, I recommend taking a look at [MDNʼs glossary of grid
terms](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/CSS_Grid_Layout#Glossary_entries).
For inclusion in your pubspec, see
[pub.dev](https://pub.dev/packages/flutter_layout_grid/install), or copy
the code below:
```yaml
dependencies:
flutter_layout_grid: ^2.0.0
```
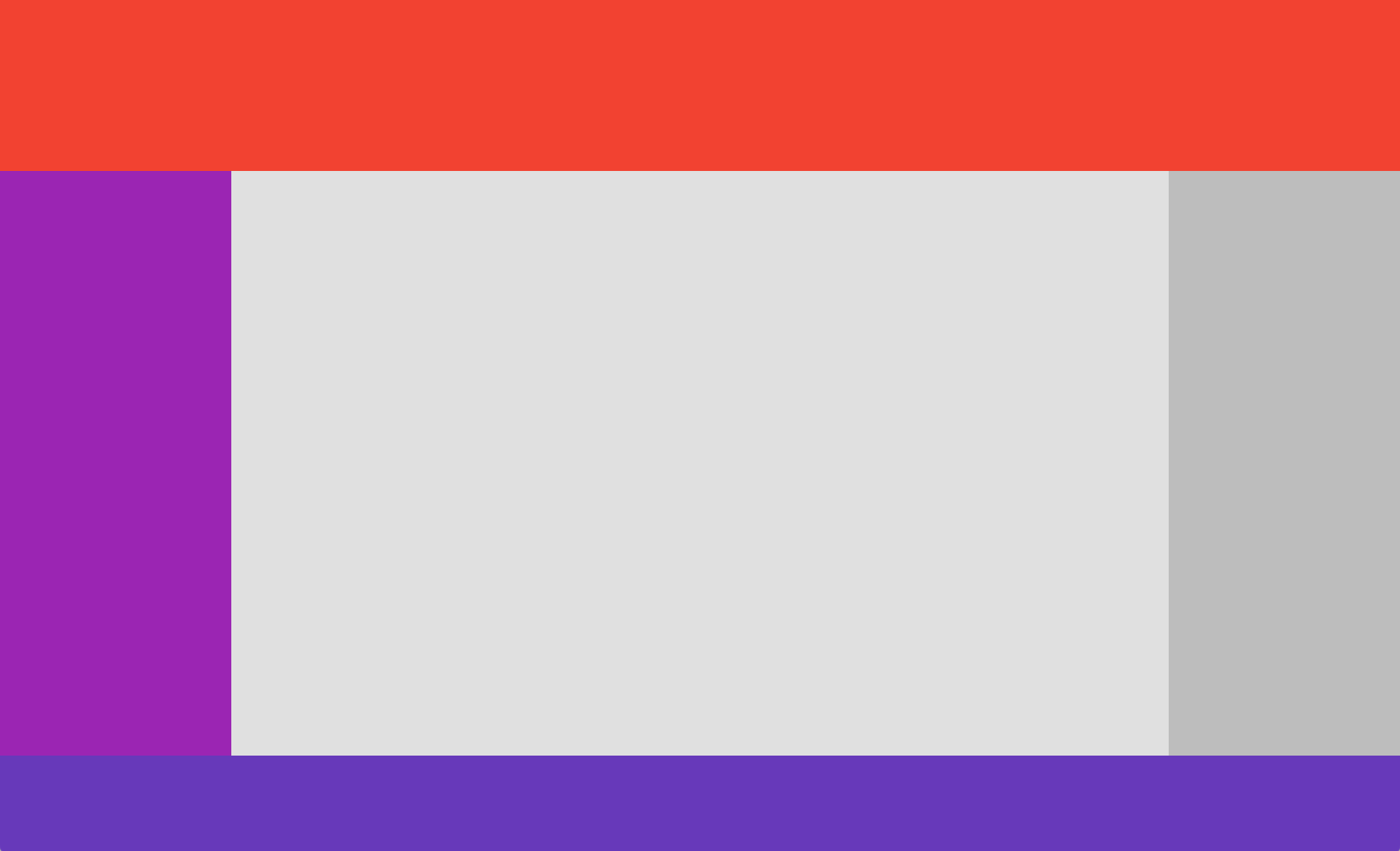
## Example
#### Visual:
#### Code:
```dart
import 'package:flutter_layout_grid/flutter_layout_grid.dart';
class App extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
color: background,
child: LayoutGrid(
// ASCII-art named areas 🔥
areas: '''
header header header
nav content aside
nav content .
footer footer footer
''',
// Concise track sizing extension methods 🔥
columnSizes: [152.px, 1.fr, 152.px],
rowSizes: [
112.px,
auto,
1.fr,
64.px,
],
// Column and row gaps! 🔥
columnGap: 12,
rowGap: 12,
// Handy grid placement extension methods on Widget 🔥
children: [
Header().inGridArea('header'),
Navigation().inGridArea('nav'),
Content().inGridArea('content'),
Aside().inGridArea('aside'),
Footer().inGridArea('footer'),
],
),
);
}
}
```
This example is available at
[`example/app_layout.dart`](https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid/tree/main/example/lib/app_layout.dart).
For a similar example that includes responsive behavior, check out
[`example/responsive_app_layout.dart`](https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid/tree/main/example/lib/responsive_app_layout.dart).
## Sizing of Columns and Rows
The sizes of the gridʼs columns and rows are set using
`LayoutGrid.columnSizes` and `LayoutGrid.rowSizes`.
Hereʼs what a 4⨉3 grid might look like (4 columns, 3 rows):
```dart
LayoutGrid(
columnSizes: [4.5.fr, 100.px, auto, 1.fr],
rowSizes: [
auto,
100.px,
1.fr,
],
)
```
Each element of `columnSizes` and `rowSizes` represents the function used to
size a column or row (collectively known as **"track sizes"**).
There are currently three way to size rows and columns:
| Class Name | Description | Usage |
| --------------------------- | ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ | -------------------------------------------------------- |
| `FixedTrackSize` | Occupies a specific number of pixels on an axis | `FixedTrackSize(64)`
`fixed(64)`
`64.px` |
| `FlexibleSizeTrack` | Fills remaining space after the initial layout has completed | `FlexibleTrackSize(1.5)`
`flexible(1.5)`
`1.5.fr` |
| `IntrinsicContentTrackSize` | Sized to contain its itemsʼ contents. Will also expand to fill available space, once `FlexibleTrackSize` tracks have been given the opportunity. | `IntrinsicContentTrackSize()`
`intrinsic()`
`auto` |
Technically, you can also define your own, but probably shouldnʼt as the API
will likely be evolving as I tackle
([#25](https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid/issues/25))
([`minmax()`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/minmax)
support).
## Naming areas of the grid
A gridʼs rows and columns can be sliced into areas — rectangular regions
containing one or more grid cells. These areas can be named (_optionally_), and
used to place gridʼs children. The areas are named using an ASCII-art string
provided to the `areas` parameter.
```dart
LayoutGrid(
areas: '''
header header
nav content
footer footer
''',
// ...
)
```
> Note: We use the same format as CSSʼs
> [`grid-template-areas`](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/grid-template-areas),
> except we use a multiline string.
If an `areas` argument has been provided to a grid, you must specify the same
number of sizes using `columnSizes` and `rowSizes` elements. For the example
above:
```dart
LayoutGrid(
areas: '''
header header
nav content
footer footer
''',
// 2 columns, 3 rows, just like the areas string
columnSizes: [
auto, // contributes width to [nav, header, footer]
1.fr, // contributes width to [content, header, footer]
],
rowSizes: [
96.px, // contributes height to [header]
1.fr, // contributes height to [nav, content]
72.px, // contributes height to [footer]
],
children: [
// ...
],
)
```
Grid children can be assigned to named areas using the `NamedAreaGridPlacement`
widget. For more information, see [assigning the child to a named
area](#child-placement-in-named-areas).
## Positioning child widgets in the `LayoutGrid`
Once you have a grid, you have to tell its `children` which rows and columns
they should occupy. There are three ways of doing this:
- [Specifying row and column indexes](#child-placement-by-row-and-column-indexes)
- [Assigning the child to a named area](#child-placement-in-named-areas)
- [Using automatic placement](#automatic-child-placement)
### Child placement by row and column indexes
A gridʼs child can be instructed to occupy a specific set of columns and rows
by using the `GridPlacement` widget.
For example, letʼs say you had a 4⨉3 grid, and you wanted a widget to be
positioned from column 1–4 and row 0–2:
```dart
LayoutGrid(
columnSizes: [1.fr, 1.fr, 1.fr, 1.fr],
rowSizes: [
1.fr,
1.fr,
1.fr,
],
children: [
GridPlacement(
columnStart: 1,
columnSpan: 3,
rowStart: 0,
rowSpan: 2,
child: MyWidget(),
),
// Alternatively, an extension method on Widget is available
MyWidget().withGridPlacement(
columnStart: 1,
columnSpan: 3,
rowStart: 0,
rowSpan: 2,
),
],
)
```
`GridPlacement` also has a super power — all of its parameters are optional.
If, for example, you do not specify a `rowStart`, the [automatic placement
algorithm](#automatic-child-placement) will attempt to place the child in the
first vacant spot that it can find.
### Child placement in named areas
If your grid has [named areas](#naming-areas-of-the-grid) defined, you can
place children in those areas using the `NamedAreaGridPlacement` widget. For
example:
```dart
LayoutGrid(
areas: '''
red red blue
red red blue
. . blue
''',
// Note that the number of columns and rows matches the grid above (3x3)
columnSizes: [64.px, 64.px, 64.px],
rowSizes: [
64.px,
64.px,
64.px,
],
children: [
// Using NamedAreaGridPlacement constructor
NamedAreaGridPlacement(
areaName: 'red',
child: Container(color: Colors.red),
),
// Alternatively, an extension method on Widget is available
Container(color: Colors.red).inGridArea('red'),
],
)
```
**NOTE:** If a `NamedAreaGridPlacement` references a named area that doesnʼt
exist, it will not be displayed in the grid. This can be helpful when switching
between responsive layouts.
### Automatic child placement
Grid children can be placed into rows and columns automatically based on partial
or non-existent placement information.
The algorithm responsible for automatic placement has several modes, selected
through the `LayoutGrid.autoPlacement` parameter. The behavior of these modes
are identical to those supported by CSSʼs grid, described [described
here](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/CSS_Grid_Layout/Auto-placement_in_CSS_Grid_Layout).
#### When no placement information is provided
If a child is provided to the grid without being wrapped in a `GridPlacement` or
`NamedAreaGridPlacement`, it will be allotted a single cell (1⨉1), and placed
into the first vacant cell in the grid.
#### When partial placement information is provided
All of the `GridPlacement` widgetʼs parameters are optional. By specifying
additional positioning or spanning information with
`columnStart`/`columnSpan`/`rowStart`/`rowSpan` parameters, more
constraints are fed into the placement algorithm.
For example, if `columnStart` is provided, but not `rowStart`, the placement
algorithm will walk across the gridʼs rows until it finds a vacant area, in the
specified column, that accommodates the child.
[Read more about CSSʼs grid placement
algorithm](https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/CSS_Grid_Layout/Auto-placement_in_CSS_Grid_Layout)
### Accessibility and Placement
Take note that the meaning you convey visually through placement may not be
clear when presented by assitive technologies, as Flutter defaults to exposing
information in source order.
In situations where your semantic (visual) ordering differs from ordering in the
source, the ordering can be configured via the `Semantics` widgetʼs
[`sortKey`](https://api.flutter.dev/flutter/semantics/SemanticsSortKey-class.html)
parameter.
For an example of this in practice, see
[example/semantic_ordering.dart](https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid/tree/main/example/lib/semantic_ordering.dart).
Automatic semantic ordering is currently being explored in
[#50](https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid/issues/50).
## Differences from CSS Grid Layout
Things in CSS Grid Layout that are not supported:
- Negative row/column starts/ends. In CSS, these values refer to positions
relative to the end of a gridʼs axis. Handy, but weʼre not there yet.
([#5](https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid/issues/5))
- Any cells outside of the explicit grid. If an item is placed outside of the
area defined by your template rows/columns, we will throw an error. Support
for automatic addition of rows and columns to accommodate out of bound items
is being considered.
([#7](https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid/issues/7))
- minmax(), percentages, aspect ratios track sizing
([#25](https://github.com/shyndman/flutter_layout_grid/issues/25))
Differences:
- In `flutter_layout_grid`, flexible tracks do not account for their contentʼs
base sizes as they do in CSS. Itʼs expensive to measure, and I opted for
speed.
- Flexible tracks whose flex factors sum to < 1
## Roadmap
- [x] Tests! (we now have a decent suite going)
- [x] Named template areas, for friendlier item placement
- [ ] Improved track sizing, including minimum/maximums and aspect ratios
- [ ] The ability to specify row and column gaps at specific line locations via
a delegate
- [ ] Implicit grid support (automatic growth along an axis as children are
added)
- [x] Performance improvements, as soon as I can get this profiler running(!!!)